VBQs How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science with solutions has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 10 Science with solutions. The following How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 10 examinations.
How do the Organisms Reproduce VBQs Class 10 Science
Question. In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by
(a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits.
(b) division of a cell into two cells.
(c) division of a cell into many cells.
(d) formation of young cells from older cells.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(a) Pollination, fertilisation, seedling, embryo
(b) Seedling, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
(c) Pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seedling
(d) Embryo, seedling, pollination, fertilisation
Answer
C
Question. The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called
(a) budding
(b) reduction division
(c) binary fission
(d) multiple fission
Answer
D
Question. Offspring formed by asexual method of reproduction have greater similarity among themselves because
(i) asexual reproduction involves only one parent.
(ii) asexual reproduction does not involve gametes.
(iii) asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction.
(iv) asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. Vegetative propagation refers to formation of new plants from
(a) stem, roots and flowers.
(b) stem, roots and leaves.
(c) stem, flowers and fruits.
(d) stem, leaves and flowers.
Answer
B
Question. In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes (germ cells) are
(a) stamen and anther
(b) filament and stigma
(c) anther and ovary
(d) stamen and style
Answer
C
Question. The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is
(a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(c) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual.
(ii) They are the sexual reproductive organs.
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants.
(iv) After fertilisation they give rise to fruits.
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
D
Question. A student while observing an embryo of a gram seed listed various parts of the embryo as listed below: Testa, Micropyle, Cotyledon, Tegmen, Plumule, Radicle.
On examining the list the teacher commented that only three parts are correct. Select these three correct parts:
(a) Cotyledon, Testa, Plumule
(b) Cotyledon, Plumule, Radicle
(c) Cotyledon, Tegmen, Radicle
(d) Cotyledon, Micropyle, Plumule
Answer
B
Question. Reproduction is essential for living organisms in order to
(a) keep the individual organism alive.
(b) fulfill their energy requirement.
(c) maintain growth.
(d) continue the species generation after generation.
Answer
D
Question. A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Spirogyra and Yeast are that
(a) they reproduce asexually.
(b) they are all unicellular.
(c) they reproduce only sexually.
(d) they are all multicellular.
Answer
A
Question. Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show
(a) only similarities with parents
(b) only variations with parents
(c) both similarities and variations with parents
(d) neither similarities nor variations
Answer
C
Question. Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
(a) pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
Answer
B
Question. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Leishmania
Answer
B
Question. The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species remains constant due to
(a) doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
(b) halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
(c) doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
(d) halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
Answer
B
Question. In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
(i) Banana (ii) Dog
(iii) Yeast (iv) Amoeba
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. In human males, the testes lie in the scrotum, because it helps in the
(a) process of mating.
(b) formation of sperm.
(c) easy transfer of gametes.
(d) all of the above.
Answer
B
Question. Factors responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on slices of bread are
(i) large number of spores.
(ii) availability of moisture and nutrients in bread.
(iii) presence of tubular branched hyphae.
(iv) formation of round shaped sporangia.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. Which among the following is not the function of testes at puberty?
(i) Formation of germ cells
(ii) Secretion of testosterone
(iii) Development of placenta
(iv) Secretion of estrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
C
Question. The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for transport of sperms is:
(a) testis → vas deferens → urethra
(b) testis → ureter → urethra
(c) testis → urethra → ureter
(d) testis → vas deferens → ureter
Answer
A
Question. During adolescence, several changes occur in the human body. Mark one change associated with sexual maturation in boys.
(a) Loss of milk teeth
(b) Increase in height
(c) Cracking of voice
(d) Weight gain
Answer
C
Question. In human females, an event that reflects onset of reproductive phase is
(a) growth of body
(b) changes in hair pattern
(c) change in voice
(d) menstruation
Answer
D
Question. Which among the following diseases is not sexually transmitted?
(a) Syphilis
(b) Hepatitis
(c) HIV – AIDS
(d) Gonorrhoea
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following are examples of vegetative reproduction in plants?
