Please see Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Exam Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry. These solved problems for Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids in Class 12 Chemistry will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry
Objective type questions:
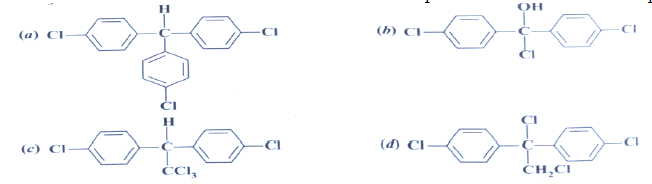
Question. CCl3CHO reacts with chlorobenzene in the presence of cocn. H2SO4 produces
Answer
C
Question.CH3CHO & C6H5CH2CHO can be distinguished chemically by
(a) Benedict’s test
(b) Iodoform test
(c) Tollen’s reagent test
(d) Fehling’s solution test
Answer
B
Question.which of the following is not soluble in NaHCO3 ?
(a) 2,4,6 Trinitrophenol
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) o- nitrophenol
(d) Benzenesulphonic acid
Answer
C
Question.The product formed by the reaction of an aldehyde with primary amine is
(a) Carboxylic acid
(b) Aromatic amine
(c) Schiff’s base
(d) ketone
Answer
C
Question.The correct order of increasing acidic strength is _________
(a) Phenol< Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid< acetic acid
(b) Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid< acetic acid
(c) Ethanol< Phenol < acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
(d) acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid< Ethanol< Phenol
Answer
C
Question.The compound Ph-O-CO-Ph can be prepared by the reaction of ________
(a) Phenol and Benzoic acid in the presence of NaOH
(b) Phenol and Benzoyl chloride in the presence of pyridine
(c) b) Phenol and Benzoyl chloride in the presence of ZnCl2
(d) Phenol and Benzaldehyde in the presence of palladium
Answer
B
Question.The incraesing order of the rate of HCN addition to the compounds A-D is
A. HCHO B, CH3CHO C. PhCOPh D. PhCOCH3
(a) A<B<C<D
(b) D<C<B<A
(c) D<B<A<C
(d) D<A<C<B
Answer
B
Question.which compound will not reduce Fehling’s solution?
(a) Methanal
(b) Ethanal
(c) Trichloroethanal
(d) Benzaldehyde
Answer
D
Question.Which of the following acids has the highest pKa value ?
(a) CH3CHFCOOH
(b) FCH2CH2COOH
(c) BrCH2CH2COOH
(d) CH3CHBrCOOH
Answer
C
Question.When prionic acid is treated with aq. NaHCO3 , CO2 is librated. The ‘C’ of CO2 comes from
(a) Methyl group
(b) carboxylic acid group
(c) methylene group
(d) bicarbonate
Answer
D
Question.Which of the folllowing on treatment with 50% aq. Solution of NaOH yields the corresponding alcohol and the acid by disproportination And the reaction is called
(a) CH3COCH3, aldol condensation
(b) C6H5CH2CHO , Claisen’s reaction
(c) C6H5CHO, Cannizaro’s reaction
(d) CH3CH2CHO Clemmensen reduction
Answer
C
Question.the major product obtained by the ozonolysis of 2,3- Dimethyl-1-butene & subsiquent reduction with Zn/H2O are
(a) methanoic acid & 2-methyl-2-butanone
(b) methanal & 3- methyl-2-butanone
(c) methanol & 2,3 –dimethyl-3-butanone
(d) methanoic acid & 2-methyl-3-butanone
Answer
B
Question. Predict the product ‘C’ in the follwing s𝐴→eries of reaction:

(a) CH3COCH=CH2
(b) CH3CH(OH)C6H5
(c) CH3CH(OH)C2H5
(d) (CH3)2 CH(OH)C6H5
Answer
D
Question. Predict the product ‘C’ in the following series of reaction:
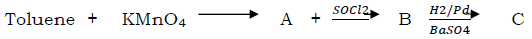
(a) C6H5CH2OH
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) C6H5COOH
(d) C6H5CH3
Answer
B
Question.the correct order of increasing acid strength of the compounds;
A. CH3COOH B. CH3OCH2COOH C . CF3COOH D. (CH3 )2CHCOOH
(a) B<D<A<C
(b) D<A<C<B
(c) D<A<B<C
(d) A<D<C<B
Answer
A
Question.Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by______________

