Please refer to the Class 9 Science Sample Paper for the current academic year given below. We have provided the latest CBSE Sample Papers for Term 1 and Term 2 for Science Class 9. All guess sample papers have been prepared based on the latest blueprint and examination pattern for the current year. All sample papers for Science Class 9 Term 1 and 2 have been given with solutions. Students can access the multiple guess papers given below. Practicing more Class 9 Science Sample Papers will help you to get more marks in upcoming exams.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Science
| Term 2 Sample Papers for Class 9 Science |
| Class 9 Science Sample Paper Term 2 Set A |
Class 9 Science Sample Paper Term 2 Set A
Question: Which of the following are types of disease-causing agents?
(a) Viruses, bacteria and fungi
(b) Measles, mumps and chicken pox
(c) Cholesterol, saturated fat and helminthes
(d) All of these
Answer:
A
Question: If the number of electrons in an ion is 10 and the number of protons is 9, then
(i) What would be the atomic number of the ion?
(ii) What is the charge on the ion?
(i) Atomic number (Z) = No. of protons = 9
(ii) Charge on the ion = –1
Here, one electron is more than proton due this extra
electron, ion attains –1 charge.
Answer: (i) Atomic number (Z) = No. of protons = 9
(ii) Charge on the ion = –1
Here, one electron is more than proton due this extra electron, ion attains –1 charge.
Question: Name the deficiency disease caused due to deficiency of (i) Vitamin A (ii) Vitamin B1
OR
What are contagious diseases? Give one example.
Answer: (i) Night blindness or Xerophthalmia
(ii) Beri-beri
OR
The diseases which spread by actual contact between infected person and healthy person are called contagious diseases. Example – Chicken pox.
Question: Name any two viral diseases which commonly occur in infants/children.
Answer: (i) Mumps
(ii) Poliomyelitis or polio
OR
Name the scientist who first discovered penicillin antibiotic. Can you name any other known antibiotic?
Answer: Sir Alexander Fleming discovered the antibiotic penicillin. Other known antibiotic is streptomycin.
Question: Which is incorrect about malarial disease?
(a) It occurs due to bite of male mosquito.
(b) Its causative organism is Plasmodium.
(c) It can be controlled by antimalarial drugs.
(d) Its symptoms include fever, paroxysms of chills, etc.
Answer:
A
For question numbers 6 and 7, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled
Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below :
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question: Assertion : Thomson’s atomic model is known as ‘raisin pudding’ model.
Reason : The atom is visualized as a pudding of positive charge with electrons (raisins) embedded in it.
Answer: A
Question: Assertion : Cathode rays get deflected towards the positive plate of electric field.
Reason : Cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles known as electrons.
Answer: In electric field, negatively charged particles always move towards positive plate and vice – versa.
Question: Assertion : Chicken pox is a mild disease and it leaves no scars and marks.
Reason : Chicken pox results in rashes which appear first on face and spread on stomach and chest later.
Answer: A
No. 8 and 9 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four sub-parts in these questions.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 8(i) to 8(v).
A mole is defined as the amount of substance containing the same number of discrete entities. The number of entities composing a mole has been experimentally determined to be 6.022 × 1023, a fundamental constant named Avogadro’s number NA. The molar mass of an element is the mass in gram of 1 mol of that substance.
Question: 52 g of He contains
(a) 4 × 6.022 × 1023 atoms
(b) 13 atoms
(c) 13 × 6.022 × 1023 atoms
(d) 4 atoms.
Answer: C
Question: The number of atoms in 0.1 mole of a triatomic gas is
(a) 6.026 × 1022
(b) 1.806 × 1023
(c) 3.6 × 1023
(d) 1.8 × 1022
Answer: C
B
Question: What is the mass of 12.044 × 1023 number of O2 molecules?
(a) 8 g
(b) 16 g
(c) 32 g
(d) 64 g
Answer:
D
Question: Mass of 3 moles of NaOH in grams is
(a) 240 g
(b) 120 g
(c) 100 g
(d) 69 g
Answer:
B
Question: How many molecules are present in one gram of hydrogen?
(a) 6.022 × 1023
(b) 6.022 × 1022
(c) 3.01 × 1023
(d) 3.0125 × 10–12
Answer:
C
Read the following and answer any four questions from 9(i) to 9(v).