(a) Tomato, lady’s finger, onion and cauliflower
(b) Potato, ginger, onion and sugarcane
(c) Cauliflower, onion, potato and tomato
(d) Lady’s finger, onion, ginger and sugarcane
Answer
B
Assertion and Reason Based MCQs :
Directions : In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (a) is followed by a statement of Reason (R).
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Question. Assertion (A): Characteristics of parental plants can be preserved through asexual reproduction.
Reason (R): Vegetative reproduction involves only mitosis.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Surgical methods are most effective methods of contraception.
Reason (R): Surgical method blocks gametes transport and hence prevent fertilisation.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Fertilization results in formation of zygote.
Reason: Zygote divides several times to form an embryo.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission.
Reason (R): Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (a): At puberty, in boys, voice begins to crack and thick hair grows on face.
Reason (R): At puberty, there is decreased secretion of testosterone in boys.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Amoeba reproduces by binary fission.
Reason (R): All unicellular organisms reproduce asexually.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Plants are vegetatively propagated even though they bear or not bear seeds.
Reason (R): Potatoes reproduces through tubers, apples by cutting etc.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion (A): Sexual reproduction increases genetic diversities and plays a role in origin of new species.
Reason (R): Sexual reproduction involves formation of gametes and fusion of gametes.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): DNA copying is necessary during reproduction.
Reason (R): DNA copying leads to the transmission of characters from parents to offspring.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion (A): Double fertilisation is unique to angiosperms.
Reason (R): Triple fusion occurs in asexual reproduction.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): In human male, testes are extraabdominal organs which are present inside scrotum.
Reason (R): Scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production and storage of sperms.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): An embryo is formed from fertilized egg.
Reason (R): A monocot embryo comprises embryonal axis with two cotyledons.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion (A): Unisexual flowers have separate male and female flowers whereas a typical monocot embryo comprises an embryonal axis with single cotyledon.
Reason (R): Cucumber, pumpkin and water melon are example of unisexual flowers.
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Give one reason.
Answer: If there is an error in DNA copying or mutation, then newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at time.
Question. What is DNA?
Answer: DNA is the carrier of hereditary information from parents to the next generation. Hereditary material is present either DNA/RNA in all living cells.
Question. Name the type of reproduction mostly seen in unicellular organisms.
Answer: Asexual reproduction.
Question. How does Plasmodium reproduce? Is this method sexual or asexual type of reproduction?
Answer: Plasmodium reproduces by a process known as multiple fission. Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction.
Question. List two unisexual flowers.
Answer: Watermelon, papaya.
Question. When a cell reproduces, what happens to its DNA?
Answer: When a cell reprodues , its DNA makes – two copies , each divided call getting one .
Question. Write the role of testes in male reproductive system.
Answer: Formation of sperms and to secrete hormone called testosterone.
Question. Name the parts of a bisexual flower that are not directly involved in reproduction.
Answer: Sepals/calyx
Petals/corolla
Thalamus
Question. Name two simple organisms having the ability of regeneration.
Answer: Planaria and Hydra.
Question. Name the organs producing sperms and ova respectively in humans.
Answer: Testis: Sperms, Ovary: Ova.
Question. What are those organisms called which bear both the sex organs in the same individual? Give one example of such organism.
Answer: Bisexual; For e.g., Hydra/Earthworm/Mustard/ Hibiscus.
Question. Why is fertilization not possible without pollination?
Answer: Pollination allows pollen grains that produce male germ cell to reach the carpel which contain the female germ cell, egg.
Thus, fertilization which involves fusion of male and female germ cells can only occur after pollination.
Question. What is a gene?
Answer: Gene is a part of DNA that encodes the instructions that allow a cell to produce a specific protein or enzyme.
Question. List two functions of ovary of human female reproductive system.
Answer: Two functions of Ovary:
(i) To produce female gamete / ovum.
(ii) To secrete female hormones / estrogen and progesterone.
Question. Name the method by which Spirogyra reproduces under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual type of reproduction?
Answer: Fragmentation, Asexual → Single parent involved.
↓
Breaking into 2 or more fragments
Question. Give reason for the statement— Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month by making its lining thick and spongy.
