VBQs Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science with solutions has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 10 Science with solutions. The following Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Science value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 10 examinations.
Periodic Classification of Elements VBQs Class 10 Science
Question. Consider the following statements about an element ‘X’ with number of protons 13.
(I) It forms amphoteric oxide.
(II) Its valency is three.
(III) The formula of its chloride is XCl.
(a) only (I)
(b) only (II)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (I) and (II)
Answer
D
Question. Which of these does not represent Dobereiner’s triad?
(a) Li, Na, K
(b) Cl, Br, I
(c) Be, Mg, Ca
(d) N, P, As
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
(i) Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses.
(ii) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number.
(iii) Isotopes of an element show same physical properties.
(iv) Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties.
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. Upto which element, the Law of Octaves was found Bto be applicable ?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Calcium
(c) Cobalt
(d) Potassium
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following elements will form an acidic oxide?
(a) An element with atomic number 7
(b) An element with atomic number 3
(c) An element with atomic number 12
(d) An element with atomic number 19
Answer
A
Question. What type of oxide would Eka– aluminium form?
(a) EO3
(b) E2O2
(c) E2O3
(d) EO
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of periodic table?
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature
(b) The number of valence electrons increases
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Answer
C
Question. An element ‘X’ is forming an acidic oxide. Its position in modern periodic table will be:
(a) Group 1 and Period 3
(b) Group 2 and Period 3
(c) Group 13 and Period 3
(d) Group 16 and Period 3
Answer
D
Question. The positions of four elements A, B, C and D in the modern periodic table are shown below. Which element is most likely to form an acidic oxide?

(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the outermost shell for elements of period 2?
(a) K shell
(b) L shell
(c) M shell
(d) N shell
Answer
B
Question. Arrange the following elements in the order of their decreasing metallic character: Na, Si, Cl, Mg, BAl.
(a) Cl > Si >Al > Mg >Na
(b) Na >Mg >Al >Si > Cl
(c) Na > Al > Mg > Cl > Si
(d) Al > Na> Si > Ca> Mg
Answer
A
Question. According to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law, the elements were arranged in the periodic table in the order of
(a) increasing atomic number
(b) decreasing atomic number
(c) increasing atomic masses
(d) decreasing atomic masses
Answer
C
Question. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, gaps were left for the elements to be discovered later. Which of the following elements found a place in the periodic table later ?
(a) Germanium
(b) Chlorine
(c) Oxygen
(d) Silicon
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following set of elements is written in order of their increasing metallic character?
(a) Be, Mg, Ca
(b) Na, Li, K
(c) Mg, Al, Si
(d) C, O, N
Answer
A
Question. Elements P, Q, R and S have atomic numbers 11, 15, 17 and 18 respectively. Which of them are reactive non-metals?
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) Q and R
(d) R and S
Answer
C
Question. Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the Modern Periodic Table?
(a) Group 8
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 18
(d) Group 10
Answer
C
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs :
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (a) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Question. Assertion (a): In a triad, the three elements have same gaps between their atomic masses.
Reason (R): Elements in a triad have similar properties.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (a): Smaller the size of an atom, greater is the electronegativity.
Reason (R): Electronegativity refers to the tendency of atom to share electrons with other atom.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (a): Mendeleev arranged element in horizontal rows and vertical columns.
Reason (R): Mendeleev ignored the order of atomic weight thinking that the atomic measurements might be incorrect.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (a): According to Mendeleev, periodic properties of elements is a function of their atomic number.
Reason (R): Atomic number is equal to the number of protons.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (a): Be and Al show similar properties.
Reason (R): The metallic radius of Be is less than the metallic radius of Al.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (a): Sixth and seventh periods in the periodic table contains 14 elements.
Reason (R): In the periodic table, 14 elements of sixth and seventh periods are known as lanthanoids and actinoids respectively.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (a): Mendeleev left the gaps under aluminium and silicon and called these Eka-aluminium and Eka-silicon, respectively.
