Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases Chapter 8 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 8 Human Health and Diseases have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Biology based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Biology for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Biology Human Health and Diseases Worksheets Class 12
Multiple Choice Questions for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Question. Identify the correct pair representing the causative agent of typhoid fever and the confirmatory test for typhoid.
(a) Salmonella typhi / Widal test
(b) Plasmodium vivax / UTI test
(c) Streptococcus pneumoniae / Widal test
(d) Salmonella typhi / Anthrone test
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following sets of diseases is caused by bacteria?
(a) Cholera and tetanus
(b) Typhoid and smallpox
(c) Tetanus and mumps
(d) Herpes and influenza
Answer
A
Question. Some of the events occur during life cycle of Plasmodium are given below. Identify the correct statement.
(a) Female mosquito take up sporozoites with blood meal.
(b) The sporozoites reproduce sexually in liver cells.
(c) When mosquito bites a man, gametocytes are injected.
(d) The gametocytes develop in RBCs.
Answer
D
Question.
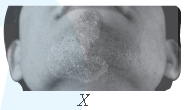
In the given figure, X is caused by
I. Wuchereria II. Microsporum
III. Haemophilus IV. Epidermophyton
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) II and IV
(d) I and IV
Answer
C
Question. Internal bleeding, muscular pain, blockage of the intestinal passage and anaemia are some of the symptoms caused due to infection by
(a) Ascaris
(b) Wuchereria
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Trichophyton.
Answer
A
Question. Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by
(a) Tse-tse fly
(b) mosquito bite
(c) drinking water containing eggs of Ascaris
(d) eating imperfectly cooked pork.
Answer
C
Question. Select the correct statement from the ones given below.
(a) Barbiturates when given to criminals make them tell the truth.
(b) Morphine is often given to persons who have undergone surgery as a pain killer.
(c) Chewing tobacco lowers blood pressure and heart rate.
(d) Cocaine is given to patients after surgery as it stimulates recovery.
Answer
B
Question. Common cold differs from pneumonia in that
(a) pneumonia is a communicable disease whereas the common cold is a nutritional deficiency disease
(b) pneumonia can be prevented by a live attenuated bacterial vaccine whereas the common cold has no effective vaccine
(c) pneumonia is caused by a virus while the common cold is caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae
(d) pneumonia pathogen infects alveoli whereas the common cold affects nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs.
Answer
D
Question. Match the causative organisms with their diseases.
| (A) Haemophilus | (1) Malignant influenzae malaria |
| (B) Entamoeba | (2) Elephantiasis histolytica |
| (C) Plasmodium | (3) Pneumonia falciparum |
| (D) Wuchereria | (4) Typhoid bancrofti |
| (E) Salmonella typhi | (5) Amoebiasis |
(a) A – 1, B – 5, C – 3, D – 2, E – 4
(b) A – 3, B – 5, C – 1, D – 2, E – 4
(c) A – 5, B –1, C – 3, D – 4, E – 2
(d) A – 1, B – 3, C – 2, D – 5, E – 4
Answer
B
Question. Which part of poppy plant is used to obtain the drug “smack”?
(a) Flowers
(b) Latex
(c) Roots
(d) Leaves
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is incorrect about cancer cells?
(a) They exhibit mass proliferation.
(b) They exhibit the property of contact inhibition.
(c) They are produced when cellular oncogenes
of normal cells are activated.
(d) They are metastatic.
Answer
B
Question. Transplantation of tissues/organs fails often due to non-acceptance by the patient’s body.
Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections?
(a) Cell-mediated immune response
(b) Hormonal immune response
(c) Physiological immune response
(d) Autoimmune response
Answer
A
Question. Short-lived immunity acquired from mother to fetus across the placenta or through mother’s milk to the infant is categorised as
(a) active immunity
(b) passive immunity
(c) CMI
(d) autoimmunity.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following immunoglobulins does constitute the largest percentage in human milk?