Answer: It is required for nourishing the embryo if fertilization takes place and reaches the uterus.
Question. In the human female reproductive system where does fertilization occur?
Answer: Oviduct or Fallopian tube.
Question. What is fertilisation? Where does it occur in a human female?
Answer: Fusion of male and female gamete is known as fertilization. It occurs in fallopian tube.
Short Answer Type Questions :
Question. How is the process of binary fission different in Amoeba and Leishmania?
Answer: Amoeba reproduces through simple binary fission.
Leishmania reproduces asexually through binary fission that occurs along a definite orientation related to the whip like structure at one end of the cell.
Question. Fallen leaves of ‘Bryophyllum’ on the ground produce new plants whereas the leaves of rose do not? Explain this difference between the two plants.
Answer: In Bryophyllum, vegetative propagation occur through leaves where buds occur on their margins.
Rose leaves do not form buds.
Question. In a flowering plant, summarize the events that take place after fertilization.
Answer: Fertilization results in formation of zygote.
Zygote divides several times to form an embryo.
The ovule develops a thick coat and changes into seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form the fruit.
Question. Give one example of each, the unisexual and bisexual flowers.
Answer: Unisexual flowers contain either stamens or carpels but never both.
Example: Papaya, watermelon.
Bisexual flowers contain both stamens and carpels.
Example: Hibiscus, Mustard.
Question. (i) What is the fate of the ovules and the ovary in a flower after fertilization?
(ii) How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Answer: (i) After fertilization, ovules become seeds and ovary forms the fruit.
(ii) Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a flower.
Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes.
Question. What is the main difference between sperms and eggs of humans? Write the importance of this difference.
Answer: Sperms contain one of the two types of sex chromosomes i.e., X—chromosomes and Y— chromosomes.
Egg contains one type of sex chromosomes only i.e., X—chromosome.
This chromosomal difference helps in determination of sex. If sperm carrying Y-chromosome fuses with egg, the resultant zygote will develop in male. If sperm with X chromosome fuses with egg, the zygote will develop into a female child.
Question. Write two functions of each (i) Testis, (ii) Ovaries.
Answer: (i) Testis: It produces sperms and secretes male sex hormones called testosterone.
(ii) Ovary: It produces ovum and secretes female sex hormones called estrogen and progesterone.
Question. List four modes of asexual reproduction.
Answer: Four modes of asexual reproduction are:
(i) Binary fission
(ii) Budding
(iii) Multiple fission
(iv) Fragmentation.
Question. (i) What is meant by vegetative propagation?
(ii) How will a plant be benefitted if it reproduces by vegetative propagation?
Answer: (i) Propagation by vegetative parts such as the roots, stems and leaves.
(ii) Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. Such method also makes possible the propagation of plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds.
Question. Mention the functions of (a) placenta, (b) fallopian tube in the human female reproductive system.
Answer: (a) Placenta: (i) Helps in the transportation of glucose and oxygen from the mother to the embryo.
(ii) Waste generated by the embryo is removed by transferring it to the mother’s blood.
(b) Fallopian tube: (i) Egg is carried from the ovary to the uterus.
(ii) Fertilization occurs here.
Question. List any two contraceptive methods practised only by women. Mention how these methods work?
Answer: (i) Oral pills: Change hormonal balance so eggs are not released.
(ii) Loop / Copper-T: Placed in the uterus. Prevent pregnancy by checking the entry of sperms through the vagina.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival-the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Justify your answer.
Answer: Any one of the following difference:
(i) In sexual reproduction, two opposite sexes are involved whereas in asexual reproduction, only one individual is involved.
(ii) In sexual reproduction, male and female gamete formation takes place whereas in asexual, no gamete formation occurs.
Sexually reproducing organisms have better chances of survival.
Because more variations are generated.
Question. In a germinating seed, which parts are known as future shoot and future root? Mention the function of cotyledon.
Answer: Future shoot–Plumule
Future root–Radicle
Function of cotyledon–It stores food for the future plant or embryo.
Question. In the context of reproduction of species, state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also, give one example of each.
