Please refer to the Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper for the current academic year given below. We have provided the latest CBSE Sample Papers for Term 1 and Term 2 for Chemistry Class 11. All guess sample papers have been prepared based on the latest blueprint and examination pattern for the current year. All sample papers for Chemistry Class 11 Term 1 and 2 have been given with solutions. Students can access the multiple guess papers given below. Practicing more Class 11 Chemistry Sample Papers will help you to get more marks in upcoming exams.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry
| Term 2 Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry |
| Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper Term 2 Set A |
Class 11 Chemistry Sample Paper Term 2 Set A
SECTION – A
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
In the presence of Lewis acid catalysts such as aluminium chloride or ferric chloride (FeCl3), alkyl halides were found to alkylate benzene to give alkyl benzenes. The reaction is called Friedel-Crafts alkylation. It involves
(A) formation of carbocation.
(B) attack of electrophile (carbocation) over ring to form arenium ion.
(C) abstraction of hydrogen.
♦ When R – X is a primary halide, a simple carbocation probably doesn’t form. Instead, the aluminium chloride forms a complex with the alkyl halide, and this complex acts as electrophile.
♦ FC alkylation is not restricted to the use of alkyl halides and aluminium chloride. Many other pairs of reagents that form carbocations (or carbocation like species) may be used as well.
♦ Polyalkylation and rearrangement of carbocation are necessary evils of FC alkylation.
♦ Highly activating and highly deactivating groups, usually don’t give good yield.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer.
(i)

Answer
D
(ii)


Which of the above mentioned Friedel-Crafts reactions is/are not feasible?
(a) II and IV only
(b) II and III only
(c) I, II and IV only
(d) I, III and IV only
Answer
D
III.

Answer
A
IV.
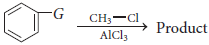
Friedel-Crafts reaction proceeds most efficiently when G is
(a) — NHR
(b) — CH3
(c) — CHO
(d) — NO2
Answer
B
OR
Among the following statements on the nitration of aromatic compounds, the false one is
(a) the rate of nitration of benzene is almost the same as that of hexadeuterobenzene
(b) the rate of nitration of toluene is greater than that of benzene
(c) the rate of nitration of benzene is greater than that of hexadeuterobenzene
(d) nitration is an electrophilic substitution reaction.
Answer
A
Following questions (Q. No. 2-6) are multiple choice questions carrying 1 mark each :
2. When Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene is carried out with n-propyl bromide, the major product is
(a) n-propyl benzene
(b) isopropyl benzene
(c) 2-ethyl benzene
(d) none of the above.
Answer
B
OR
The main product of the reaction is

Answer
D
3. The intermolecular interaction that is dependent on the inverse cube of distance between the molecules is
(a) London force
(b) hydrogen bond
(c) ion – ion interaction
(d) ion-dipole interaction.
Answer
B
4. Both lithium and magnesium display several similar properties due to the diagonal relationship, however, the one which is incorrect, is
(a) both form nitrides
(b) nitrates of both Li and Mg yield NO2 and O2 on heating
(c) both form basic carbonates
(d) both form soluble bicarbonates.
Answer
C
OR
Among LiCl, RbCl, BeCl2, MgCl2 the compounds with greatest and least ionic character respectively are
(a) LiCl and RbCl
(b) RbCl and BeCl2
(c) RbCl and MgCl2
(d) MgCl2 and BeCl2
Answer
B
5. An organic compound with molecular formula C6H12 upon ozonolysis gave only acetone as the product. The compound is
(a) 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene
(b) 3-hexene
(c) 2-hexene
(d) 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
Answer
D
6. A reaction is spontaneous at high temperatures if
(a) ΔH and ΔS both are negative
(b) ΔH and ΔS both are positive
(c) ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
In the following questions (Q. No. 7 and 8 ), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
7. Assertion : Kp can be less than, greater than or equal to Kc.
Reason : Relation between Kp and Kc depends on the change in number of moles of gaseous reactants and products (Δn).
Answer
A
8. Assertion : Although aluminium is above hydrogen in electrochemical series, it is stable in air and water. Reason : The thin protective layer of oxide (Al2O3) on aluminium is stable in air and water.
Answer
A
OR
Assertion : Carbon atom is tetravalent though it has two unpaired electrons.
Reason : Carbon has unique ability to form pπ – pπ multiple bonds like C = C , C = C .
Answer
B
SECTION – B
The following questions, Q. No. 9 – 12 are short answer type and carry 2 marks each.
9. 10 g of argon gas is compressed isothermally and reversibly at a temperature of 27° C from 10 litre to 5 litre. Calculates q, W and ∆U for this process.
(R = 2.0 cal K–1 mol–1, atomic weight of Argon = 40)
Answer :