(a) IgA
(b) IgG
(c) IgD
(d) IgM
Answer
C
Question. The blood does not clot inside the body because of
(a) oxygenation of blood
(b) movement of blood
(c) presence of heparin in blood
(d) absence of fibrinogen in blood.
Answer
C
Question. Read the statements.
(i) IgE antibodies are produced in an allergic reaction.
(ii) B-lymphocytes mediate cell mediated immunity.
(iii) The yellowish fluid colostrum has abundant IgE antibodies.
(iv) Spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ.
(a) (i) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i) and (ii) are correct
(c) (ii) and (iii) are correct
(d) (iii) and (iv) are correct.
Answer
A
Question. The cell-mediated immunity inside the human body is carried out by
(a) thrombocytes
(b) erythrocytes
(c) T-lymphocytes
(d) B-lymphocytes.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to immunity?
(a) Preformed antibodies need to be injected to treat the bite by a viper snake.
(b) The antibodies against small pox pathogen are produced by T-lymphocytes.
(c) Antibodies are protein molecules, each of which has four light chains.
(d) Rejection of a kidney graft is the function of B-lymphocytes.
Answer
A
Question. In the immune system, interferons are a part of
(a) physiological barriers
(b) cellular barriers
(c) physical barriers
(d) cytokine barriers
Answer
D
Question. Select the correct statement with respect to diseases and immunisation.
(a) If due to some reason B and T lymphocytes are damaged, the body will not produce antibodies against a pathogen.
(b) Injection of dead/inactivated pathogens causes passive immunity.
(c) Certain protozoans have been used in mass production of hepatitis B vaccine.
(d) Injection of snake antivenom against snake bite is an example of active immunisation.
Answer
A
Question. The toxic substance, ‘haemozoin’, related to the high fever and chill, is released during which of the following disease?
(a) Dengue
(b) Malaria
(c) Diphtheria
(d) Phenumonia
Answer
B
Question. The pathogens of genera, Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermorphyton are responsible for
(a) botulism
(b) conjunctivitis
(c) ringworms
(d) skin allergy
Answer
C
Question. Food poisoning is caused by
(a) Entamoeba histolytica
(b) Escherichia coli
(c) Clostridium botulinum
(d) Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Answer
C
Question. Vector for kala azar is:
(a) sandfly
(b) bedbug
(c) louse
(d) housefly
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a communicable disease?
(a) Malaria
(b) Diabetes
(c) Hypertension
(d) Kwashiorkar
Answer
A
Question. Mumps is a viral disease and painful swelling of
(a) parotid glands
(b) thyroid
(c) thymus
(d) sublingual glands
Answer
A
Question. In which of the following disease, there is always a time lag between the infection and appearance of the symptoms of that particular disease?
(a) AIDS
(b) Allergy
(c) Cancer
(d) Alcoholism
Answer
A
Question. Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by
(a) eating imperfectly cooked pork.
(b) tse-tse fly.
(c) mosquito bite.
(d) drinking water containing eggs of Ascaris.
Answer
D
Question. To which type of barriers under innate immunity, do the saliva in the mouth and the tears from the eyes, belong?
(a) Physical barriers
(b) Cytokine barriers
(c) Cellular barriers
(d) Physiological barriers
Answer
D
Question. Immunoglobulins are
(a) antigen
(b) antibodies
(c) antiseptics
(d) antibiotics
Answer
B
Question. A cell-coded protein that is formed in response to infection with most animal viruses is called
(a) interferon
(b) antigen
(c) histone
(d) antibody
Answer
A
Question. The letter T in T-lymphocyte refers to :
(a) thymus
(b) thyroid
(c) thalamus
(d) tonsil
Answer
A
Question. Passive immunity is defined as immunity
(a) inherited from the parents.
(b) achieved through vaccination.
(c) acquired through first exposure to the disease.
