VBQs Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry with Biomolecules has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Biomolecules. The following Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Biomolecules VBQs Class 12 Chemistry
Question. The secondary structure of a protein refers to
(a) fixed configuration of the polypeptide backbone
(b) α – helical backbone
(c) hydrophobic interactions
(d) sequence of α – amino acids
Answer
B
Question. Select the uses of carbohydrates.
(a) Honey is used as instant source of energy by vaids in ayurvedic system of medicine
(b) These are used as storage molecules
(c) They are used in furniture, cotton fibre, lacquers
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. An insulin is a ______ which contains _____ amino acids.
(a) protein, 74
(b) protein, 51
(c) hormone, 51
(d) hormone, 74
Answer
B
Question. One of essential α-amino acid is
(a) lysin
(b) serine
(c) glycine
(d) proline
Answer
A
Question. Proteins are polypeptide of
(a) β-amino acid
(b) α-hydroxy acid
(c) D-α-amino acid
(d) L-α-amino acid
Answer
D
Question. Simplest proteins has one peptide linkage. It is
(a) tripeptide
(b) dipeptide
(c) tetrapeptide
(d) oligopeptide
Answer
B
Question. Two functional group that are present in all amino acids are the
(a) hydroxy, amine
(b) hydroxy, amide
(c) carboxyl, amino
(d) carboxyl, amide
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is an example of globular proteins?
(a) Glycine
(b) Albumin
(c) Alanine
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Amylopectin is a ________ polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by _______ glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by ________ glycosidic linkage.
(a) branched chain, C1– C6, C1– C4.
(b) branched chain, C1– C4, C1– C6.
(c) unbranched chain, C1– C4, C1– C6.
(d) unbranched chain, C1– C6, C1– C4.
Answer
B
Question. In aqueous solution, an amino acid exists as
(a) cation
(b) anion
(c) dianion
(d) zwitter ion
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is true about a peptide bond (RCONHR)?
(a) It is non planar.
(b) It is capable of forming a hydrogen bond.
(c) The cis configuration is favoured over the trans configuration.
(d) Single bond rotation is permitted between nitrogen and the carbonyl group.
Answer
B
Question. Amino acids generally exist in the form of Zwitter ions. This means they contain
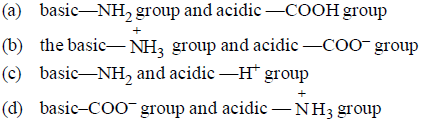
Answer
D
Question. The structural feature which distinguishes proline from natural α-amino acids?
(a) Proline is optically inactive
(b) Proline contains aromatic group
(c) Proline is a dicarboxylic acid
(d) Proline is a secondary amine
Answer
D
Question. Secondary structure of protein is mainly governed by
(a) hydrogen bonds
(b) covalent bonds
(c) ionic bonds
(d) disulphide bonds
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following structures represents the peptide chain?
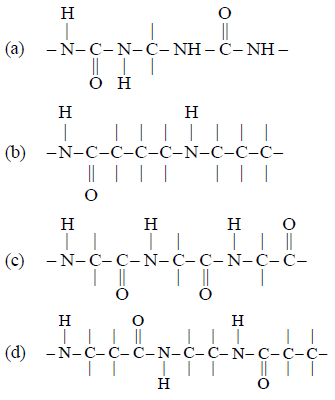
Answer
C
Question. The helical structure of protein is stabilized by
(a) dipeptide bonds
(b) hydrogen bonds
(c) ether bonds
(d) peptide bonds
Answer
B
Question. A nanopeptide contain how many peptide bond
(a) 7
(b) 9
(c) 8
(d) 10
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is incorrect about cellulose?
(a) It is a major constituent of cell wall of plant cells.
(b) It is a branched chain disaccharide
(c) It is composed of only β-D-glucose units.
(d) The glycosidic linkage between two units is found between C1 of one unit and C4 of next unit.
