Students should refer to Worksheets Class 10 Science Human Eyes and Colourful World Chapter 11 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 10 Science based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 10 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 10 Science for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Human Eyes and Colourful World Worksheets Class 10 Science
Question. The least distance of distinct vision for a young adult with normal vision is about
(a) 25 m
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 2.5 m
Answer
C
Question. The human eye forms the image of an object at its
(a) cornea
(b) iris
(c) pupil
(d) retina
Answer
D
Question. The human eye can focus objects at different distances by adjusting the focal length of the eye lens. This is due to
(a) presbyopia
(b) accommodation
(c) near-sightedness
(d) far-sightedness
Answer
B
Question.The change in focal length of an eye lens is caused by the action of the
(a) pupil
(b) retina
(c) ciliary muscles
(d) iris
Answer
C
Question. Twinkling of stars is a phenomenon that occurs due to
(a) Refraction
(b) Reflection
(c) Varying conditions of the earth’s atmosphere
(d) a and c
Answer
D
Question. Aging causes weakness of the_________ resulting in presbyopia.
(a) Lens
(c) Ciliary muscles
(b) Retina
(d) Optic nerve
Answer
C
Question. In a spectrum of light the colour that has the least wavelength is –
(a) Red
(b) Violet
(c) Green
(d) Yellow.
Answer
B
Question. In the condition myopia the person
(a) Cannot see far off things
(b) Can see things close by clearly
(c) Can be corrected using a concave lens
(d) All of the above.
Answer
D
Question. The eye defect Hypermetropia can be corrected by using a
(a) Plano convex lens
(b) Double convex lens
(c) Plano concave lens
(d) Double concave lens
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A). The sky appears dark to people flying at high altitudes.
Reason(R). The atmosphere is denser close to the earth.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A). A rainbow always appears on the same side as the sun.
Reason(R). A rainbow is a natural spectrum which occurs after a shower.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
(c) A is true but R is false
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Why does the Sun appear reddish at sunrise?
Answer: The Sun appears reddish at sunrise is due to scattering of light by the particles present in the atmosphere.
Question. State the function of each of the following parts of human eye:
(i) Cornea
(ii) Pupil
Answer: (i) Cornea : It is a transparent bulge on the fron surface of eyeball which refracts most of the light rays entering the eye.
(ii) Pupil : It controls the amount of light entering into the eye.
Question. State one function of the crystalline lens in the human eye.
Answer: The crystalline lens of human eye focuses the light that enters the eye and form the image on the retina.
Question. Give an example of a phenomenon where Tyndall effect can be observed.
Answer: The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particle give rise to Tyndall effect.
Question. State one function of iris in human eye.
Answer: Iris is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil.
Question. What will be the observed colour of sky on a planet where there is no atmosphere? Why?
Answer: Observed colour of the sky on a planet where there is no atmosphere will be black because there is no air molecules to scatter the light coming from the sun.
Question. Name the part of our eyes that helps us to focus near and distant objects in quick succession.
Answer: Crystalline lens.
Question. Why is the colour of clear sky blue?
Answer: The colour of clear sky is blue due to the scattering of light having shorter wavelength by the air molecules present in the atmosphere.
Question. Give reasons for the sun can be seen about two minutes before actual sunrise.
Answer: The sun can be seen about two minutes before actual sunrise because when the sun is below the horizon, its light entering the earth’s atmosphere goes continuous refraction and thus we can able to see the apparent position of the sun (above horizon).
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. (a) What is Presbyopia? State the cause of presbyopia. How is Presbyopia of a person corrected?
(b) What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye of a person?
Answer: (a) : Presbyopia is a defect in eye where an old person is not able to see the nearby object distinctly.
Cause : Presbyopia is caused by the gradual
weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of eye lens.
Correction : Presbyopia can be corrected by using appropriate convex lens or bifocal lens if he suffers from both myopia or hypermetropia.
(b) Power of accommodation of the of a person is the ability of crystalline lens to adjust its focal length.
Question. (a) List the parts of the human eye that control the amount of light entering into it. Explain how they perform this function?
Answer: (a) The part of the human eye that control the amount of light entering into it is pupil.