(d) achieved through the sera of other animals enriched in antibodies.
Answer
C
Question. Short -lived immunity acquired from mother to foetus across placenta or through mother’s milk to the infant, is categorized as
(a) active immunity
(b) passive immunity
(c) cellular immunity
(d) innate non-specific immunity
Answer
B
Question. Antigen binding site in an antibody is found between
(a) two light chains
(b) two heavy chains
(c) one heavy and one light chain
(d) either between two light chains or between one heavy and one light chain depending upon the nature of antigen.
Answer
C
Question. Resistance in body against diseases is given by
(a) vaccinations
(b) histamine
(c) immunoglobulins
(d) antigens
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following results in fever when released in body during disease ?
(a) Pyrogens
(b) Antibodies
(c) Interferons
(d) Interleukins
Answer
A
Question. When a quick immune response is required due to infection of a deadly microbe, the patient is injected with
(a) protein of pathogen
(b) inactivated or weakened pathogen
(c) preformed antibodies
(d) vaccine
Answer
C
Question. B-lymphocytes are associated with
(a) humoral immunity
(b) production of heparin
(c) cell mediated immunity
(d) internal cleansing
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is trapped in the lymph nodes and responsible for the activation of lymphocytes present there and cause the immune response?
(a) Antigen
(b) Antibody
(c) Pathogen
(d) Lymph fluid
Answer
A
Question. Hepatitis B and AIDS are
(a) caused by Retro-viruses.
(b) transmitted through sexual contact.
(c) congenital diseases.
(d) transmitted through infected blood.
Answer
D
Question. The cell in the human body invaded by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is
(a) B – cell
(b) macrophage
(c) erythrocyte
(d) T- helper cell
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following endocrine glands is often referred in relation with AIDS?
(a) Thyroid
(b) adrenal
(c) Thymus
(d) Pancreas
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following non-infectious disease is a major cause of death in human beings?
(a) AIDS
(b) Cirrhosis
(c) Cancer
(d) Asthma
Answer
C
Question. Metastasis is
(a) part of regeneration.
(b) transfer of cancer cells from one part of the body to another.
(c) fast mitosis in cancer cells
(d) all of the above
Answer
B
Question. The use of antihistamine, adrenaline and steroids quickly reduce the symptoms of
(a) fungal disease
(b) viral disease
(c) allergy
(d) helminthes disease
Answer
C
Question. LSD is obtained from
(a) Cannabis sativus
(b) Erythroxylon cocca
(c) Claviceps purpurea
(d) Papaver somniferum
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are hallucinogens ?
(a) Charas
(b) Bhang
(c) Ganja
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Cyclosporin is used as is
(a) allergic eczema
(b) immunosuppressant
(c) prophylactic for viruses
(d) prophylactic for marasmus
Answer
B
Question. From which part of Atropa belladonna is the drug’belladona’ obtained?
(a) Stems
(b) Flowers
(c) Leaves
(d) Dried leaves and roots
Answer
D
Question. Hashish and charas are obtained from
(a) Rauwolfia serpentina
(b) Cannabis sativus
(c) Papaver somniferum
(d) Claviceps purpurea
Answer
B
Question. Ergot, a drug is derived from fungus
(a) Aspergillus
(b) Phytopthora
(c) Clavicep
(d) Perenospora
Answer
C
Question. Atropine, an alkaloid, is obtained from
(a) Datura anaroxia
(b) Atropa belladonna
(c) Hyocyamus niger
(d) Withania somnifera
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Question. Which of the following statement is correct ?
(a) Injecting microbes during immunization induces passive immunity.
(b) Cell-mediated immune response is responsible for graft rejection.
(c) Colostrum during initial days of lactation provides active immunity to infant.
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. What is true about T-lymphocytes in mammals ?
(a) These are produced in thyroid.
(b) These originate in lymphoid tissues.
(c) They scavenge damaged cells and cellular debris.