Answer
D
Question. Match the common names given in column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II
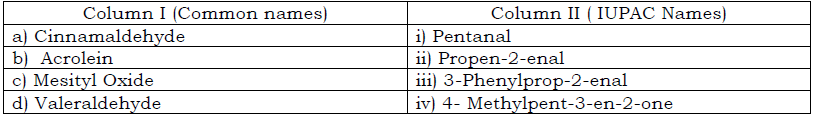
(a) a-iii b-ii c-iv d- i
(b) a-ii b-iii c-iv d- I
(c) a-i b-ii c-iii d- iv
(d) a-iv b-iii c-ii d- I
Answer
A
Question.Match the Name Reaction given in column I with the reagent/ catalyst given in Column II
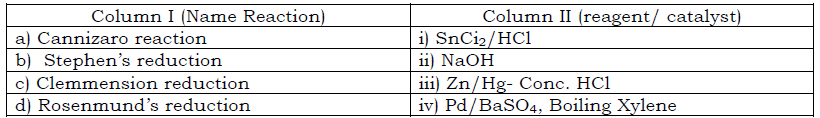
(a) a-iii b-ii c-iv d- i
(b) a-ii b-i c-iii d- iv
(c) a-i b-ii c-iii d- iv
(d) a-iv b-iii c-ii d- I
Answer
B
Assertion Reason type Question
a statement of Assertion followed by a statement reason is given. Choose the correct options out of the following choices.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct statements, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct statements, but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct, but reason is wrong statement.
(D) Assertion is wrong, but reason is correct statement
Question. Assertion: Compounds containing –CHO group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason: Aldehydes cantains C-H bond cannot be easily broken.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: aromatic aldehyde & formaldehyde undergo cannizaro reaction.
Reason: aromatic aldehydes are as reactive as formaldehyde
Answer
D
VSA type questions
Question. Higher carboxylic acid are insoluble in water why?
Answer. this is due to increased hydrophobic part, H bonding does not takes place.
Question. Why p-nitro benzoic acid has higher Ka value than benzoic acid?
Answer. higher Ka value stronger is the acid.as nitro group has –R as well as –I effect which makes the O-H more polar.hence p-nitro benzoic acid is stronger acid. So it has higher Ka value.
Question. Arrange the following in order of increasing reactivity towards nucleophillic addition reaction Ehanal, propanal, propanone, butanone
Answer. due to steric hindrance & +I effect the reactivity decreases . so order is butanone, propanone, propanal, ethanol.
Question. what is the role of acid catalysts in nucleophillic addition reaction?
Answer. it increases the +ve charge on carbonyl carbon and make it more electrophillic as a result weak nucleophile can easily attack.
Question. What are acetal?
Answer. when aldehydes react with Alcohols in the presence of dry HCl gas it form alkoxyalcohol (Hemiacetal) then with another molecule of alcohol ot form gem-dialkoxy compound known as acetal.
Question. Why th pH should be around 3.5 during the addition of ammonia derivative compounds to aldehyde/ ketone?
Answer. when the medium is too acidic ammonia derivative get protonated, and they can not act as nucleophile.
But when the medium is slightly acidic the protonation of carbonyl cabon will not takes place, hence the pH shoul be around 3-5.
Question. what is Tollen,s reagent?
Answer. it is an ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate. Ag[ (NH3)2]OH. It give silver mirror test with aldehydes. Ketones do not give this test, it is used to distinguish between aldehydes& ketones.
Question. What is Fehling’s solution?
Answer. it is alakaline solution of CuSO4 containing some Rochelle salt i.e. sodium potassium tartrate.
Fehling A- Aq. Solution of CuSO4 + Fehling B ( Alkaline solution of Rochelle salt)
Aldehydes give red ppt with fehling solution
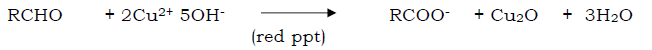
Question. What is formalin?
Answer.It is 40% aq. Solution of formaldehyde , used to preserve the biological specimens.
Question. what is popoff’s rule?
Answer. when asymmetric ketone is oxidised to carboxylic acid, then rupturing of the C-C bond takes place in such a way that CO group goes with the less number of carbon. It is known as popoff’s rule.
Question. What is the similiarity between alkene and carbonyl compounds?
Answer. i In alkene and carbonyl compounds C is sp2 hybridised.
ii. C is planer.
iii both undergoes addition reaction.
Question. What is the dissimiliarity between alkene and carbonyl compounds ?
Answer. i. carbonyls under nucleophillic addition reaction whereas alkenes undergoes electrophillic addition reaction.
ii. C-C bond in alkene is longer than C-O bond of carbonyl group.
Question. Which is more reactive towards nucleophillic addition reaction: p-nitro benzaldehyde or benzaldehyde?
Answer. p-nitrobenzaldehyde. As withdrawing group increases the reactivity towards nucleophillic addition reaction.
Question. A & B are the two isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH/I2 B form yellow ppt. of iodoform but A does not. Write the structure of A & B
Answer. The two possible isomer of C3H6O are: CH3CH2CHO (A) & CH3COCH3 (B)
As B on heating with NaOH/I2 form yellow ppt of iodoform it must be methyl ketone.