OR
The molar heat of formation of NH4NO3(s) → is – 367.54 kJ and those of N2O(g) and H2O(l) are +81.46 kJ and –285.78 kJ respectively at 25° C and 1.0 atmospheric pressure. Calculate ΔH and ∆U for the reaction, NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2H2O(l)
Answer :

10. BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised through chlorine bridging. Give reason. Also explain the structure of the dimer of AlCl3.
Answer : Due to absence of d-orbitals in boron, BCl3 exists as an electron deficient monomer and achieves stability through accepting electrons from a base like NH3. BCl3 cannot exist as dimer due to small size of B which cannot accommodate four bigger size Cl-atoms around it. AlCl3 achieves stability by forming a dimer as shown :
OR
Discuss the Lewis acid nature of boron halides.
Answer : The Lewis acid character of boron trihalides follows the order :
BI3 > BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3.
The above order is just the reverse of the expected order on the basis of relative electronegativities of the halogens. This can be explained on the basis of the tendency of the halogen atom to back-donate its electrons to the boron atoms resulting in the formation of an additional pπ–pπ bond. This type of bond formation is known as dative or back bonding.

Formation of back bonding between boron and fluorine in BF3 molecule.
As a result of back donation of electrons from fluorine to boron, the electron deficiency of boron atom gets compensated and therefore, the Lewis acid character of BF3 decreases.
The tendency to form pπ–pπ bond is maximum in the case of BF3 and falls rapidly as we move to BCl3 and BBr3.
11. An iron cylinder contains helium at a pressure of 250 kPa at 300 K. The cylinder can withstand a pressure of 1 × 106 Pa. The room in which cylinder is placed catches fire. Predict whether the cylinder will blow up before it melts or not (melting point of the cylinder = 1800 K).
Answer :

As the cylinder can withstand a pressure of 106 Pa = 103 kPa = 1000 kPa, hence, it will blow up.
12. (i) Name the chief factors responsible for the anomalous behaviour of lithium.
(ii) Complete the following reactions :
(a) 4LiNO3 →Δ
(b) 2NaNO3 →Δ
Answer : (i) Chief factors responsible for the anomalous behaviour of lithium are :
• its very small size
• high electronegativity
• high ionization enthalpy and
• absence of vacant d-atomic orbital in the valence shell.

SECTION – C
Q. No. 13 and 14 are short answer type II carrying 3 marks each.
13. At 300 K, the standard enthalpies of formation of C6H5COOH(s), CO2(g) and H2O(l) are – 408, – 393 and – 286 kJ mol–1, respectively. Calculate the heat of combustion of benzoic acid at (i) constant pressure and (ii) constant volume. (R = 8.314 J mol–1 K–1)
Answer :

14. (a) Benzene is highly unsaturated compound but behaves like a saturated compound. Why?
(b) Out of benzene, m-dinitrobenzene and toluene which will undergo nitration most easily and why?
Answer : (a) The benzene molecule is unsaturated but the double bonds present inside the benzene ring are delocalized due to bond resonance (π-structure). This makes the double bonds of benzene much less reactive than more discrete double bonds. This makes it behave more like a saturated compound.
(b) During nitration, the electrophile NO2+ attacks the benzene ring. Nitration will be easier if the benzene ring shows increased electron density. This happens when electron releasing groups such as –R, –NH2, –NHCOCH3, –OH,–OMe etc. are attached to the ring whereas, the attachment of electron withdrawing groups such as –NO2, –CHO, –COR,–COOH reduces the electron availability for NO2+ and nitration becomes difficult.
Therefore, relative ease of nitration of given molecules may be arranged as :

OR
(a) Identify ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ and ‘D’ in the following sequence of reactions :

(b) Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty?
Answer :

(b) Due to the presence of an electron cloud containing 6 π-electrons above and below the plane of the ring, benzene is a rich source of electrons. Consequently, it attracts the electrophiles (electron-deficient reagents) towards it and repels nucleophiles (electron-rich reagents). As a result, benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty.
SECTION – D
Q. No. 15 and 16 are long answer type carrying 5 marks each.
15. (a) Classify the following as acid or base and also mention the concept on the basis of which these are so.
(i) HCl(aq) (ii) Na2CO3(aq) (iii) H2O (iv) NH4+
(b) Predict whether a precipitate will be formed or not on mixing equal volumes of 2 × 10–4 M BaCl2 solution and 2 × 10–5 M Na2SO4 solution if solubility product of BaSO4 is 1 × 10–10.
Answer : (a) (i) HCl(aq) : Acid, according to Arrhenius concept and Bronsted–Lowry concept,


