Please refer to Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Chemistry with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids in Class 12 Chemistry. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on latest examination guidelines.
Question. What represents the best method for producing salicylic acid?
(a) Benzoic acid, strong base, high temperature
(b) Toluene, strong base, water, high temperature
(c) Phenol, base carbondioxide then acid
(d) Bromobenzene, carbonic acid, high temperature
Answer
C
Question. Which reaction is suitable for the preparation of α-chloroacetic acid?
(a) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
(b) Nefreaction
(c) Stephen’s reaction
(d) Perkin condensation
Answer
A
Question. Cross aldol condensation occurs between
(a) two same aldehydes
(b) two same ketones
(c) two different aldehydes and ketones
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Match the following columns.
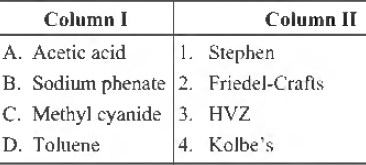
A B C D
(a) 3 1 4 2
(b) 4 2 2 1
(c) 2 3 1 4
(d) 3 4 1 2
Answer
D
Question. Main product obtained from the reaction of ammonia and formaldehyde is
(a) formic acid
(b) methylamine
(c) methanol
(d) urotropine
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following compounds would be the main product of an aldol condensation of acetaldehyde and acetone?
(a) CH3CH = CH·CHO
(b) CH3CH = CHCOCH3
(c) (CH3)2C = CH·CHO
(d) (CH3)2C = CHCOCH3
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following, is an example of aJdol condensation?
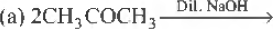
Answer
A
Question. In which of the below reaction do we find α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds undergoing a ring closure reaction with conjugated dienes?
(a) Perkin reaction
(b) Diels-Alder reaction
(c) Claisen rearrangement
(d) Hofmann reaction
Answer
B
Question. A compound ‘A’ having the molecular formula C5H12O,on oxidation gives a compound ‘B’ with molecular formula C5H10O. Compound ‘B’ gave a 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine derivative but did not answer haloform test or silver mirror test. The structure of compound ‘A’ is

Answer
C
Question. An organic compound of molecular formula C3H6O did not give a silver mirror with Tollen ‘s reagent, but gave an oxime with hydroxylarnine, it may be
(a) CH3—CO—CH3
(b) C2H5CHO
(c) CH2 = CH—CH2—OH
(d) CH3—O—CH = CH2
Answer
A
Question.

Answer
C
Question. The most reactive compound towards formation of cyanohydrin on treatment with HCN followed by acidification is
(a) benzaldehyde
(b) p -nitrobenzaldehyde
(c) phenylacetaldehyde
(d) p-hydroxybenzaldehyde
Answer
B
Question. What product is formed in the reaction

