Please refer to Chemical Kinetics HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with Chemical Kinetics. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (1 Mark)
Question. The half life period of a first order reaction is 100° seconds. Its rate constant is:
(a) 0.693 sec–1
(b) 6.93 × 10–3 sec–1
(c) 6.93 × 10–2 sec–1
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. In Arrehenius equation if a graph is plotted between 10 gK and 1/T, the slope of the curve will be:

Answer
B
Question. The rate low for a reaction 2C + D → A + E is

if C is present in large excess, the order of the reaction will be:
(a) zero
(b) first
(c) second
(d) third
Answer
B
Question. What is the activation energy for the reverse of this reaction?
N2O4(g) → 2NO2(g)
Data for the given reaction is ΔH = 54 KJ/mol and εa = 57.2 KJ.
(a) – 54 KJ
(b) 3.2 KJ
(c) 60.2 KJ
(d) 111.2 KJ
Answer
B
Question. The rate constant of a reaction becomes equal to the pre exponential factor when:
(a) the absolute temperature is zero
(b) the activation energy is infinity
(c) the absolute temperature is infinity
(d) the activation energy is zero
Answer
C
Question. The following graph show that the reaction is:

(a) zero order
(b) first order
(c) second order
(d) fractional order
Answer
A
Question. A second order reaction between A and B is elementary reaction:
A + B → Product
rate law expression of this reaction will be:
(a) Rate = K[A][B]
(b) Rate = K[A]0[B]2
(c) Rate = K[A]2[B]0
(d) Rate = K[A]3/2[B]1/2
Answer
A
Question. The order and molecularity of the chain reaction,
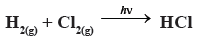
(a) 2, 0
(b) 0, 2
(c) 1, 1
(d) 3, 0
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is pseudo first order reaction?
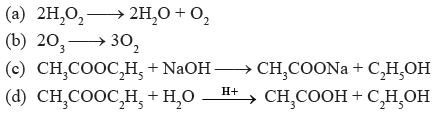
Answer
D
Question. A large increase in the rate of reaction for rise in temperature is due to:
(a) Increase in the number of collisions
(b) Increase in the number of activated molecules
(c) Lowering of activation energy
(d) Shortening of the mean free path.
Answer
B
Question. For a creactionj, the following data were obtained:
Concentration (mol/L) 0.1 0.05 0.025 0.0125
Half life in (sec) 30 29.9 30.1 30
the order of reaction is:
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) fractional
Answer
B
Question. For the formation of SO3 in the following reaction, it is given that
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3 Ea = Activation energy
SO2 + 1/2 O2 → SO3 E′a = Activation energy
(a) Ea > E1a
(b) Ea < E1a
(c) E1a = Ea1/2
(d) Ea = E1a
Answer
D
Question. A first order reaction is 20% complete in one hour. At the end of 3 hrs the extent of the reaction is:
(a) 60%
(b) 52.2%
(c) 48.8%
(d) 44.4%
Answer
C
Question. Radioactive decay is an example of:
(a) first order
(b) second order
(c) zero order
(d) 0.5 order
Answer
A
Question. At 227°C, the presence of catalyst causes the activation energy of a reaction to decrease by 4.606 KCal, the rate of the reaction will be increased by:
(a) 2 times
(b) 10 times
(c) 100 times
(d) 1000 times
Answer
C
Question. The decomposition of N2O5 occurs as, 2N2O5 → 4NO2 + O2 and follows first order kinetics, hence:
(a) the reaction is bimolecular
(b) the reaction is unimolecular
(c) tyz ∝ a°
(d) unit of K = mol/L sec−1
Answer
C
Question. Rate of which reactions increases with temperature:
(a) of any reactionj
(b) of exothermic reaction
(c) of endothermic reaction
(d) of none
Answer
A
Question. For the reaction, N2O5 → 2NO2 + O2; Given
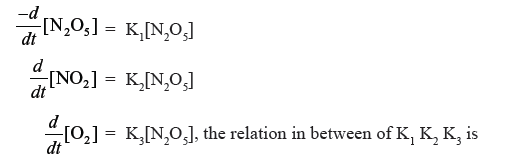
(a) 2K1 = K2 = 4 K3
(b) K1 = K2 = K3
(c) 2K1 = 4K2 = K3
(d) 2K1= 2K2 = 3K3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement is/are correct about order of reaction:
(a) order of reaction is determined experimentally
(b) order of reaction can not have fractional value
(c) it does not necessarily depend on stoichiometric coefficients.
(d) it is the sum of power of concentration terms in rate low expression
Answer
A,C,D
Question. Which one is correct for first order reaction.