In Newtonian physics,free fall is defined as the motion of an object where gravity is the only force acting upon it. A set of equations describe the resultant trajectories when objects move owing to a constant gravitational force under normal Earth-bound conditions. When a body is falling vertically downwards, its velocity is increasing and when body is thrown vertically upwards, its velocity is decreasing. Near the surface of the Earth, an object in free fall in a vacuum will accelerate at approx. 9.8 m/s2, independent of its mass. With air resistance acting on an object that has been dropped, the object will eventually reach a terminal velocity, which is around 53 m/s for a human skydiver.

Question: An object is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity u, the greatest height h to which it will rise before falling
back is given by
(a) u/g
(b) u2/2g
(c) u2/g
(d) u/2g
Answer:
B
Question: Two objects of different masses falling freely near the surface of Moon would
(a) have same velocities at any instant
(b) have different accelerations
(c) experience forces of same magnitude
(d) undergo a change in their inertia.
Answer:
A
Question: The value of g on the surface of the Moon
(a) is the same as on the Earth
(b) is less than that on the Earth
(c) is more than that on the Earth
(d) keeps changing day by day.
Answer:
B
Question: If a ball is dropped from a height of 20 m, then the speed of the ball when it hits the ground is
(a) 20 m/s
(b) 400 m/s
(c) 40 m/s
(d) 4 m/s
Answer:
A
Question: If a ball is thrown up with a speed 15 m/s, how high will it go before it begins to fall? ( g = 9.8 m/s2)
(a) 1.14 m
(b) 11.4 m
(c) 114 m
(d) 0.114 m
Answer:
B
Question: Which of the two elements would be more reactive, element A having atomic number 18 or element B having atomic number 19? Give reason.
Answer: The electronic configurations of elements A and B are given below :
18A 2 8 8
19B 2 8 8 1
Since the outermost shell of element A is completely filled, it is stable and unreactive. The outermost shell of element B contains one electron only. Hence, it is more reactive.
Question: Two bodies of equal masses move with the uniform velocities v and 3 v respectively. Find the ratio of their kinetic energies.
OR
In a tug of war one team is slowly giving way to the other. What work is being done and by whom ?
Answer:
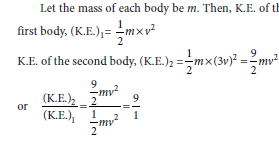
Thus, the kinetic energy of the second body is nine times the kinetic energy of the first body.
OR
The work is done by the winning team and is equal to the product of resultant force applied by the two teams and displacement that the losing team suffers.
Question: A sample of ethane (C2H6) gas has the same mass as 1.5 × 1020 molecules of methane (CH4). How many C2H6 molecules does the sample of gas contain?
Answer:
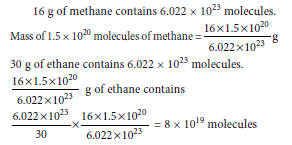
Question: What are the properties of gravitational force?
Answer: Gravitational force shows the following properties :
(i) Gravitational force is an action-at-a-distance force.
This means the gravitational force always exists between two particles irrespective of the medium which separates them.
(ii) Gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two particles.
(iii) Gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two particles.
Question: A sample of ammonia (NH3) weighs 2.00 g. What mass of sulphur dioxide (SO2) contains the same number f molecules as are in 2.00 g of ammonia?
Answer:
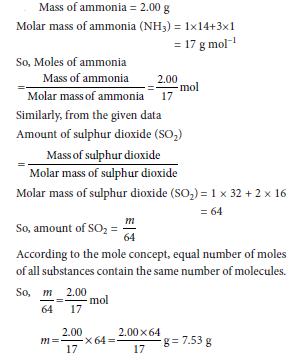
Question: Mention the possible causes that you can think of when a baby is suffering from diarrhoea, while other babies in the same locality do not. Which among them will you rate as immediate cause and what term is given to other causes?
OR
‘A person suffered once from small pox cannot suffer from it again’. Give reason.
Answer: Possible causes by diarrhoea in baby are:
(i) The baby may have contracted the pathogen from the contaminated food and/or water.
(ii) The baby is not nourished properly and does not have strong immunity.
(iii) The genetic make up of the baby is not able to fight against the infection.
Pathogen through contaminated food and water is the immediate cause, while others are contributory causes.