Answer
B
Question. When acetaldehyde is heated with Fehling’s solution, a red precipitate is formed. Which of the following is that?
(a) Cu2O
(b) Cu
(c) CuO
(d) CuSO4
Answer
A
Question. What is the oxidation number of carbonyl carbon in acetophenone?
(a) + 3
(b) + 1
(c) + 2
(d) Zero
Answer
C
Question. p-cresol reacts with chloroform in alkaline medium to give the compound A which adds hydrogen cyanide to form the compound B. The latter on acidic hydrolysis gives chiral carboxylic acid. The structure of the carboxylic acid is
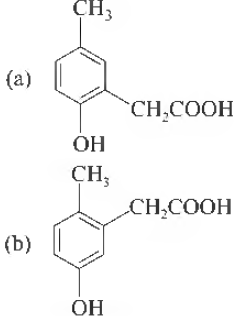
Answer
C
Question. In a reaction RCHO is reduced to RCH3 using amalgamated zinc and concentrated HCl and wanning the solution. The reaction is known as
(a) Meerwein-Ponndorf reaction
(b) Clemmensen’s reduction
(c) Wolff-Kishner reduction
(d) Schiff’s reaction
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following reactions can be used to change benzaldehyde to cinnarnic acid?
(a) Perkin’s reaction
(b) Knoevenagel reaction
(c) Reformatsky reaction and ketones
(d) Benzoin condensation
Answer
A
Question. An organic compound Xis oxidised by using acidified K2Cr2O7 . The product obtained reacts with phenyl hydrazine but does not answer silver mirror test. The possible structure of X is
(a) CH3CH2OH
(b) CH3—C—CH3
ll
O
(c) (CH3 )2 CHOR
(d) CH3CHO
Answer
C
Question. CH3COOH →LialH4 X →300°C Cu y →NaOHDilute Z In the above reaction, Z is
(a) butanol
(b) aldol
(c) ketol
(d) acetal
Answer
B
Question. Which factor/s will increase the reactivity of ›C = O group?
I. Presence ofa group with positive inductive effect.
II. Presence of a group with negative inductive effect.
III. Presence of large alkyl group.
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) I and III
(d) II and III
Answer
B
Question. Benzaldehyde reacts with ammonia to form
(a) benzaldehyde ammonia
(b) urotropine
(c) hydrobenzamide
(d) ammonium chloride
Answer
C
Question. Which product is obtained on reduction of methanal in the presence of concentrated NaOH?
(a) Formic acid and methyl alcohol
(b) CO + H2
(c) Methyl alcohol
(d) Formic acid
Answer
A
Question. An aromatic compound ‘X’ with molecular formula C9H10O gives the following chemical tests
I. Forms 2, 4-DNP derivative,
II. Reduces Tollen’s reagent,
III. Undergoes Cannizzaro reaction and,
IV. On vigorous oxidation 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid is obtained. Xis
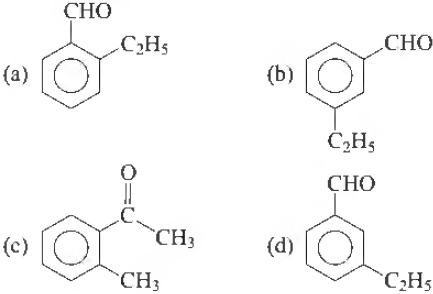
Answer
A
Question. In the following reaction sequence, the correct structures of E, F and G are
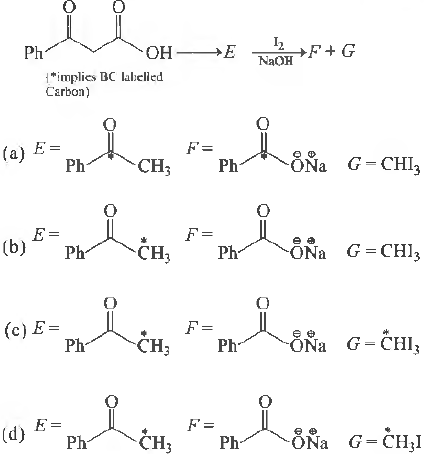
Answer
C
Question. Acetone on addition to methyl magnesiwn bromide forms a complex, which on decomposition with acid gives X and Mg(OH)Br. Which one of the following is X?
(a) CH3 OH
(b) (CH3)3 COH
(c) (CH3)2 CHOH
(d) CH3CH2OH
Answer
B
Question. C6H5CHO→NH3?
(a) (C6H5CHN)2 CH·C6H5
(b) C6H5NHCH3
(c) C6H5CH2NH2
(d) C6H5NHC6H5
Answer
A
Question. Predict the product,

Answer
B
Question. The end product ‘C’ in the following sequence of chemical reactions is
CH3COOH →CaCO3 A →HeatB →NH2OH C
(a) acetaldehyde oxime
(b) formaldehyde oxime
(c) methyl nitrate
(d) acetoxime
Answer
D
Question. Which reaction, intermediate is formed during the condensation reaction between acetaldehyde and formaldehyde?
(a) : –CH2CHO
(b) +CH2CHO
(c) +CH2OH
(d) : –CHCHO
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following organic compounds answers to both iodoform test and Fehling’s test?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Methanal
(c) Ethanal
(d) Propanone
Answer
C
Question. On reaction with hydroxylamine, aldehydes produce
(a) ketoxime
(b) hydrazone
(c) semicarbazone
(d) aldoxime
Answer
D
Question. Benzaldehyde and acetone can be best distinguished using
(a) Fehling’s solution
(b) sodium hydroxide solution
(c) 2, 4-DNP
(d) Tollen’s reagent
Answer
D
Question. Identify the reaction which is used to obtain β- hydroxy ketone.
(a) Condensation reaction
(b) Aldo! condensation
(c) Cross aldol condensation
(d) Cannizzaro reaction
Answer
B
Question. CH3CHO + HCHO →HeatDil. NaOH A
→H3O+HCN B
The structure of compound B is