OR
(a) For the exothermic formation of sulphur trioxide from sulphur dioxide and oxygen in the gas phase :
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
Kp = 40.5 atm–1 at 900 K and ∆rH = –198 kJ mol–1
(i) Write the expression for the equilibrium constant for the reaction.
(ii) At room temperature (≈ 300 K) will Kp be greater than, less than or equal to Kp at 900 K?
(iii) How will the equilibrium be affected if the volume of the vessel containing the three gases is reduced, keeping the temperature constant. What happens?
(iv) What is the effect of adding 1 mole of He(g) to a flask containing SO2, O2 and SO3 at equilibrium at constant volume?
(b) A vessel at 1000 K contains carbon dioxide at a pressure of 0.5 atm. Some of the carbon dioxide is converted to carbon monoxide on addition of graphite. Calculate the value of K, if the total pressure at equilibrium is 0.8 atm.
Answer : (a) (i) The equilibrium constant for this reaction is written in terms of the partial pressure of the reactants and products. So,

(ii) This reaction is exothermic. So, its equilibrium constant should increase with the lowering of temperature (d lnK/dT= Δr H°/RT2). Therefore, the value of Kp at 300 K will be greater than the value at 900 K.
(iii) When the volume of the vessel is reduced, the volume of the reaction mixture will decrease. As a
result, pressure of the gaseous mixture will increase. According to the Le Chatelier’s principle, the system will move in a direction to undo the effect of the pressure increase. The system therefore will move in a direction so as to decrease the number of moles of the gaseous substances in the system. The number of moles decrease in going from reactants to the product side. Therefore, a decrease in the volume of the reacting system will shift the equilibrium to the right. That is, more SO3(g) will
be formed from the reactants.
(iv) Addition of helium to the reaction mixture at equilibrium under constant volume has no effect on
the equilibrium.
(b) CO2 + C(graphite) ⇌ 2CO
Let the decrease in pressure of CO2 after reaction = p atm
Then, increase in pressure due to CO after reaction = 2p atm

16. (a) Explain the difference in properties of diamond and graphite on the basis of their structures.
(b) Rationalise the given statements and give chemical reactions :
(i) Lead (II) chloride reacts with Cl2 to give PbCl4.
(ii) Lead (IV) chloride is highly unstable towards heat.
(iii) Lead is known not to form an iodide, PbI4.
Answer : (a)

(b) (i) PbCl2 + Cl2 →x PbCl4
Lead is more stable in +2 oxidation state than in +4 state due to inert pair effect. Thus, the reaction is not feasible.
(ii) PbCl4 →Δ PbCl2 + Cl2
Pb is more stable in its +2 oxidation state due to inert pair effect. As a result, when subjected to heat, Pb (IV) goes to Pb (II) state.
(iii) Pb + 2I2 →x PbI4
I– is a good reducing agent and therefore, reduces Pb (IV) to Pb (II) easily. That is why, PbI4 does not exist.
OR
(a) How can the fullerenes be prepared?
(b) Account for the following : PbCl4 is a powerful oxidising agent.
(c) Account for the following :
(i) PbCl2 is more stable than PbCl4.
(ii) [SiF6]2– is known whereas [SiCl6]2– not.
(d) Why carbon shows anomalous behaviour?
Answer : (a) Fullerenes are made by the heating of graphite in an electric arc in the presence of inert gases such as helium or argon.
(b) In PbCl4, the oxidation state of Pb is +4. Due of inert pair effect, Pb2+ is more stable than Pb4+. Hence, Pb4+ is easily reduced to Pb2+, thereby acting as a good oxidising agent.
(c) (i) +2 oxidation state of Pb is more stable due to inert pair effect. Thus, lead (IV) chloride readily
decomposes to lead(II) chloride.
PbCl4 →Δ PbCl2 + Cl2
(ii) Due to small size of F, six fluorine atoms can be accommodated around silicon but six chlorine atoms cannot due to large size of Cl-atoms.
(d) Due to its smaller size, higher electronegativity, higher ionisation enthalpy and unavailability of
d-orbitals.