Reason (R): Dobereiner arranged elements on the basis of increasing atomic number.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (a): Noble gases are highly reactive.
Reason (R): Noble gases have stable closed shell electronic configuration.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion (a): The atomic and ionic radii generally decreases towards right in a period.
Reason (R): The ionisation enthalpy increases on moving towards left in a period.
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Write the total number of periods in modern periodic table.
Answer: The total number of periods in modern periodic table is seven.
Question. Name any two elements that have two electrons in their valence shell.
Answer: (i) Magnesium: 2, 8, 2
(ii) Calcium : 2, 8, 8, 2.
Question. How many vertical columns are present in modern periodic table? What are they called?
Answer: There are 18 vertical columns in the modern periodic table and these are known as groups.
Question. How does valency of an element vary across a period?
Answer: The valency of an element first increases and then decreases across a period.
Question. How many horizontal rows are present in modern periodic table? What are they called?
Answer: There are seven horizontal rows in the modern periodic table. These rows are called periods.
Question. State one reason for placing Mg and Ca in the same group of the periodic table.
Answer: Due to the presence of 2 electrons in the valence shell and similar chemical properties.
Question. Define electropositivity.
Answer: Electropositivity is the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions in a chemical reactions.
Question. The atomic radii of first group elements are given below:
Group I element Atomic radii (pm)
Na 86
K 231
Rb 244
Cs 282
State the reason behind the observed trend in the above elements.
Answer: In a group, as we move from top to bottom, the number of shells increases. Hence, the atomic radius increases.
Question. How many elements are in 2nd and 5th period of Modern Periodic table.
Answer: 2nd period has 8 elements, 5th period has 18 elements.
Question. State the formula to fill up the maximum number of electrons in a shell.
Answer: 2n2, where n is the number of shell.
Question. If the atomic number of three element X, Y and Z are 3, 11 and 17 respectively. Which two elements will show similar chemical properties. Justify.
Answer: X and Y will show similar chemical properties as these have same valence electrons.
X = 2, (1)
Y = 2, 8, (1)
Question. State one reason that explains the position of Hydrogen in group I.
Answer: Hydrogen should be placed in group I, since it has only one electron in its outermost shell.
Question. Why noble gases are placed in a separate group in the modern periodic table?
Answer: It is because they resemble with each other but do not resemble with other group elements.
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. An element ‘X’ has mass number 35 and 18 number of neutrons. Therefore, electronic configuration of X= 2, 8, 7. Write atomic number and electronic configuration of ‘X’. Also write group number, period number and valency of ‘X’.
Answer: Atomic number of X = Mass number of X – Number
of neutrons
35 –18 =17
Therefore, Electronic configuration of X= 2, 8, 7
Group number =17
Period number = 3
Valency = 8 – 7 = 1
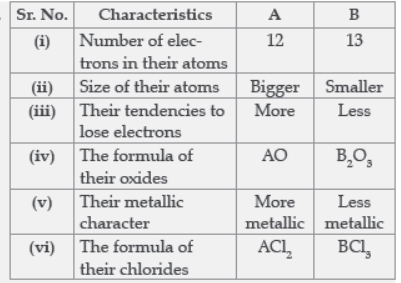
Question. Two elements ‘A’ and ‘B’ belong to the 3rd period of Modern periodic table and are in group and 13 respectively. Compare their following characteristics in tabular form:
(i) Number of electrons in their atoms
(ii) Size of their atoms
(iii) Their tendencies to lose electrons
(iv) The formula of their oxides
(v) Their metallic character
(vi) The formula of their chlorides.
Answer:
Question. Study the data of the following three categories A. B and C.
(i) From the given three categories A, B and C, pick the one which forms Dobereiner’s Triads.
(ii) Why did Mendeleev placed elements of category A, B and C in three different groups ?