Light enters the eye through a thin membrane called the cornea. It forms the transparent bulge on the front surface of the eyeball most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at the outer surface of the cornea, the crystalline lens merely provides the linear adjustment of focal length required to focus objects at different distances on the retina. Iris which is behind the cornea controls the size of the pupil. The pupil regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Question. Millions of people of the developing countries of world are suffering from corneal blindness.
These persons can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of a donated eye. A charitable society of your city has organised a campaign in your neighbourhood in order to create awareness about this fact. If you are asked to participate in this mission how would you contribute in this noble cause?
(i) State the objective of organising such campaigns.
(ii) List two arguments which you would give to motivate the people to donate their eyes aftdeath.
(iii) List two values which are developed in the persons who actively participate and contribute in such programmes.
Answer: (i) The objective of organising such campaign is to make people aware and realize their duties towards society.
(ii) (a) By donating our eyes after the die, we can light the life of a blind person.
(b) One pair of eyes gives vision to two corneal Blind people.
(iii) (a) It shows the concern for others.
(b) It also shows the responsible behavior towards the society.
Question. Do you know that the corneal-impairment can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of the donated eye? How and why should we organise groups to motivate the community members to donate their eyes after death?
Answer: Yes, we know that the corneal – impairment can be cured by replacing the objective cornea with the cornea of the donated eye. We can provide the importance of eye donation to the community members. Our eyes can live even after our death.
By donating our eyes after die, we can light the life of a blind person. The human eye is one of the most valuable and sensitive sense organs. It enables us to see the wonderful world and colours around us It is however, impossible to identify colours while closing the eyes. Thus of all the sense organs, the human eye is the most significant one as it enables as to see the beautiful colourful word around us.
Hence, we should donate our eyes after death.
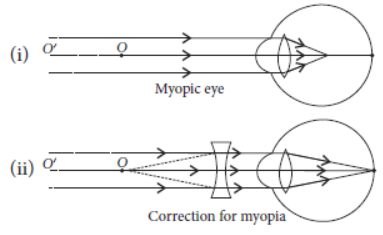
Question. What is myopia? List two causes for the development of this defect? How can this defect be corrected using a lens? Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation in case (i) defective eye and (ii) corrected eye.
Answer: Myopia is also known as near–sightedness defect in which a person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly.
This defect may arise due to
(a) excessive curvature of the eye.
(b) elongation of the eye ball.
This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power. A concave lens of suitable power will being the image back on the retina and thus the defect is corrected.
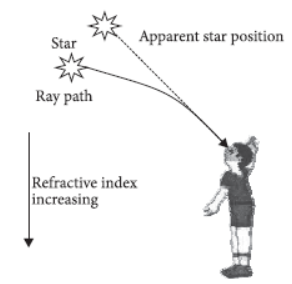
Question. A star appears slightly higher (above) than its actual position in the sky. Illustrate it with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer: A star appears slightly above than its actual position in the sky. Since the starlight, on entering the earth’s atmosphere undergoes refraction continuously in a medium of gradually changing refractive index, before it reaches the earth.
Since the atmosphere bends starlight towards the normal, the star appears slightly above than its actual position.
Question. Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass prism. Mark on it (a) the incident ray, (b) the emergent ray and (c) the angle of deviation.
Answer:

i = angle of incidence
(a) PE = incident ray
(b) FS = emergent ray
(c) ∠D = angle of deviation
Question. Why do stars appear to twinkle ? Explain.
Answer: Since the stars are very distant, they are approximately point-sized sources of light. As the path of rays of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering the eye flickers – the star sometimes appears brighter, and at some other time, fainter, which is the twinkling effect.
Question. (a) A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum when white light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce any spectrum. Explain why it is so.
Answer: (b) A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum but glass slab doesn’t produce spectrum because in case of a prism, when a white light passes through each of the constituent wavelength of light undergoes different extent of deviation. This result in dispersion of white light. On the other hand, when the light enters through the parallel sides of glass slab, each constituent wavelength of white light doesn’t undergo any net deviation. Hence, the white light does not split into constituent spectrum.
Question. Write about power of accommodation of human eye. Explain why the image distance in the eye does not change when we change the distance of an object from the eye?
