Please refer to Chemistry in Everyday Life HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with Chemistry in Everyday Life. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Chemistry in Everyday Life Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
1 marks Questions.
Question. What is the harmful effect of hyperacidity?
Answer.Ulcer development in stomach.
Question. What are antiseptics?
Answer.Antiseptics are chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms and are applied to living tissues.
Question. What is the commonality between the antibiotic arsphenamine and azodye?
Answer.Arsphenamine possesses —As=== As— linkage that resembles —N=== N— linkages in azodyes.
Question. Which type of drugs come under antimicrobial drugs?
Answer.Antiseptics, antibiotics and disinfectants.
Question. What is the average molecular mass of drugs?
Answer.~100–500u.
Question. Where are receptors located?
Answer.Receptors are embedded in cell membrane.
Question. Which class of drugs is used in sleeping pills?
Answer.Tranquilizers
Question. Which site of an enzyme is called allosteric site?
Answer.Sites different from active site of enzyme where a molecule can bind and affect the active site is called allosteric site. Some drugs may also bind at this site.
Question. Write the uses of medicines.
Answer.Medicines are used in diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases.
Question. What type of forces are involved in binding of substrate to the active site of enzyme?
Answer.Ionic bonding, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals interaction, dipole-dipole interaction.
Question. Define the term Chemotherapy?
Answer. The branch of chemistry which deals with the treatment of disease using chemicals is called chemotherapy.
Question. What is BHA and BHT?
Answer. BHA is butylated hydroxyl anisole whereas BHT is butylated hydroxyl toluene. Both are used as antioxidant in food.
Question. What is tincture of iodine?
Answer. A 2‐3% solution of iodine in alcohol – water mixture is known as tincture of iodine. It is used as an antiseptic.
Question. What is meant by narrow spectrum antibiotics?
Answer. Those antibiotics which are effective against only one particular micro organisms are called narrow spectrum antibiotics.
Question. Name the substance that can be used as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
Answer. 0.2% solution of phenol act as an antiseptic and 1% of the solution acts as a disinfectant.
2 Marks Questions.
Question. What are analgesics? How are they classified?
Answer. The drugs which give relief from the pain are known as analgesics. They are classified as
1.) Non‐Narcotics: They do not cause addiction. eg. Aspirin
2.) Narcotics: They are habit forming. eg. Morphine
Question. A) Why is Bithional added to soap?
B) Give the composition of Dettol.
Answer. A) Bithional is an antiseptic which reduces the odour produced by bacteria decomposition of organic matter on skin.
B) Dettol is a mixture of chloroxyenol and terpineol.
Question. Why are cimetidine and ranitidine better antacids than sodium bicarbonate or aluminium hydroxide?
Answer. NaHCO3 or Mg(OH)2 or Al(OH)3 ; if taken in excess makes the stomach alkaline and thus triggers the release of even more HCl causing ulcers in stomach , whereas cimetidine and ranitidine prevent the interaction of histamine with the receptor cells in the stomach wall, resulting in release of lesser amount of HCl.
Question. What are biodegradable and non‐ biodegradable detergents ? Give one example each.
Answer. Biodegradable detergents are decomposed by microorganisms like bacteria into harmless product.
They do not create water pollution. Detergents having linear alkyl chains are biodegradable. Eg. Sodium lauryl sulphate.
Non‐Biodegradable are not decomposed by microorganisms. They create water pollution.eg. Cetymethyl, Ammonium bromide.
Question. How antiseptics are different from disinfectant. Give one example of each.
Answer.
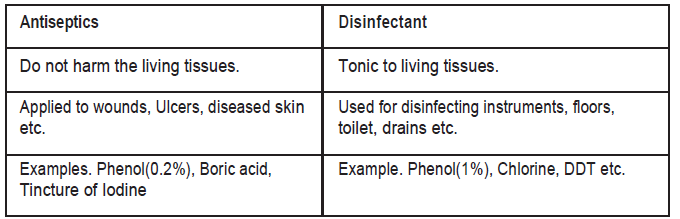
3 marks Questions.
Question. What are the following substances, give one example of each.
(a) Tranquilizers (b) Food preservatives (c) Antihistamines.
Answer. (a) Tranquilizers: ‐ These chemicals are used for the treatment of stress, fatigue and mental diseases. They release anxiety, stress irritability, etc.
example‐ Equanil, Luminal.
(b) Food preservatives: ‐ These chemical substances are added to the food materials to prevent their spoilage due to microbial growth.
example: ‐ Sodium benzoate, Sodium chlorate.
(c) Antihistamines: ‐ These drugs interfere with the natural action of histamine by competing with histamine for bonding sites of receptor with histamine exerts its effects.
example: ‐ Cetrizine
Question. (a) Name two artificial sweetness used in food materials.
(b) Give one examples of (i) bactericidal antibiotic (ii) bacteriostatic antibiotic
(c) Give an example of sulpha drug.
Answer. (a) Aspartame and Alitame
(b) (i) Penicillin (ii) Tetracycline
(c) Sulpha pyridine or Sulpha guanidine
Question. Explain the following terms with suitable examples (a) cationic detergents (b) anionic detergents
(c) neutral detergents.
Answer. (a) Cationic detergents are generally quaternary Ammonium salts as Chlorides, Bromides or acetates.
These detergents are quite expensive and find limited u s e . Some of these detergents have germicidal properties and are used as germicides.
(b) Anionic detergents: ‐ A detergent whose hydrophilic activity hinges on an anionic group. Fatty acids are natural anionic detergents (AD), but are neither used as detergents nor functional in biological systems; the main synthetic ADs are aliphatic Sulphate esters (e.g., Sodium dodecyl sulphate).
(c) Neutral Detergents the most common measure of fibre used for animal feed analysis, but it does not represent a unique class of chemical compounds. NDF measures most of the structural components in plant cells (i.e. Lignin, Hemicellulose and Cellulose)
Question. Define: (a) Receptors (b) Agonists (c) Antagonists.
Answer. (a) Receptors: ‐ Proteins which are crucial to communication system in the body are called receptors. Receptors are embedded in cell membrane.
(b) Agonists: ‐ Drugs that mimic the natural messenger by switching on the receptor are called agonists.
(c) Antagonists: ‐ Drugs that bind the receptors site and inhibit its natural function are called antagonist.