(d) There are three main types of T-lymphocytes – cytotoxic T cells, helper T cells and suppressor T cells.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Malignant tumours may exhibit metastasis.
(b) Patients who have undergone surgery are given cannabinoids to relieve pain.
(c) Benign tumours show the property of metastasis.
(d) Heroin accelerates body functions.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to AIDS?
(a) The causative HIV retrovirus enters helper T-lymphocytes thus reducing their numbers.
(b) The HIV can be transmitted through eating food together with an infected person.
(c) Drug addicts are least susceptible to HIV infection.
(d) AIDS patients are being fully cured cent per cent with proper care and nutrition.
Answer
A
Question. Sporozoites of the malarial parasite are found in
(a) salivary glands of freshly moulted female Anopheles mosquito.
(b) saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
(c) red blood corpuscles of humans suffering from malaria.
(d) spleen of infected humans.
Answer
B
Question. Select the correct statement with respect to diseases and immunization.
(a) Certain protozoans have been used to produce hepatitis B vaccine.
(b) Injection of snake antivenom against snake bite is an example of active immunization.
(c) If due to some reason B-and T-lymphocytes are damaged, the body will not produce antibodies against a pathogen.
(d) Injection of dead / inactivated pathogens causes passive immunity.
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following in not a property of cancerous cells ?
(a) They divide in an uncontrolled manner.
(b) They show contact inhibition.
(c) They compete with normal cells for vital nutrients.
(d) They do not remain confined in the area of formation.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease.
(b) The use of drugs like antihistamine, adrenaline, and steroids quickly reduces the symptoms of bacterial infection.
(c) Several genes (called cellular oncogenes) have been identified in normal cells which when activated under certain conditions, could lead to oncogenic transformation of the cells.
(d) The vaccine also generates memory – B and T cells that recognize the pathogen quickly on subsequent exposure and overwhelm the invaders with a massive production of antibodies.
Answer
B
Case Based MCQs for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Case I : Read the following passage and answer questions below:
X and Y are communicable diseases whereas W and Z are non-communicable diseases. X is transmitted through vectors whereas Y is transmitted through droplet infection. W is caused due to a hormone deficiency whereas Z is a degenerative disease.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
Question. Identify W, X, Y and Z.

Answer
B
Question. If X and Y both are usual diseases then which of the following holds true?
(a) X could be dengue caused by flavivirus and Y could be AIDS caused by HIV.
(b) X could be chikungunya whereas Y could be rhinitis.
(c) X could be hepatitis whereas Y could be rabies.
(d) X could be chicken pox caused by Varicella zoster virus whereas Y could be yellow fever caused by flavivirus.
Answer
B
Question. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement A : Communicable diseases could be contagious or non-contagious.
Statement B : Diseases that spread through vectors are non-contagious disease.
(a) Both statements A and B are true.
(b) Statement A is true but statement B is false.
(c) Statement A is false but statement B is true.
(d) Both statements A and B are false.
Answer
A
Case II : Read the following passage and answer questions below:
In a study to test a new vaccine against a viral disease, mouse model testing is done. In this process, mice are vaccinated and their blood samples were tested. Mice developed mild disease symptom. After few days those mice were again infected with the virus. This time they do not show any disease symptoms. Their blood samples were tested. Two graphs show antibody concentration for the first and second infection in mice blood.
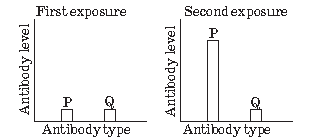
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
Question. Which form of pathogen is used in vaccination?
(a) Activated and strong pathogenic antigens
(b) Inactivated and weakened pathogenic antigens
(c) Hyperactive and strong pathogen
(d) Preformed antibodies
Answer
B
Question. How does vaccination work?
(a) The immune system produces antibodies which stay in the blood.
(b) Memory lymphocytes remain in the body to fight off any future infection with the same pathogen.