Answer
A
Question.
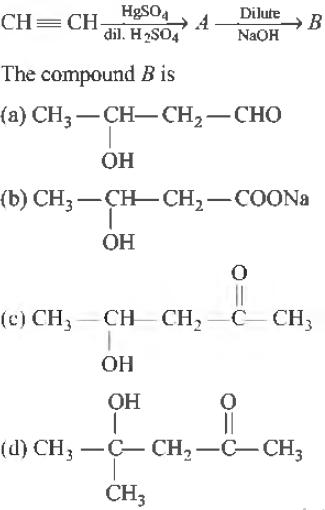
Answer
A
Question. Self condensation of acetaldehyde in the presence of dilute alkalies gives
(a) an acetal
(b) an aldol
(c) mesitylene
(d) propionaldehyde
Answer
B
Question.
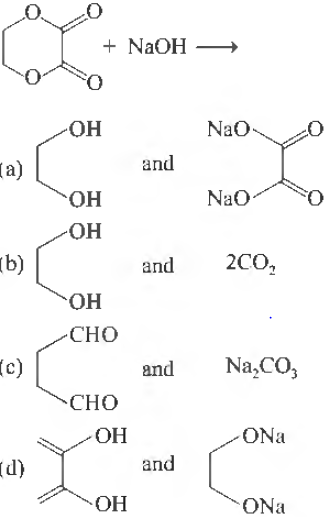
Answer
A
Question. The reaction of CO2 with sodium phenoxide at 400 K result in
(a) benzoic acid
(b) sodium benzoate
(c) salicylaldehyde
(d) sodium salicylate
Answer
D
Question. Q11T2
Identify Z from the following.
(a) Ethyl acetate
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Propanoic acid
(d) Methyl acetate
Answer
B
Question. Claisen condensation is not given by

Answer
A
Question. Formalin is the commercial name of
(a) formic acid
(b) fluroform
(c) 40% aqueous solution of methanal
(d) para-formaldehyde
Answer
C
Question. Which does not react with Fehling’s solution?
(a) CH3CHO
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) C6H12O6
(d) HCOOH
Answer
B
Question.
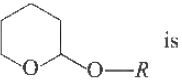
(a) an ester
(b) an anhydride
(c) acetal
(d) hemiacetal
Answer
C
Question. The product formed when hydroxylamine condenses with a carbonyl compound is called
(a) hydrazide
(b) oxime
(c) hydrazine
(d) hydrazone
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following acids dissociates to the greatest extent in aqueous solution?
(a) Trichloroacetic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Chloroacetic acid
(d) Dichloroacetic acid
Answer
A
Question. With reference to the scheme given, which of the given statement (s) about T,U, V and Wis (are) correct?

(a) Tis soluble in hot aqueous NaOH
(b) U is optically active
(c) Molecular formula of Wis C10H18O4
(d) V gives effervescence on treatment with aqueous NaHCO3
Answer
A,C,D
Question. The total number of carboxylic acid groups in the product P is
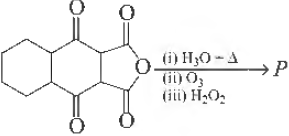
(a) 5
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer
B
Question. Benzaldehyde reacts with methyl amine to give
(a) C6H5NH2
(b) C6H5CH2 NI-I2
(c) C6H5CH=NCH3
(d) C6H5CONH2
Answer
C
Question. CH3COOH →Br2/P Y→(i) KC(ii)H3O+ X. Here, X is
(a) glycollic acid
(b) α-hydroxy propionic acid
(c) succinic acid
(d) malonic acid
Answer
D
Question. The compound I, is
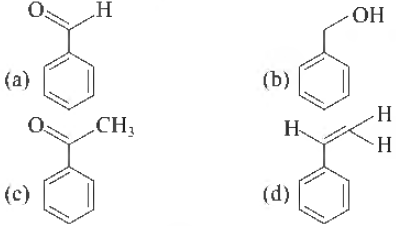
Answer
A
Question. Compound (A )(molecular formula C3H8O) is treated with acidified potassium dichromate to form a product B (molecular formula C3H6O). ‘B’ forms a shining silver m.itTor on wanning with ammoniacal silver nitrate. ‘B’ when treated with an aqueous solution of H2NCONHNH2 · HCl and sodium acetate gives a product’ C’. Identify the structure of ‘C’.
(a) CH3CH2CH = NNHCONH2
(b) (CH3)2C=NNHCONH2
(c) (CH3)2C = NCONHNH2
(d) CH3CH2CH=NCONHNH2
Answer
D
Question. The product fonned in the reaction

