Please refer to Biomolecules MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Chemistry with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Biomolecules will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Biomolecules MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Biomolecules in Class 12 Chemistry. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on latest examination guidelines.
Question. The total number of basic groups in the following form of lysine is
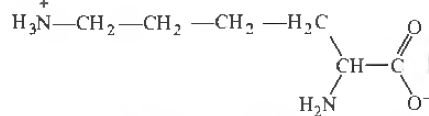
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. Biuret test is not given by
(a) carbohydrates
(c) urea
(b) polypeptides
(d) proteins
Answer
A
Question. The substituents R1 and R2 for nine peptides are listed in the table given below. How many of these peptides are positively charged at pH = 7.0?

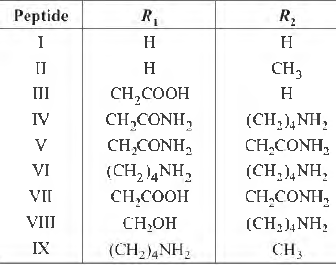
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a heterocyclic amino acid?
(a) Glycine
(b) Alanine
(c) Phenylalanine
(d) Tryptophan
Answer
D
Question. A compound with molecular mass 180 is acylated with CH3COCI to get a compound with molecular mass 390. The number of amino groups present per molecule of the former compound is
(a) 2
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 6
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following set consists only of essential amino acids?
(a) Alanine, tyrosine, cystine
(b) Leucine, lysine, tryptophane
(c) Alanine, glutamine, lycine
(d) Leucine, proline, glycine
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is not a protein?
(a) Wool
(b) Nail
(c) Hair
(d) DNA
Answer
D
Question. α-helix is found in
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) lipid
(d) carbohydrates
(e) protein
Answer
E
Question. Which one of the following does not correctly match with each other?
(a) Silk-polyamide
(b) Lipase-enzyme
(c) Butter-fat
(d) Oxytocin-enzyme
Answer
D
Question. The number of disulphide linkages present in insulin are
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
B
Question. A decapeptide (mol. wt. 796) on complete hydrolysis gives glycine (mol. wt. 75), alanine and phenylalanine. Glycine contributes 47% to the total weight of the hydrolysed products. The number of glycine units present in the decapeptide is
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer
D
Question. A Zwitter ion is
(a) negatively charged ion without metal atom
(b) a heavy ion with a small charge on it
(c) an ion with positive and negative charge at different points on it
(d) a positively charged ion without a metal atom
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a simplest amino acids?
(a) Glycine
(b) Alanine
(c) Leucine
(d) Valine
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following element is present in haemoglobin?
(a) Na
(b) Ca
(c) Fe
(d) Au
Answer
C
Question. The number of amino acids and number of peptide bonds in a linear tetrapeptide (made of different amino acids, are respectively
(a) 4 and 4
(b) 5 and 5
(c) 5 and 4
(d) 4 and 3
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following describes the overall three dimensional folding of a polypeptide?
(a) Primary structure
(b) Secondary structure
(c) Tertiary structure
(d) Quaternary structure
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compound shows aromatic properties?
(a) Valine
(c) Serine
(b) Leucine
(d) Tyrosine
Answer
D
Question. A tetrapeptide has – COOH group on alanine. This produces glycine (Gly), valine (Val), phenyl alanine (Phe) and alanine (Ala), on complete hydrolysis. For this tetrapeptide, the number of possible sequences (primary structures) with — NH2 group attached to a chiral centre is
(a) 7
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 8
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) All amino acids except lysine are optically active
(b) All amino acids are optically active
(c) All amino acids except glycine are optically active
(d) All amino acids except glutamic acids are optically active.
Answer
C
Question. Hydrolysis of proteins give
(a) α-amino acids
(b) β-amino acids
(c) ϒ-amino acids
(d) mixture ofall, i.e.α,βϒ-amino acids
Answer
A
Question. 1.78 g of an optically active L-amino acid (A) is treated with Na NO2 /HCI at 0°C, 448 cm3 of nitrogen was at STP is evolved. A sample of protein has 0.25% of this amino acid by mass. The molar mass of the protein is
(a) 36500 g mol – 1
(b) 34500 g mol – 1
(c) 35400 g mol – 1
(d) 35600 g mol – 1
Answer
D
Question. The enzyme pepsin hydrolyses
(a) proteins to amino acids
(b) fats to fatty acids
(c) glucose to ethyl alcohol
(d) poloysaccharides to monosaccharides
Answer
A
Question. An electric current is passed through an aqueous solution of a mixture of alanine (isoelectric point 6.0) glutamic acid (3.2) and arginine (10.7) buffered at pH 6. What is the fate of the three acids?