(c) Antigenic proteins of pathogens generate primary immune response and the memory B and T cells.
(d) All of these.
Answer
D
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Some diseases that occurred in childhood do not attack again.
Reason : Memory cells plays an important role.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Smack is a by-product of heroin synthesis.
Reason : Heroin is an opium alkaloid.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Immunity is the ability of the body to protect-against all type of foreign bodies that enters the body.
Reason : Spleen is the only organ involved in immunity.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Cancer patients are given chemotherapeutic treatments.
Reason : Chemotherapeutic agents are used to destroy malignant cells.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Mucous membrane are physiological barriers.
Reason : Microorganisms and dust particles entering the respiratory tract are trapped in the mucus.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
Reason : Injecting the microbes intentionally during immunization or infectious organisms gaining access into body during natural infection induces active immunity.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: Inspire of exposure to large number of infectious agents humans are resistive to diseases.
Reason: Humans are able to defend against most of the foreign agents due to the ability to fight disease-causing organisms.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Artificially acquired passive immunity results when antibodies or lymphocytes produced outside the host are introduced into a host.
Reason: A bone marrow transplant given to a patient with genetic immunodeficiency is an example of artificially acquired passive immunity.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: IgG is the most abundant class of lgs in the body.
Reason: IgG is mainly found in sweet, tears, saliva, mucus, colostrum and gastro-intestinal secretions.
Answer
D
Very Short Answer Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Question. How does saliva act in body defence?
Answer : Saliva contains lysozyme which kills the microorganisms that come with food and drink, thus act in body defence.
Question. When is tumour referred to as malignant?
Answer : Tumour is called malignant when it invades and destroys the tissue in which it originates and has the potential to spread to other sites in the body via the bloodstream and lymphatic system.
Question. What does the enzyme reverse transcriptase catalyze?
Answer : Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme, found mainly in retroviruses, that catalyses the synthesis of DNA from RNA.
Question. Name any two infectious diseases that are transmitted through fecal-oral route.
Answer : Poliomyelitis and Shigellosis
Question. How does colostrum provide initial protection against diseases to new born infants?
Answer : Colostrum provides protection against disease to new born babies because it is rich in antibodies, e.g. IgA.
Short Answer Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Question. How does moderate fever help a person in combating infections? What is to be done to bring down very high body temperature?
Answer : Moderate fever strengthens the defence mechanism by activating the phagocytes and by inhibiting the growth of microbes. A very high temperature may prove dangerous. It must be quickly brought down by giving antipyretics (fever reducing drugs e.g., aspirin) and by applying cold packs.
Question. How does the skin serve as the first line of defence?
Answer : The oil and sweat (chemical barriers) secreted by sebaceous and sudoriferous glands of skin contains fatty acids and lactic acid, which make the skin surface acidic.
These have antibacterial and antifungal activity. Lysozyme present in sweat, also kills many bacteria. Thus it provides first line of defence.
Question. A young boy when brought a pet dog home started to complain of watery eyes and running nose. The symptoms disappeared when the boy was kept away from the pet.
(a) Name the type of antibody and the chemicals responsible for such a response in the boy.
(b) Mention the name of any one drug that could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Answer : (a) Such a response in the boy is called allergy which occurs due to production of IgE antibodies and chemicals like histamine and serotonin from the mast cells.
(b) Anti-histamine could be given to the boy for immediate relief from such a response.
Question. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours.
Answer : Benign tumour does not invade and destroy the tissues in which it originates or spread to distant sites in the body, i.e., a tumour that is not cancerous. Benign tumour may nonetheless cause serious morbidity or mortality by compressing or obstructing vital structures.
Malignant tumour invades and destroys the tissue in which it originates and has the potential to spread to other sites in the body via the blood stream and lymphatic system.
Question. Name one plant and the addictive drug extracted from its latex. How does this drug affect the human body?