Answer: Fission: It is the method of asexual reproduction in unicellular forms of life.
In this process, the parent organism splits to form two or more daughter cells.
Example: Amoeba / Plasmodium / Paramecium.
Fragmentation: It is the process found in multicellular organisms. The filament breaks up into two or more pieces upon maturation. These pieces then grow into new individuals.
Example: Spirogyra.
Question. What is regeneration? Give one example of an organism that shows this process and one organism that does not. Why does regeneration not occur in the latter?
Answer: (i) Regeneration: Ability of organisms to give rise to new individual organisms from their body parts.
(ii) Planaria/Hydra
iii) Amoeba / Rhizopus / Banana / Sugarcane / any other does not show regeneration.
(iv) Regeneration is carried out by specialized cells which are not present in non-regenerating organisms.
Question. What happens when:
(a) Accidently, Planaria gets cut into many pieces?
(b) Bryophyllum leaf falls on the wet soil?
(c) On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus bursts?
Answer: (a) Each piece regenerates into new Planaria.
(b) Buds called leaf buds at its notches develop into new plants.
(c) It releases spores which germinate into new mycelium in moist conditions.
Question. How do organisms, whether reproduced asexually or sexually maintain a constant chromosome number through several generations?
Explain with the help of suitable example.
Answer: (i) When organisms reproduce asexually, only mitotic divisions are involved and the chromosome number remains the same.
(ii) During asexual reproduction, the DNA (in the chromosomes) or the cells involved are copied and then equally divided among the two daughter cells.
Thus, chromosome number remains unchanged.
(iii) In sexual reproduction, organisms produce gametes through a special type of division called meiosis or reductional division, in which the original number of chromosomes is reduced to half.
These two male & female gametes fuse to form the zygote and the original number of chromosomes is restored.
(iv) In sexual reproduction, specialized cells / germ cells with only half the number of chromosomes are formed. When these germ cells from two individuals combine to form a new individual, the original chromosome number is restored.
(v) Example: In humans, the parents (father and mother) each have 46 or 23 pairs of chromosomes.
In the gametes, the sperm has half the number of chromosomes i.e., 23 and the egg also has 23 chromosomes. When the sperm and the egg fuse, the zygote has 46 or 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Thus, the chromosome number remains constant.
Question. What is multiple fission? How does it occur in an organism? Explain briefly. Name one organism which exhibits this type of reproduction.
Answer: Multiple fission: The process of reproduction in which many individuals are formed or produced from the parent cell.
In this process, the nucleus divides repeatedly to produce large number of nuclei. Each nucleus gathers a bit of cytoplasm around itself, develops a membrane around each structure.
Many daughter cells develop which on liberation grow into adult organism.
Plasmodium exhibits this type of fission.
Question. (a) List in tabular form two differences between binary fission and multiple fission.
(b) What happens when a mature Spirogyra filament attains considerable length?
Answer: (a) Difference between binary fission and multiple fission:

(b) Spirogyra reproduces asexually by fragmentation.
In this, the body breaks up into two or more small pieces of fragments upon maturation. These fragments grow into new Spirogyra.
Question. (a) Budding, fragmentation and regeneration, all are considered as asexual mode of reproduction. Why?
(b) With the help of neat diagram, explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Answer: (a) Because these methods involve only one parent / organisms are formed as a result of mitotic division / progeny (organisms) are similar in their genetic make up and no variations is seen.
(b)
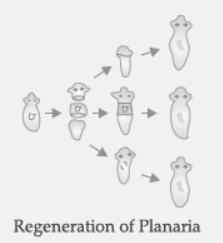
Planaria can be cut into many number of pieces and each piece grows through specialized cells into a complete organism.
Question. Explain the term “Regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Answer: Regeneration: It is the ability of an organism to give rise to a new organism/individual from their body parts.
Regeneration in Hydra:
(i) The body of Hydra by any means is cut into number of pieces.
(ii) Each piece contains specialized cells.
(iii) These cells, proliferate and make large number of cells.
(iv) From this mass of cells, different cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues, which finally develops into a new organism.