OR
A person suffered once from small pox cannot suffer from it again. This is because when the immune system of person’s body first comes across an infectious organism like a virus causing small pox, it responds against virus and then remembers it specifically. When next time that particular microbe or its close relatives enter the body, the immune system of the body responds with the pathogen even with greater vigour. This eliminates the infection more quickly than the first time and thus, we do not suffer with the same disease again.
Question: Give reasons for the following :
(a) Isotopes of an element are chemically similar.
(b) An atom is electrically neutral.
(c) Noble gases show least reactivity.
(d) Nucleus of an atom is heavy and positively charged.
(e) Ions are more stable than atoms.
OR
(a) The diagram given below shows an atom of element Y having atomic number 20 and mass number
(i) Deduce the proton number of Y.
(ii) Deduce the nucleon number of Y.
(iii) Give the electronic configuration of Y2+.
(b) Arrange the given elements in the increasing order of their reactivity.
19X39, 12Y24, 14W28
Answer: (a) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number as well as electronic configuration. Since the chemical properties of elements are related to their electronic configuration, i.e., the elements with similar configuration will have similar properties. Thus, the isotopes of an element are chemically similar.
(b) In an atom, the number of protons in the nucleus is equal to the number of electrons in the extra-nuclear portion. Since each proton and each electron has the same charge but with opposite magnitude, the atom is electrically neutral.
(c) The atoms of noble gas elements have complete outermost shells. Hence, they are least reactive.
(d) Nucleus of an atom is made up of protons which are positively charged and neutrons that are neutral. The total mass of neutron and proton makes it heavy (e) When an atom changes into an ion (cation or anion) the valence shell of the ion has a compete octet or duplet which makes ions more stable than atoms.
OR
(a) (i) Z = p = 20
(ii) A = n + p = 40
(iii) 2, 8, 8
(b) Electronic configuration of 19X39, 12Y24, 14W28 are given as :
X (19) : 2, 8, 8, 1 ; Y (12) : 2, 8, 2 ; W (14) : 2, 8, 4
Due to presence of less number of valence electrons, the reactivity of element X is greater.
∴ Increasing order of their reactivity is W, Y, X.
Question: What is power? How do you differentiate kilowatt from kilowatt hour? The Jog Falls in Karnataka state are nearly 20 m high. 2000 tonnes of water falls from it in a minute. Calculate the equivalent power if all this energy can be utilized? (g = 10 m s–2)
OR
Answer the following :
(a) The casing of a rocket in flight burns up due to friction. At whose expense is the heat energy required for burning obtained? The rocket or the atmosphere?
(b) Comets move around the sun in highly elliptical orbits. The gravitational force on the comet due to the sun is not normal to the comet’s velocity in general. Yet the work done by the gravitational force over every complete orbit of the comet is zero. Why?
(c) An artificial satellite orbiting the earth in very thin atmosphere loses its energy gradually due to dissipation against atmospheric resistance, however small. Why then does its speed increase progressively as it comes closer and closer to the earth?
Answer: Power is defined as the rate of doing work or the rate of transfer of energy.
Kilowatt is the unit of power and kilowatt hour is the unit of energy or work.
As kilowatt hour = unit of power × unit of time.
Energy possessed by 2000 tonnes (= 2000 × 103 kg)
water at a height of 20 m,
Ep = mgh = 2000 × 103 × 10 × 20 = 4 × 108 J
Power generated if all this energy can be utilized,
P= Ep/t
= 4 x108 j/ 60s(∴t min= 60s) = 6.6 × 106 W
OR
(a) When the casing burn up, mass of the rocket decreases due to which total energy of the rocket also decreases. According to conservation of energy
Total energy = P.E + K.E
= mgh + 1/2 mv2
Hence, total energy of the rocket in flight depends on its mass. Therefore, heat energy required for burning is obtained from the rocket itself and not from the atmosphere.
(b) This is because gravitational force is path independent. Work done by the gravitational force of the sun over a closed path in every complete orbit of the comet is zero.
(c) When the artificial satellite orbiting the earth comes closer and closer to earth, its potential energy decreases. As sum of potential energy and kinetic energy is constant, therefore, K.E. of satellite and hence its velocity goes on increasing. However, total energy of the satellite decreases a little on account of dissipation against atmospheric resistance.