Answer : Heroin commonly called smack is chemically diacetylmorphine obtained by acetylation of morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papaver somniferum.
It is a depressant and slows down body functions. It induces drowsiness and lethargy. Its after effects include indigestion, reduced vision, decreased weight, sterility and total loss of interest in work.
Question. The diagram below illustrates the attack of a virus on a host cell.
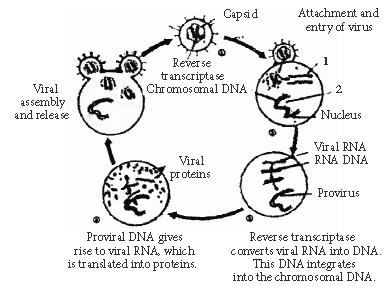
(i) Name the parts numbered 1 and 2.
(ii) Describe the functions performed by the part labelled number 1 on its entry into host cell.
(iii) What are such viruses called?
(iv) Name any two human diseases caused by such viruses.
Answer : (i) 1 is viral RNA and 2 is provirus.
(ii) Viral RNA initiates the formation of viral DNA in the host.
(iii) Retroviruses.
(iv) Cancer, AIDS.
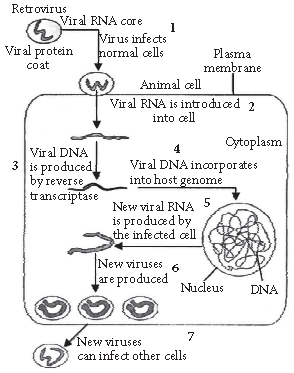
Question. Name the type of cell the AIDS virus first enters into after getting inside the human body.
Explain the sequence of events that the virus undergoes within these cells to increase their progeny.
Answer : The AIDS virus first enters into macrophages after getting inside the human body.
Sequence of events are as follows:
Question. (a) What is meant by addictive disorder?
(b) Name any two opiate narcotics.
(c) How does amphetamines affect human body?
Answer : (a) Addictive disorder is a state in which a person has a strong desire to take the addictive substance (drugs, alcohol, tobacco etc.).
(b) The two opiate narcotics are morphine and heroin.
(c) Amphetamines are called antisleep drugs as they are CNS stimulants. They cause alertness, self-confidence, talkativeness and increased work capacity. They suppress hunger. High doses produce euphoria, depression and insomnia. After effects include nausea and vomiting.
Question. How is the fetus with Rh-positive blood affected if the mother is Rh-negative?
Answer : An Rh-ve person, if exposed to Rh+ve blood, will form specific antibodies against the Rh antigens. This is observed in case of Rh-ve blood of a pregnant mother with Rh+ve blood of the foetus. Rh antigens of the foetus do not get exposed to the Rh-ve blood of the mother in the first pregnancy as the two bloods are well separated by the placenta. However, during the delivery of the first child, there is a possibility of exposure of the maternal blood to small amounts of the Rh+ve blood from the foetus. In such cases, the mother starts preparing antibodies against Rh antigen in her blood. In case of her subsequent pregnancies, the Rh antibodies from the mother (Rh-ve) can leak into the blood of the foetus (Rh+ve) and destroy the foetal RBCs. This could be fatal to the foetus or could cause severe anaemia and jaundice to the baby. This condition is called erythroblastosis foetalis. This can be avoided by administering anti-Rh antibodies to the mother immediately after the delivery of the first child.
Question. (a) List any two situations when a medical doctor could recommend injection of preformed antibodies into the body of a patient. Name this kind of immunization and mention its advantages.
(b) Name the kind of immunity attained when instead of antibodies, weakened antigens are introduced into the body.
Answer : (a) If a person is infected with some deadly microbes to which quick immune response is required as in tetanus, we need to directly inject the preformed antibodies or antitoxin.
Even in the cases of snakes bites the injection which is given to the patients, contain preformed antibodies against the snake venom. This type of immunization is called passive immunization. It provides immediate relief.