Question. write the IUPAC name of CH3CH(OH) CH2 CH2CHO
Answer. 4- Hydroxypentanal
Long Answer type question:
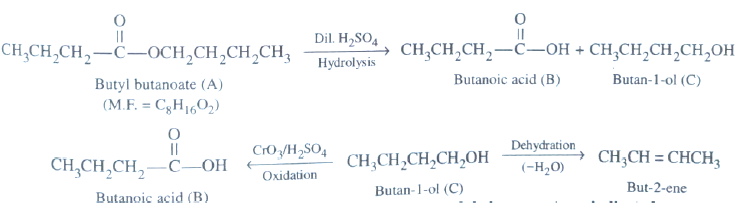
Question. An organic compound A (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dil. Sulphuric acid to give carboxylic acid (B) & alcohol (C). C on oxidation with chromic acid produced B. C on dehyderation gives but-2-ene as the major product. Write the equation for the reactions involved.
Answer. i)A is ester as it produces carboxylic acid & alcohol.
ii) Alcohol on oxidation produces B Carboxylic acid, it means both have same number of carbons.
iii) C alcohol on dehydration produces but-2-ene, it means C must be 1-butanol. B must be butanoic acid.
So compound A must be CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH2CH2CH3
Question. An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2,4-DNP derivative, reduces tollen reagent and undergoes cannizaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation it gives 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer. i Since it reduces Tollen’s reagent it must be aldehyde.
ii. since it undergoes Cannizaro reaction, CHO group must be directly attached to benzene ring.
iii. On vigorous oxidation it gives 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, it must be ortho substituted benzaldehyde, so the compound is 2- Ethylbenzaldehyde.

Question.How would you distinguished between: propanal & propanone
Answer. As propanone contain CH3CO- group it will give positive iodoform test, propanal do not give iodoform test.
Question. Complete the reaction
Answer. C6H5CHO + H2NCONHNH2 →C6H5CHO= NCONHNH2 (Benzaldehyde semicabazide)
Question. Give plausible explanation: cyclohexanone forms cynohydrins in good yield but 2,2,6-trimetheylcyclohexanone does not:
Answer. Due to steric hindrance 2,2,6-trimetheylcyclohexanone does not form cyanohydrins as compared to cyclohexanone.
How will you convert?
Question. Proponoic acid to 1-propanol
Answer.
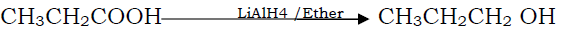
Question. Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
Answer.

Question. Benzoic acid to benzamide
Answer.

Question. Bezotrichloride to benzoic acid
Answer.

Question. Benzene to benzoic acid
Answer.
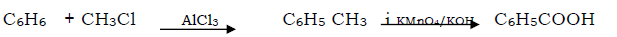
Question. Propanone to propane -2-ol
Answer.
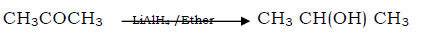
Question. Propanone to propane
Answer.
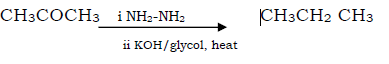
Question. Ethenol to Propanol
Answer.

Question. Propyne to acetone
Answer.
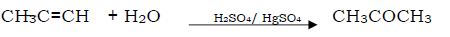
Question. Formaldehyde to urotropine
Answer. HCHO + NH3 → (CH2)6 N4
Some important name reactions
Question. Aldol condensation
Answer. Aldehydes /ketone containing α H when treated dil solution of base undergoes condensation to from β hydroxyaldehyde/ketone known as aldol condensation.
2CH3CHO + KOH (dil) → CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO
Question.Cannizaro reaction
Answer. Aldehydes which do not have α H when treated conc. solution of base undergoes disproportionation reaction to produce alcohol & Carboxylic acid.
2HCHO + KOH (conc.) → CH3OH + HCOOK
Question. Wolf kishner reduction
Answer. Aldehydes /ketone when treated with NH2-NH2 & then with KOH/ glycol, heat produces corresponding hydrocarbon.
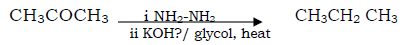
Question. Clemmensen reduction
Answer. Aldehydes /ketone when treated with Zn/Hg produces corresponding hydrocarbon

Question. Etard reaction
When toluene treated with chromyl chloride in CS2 it form brown resin which on hydrolysis in acidic medium it from benzaldehyde.
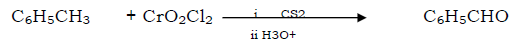
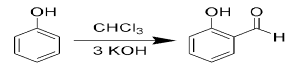
Question. Reimer Teimann reaction.
When phenol is treated with Chloroform in the presence of Base followed by acidic hydrolysis it form salicyldehyde.