Answer: The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length is called power of accommodation.
The ciliary muscles modifies the curvature to some extent. The change in the curvature of the eye lens can thus change its focal length. Thus, the focal length of the human lens increases or decreases depending on the distance of the object value to this distance of the image does not change. For example, when the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the lens becomes thin and its focal length increases, thus enables us to see distant object clearly.
Question. What will be the colour of the sky when it is observed from a place in the absence of any atmosphere?
Answer: If the earth had no atmosphere, there would not have been any scattering. Then, the sky would look dark.
Question. Explain why the planets do not twinkle?
Answer. Planets do not twinkle because they appear larger in size than the stars as they are relatively closer to earth. Planets can be considered as a collection of a large number of point-size sources of light. The different parts of these planets produce either brighter or dimmer effect in such a way that the average of brighter and dimmer effect is zero. Hence, the twinkling effects of the planets are nullified and they do not twinkle.
Question. A student has difficulty reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could be the defect the child is suffering from? How can it be corrected?
Answer. A student has difficulty in reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. It shows that he is unable to see distant objects clearly. He is suffering from myopia. This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens.
Question. A person needs a lens of power −5.5 dioptres for correcting his distant vision. For correcting his near vision he needs a lens of power +1.5 dioptre. What is the focal length of the lens required for correcting (i) distant vision, and (ii) near vision?
Answer. For distant vision = −0.181 m, for near vision = 0.667 m
The power P of a lens of focal length f is given by the relation
P = 1 / f ( in meters)
(i) Power of the lens used for correcting distant vision = −5.5 D
Focal length of the required lens, f = 1 / P
f = 1 / -5.5 = -0.181m
The focal length of the lens for correcting distant vision is −0.181 m.
(ii) Power of the lens used for correcting near vision = +1.5 D
Focal length of the required lens, f = 1 / P
f = 1 / 1.5 = +0.667m
The focal length of the lens for correcting near vision is 0.667 m.
Question. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Answer. The near point of the eye is the minimum distance of the object from the eye, which can be seen distinctly without strain. For a normal human eye, this distance is 25 cm.
The far point of the eye is the maximum distance to which the eye can see the objects clearly. The far point of the normal human eye is infinity.
Question. Ritu needs a lens of power -2D for correct of her vision.
(a) What kind of defect in vision is she suffering from?
(b) What are the possible cause of this defect?
(c) What is the nature of corrective lens?
Answer: (a) Ritu is suffering from myopia or short sightedness.
(b) Two possible causes of this effect are:Increase in size of eye ball or decrease in focal length of eye lens.
(c) Concave lens / diverging lens
Question. List the three phenomenon of light which is responsible for formation of rainbow in sky?
Answer: Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection.
Question. Why are ‘danger’ signal lights red in colour?
Answer: Danger signals are red in colour because the red coloured light having lower wavelength is scattered the least by fog or smoke. Therefore, it can be seen clearly from a distance.
Question. A person needs a lens of power 4.5 D for correction of her vision.
(a) What kind of defect in vision is she suffering from?
(b) What is the focal length of the corrective lens?
(c) What is the nature of the corrective lens?
Answer: (a)Hypermetropia.
(b) f=1/4.5 = 0.22m
(c) Convex lens
Question. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision?
Answer: For normal vision, the near point is about 25cm and far point is infinity. Thus, a normal eye can see objects clearly that are between 25cm and infinity.
Question. Give reasons why the planets do not twinkle
Answer: Planets are much closer to the earth as compared to the stars they are bigger when we observe them from earth. Planets are made up of large number of point sources. Due to atmospheric refraction each point source will appear to twinkle, the total effect will be nullified.
Question. What is meant by dispersion and recombination? What is a spectrum? Name the various colours of spectrum of white light in proper sequence.
Answer: The splitting of white light into its component colours on passing through a prism is called dispersion. When an inverted prism is kept in the path of these seven colours, they combine to form white light. This is called recombination.The band of seven colours formed due to dispersion of white light is called ‘spectrum’. Seven colours of spectrum are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red also known as ‘VIBGYOR’
Question. Why do stars twinkle?