Answer
B
Question. In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by
(a) van der waals forces
(b) electrostatic forces of attraction
(c) hydrogen bonds
(d) covalent bonds
Answer
D
Question. Coagulation of protein is known as
(a) dehydration
(b) decay
(c) deamination
(d) denaturing
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not an optically active amino acid?
(a) Valine
(b) Glycine
(c) Leucine
(d) Arginine
Answer
B
Question. Proteins are condensation polymers of
(a) α-amino acids
(b) β-amino acids
(c) α-hydroxy acids
(d) β-hydroxy acids
Answer
A
Question. A polypeptide with more than hundred amino acid residues, having molecular mass higher than 10,000 u is called_____.
(a) nucleic acid
(b) hormone
(c) protein
(d) enzyme
Answer
C
Question. Tertiary structure of protein arises due to
(a) folding of polypeptide chain
(b) folding, coiling and bonding of polypeptide chain
(c) linear sequence of amino acid in polypeptide chain
(d) denatured proteins
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is incorrect regarding enzymes?
(a) Most of them are globular proteins.
(b) They are very specific for a particular reaction but not for a particular substrate.
(c) They are generally named after the compound or class of compounds upon which they work.
(d) All the above statements are incorrect.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following molecules is capable of forming Zwitter ion?
(a) NH2CH2COOH
(b) CH3CH2NH2
(c) CH3CH2COOH
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. Enzymes take part in a reaction and
(a) decrease the rate of a chemical reaction
(b) increase the rate of a chemical reaction
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristics of fibrous proteins?
(a) In the fibrous proteins polypeptide chains are held together by hydrogen and disulphide bonds.
(b) These have fibre like structure.
(c) These are generally soluble in water.
(d) These have elongated shape.
Answer
C
Question. The strongest form of intermolecular bonding that could be formed involving the residue of the amino acid serine is.
(a) ionic bond
(b) hydrogen bond
(c) van der Waals interactions
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. The number of essential amino acids in man is
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 18
(d) 20
Answer
B
Question. The protein that transport oxygen in the blood stream is
(a) haemoglobin
(b) insulin
(c) collagen
(d) albumin
Answer
A
Question. Globular proteins are present in
(a) blood
(b) eggs
(c) milk
(d) all of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) In α-helix structure a polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right handed screw.
(b) In β-structure of proteins all peptide chains are stretched out to nearly maximum extension.
(c) During denaturation 1° and 2° structures are destroyed but 3° structure remains intact.
(d) All the above statements are incorrect.
Answer
C
Question. Chemically amylose is a _________ with 200–1000 α-D-(+)-glucose units held by ______ glycosidic linkage
(a) long unbranched chain, C1– C6.
(b) branched chain, C1 – C4.
(c) long unbranched chain, C1– C4.
(d) branched chain, C1– C6.
Answer
C
Question. The linkage present in proteins and peptides is
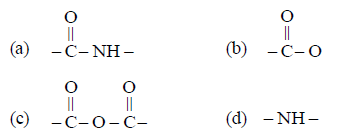
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a fibrous protein?
(a) Keratin
(b) Myosin
(c) Insulin
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is also known as animal starch?
(a) Glycine
(b) Glycogen
(c) Amylose
(d) Cellulose
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following indicates the order in which amino acids are linked together in a protein ?
(a) Primary structure
(b) Secondary structure
(c) Tertiary structure
(d) Quaternary structure
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the amino acids can be synthesised in the body?
(a) Alanine
(b) Lysine
(c) Valine
(d) Histidine
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following terms indicates to the arrangement of different protein subunits in a multiprotein complex ?
(a) primary structure
(b) secondary structure
(c) tertiary structure
(d) quaternary structure
Answer
D
Question. Amino acids are the building blocks of
(a) fats
(b) proteins
(c) vitamins
(d) carbohydrates
Answer
B
Question. Denaturation of proteins leads to loss of its biological activity by
(a) Formation of amino acids
(b) Loss of primary structure
(c) Loss of both primary and secondary structures
(d) Loss of both secondary and tertiary structures
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) All amino acids except lysine are optically active
(b) All amino acids are optically active
(c) All amino acids except glycine are optically active
(d) All amino acids except glutamic acids are optically active
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following terms refers to the overall three dimensional shape of a protein.