(iii) Is Newland law of octaves applicable to all the three categories?
Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: (i) Category A (Li, Na, K) shows Dobereiner’s triads.
(ii) Mendeleev arranged the elements in increasing order of atomic mass and grouped them as per similar chemical property. The elements in A, B and C are similar among themselves but have different chemical properties.
(iii) No, Newland law of Octaves is not applicable because in the three categories every eighth element will not show same property as first. Also, Newland Octaves law is applicable only upto calcium.
Question. The atomic number of an element is 14. Examine if this element will have metallic properties or not. Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: Atomic number =14
Electronic configuration = 2, 8, 4
Hence, the element is silicon. This element exhibit the properties of both metals and non-metals. Hence, it is semimetal or metalloid.
Question. The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 4. State its: (a) group and period in the Modern Periodic Table. (b) name and write its one physical property.
Answer: (a) Group – 14, Period – 3
(b) Silicon
Metalloid / poor conductor of electricity
Question. The electronic configuration of an element ‘X’ is 2, 8, 6. To which group and period of the modern periodic table does ‘X’ belong. State its valency.
Answer: X: 2, 8, 6
(a) Since ‘X’ has three energy shells and period number of an element is equal to the number of energy shells, X belongs to 3rd period.
(b) X has 6 valence electrons it belongs to group 16.
(c) Valency will be 2. To acquire noble gas configuration it will gain 2 electrons.
Question. Define the following terms ? (i) Valency, (ii) Atomic size.
Answer: (i) Valency: The combining power or the combining capacity of an atom is called its valency.
(ii) Atomic size: Atomic size or atomic radius is the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom.
Question. How it can be proved that the basic structure of the Modern Periodic Table is based on the electronic configuration of atoms of different elements ?
Answer: Modern periodic table consists of groups and periods, where number of valence electrons determines the group and number of shells determines the period.
Question. (i) Name the element with atomic number 17.
(ii) To which period does it belong ?
(iii) To which group does it belong ?
(iv) Write its electronic configuration.
Answer: (i) Chlorine
(ii) 3rd period
(iii) 17th group
(iv) 2, 8, 7.
Question. Three elements ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ have atomic numbers 7, 8 and 9 respectively.
(a) State their positions (Group number and period number both) in the Modern Periodic Table.
(b) Arrange these elements in the decreasing order of their atomic radii.
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ combines with ‘Z’.
Answer: (a) X (7) – 2,5 Group 15; Period 2
Y(8 ) – 2,6 Group 16; Period 2
Z(9) – 2,7 Group 17; Period 2
(b) X > Y > Z
(c) XZ3
Question. Two elements X and Y have atomic numbers 12 and 16 respectively. To which period of the modern periodic table do these two elements belong?
What type of bond will be formed between them and why? Also give the chemical formula of the compound formed.
Answer: Electronic configuration of X: 2, 8, 2, Y: 2, 8, 6 Both X and Y belongs to 3rd period.
Ionic bond will be formed.
Reason: X will lose 2 electrons and Y will gain 2 electrons to complete their octet and become stable.
Formula is XY.
Question. An element ‘X’ with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with two radicals, (NO3)– and (SO4)2–.
(i) Is ‘X’ a metal or a non-metal ? Write the nature of its oxide.
(ii) Write the formula of the compounds of ’X’ formed by the combination of these radicals. Are these compounds covalent or electrovalent ?
Answer: (i) X is a metal. Nature of its oxide is basic.
(ii) X(NO3)2, XSO4
These compounds are ionic/electrovalent.
Question. The electronic configuration of an element ‘X’ is 2, 8, 6. To which group and period of the modern periodic table does ‘X’ belong. State its valency and justify your answer in each case.
Answer: X: 2, 8, 6
(a) Since ‘X’ has three energy shells and period number of an element is equal to the number of energy shells. X belongs to 3rd period.
(b X has 6 valence electrons it belongs to group 16.