Answer
B
Question. A compound, containing only carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, has a molecular weight of 44. On complete oxidation, it is converted into a compound of molecular weight 60. The original compound is
(a) an aldehyde
(b) an acid
(c) an alcohol
(d) an ether
Answer
A
Question. CH3—CHO+ HCN→ A
Compound A on hydrolysis gives
(a) CH3 — CH2 — COOH
(b) CH3 — CH2 — CH2 — NH2
(c) CH3 — CO — COOH
(d) CH3 — CO — CH=NOH
(e) CH3 — CH — COOH
l
OH
Answer
E
Question. Which of the following does not undergo Cannizz.aro’s reaction?
(a) Benzaldebyde
(b) 2-methylpropanal
(c) p-methoxybenzaldebyde
(d) 2, 2-dimethylpropanal
(e) Formaldehyde
Answer
D
Question. Cyanohydrin of which of the following forms lactic acid?
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3COCH3
(c) CH3CHO
(d) CH3CH2CHO
Answer
C
Question. A and B in the following reaction are
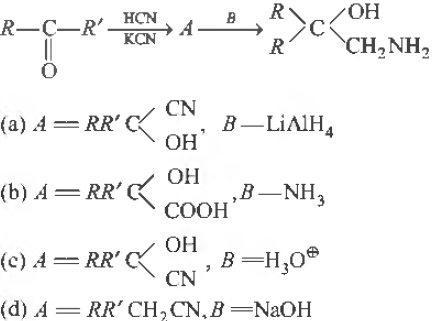
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?
(a) Ethyl acetate
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Acetamide
(d) Butan-2-one
Answer
D
Question.

Answer
B
Question. Aldehyde with NH2 · NH2 forms
(a) hydrazones
(b) aniline
(c) nitrobenzene
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The increasing order of the rate of HCN addition to compounds A – D is
(A) HCHO
(B) CH3COCH3
(C) PhCOCH3
(D) PhCOPh
(a) A < B < C < D
(b) D < B < C < A
(c) D < C < B < A
(d) C < D < B < A
Answer
C
Question. The enol form of acetone after treatment with D2O, give

Answer
A
Question. Benedict’s solution is not reduced by
(a) formaldehyde
(b) acetaldehyde
(c) glucose
(d) acetic anhydride
Answer
D
Question. Acetone reacts with Grignard reagent to form
(a) 3° alcohol
(b) 2° alcohol
(c) ether
(d) No reaction
Answer
A
Question. Q

The compound (X) is
(a) CH3—COOH
(b) BrCH2—COOH
(c) (CH3CO)2O
(d) CHO—COOH
Answer
C
Question. Benzyl alcohol and sodium benzoate is obtained by the action of sodium hydroxide on benzaldehyde. This reaction is known as
(a) Perkin’s reaction
(b) Cannizzaro’s reaction
(c) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(d) Claisen condensation
Answer
B
Question. The end products in benzaldehyde are
(a) PhCO2H,PhCH2OH
(b) PhCO2H,PhCH2CO2H
(c) PhCH2OH, PhCOCH3
(d) PhCO2H,PhCOCH3
Answer
A
Question. Acetals are
(a) ketones
(b) di ethers
(c) aldehyde
(d) hydroxy aldehydes
Answer
B
Question. Aldehydes can be oxidised by
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Fehling’s solution
(c) Benedict solution
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question.

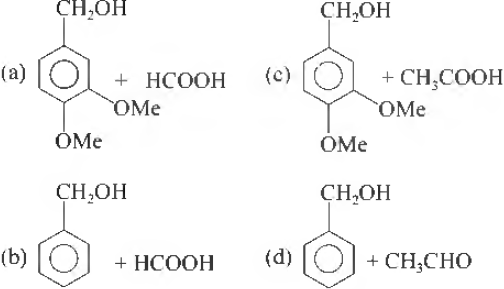
Answer
A
Question. CH3COCH3 and CH3CH2CHO can be distinguished by
(a) FeCl3
(b) Tollen’s reagent
(c) NaHSO3
(d) 2, 4-DNP
Answer
B
Question. How will you convert butan-2-one to propanoic acid?
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Fehling’s solution
(c) NaOH/I2/H+
(d) NaOH/ NaI/ H+
Answer
C
Question. Acetone and acetaldehyde can be distinguished by
(a) Molisch test
(b) Tollen’s test
(c) Schiffs test
(d) lodoform test
Answer
B