(a) Primary structure
(b) Secondary structure
(c) Tertiary structure
(d) Quaternary structure
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not a function of proteins?
(a) Formation of hair, wool, skin and nails
(b) As a biological catalysts in the form of enzymes.
(c) As food in the form of meat, eggs
(d) As energy provider for metabolism
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following indicates to ‘regions of ordered structure within a protein’.
(a) Primary structure
(b) Secondary structure
(c) Tertiary structure
(d) Quaternary structure
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is not true about secondary structure of protein ?
(a) The alpha helix, beta pleated sheet and beta turns are examples of secondary structure of protein.
(b) The ability of peptide bonds to form intramolecular hydrogen bonds is important to secondary structure.
(c) The steric influence of amino acid residues is important to secondary structure.
( d) The hydrophilic/ hydrophobic character of amino acid residues is important to secondary structure.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following protein destroy the antigen when it enters in body cell?
(a) Antibodies
(b) Insulin
(c) Chromoprotein
(d) Phosphoprotein
Answer
A
Question. Primary structure of a protein is
(a) sequence in which α-amino acid are linked to one another
(b) sequence in which amino acids of one polypeptide chain are joined to other chain
(c) the folding patterns of polypeptide chains
(d) the pattern in which the polypeptide chain are arranged
Answer
A
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the columns
Column – I Column – II
(A) Vitamin B6 (p) Fat soluble
(B) Vitamin K (q) Xerophthalmia
(C) Vitamin D (r) Convulsions
(D) Vitamin A (s) Delayed blood clotting
(a) A – (p,q), B – (p,s), C – (p), D – (r)
(b) A – (r), B – (p,s), C – (p), D – (p, q)
(c) A – (p,s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (p,q)
(d) A – (r), B – (p,s), C – (p,q), D – (p)
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns
Column – I Column – II
(A) Vitamin A (p) Scurvy
(B) Vitamin B12 (q) Hemorrhagic condition
(C) Vitamin C (r) Sterility
(D) Vitamin E (s) Xerophthalmia
(E) Vitamin K (t) Pernicious anaemia
(a) A – (t), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r), E – (r)
(b) A – (s), B – (t), C – (p), D – (q), E – (r)
(c) A – (s), B – (t), C – (p), D – (r), E – (q)
(d) A – (t), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r), E – (q)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns.
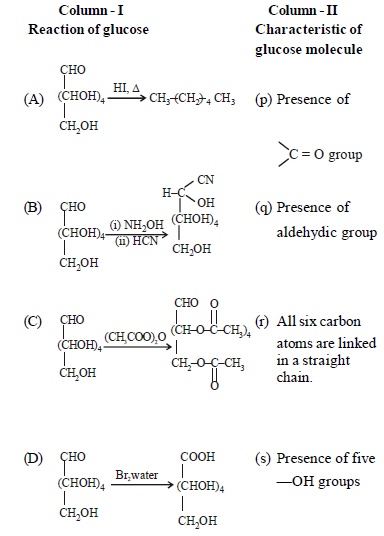
(a) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
(b) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
(c) A – (r), B – (p), C – (s), D – (q)
(d) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)
Answer
C
Question. Match the columns
Column – I Column – II
(Enzymes) (Reactions)
(A) Invertase (p) Decomposition of urea into NH3 and CO2
(B) Maltase (q) Conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol
(C) Pepsin (r) Hydrolysis of maltose into glucose
(D) Urease (s) Hydrolysis of cane sugar
(E) Zymase (t) Hydrolysis of proteins into peptides
(a) A – (s), B – (r), C – (t), D – (p), E – (q)
(b) A – (r), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p), E – (t)
(c) A – (q), B – (p), C – (r), D – (s), E – (t)
(d) A – (s), B – (p), C – (t), D – (q), E – (r)
Answer
A