(b) In vaccination, a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogens or inactivated weakened pathogens are introduced into the body. This produces immune response and the type of immunity is called active immunity.
Question. What is the role of each of the following in the body defences.
(i) Antihistamine
(ii) Plasma cells
(iii) Helper T cells
Answer : (i) Antihistamine is a drug that inhibits the action of histamine in the body by blocking either of two types of receptors for histamine, H1 or H2. When stimulated by histamine, H1 receptors may produce such allergic reactions as hay fever, pruritus (itching), and urticaria (nettle rash).
Antihistamines that block H1 receptors (H1-receptor antagonists) are used to relieve these conditions.
(ii) Plasma cells are antibody-producing cells found in blood forming tissues and also in the epithelium of the lungs and gut. They develop in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen when antigens stimulate B-lymphocytes to produce the precursor cells that give rise to them.
(iii) Helper T cell is a type of T-lymphocyte that plays a key role in cell-mediated immunity by recognizing foreign antigen on the surface of antigen-presenting cells when associated with the individual’s MHC antigens, which is further processed by antigen-presenting cells. Helper T-cell stimulates the production of cytotoxic T-cell, which destroys the target cells.
Question. What is metastasis? List any four danger signals of cancer.
Answer : Metastasis is the phenomenon in which cancer cells spread to distant sites through body fluids to develop secondary tumour. This occur by three main routes :
(i) through the blood stream (haematogenous),
(ii) through the lymphatic system,
(iii) across body cavities.
The four danger signals of cancer are :
– A lump or hard area in the breast.
– Unexplained loss of weight and low-grade fever
– An uncurable ulcer.
– Non-injury bleeding from the surface of skin, mouth or any other opening of the body.
Long Answer Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases
Question. Describe the asexual and sexual phases of life cycle of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans.
Answer : Malaria is caused by the toxins produced in the human body by malarial parasite Plasmodium. Life cycle of Plasmodium requires two hosts for completion.
Life cycle of Plasmodium in man (asexual phase): The infective stage of Plasmodium is sporozoite. When the mosquito bites man, sporozoites present in the salivary gland of female Anopheles mosquito are injected into the blood of the man. The parasites initially multiply within the liver cells and then attack the red blood cells (RBCs) resulting in their rupture. The rupture of RBCs is associated with release of a toxic substance, haemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days. The released parasites from the ruptured RBCs infect new RBCs and develop into gametocytes (male and female). When a female Anopheles mosquito sucks the blood of an infected human host, it receives RBCs containing gametocytes.
Life cycle of Plasmodium in mosquito: The gametocytes come out of the RBCs into the lumen (cavity) of the stomach of the mosquito. Inside the stomach of the mosquito, the male and female gametocytes fuse (fertilize) to form zygote called oocyst. The nucleus of oocyst divides first by meiosis and subsequently by mitosis, forming large number of small haploid nuclei. At the same time, spindle shaped bodies called sporozoites are formed. When mature oocysts rupture, the sporozoites are liberated into the haemocoel (body cavity filled with blood) of the mosquito. Being motile, the sporozoites move to different organs in the body cavity of the mosquito, but many of them penetrate the salivary glands. The mosquito now becomes infective. When the female Anopheles mosquito bites a healthy person, the sporozoites are injected in his/her blood along with saliva. These sporozoites start the cycle again in human body.
Question.. Give the scientific name of the organism that causes whooping cough. Give two main symptoms of this disease. What vaccine gives protection from this disease?
Answer : Whooping cough or pertussis is caused by Bordetella pertussis and is common childhood disease.
It causes constant cough leaving the child breathless, tired and red in face. Later the voice becomes hoarse and the cough gives a whoop or a loud crowing sound while inhaling. The child usually vomits and there is frothy discharge from his mouth and nose.
Immunisation of the disease is done by DPT vaccination within six weeks of birth.