(a) Glutamic acid migrates to anode at pH 6. Arginine present as a cation and migrates to the cathode Alanine in a dipolar ion remains uniformly distributed in solution
(b) Glutamic acid migrates to cathode and others remain uniformly distributed in solution
(c) All three remain uniformly distributed in solution
(d) All three move to cathode
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is present in animals like cow, buffaloes etc. to digest compound like paper, cloth etc?
(a) Urease
(b) Cellulase
(c) Silicones
(d) Sucrose
Answer
B
Question. The compound, which give a positive ninhydrin test and a negative Benedict’s solution test, is
(a) a monosaccharide
(b) a disaccharide
(c) a lipid
(d) a protein
Answer
D
Question. Dialysis can be used to separate
(a) protein and starch
(b) glucose and protein
(c) glucose and NaCl
(d) glucose and fructose
Answer
B
Question. Denaturation of proteins leads to the loss of its biological activity by
(a) formation of amino acids
(b) loss of primary structure
(c) loss of both primary and secondary structures
(d) loss of both secondary and tertiary stuctures
Answer
D
Question. A tripeptide is written as glycine-alanine-glycine. The correct structure of the tripeptide is
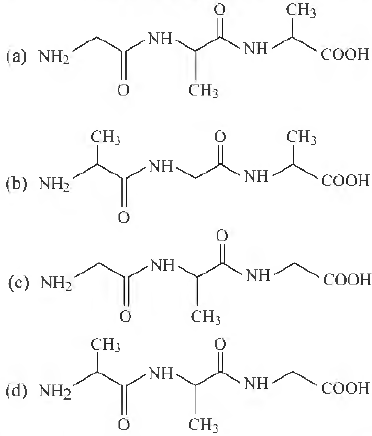
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following exists as Zwitter ion ?
(a) p-aminophenol
(b) Salicylic acid
(c) Sulphanilic acid
(d) Ethanolamine
(e) p-amino acetophenone
Answer
C
Question. Which amino acid has irnidazole ring?
(a) Alanine
(b) Leucine
(c) Tyrosine
(d) Histidine
Answer
D
Question. Which amino acid has phenyl—OH group?
(a) Lysine
(b) Arginine
(c) Proline
(d) Tyrosine
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statements about amino acids is not trne?
(a) They are constituents of all proteins
(b) They are all high melting solids
(c) Most naturally occurring amino acids have D-configuration
(d) They are characterised by isoelectric point
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is a conjugated protein?
(a) Phosphoprotein
(b) Glycoprotein
(c) Chromoprotein
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. The enzyme that is used to dissolve blood clot is
(a) trypsin
(b) renin
(c) streptokinase
(d) tyrosinase
Answer
C
Question. Which destroy antigens?
(a) Insulin
(b) Antibodies
(c) Chromoprotein
(d) Phosphoprotein
Answer
B
Question. The a-amino acid which does not give purple colour in the ninhydrin test is
(a) proline
(b) glycine
(c) lysine
(d) aspartic acid
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following will explain synthesis of RNA?
(a) Translation
(b) Coagulation
(c) Transcription
(d) Replication
Answer
C
Question. In an alkaline medium, glycine predominantly exists as/in a/an
(a) cation
(b) anion
(c) Zwitter ion
(d) covalent form
Answer
B
Question. The amino acid which is not optically active is
(a) lactic acid
(b) serine
(c) alanine
(d) glycine
Answer
D
Question. The main structural feature of protein is
(a) ester linkage
(b) ether linkage
(c) peptide linkage
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. The presence or absence of hydroxy group on which carbon atom of sugar differentiates RNA and DNA ?
(a) 1st
(b) 2nd
(c) 3rd
(d) 4th
Answer
B
Question. The correct statement in respect of protein haemoglobin is that it
(a) functions as a catalyst for biological reactions
(b) maintains blood sugar level
(c) act as an oxygen carrier in the blood
(d) forms antibodies and offers resistance to diseases
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is an amphoteric acid?
(a) Glycine
(b) Salicylic acid
(c) Benzoic acid
(d) Citric acid
Answer
A
Question. At pH = 4, glycine exists as
(a) H3N+—CH2 — COO–
(b) H3N+—CH2 — COOH
(c) H2N—CH2 — COOH
(d) H2N—CH2 — COO–
Answer
B
Question. Polypeptides having molecular weights above 10000 are known as
(a) amino acids
(b) hormones
(c) proteins
(d) terminal amino acids
Answer
C
Question. The sugar moiety present RNA molecule is
(a) β-D-2-deoxyribose
(b) β-D-galactose
(c) β-D-fructofuranose
(d) β-D-ribose
(e) β-D-glucopyranose
Answer
D
Question. The secondary structure of a protein refers to
(a) α-helical backbone
(b) hydrophobic interactions
(c) sequence of a -amino acids
(d) fixed configmatjon of the polypeptide backbone
Answer
A
Question. Which one is the correct representation of peptide bond?