(c) Valency will be 2. To acquire noble gas configuration it will gain 2 electrons.
Question. Write the electronic configuration of two elements P (atomic number 17) and Q (atomic number 19) and determine their group numbers and period numbers in the Modern Periodic Table.
Answer: Electronic configuration of ‘P’ — 2, 8, 7
Group number — 17
Period number — 3rd
Electronic configuration of ‘Q‘ — 2, 8, 8, 1
Group number — 1
Period number — 4th
Question. How does the tendency of the elements to lose electrons change in the Modern Periodic Table in (i) a group, (ii) a period and why ?
Answer: (i) Increases down a group.
Reason: At each succeeding element down a group, the number of shells increases, so the distance of the valence shell from the nucleus increases, the effective nuclear force of attraction decreases in the last shell, so it becomes easy for the atom to lose electrons.
(ii) Decreases in a period from left to right.
Reason: As the effective nuclear charge on the valence electron increases, the attraction between the valence electron and nucleus increases, so it becomes difficult to lose electrons.
Question. An element ‘X’ belong to 3rd period and group 13 of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Determine the valence electrons and the valency of ‘X’.
(b) Molecular formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ reacts with an element ‘Y’(atomic number = 8).
(c) Write the name and formula of the compound formed when ‘X’ combines with chlorine.
Answer: (a) Group 13 means valence electrons are 3 and valency is 3.
(b) Y (8) – 2, 6 X = 2, 8, 3
Valency – 2 Valency – 3
Compound formed – X2Y3 /Al2O3
(c) X Chlorine Cl
Valency -3 Valency -1
Compound formed – XCl3 /AlCl3
Question. The atomic number of an element is 20.
(a) Write its electronic configuration and determine its valency.
(b) Is it a metal or a non-metal ?
(c) Write the formula of its chloride.
(d) Is it more reactive or less reactive than Mg (atomic
number 12) ? Give reason for your answer.
Answer: (a) Electronic Configuration, X(20) – 2, 8, 8, 2
Valence electrons- 2
Hence valency is 2
(b) It is a metal
(c) XCl2
(d) It is more reactive than Mg as reactivity increases down the group. Mg- III Period and X20 (Ca)- IV Period.
Question. Write the name, symbol and electronic configuration of an element X whose atomic number is 11.
Answer: Name – Sodium
Symbol – Na
Electronic configuration – 2, 8, 1
Question. Can the following groups of elements be classified as Dobereiner’s triad ?
(a) Na, Si, Cl
(b) Be, Mg, Ca
Atomic mass of Be-9; Na-23, Mg-24, Si-28, Cl-35,
Ca-40.
Justify your answer in each case.
Answer: (a) Na, Si, Cl – Average of atomic masses of Na and Cl is not equal to the atomic mass of Si.
(b) Be, Mg, Ca – The average of atomic masses of Be and Ca is equal to the atomic mass of Mg.
Atomic mass of Mg = Atomic mass of Be + Atomic mass of Ca/2
= 9 + 40/2 = 49/2 = 24.5
Question. Write the electronic configuration of two elements X and Y whose atomic numbers are 20 and 17 respectively. Write the molecular formula of the compound formed when element X reacts with element Y. Draw electron-dot structure of the product and also state the nature of the bond formed between both the elements.
Answer: X(20) – 2, 8, 8, 2
Y(17) – 2, 8, 7
XY2
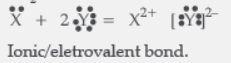
Question. An element ‘M’ has atomic number 12.
(i) Write its electronic configuration and valency.
(ii) Is ‘M’ a metal or a non-metal ? Give reason in support of your answer.
(iii) Write the formula and nature (acidic/basic) of the oxide of M.
Answer: (i) Electronic Configuration — 2, 8, 2
Valency — 2.
(ii) Metal
There are two electrons in its outermost shell and it easily loses them to form a positive ion. 10
Chemical formula M2O2 = MO
It is a basic oxide.