Answer. Stars emit their own light and they twinkle due to the atmospheric refraction of light. Stars are very far away from the earth. Hence, they are considered as point sources of light. When the light coming from stars enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets refracted at different levels because of the variation in the air density at different levels of the atmosphere. When the star light refracted by the atmosphere comes more towards us, it appears brighter than when it comes less towards us. Therefore, it appears as if the stars are twinkling at night.
Question. The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
Answer. The person is suffering from an eye defect called myopia. In this defect, the image is formed in front of the retina. Hence, a concave lens is used to correct this defect of vision.
Object distance, u = infinity = ∞
Image distance, v = −80 cm
Focal length = f
According to the lens formula,
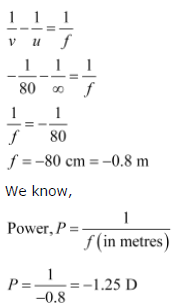
A concave lens of power −1.25 D is required by the person to correct his defect.
Question. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye?
Answer. Since the size of eyes cannot increase or decrease, the image distance remains constant.
When we increase the distance of an object from the eye, the image distance in the eye does not change. The increase in the object distance is compensated by the change in the focal length of the eye lens. The focal length of the eyes changes in such a way that the image is always formed at the retina of the eye.
Question. Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Answer. A person suffering from hypermetropia can see distinct objects clearly but faces difficulty in seeing nearby objects clearly. It happens because the eye lens focuses the incoming divergent rays beyond the retina. This defect of vision is corrected by using a convex lens. A convex lens of suitable power converges the incoming light in such a way that he image is formed on the retina, as shown in the following figure.
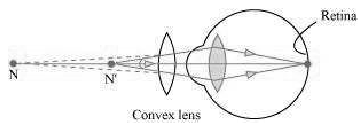
The convex lens actually creates a virtual image of a nearby object (N’ in the figure) at the near point of vision (N) of the person suffering from hypermetropia.
The given person will be able to clearly see the object kept at 25 cm (near point of the normal eye), if the image of the object is formed at his near point, which is given as 1m.
Object distance, u = −25 cm
Image distance, v = −1 m = −100 m
Focal length, f
Using the lens formula,
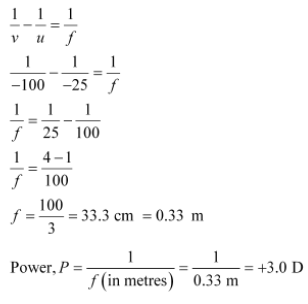
A convex lens of power +3.0 D is required to correct the defect.
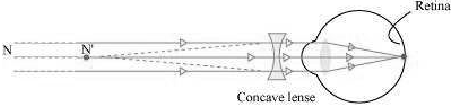
Question. A person with a myopic eye cannot see objects beyond 1.2 m distinctly. What should be the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision?
Answer. The person is able to see nearby objects clearly, but he is unable to see objects beyond 1.2 m. This happens because the image of an object beyond 1.2 m is formed in front of the retina and not at the retina, as shown in the given figure.

To correct this defect of vision, he must use a concave lens. The concave lens will bringthe image back to the retina as shown in the given figure.
Question. Why does the Sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer. During sunrise, the light rays coming from the Sun have to travel a greater distance inthe earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. In this journey, the shorter wavelengths of lights are scattered out and only longer wavelengths are able to reach our eyes. Since blue colour has a shorter wavelength and red colour has a longer wavelength, the red colour is able to reach our eyes after the atmospheric scattering of light. Therefore, the Sun appears reddish early in the morning.
Question. What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye?
Answer. When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant objects are clearly visible to the eyes. To see the nearby objects clearly, the ciliary muscles contract making the eye lens thicker. Thus, the focal length of the eye lens decreases and the nearby objects become visible to the eyes. Hence, the human eye lens is able to adjust its focal length to view both distant and nearby objects on the retina. This ability is called the power of accommodation of the eyes.
Question. Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer. The sky appears dark instead of blue to an astronaut because there is no atmosphere in the outer space that can scatter the sunlight. As the sunlight is not scattered, no scattered light reach the eyes of the astronauts and the sky appears black to them.