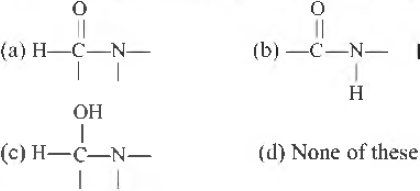
Answer
B
Question. In alkaline medium, alanine exits predominantly as
(a) anion
(b) Zwitter ion
(c) cation
(d) covalent form
Answer
A
Question. Give the pOH range for the isoelectric point of the amphoteric ion of an amino acid
(a) 5.5 to 6.3
(b) 2.5 to 5.0
(c) 7.7 to 8.5
(d) 9.0 to 10.7
Answer
C
Question. In aqueous solution, amino acids mostly exist as
(a) NH2 — CHR — COOH
(b) NH2 — CHR — COO–
(c) NH+3 — CHR — COOH
(d) NH+3 — CHR — COO–
Answer
D
Question. An example of a sulphur containing amino acid is
(a) lysine
(b) serine
(c) cysteine
(d) tyrosine
Answer
C
Question. The product formed in the reaction of glycine with benzoyl chloride+ aq. NaOH is
(a) PhCOCH2NH2
(b) PhCH2NH2
(c) PhCONHCH3
(d) PhCONHCH2CO2H
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following structures represents the peptide chain ?

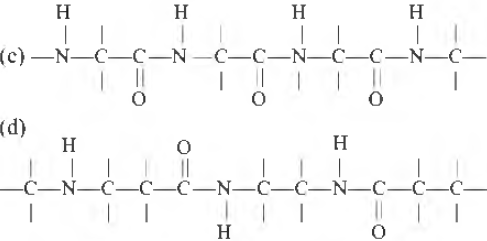
Answer
C
Question. RNA contains
(a) ribose sugar and thymine
(b) ribose sugar and uracil
(c) deoxyribose sugar and uracil
(d) deoxyribose sugar and thymine
Answer
B
Question. Zwitter ion is formed by
(a) aniline
(b) acetanilide
(c) benzoic acid
(d) glycine
Answer
D
Question. Amino acids have peptide linkage which is
(a) —CO—NH—
(b) —C—NH2
(c) SO—NH—
(d) —CO—N—
Answer
A
Question. Pick out the one which does not belong to the family.
(a) Pepsin
(b) Cellulose
(c) Ptyalin
(d) Lipase
Answer
B
Question. If one strand of DNA has the sequence TATGACTG, the sequence in the complimentary strand would be
(a) ATACAC T C
(b) ACGTTGAC
(c) ATACTGAC
(d) ATACTGCA
Answer
C
Question. An achiral amino acid
(a) alanine
(b) valine
(c) leucine
(d) glycine
Answer
D
Question. Protein gives blue colour with
(a) benedict reagent
(b) iodine solution
(c) ninhydrin
(d) biurete
Answer
C
Question. Which one is not a constituent of nucleic acid?
(a) Uracil
(b) Guanidine
(c) Phosphoric acid
(d) Ribose sugar
Answer
B
Question. The reason for double helical structure of DNA is operation of
(a) van der Waals’ forces
(b) dipole-dipole interaction
(c) hydrogen bonding
(d) electrostatic attractions
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following hormone, is responsible for the growth of animals?
(a) Auxin
(b) Insulin
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Somatotropin
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is true?
(a) Nucleoside + phosphoester bond= nucleotide
(b) DNA’s are nucleotide and RNA’s are nucleoside
(c) Nucleotide + phosphoester bond= nucleoside
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following biomolecules acts as specific catalysts in biological reaction ?
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Lipids
(c) Vitamins
(d) Enzymes
Answer
D
Question. Monomer of nucleic acid is
(a) nucleotides
(b) nucleoxides
(c) aminoacids
(d) carboxylic acid
Answer
A
Question. Metabolic function in hwnan bodies is carried out by
(a) lipids
(b) peptides
(c) nucleic acid
(d) enzymes
Answer
D
Question. A nanopeptide contains …. .. peptide linkages.
(a) 10
(b) 8
(c) 9
(d) 18
Answer
B
Question. A sequence of how many nucleotides in messenger RNA makes a codon for an amino acid ?
(a) Three
(b) Four
(c) One
(d) Two
Answer
A
Question. Peptides are formed from
(a) aliphatic amines
(c) a -amino acids
(b) carbohydrates
(d) aromatic amines
Answer
C
Question. In DNA, the consecutive deoxynucleotides are connected via
(a) phosphocliester linkage
(b) phosphomonoester linkage
(c) phosphotriester linkage
(d) amide linkage
Answer
A
Question. Proteins are
(a) polypeptides with low molecular weights
(b) polypeptides with high molecular weights
(c) polymers of amides
(d) polymers of secondary amines
Answer
B
Question. Progesterone is secreted by … . . . .
(a) thyroid
(b) ovaries
(c) adrenal
(d) testes
Answer
B