Question. Write the number of periods and groups in the Modern Periodic Table. How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving (i) from left to right in a period, and (ii) down a group ?
Answer: • Periods – 7, Groups – 18
• Metallic character decreases along the period because effective nuclear charge increases on the valence electrons hence decrease in tendency to lose electrons.
• Metallic character increases down a group because effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons decrease, hence tendency to lose electron increases.
Question. The following table shows the position of five elements A, B, C, D and E in the modern periodic table.
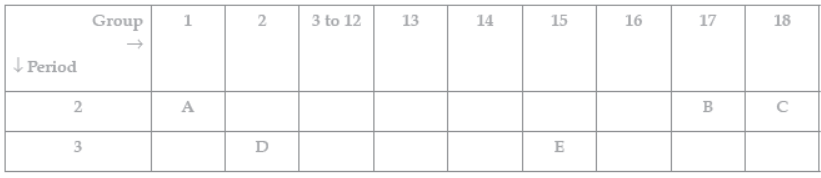
Answer the following giving reasons:
(i) Which element is a metal with valency two? (ii) Which element is least reactive?
(iii) Out of D and E which element has a smaller atomic radius?
Answer: (i) D, as it is on the left side of the table in group 2. (ii) C, as it is in the group 18/ Noble gas.
(iii) E, as we move from left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases.
Question. Define atomic size. Give its unit of measurement.
In the modern periodic table what trend is observed in the atomic radius in a group and a period and why is it so?
Answer: Atomic Size: The distance from centre of nucleus to outermost shell of an atom is atomic radius.
Atomic size is measured in Angstroms, (A°).
where 1 Angstroms = 10-10 metres.
Along the period from left to right atomic radius decreases.
Reason: Nuclear charge increases which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus.
Down the group: Atomic radius increases
Reason: Number of shells increases on going down the group.
Question. Define groups in the Modern Periodic Table. How do valency, atomic size and metallic character vary in a group.
Answer: Group : Vertical columns in the modern periodic table are known as ‘groups’. There are 18 groups.
(i) Valency remain same in a group.
(ii) Atomic size increases from top to bottom in a group.
(iii) Metallic character also increases from top to bottom in a group.
Question. How does the atomic radius of the elements change on going (i) from left to right in a period, and
(ii) down a group
in the Modern Periodic Table ? Give reason in support of your answer.
Answer: (i) Atomic radius decreases.
Reason: Nuclear charge increases which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus.
(ii) Atomic radius increases.
Reason: Number of shells increases on going down the group.
Question. Write the names given to the vertical columns and horizontal rows in the Modern Periodic Table.
How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving down a vertical column ? How does the size of atomic radius vary on moving left to right in a horizontal row ? Give reason in support of your answer in the above two cases.
Answer: Vertical Column — Groups
Horizontal Rows — Periods
(i) Metallic character increases.
Reason: Ability to lose electrons increases on moving down the group due to increase in distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons/ decrease in the attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
(ii) Atomic radius decreases.
Reason: The nuclear charge increases on moving from left to right across a period resulting in increase in the attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
Question. Na, Mg and Al are the elements of the 3rd period of the Modern Periodic Table having group number 1, 2 and 13 respectively. Which one of these elements has the (a) highest valency,
(b) largest atomic radius, and
(c) maximum chemical reactivity ?
Justify your answer stating the reason for each.
Answer: In the modern periodic table, there are 18 vertical columns known as Groups and 7 horizontal rows known as Periods.
Metallic character increases on moving down a group in the Modern Periodic table. As we move down the group, the electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electron decreases due to increase in the distance between them. This happens because on moving down the group a new shell is added. So, the valence electron can be easily lost by the element, thereby metallic character increases on moving down a group.