Answer
C,D
Question. Match the column and found out correct option.

(a) A–R, B–Q, C–P
(b) A–P, B–Q, C–R
(c) A–Q, B–R, C–P
(d) A–R, B–P, C–Q
Answer
C
Question. Integer type Question:
For first order reaction: t99.9/t50 = x, Here x is
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 10
Answer
C
Fill in the blanks type Questions
Question. The reactions taking place in one step is called …………… reactions.
Answer
elementary
Question. The order of reaction is …………… determined.
Answer
experimentally
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the following and answer the questions given below.
The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the concentration of reactant to decrease by half,
i.e., [ A]t =1/2 [ A]
For first order reaction, t1/2 = 0.693/k
this means t1/2 is independent of initial concentration.
Figure shows that typical variation of concentration of reactant exhibiting first order kinetics. It may be noted that though the major
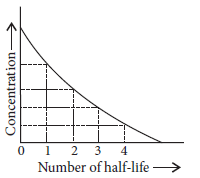
portion of the first order kinetics may be over in a finite time, but the reaction will never cease as the concentration of reactant will be zero only at infinite time.
Question. The rate of a first order reaction is 0.04 mol L–1 s–1 at 10 minutes and 0.03 mol L–1 s–1 at 20 minutes after initiation. The half-life of the reaction is
(a) 4.408 min
(b) 44.086 min
(c) 24.086 min
(d) 2.408 min
Answer
C
Question. For the half-life period of a first order reaction, which one of the following statements is generally false?
(a) It is independent of initial concentration.
(b) It is dependent on rate of the reaction.
(c) At t1/2, the concentration of the reactant is reduced by half.
(d) None of these.
Answer
B
Question. A first order reaction has a rate constant k = 3.01 × 10–3 /s. How long it will take to decompose half of the reactant?
(a) 2.303 s
(b) 23.03 s
(c) 230.3 s
(d) 2303 s
Answer
C
Question. The plot of t1/2 vs initial concentration [A]0 for a first order reaction is given by
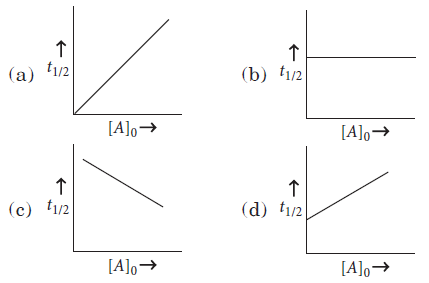
Answer
B
Question. The rate constant for a first order reaction is 7.0 × 10–4 s–1. If initial concentration of reactant is 0.080 M, what is the half life of reaction?
(a) 990 s
(b) 79.2 s
(c) 12375 s
(d) 10.10 × 10–4 s
Answer
A
Case II : Read the following and answer the questions given below.
For a first order reaction, A → Products,
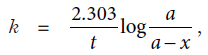
where a is the initial concentration of A and (a–x) is the concentration of A after time t. k is rate constant. Its value is constant at constant temperature for a reaction. The time in which half of the reactant is consumed is called half-life period. Half-life period of a first order reaction is constant. Its value is independent of initial concentration or any other external conditions.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion : For a first order reaction,the concentration of the reactant decreases exponentially with time.
Reason : Rate of reaction at any time depends upon the concentration of the reactant at that time.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : For the first order reaction,half-life period is expressed as t1/2=(2.303/k) 2log .
Reason : The half-life time of a first order reaction is not always constant and it depends upon the initial concentration of reactants.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Rate of reaction doubles when concentration of reactant is doubled if it is a first order reaction.
Reason : Rate constant also doubles.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Half-life period for a first order reaction is independent of initial concentration of the reactant.
Reason : For a first order reaction, t1/2 = 0.693/k, where k is rate constant.
Answer
A
Case III : Read the following and answer the questions given below.
Number of molecules which must collide simultaneously to give product is called molecularity. It is equal to sum of coefficients of reactants present in stoichiometric chemical equation.
For reaction, m1A + m2B → Product