The size of atomic radius decreases on moving left to right in a horizontal row. When, we move across a period, the number of electrons in the same shell increases. This leads to greater electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electron. This increased attraction pulls the outermost electron closer to the nucleus, thereby decreasing the atomic size.
Question. Consider the following elements (atomic numbers are given in parenthesis)
Ca(20); K(19); F(9); Be(4) [CBSE OD Comptt
(a) Select:
(i) The elements having one electron in the outermost shell.
(ii) Two elements of the same group. Write the number of this group.
(b) Write the formula of the compound formed by the union of Ca(20) and the element X(2, 8, 7).
Answer: (a) (i) K (Potassium — 2, 8, 8, 1)
(ii) Be and Ca in same group because both have same number of valence electrons in their outermost
shell. The number of this group is 2.
(b) Ca X
Valency 2 1
Thus, the formula of the compound is Ca1X2 = CaX2
Question. What is periodicity in properties of elements with reference to the Modern Periodic Table? Why do all the elements of the same group have similar properties? How does the tendency of elements to gain electrons change as we move from left to right in a period? State the reason of this change.
Answer: • Repetition of similar properties of elements after regular intervals.
• Because of the same number of valence electrons.
• It increases due to increase in effective nuclear charge which pulls the electrons towards it.
Question. The elements 4Be, 12Mg and 20Ca each having two valence electrons in their valence shells are in periods 2, 3 and 4 respectively of the modern periodic table. Answer the following questions associated with these elements, giving reason in each case,
(i) In which group should they be?
(ii) Which one of them is least reactive ?
(iii) Which one of them has the largest atomic size ?
Answer: (i) They all belong to group 2 because all three have 2 electrons in their outermost shell.
(ii) Be is least reactive because it has 2 shells and due to more nuclear change it is not easy to take electrons from it.
(iii) Ca is the element having largest atomic radius because it has 4 shells. {Hence, it has the largest atomic size.}
Question. Name any two elements of group one and write their electronic configurations. What similarity do you observe in their electronic configurations ?
Write the formula of oxide for any of the above said element.
Answer: (i) Two elements of group 1 are Na, K / Sodium, potassium.
Electronic configurations Na = 2,8,1; K = 2,8,8,1
(ii) Similarity: Both have one valence electron / One electron in outermost shell.
(iii) Oxide – Na2O / K2O.
Question. An element ‘X’ has mass number 35 and number of neutrons 18. Write atomic number and electronic configuration of ‘X’. Also write group number,
period number and valency of ‘X’.
Answer: Atomic number of X = Mass number of X – No. of neutrons
= 35 – 18 = 17
Therefore, Electronic configuration of
X = 2, 8, 7 ½
Group number =17
Period = 3
Valency = 8 – 7 = 1
Question. The position of eight elements in the modern periodic table is given below where atomic numbers of elements are given in the parenthesis.

i) State electronic configuration of Ca.
(ii) Predict the number of valence electrons in Rb.
(iii) What is the number of shells in Sr ?
(iv) Predict whether K is a metal or a non-metal.
(v) Which one of these elements has the largest atom in size ?
(vi) Arrange Be, Ca, Mg and Rb in the increasing order
of the size of their respective atoms.
Answer: (i) Ca = 2, 8, 8, 2
(ii) Valence electrons in Rb = 1
(iii) Five
(iv) Metal
(v) Rb is biggest in size.
(vi) Be < Mg < Ca < Rb.
Question. An element P (atomic number 20) reacts with an element Q (atomic number 17) to form a compound.
Answer the following questions by giving reason:
Write the position of P and Q in the Modern Periodic Table and the molecular formula of the compound formed when P reacts with Q.
Answer:

Question. State the main aim of classifying elements.
Which is more fundamental property of elements that is used in the development of Modern Periodic Table ? Name and state the law based on this fundamental property. On which side of the periodic table one can find metals, non-metals and metalloids ?
OR
Write the main aim of classifying elements.
Name the basic property of elements used in the development of Modern Periodic Table. State the Modern Periodic Law. On which side (part) of the Modern Periodic Table do you find metals, metalloids and non-metals ?
Answer: (i) Aim of Classification: For systematic and simplified study of elements and their
compounds.
(ii) Basic property: Atomic Number.
(iii) Modern periodic Law: The properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
(iv) Metals are found on the left side and centre of the Modern Periodic Table.
(v) Metalloids are found in a zig-zag manner between the metals and the non-metals.
(vi) Non-metals are found on the right side of the Modern Periodic Table.
Question. Four elements A, B, C and D have atomic numbers 12, 13, 14 and 15 respectively.
Answer the following questions giving reasons:
(i) What is the number of valence electrons and valency of D ?
(ii) Which of them will have largest atomic radii ?
(iii) Which of these elements will form the most basic oxide ?
Answer: (i) Valence electrons in ‘D’ = 5 and Valency of ‘D’ = 3.
(ii) ‘A’ will have largest atomic radii because atomic radius decreases across a period from left to right.
(iii) ‘A’ will form the most basic oxide as it is most metallic.
Question. An element ‘X’ belongs to 3rd period and group 16 of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Determine the number of valence electrons and the valency of ‘X’.
(b) Molecular formula of the compound when ‘X’ reacts with hydrogen and write its electron dot structure.
(c) Name the element ‘X’ and state whether it is metallic or non-metallic.
Answer: (a) Electronic Configuration of X -2, 8, 6
Valence electrons = 6
Valency = 8 – 6 = 2
(b) Formula with hydrogen- H2X or H2S
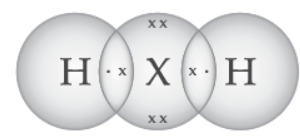
(c) Sulphur; Non-metal
Question. An element ‘M’ with electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) combines separately with (NO3)–, (SO4)2– and (PO4)3– radicals. Write the formula of the three compounds so formed. To which group and period of the Modern Periodic Table does the elements ‘M’ belong ? Will ‘M’ form covalent or ionic compounds? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer: The electronic configuration (2, 8, 2) of the element ‘M’ suggests that it belongs to group 2 and period 3 of the Modern Periodic Table and its valency is 2.
The chemical formula of the compounds are:
M(NO3)2 /Mg(NO3)2: MSO4 / MgSO4: M3 (PO4)2
Mg3(PO4)2
‘M’ will form ionic compounds by losing two electrons
Question. In the following table, the positions of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are given as they are in the Modern Periodic Table:

On the basis of the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the element which forms only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a non-metal with valency three.
(iii) Name the element which is a non-metal with valency three.
(iv) Out of B and C, whose atomic radius is bigger and why ?
(v) Write the common name for the family to which the elements D and F belong.
Answer: (i) E
(ii) B
(iii) C
(iv) B, because atomic radius decreases from left to right due to increase in the nuclear charge.
(v) Noble gases.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. (a) The modern periodic table has been evolved through the early attempts of Dobereiner, Newland and Mendeleev. List one advantage and one limitation of all the three attempts.
(b) Name the scientist who first of all showed that atomic number of an element is a more fundamental property than its atomic mass.
Answer: (a) (i) Dobereiner Periodic Table Advantage: To predict the atomic mass of middle element in each triad.
Limitation: Dobereiner could identify only three triads.
(ii) Newland Periodic table
Advantage: Every eighth element had properties similar to that of first and co-related the properties of elements with their atomic mass.
Limitation: It was only applicable upto Calcium/ only 56 elements and no future element.
(iii) Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
Advantage: Elements with similar properties could be grouped. He predicted the existence of new elements that had not been discovered at that time.
Limitation: No fixed position for hydrogen and isotopes. Atomic masses do not increase in a regular manner.
(b) Henry Moseley: Properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
Question. Explain giving justification the trends in the following properties of elements, on moving from left to right in a period, in the Modern periodic Table:
(a) Variation of valency.