Molecularity = [m1 + m2]
In complex reaction each step has its own molecularity which is equal to the sum of coefficients of reactants present in a particular step. Molecularity is a theoretical property. Its value is any whole number. Number of concentration terms on which rate of reaction depends is called order of reaction or sum of powers of concentration terms present in the rate equation is called order of reaction.
If rate equation of reaction is : Rate = k CAm1 CBm2
Then order of reaction = m1 + m2.
In simple reaction, order and molecularity are same.In complex reaction, order of slowest step is the order of over all reaction. This step is known as rate determining step. Order is an experimental property. Its value may be zero, fractional or negative.
Question. The molecularity of the reaction :
6FeSO4 + 3H2SO4 + KClO3 → KCl + 3Fe2(SO4)3 + 3H2O is
(a) 6
(b) 3
(c) 10
(d) 7
Answer
C
Question. The rate of the reaction, A + B + C → products, is given by
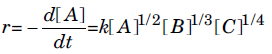
The order of the reaction is
(a) 1/3
(b) /14
(c) 1/2
(d) 13/12
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is false in the following?
(a) Order of a reaction may be even zero.
(b) Molecularity of a reaction is always a whole number.
(c) Molecularity and order always have same values for a reaction.
(d) Order of a reaction depends upon the mechanism of the reaction.
Answer
C
Question. The rate of reaction, A + 2B → products, is given by the following equation:
− d[A]/dt =k [A][B ]2
If B is present in large excess, the order of the reaction is
(a) zero
(b) first
(c) second
(d) third.
Answer
B
Case IV : Read the following and answer the questions given below.
For the reaction : 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g), the following data were collected. All the measurements were taken at 263 K.
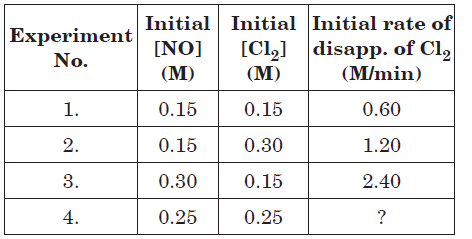
Question. The expression for rate law is
(a) r = k[NO][Cl2]
(b) r = k[NO]2[Cl2]
(c) r = k[NO][Cl2]2
(d) r = k[NO]2[Cl2]2
Answer
B
Question. The initial rate of disappearance of Cl2 in experiment 4 is
(a) 1.75 M min–1
(b) 3.23 M min–1
(c) 2.25 M min–1
(d) 2.77 M min–1
Answer
D
Question. The overall order of the reaction is
(a) 2
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 3
Answer
D
Question. The molecularity of the reaction is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
C
Question. The value of rate constant is
(a) 150.32 M–2 min–1
(b) 200.08 M–1 min–1
(c) 177.77 M–2 min–1
(d) 155.75 M–1 min–1
Answer
C
Case V : Read the following and answer the questions given below.
A reaction is said to be of the first order if the rate of the reaction depends upon one concentration term only. For a first order reaction of the type A → Products, the rate of the reaction is given as :
rate = k[A]. The differential rate law is given as :
dA/dt = – k[A]. The integrated rate law is :
ln [A ]/[A ]0 = – kt, where [A] is the concentration of reactant left at time t and [A]0 is the initial concentration of the reactant, k is the rate constant.
Question. 50% of a first order reaction is complete in 23 minutes. Calculate the time required to complete 90% of the reaction.
(a) 70.4 minutes
(b) 76.4 minutes
(c) 38.7 minutes
(d) 35.2 minutes
Answer
B
Question. Half-life period of a first order reaction is 10 min. Starting with initial concentration 12 M, the rate after 20 min is
(a) 0.693 × 3 M min–1
(b) 0.0693 × 4 M min–1
(c) 0.0693 M min–1
(d) 0.0693 × 3 M min–1
Answer
D
Question. The half-life period of a 1st order reaction is 60 minutes. What percentage will be left over after 240 minutes?
(a) 6.25%
(b) 4.25%
(c) 5%
(d) 6%
Answer
A
Question. The unit of rate constant for a first order reaction is
(a) s–1
(b) mol L–1 s–1
(c) L mol–1 s–1
(d) L2 mol–2 s–1
Answer
A
Question. For a first order reaction, (A) → products,the concentration of A changes from 0.1 M to 0.025 M in 40 minutes. The rate of reaction when the concentration of A is 0.01 M, is
(a) 3.47 × 10–4 M/min
(b) 3.47 × 10–5 M/min
(c) 1.73 × 10–4 M/min
(d) 1.73 × 10–5 M/min
Answer
A