(b) Change of atomic radius.
(c) Metallic to non-metallic character.
(d) Electronegative character.
(e) Nature of oxides.
Answer: (a) Valency first increases, then decreases
(b) Decreases
(c) Increase
(d) Increases
(e) Change from basic to acidic
Question. (i) Why do we classify elements ?
(ii) What are the two criteria used in the development of Modern Periodic Table ?
(iii) State the position of (a) metals, (b) non-metals and (c) metalloids in the periodic table.
(iv) Would you place two isotopes of chlorine; Cl–35 and Cl–37 in different slots of the periodic table because of their different atomic masses or in the same slot because their chemical properties are same ? Justify your answer.
Answer: (i) To study the properties of elements and to keep the elements with similar properties together.
(ii) Chemical properties of elements and atomic number.
(iii) Metals lie on extreme left, metalloids lie in the middle and non-metals lie on the right side.
(iv) They should be placed in the same slot. Since they have same numbers of electrons/atomic number and Modern Periodic Table is based on atomic number and not on atomic mass.
Question. The electrons in the atoms of four elements A, B, C and D are distributed in three shells having 1, 3, 5 and 7 electrons respectively in their outermost shells. Write the group numbers in which these elements are placed in the Modern Periodic Table, configuration of the atoms of B and D and the molecular formula of the compound formed when B and D combine.
Answer:
A B C D
1 3 5 7
• Group no. 1st 13th 15th 17th
• Electronic Configuration B = 2, 8, 3 D = 2 , 8 , 7
1 + 1
• BD3
Question. (a) List any three observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
(b) How does the metallic character of elements vary on moving from
(i) left to right in a period,
(ii) From top to bottom in a period of the Modern Periodic Table ? Given reason for your answer.
Answer: (a) (i) No fixed position of H in the periodic table.
(ii) Position of isotopes not clear.
(iii) Atomic mass does not increase in a regular manner
(or any other).
(b) (i) Left to right metallic character decreases.
Reason: Effective nuclear charge increases / tendency to loose electrons decrease / electropositivity decreases. (any one reason)
(ii) Top to bottom metallic character increases.
Reason: Size of atom increase/tendency to loose electron increases(any one reason).
Question. The position of certain elements in the Modem Periodic Table are shown below: 1
Using the above table answer the following questions giving reasons in each case:
(i) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a non-metal with valency 2 ?
(iii) Which element is a metal with valency 2 ?
(iv) Out of H, C and F which has largest atomic size ?
(v) To which family does H, C and F belong ?
Answer: (i) Element E is Silicon. It will form covalent bond only as it has four electrons in its outermost orbit and need only four more electrons to become stable.
(ii) Non-metal with valency 2 is B, which is Oxygen.
(iii) Element D is a metal with valency 2. Element D is Magnesium. Due to its low electronegativity, it has a higher tendency to donate electrons.
(iv) Element F has the largest atomic size. Element F is Argon. Argon occupies 3 energy shells compared to elements H and C, which occupies one and two energy shells. Due to this, the atomic radius of Argon is the largest.
(v) Elements H, C and F belong to Group number 18, which means according to their electronic configuration, their octet is complete and thus these elements are stable. They have very low tendency to react with other elements.
Group 18 elements belong to noble gas family.
Question. (a) What was the basis of Mendeleev’s classification of elements ?
(b) List two achievements of Mendeleev’s Periodic table.
(c) List any two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s periodic law.
Answer: (a) Atomic mass
(b) (i) He could classify all the 63 elements known at that time.
(ii) He left gaps for the yet to be discovered elements.
(iii) He predicted the properties of such elements.
(c) (i) Position of isotopes
(ii) Irregular increase in atomic masses in going from one element to the next, making the prediction of undiscovered elements difficult.
(iii) Position of Hydrogen.