Question. Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.
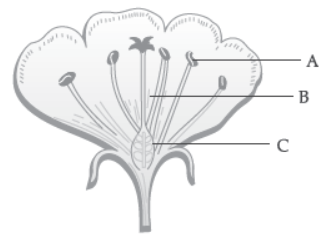
Answer: A. Anther: It produces pollen grains.
B. Style: It provides the path through which the pollen tube grows and reaches the ovary.
C. Ovary: It contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell/female gamete. It develops into fruit after fertilization.
Question. Define reproduction. How does it help in providing stability to the population of species?
Answer: Reproduction: It is a (biological) process by which new individuals of the same species are produced by the existing organisms.
(i) Populations of organisms live in well-defined places called niches in the ecosystem using their ability to reproduce.
(ii) Reproduction involves DNA copying which is the source of information for making proteins thereby controlling body design.
(iii) These body designs allow the organism to use a particular niche for the stability of the population of a species.
(iv) (Minor) variations may also lead to the stability of the species.
Question. Distinguish between pollination and fertilisation.
Mention the site and the product of fertilisation in a flower.
Answer: Pollination: Transfer of pollen grains from stamen/anther to stigma.
Fertilization: Fusion of male & female gamete (or germ cells)
Site of fertilisation: Ovary/ Ovule
Product: Zygote.
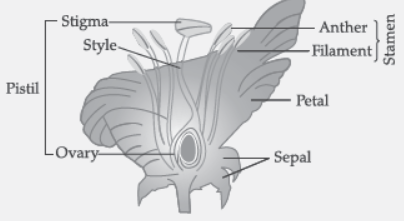
Question. What is carpel? Write the function of its various parts.
Answer: Female reproductive part of the plant.
(i) Stigma: Receive pollen grains
(ii) Style: Passage for the growth of pollen tube
(iii) Ovary: Site for fertilization
Question. What is sexual reproduction? List its four significance.
Answer: Two major processes namely formation of gametes and fusion of gametes constitute sexual reproduction.
Significance–(i) Incorporates the process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction.
(ii) Increases genetic variation.
(iii) Promotes diversity in the offsprings.
(iv) Plays a role in the origin of new species.
Question. Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm.
Where are these parts located? Explain in brief the structure of its female reproductive parts.
Answer: (i) Stamen and Carpel.
(ii) Located in the flower.
(iii) The female reproductive part is Carpel. It is made up of three parts–the bottom swollen part is ovary, middle elongated part is the style, terminal sticky part is stigma.
Question. Define the term pollination. Differentiate between self pollination and cross pollination.
What is the significance of pollination?
Answer: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is known as pollination.
The two types of pollination are:
(a) Self pollination: When the pollen grains from the stamens of a flower fall on the stigma of the same flower, then it is called self pollination.
(b) Cross pollination: When pollen grains from the stamens of a flower fall on the stigma of another flower, it is called cross pollination.
Significance of pollination:
(i) It is a significant event because it precedes fertilization.
(ii) It brings the male and female gametes closer for the process of fertilization.
(iii) Cross-pollination introduces variations in plants because of the mixing of different genes. These variations further increase the adaptability of plants towards the environment or surroundings.
Question. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower exhibiting germination of pollen on stigma and label.
(i) Ovary, (ii) Male germ-cell, (iii) Female-germ cell and (iv) ovule on it.
Answer:
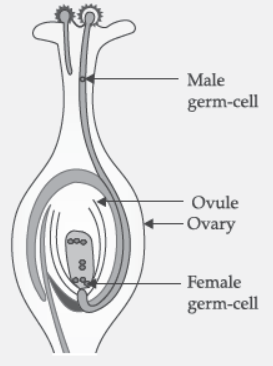
Four correct labelling, viz., ovary, male germ cell, female germ cell and ovule.
Question. Draw longitudinal section of a bisexual flower and label the following parts on it:
(i) Anther, (ii) Ovary, (iii) Stigma, (iv) Style.
Answer:
4 correct labellings (i) Anther (ii) Ovary (iii) Stigma
(iv) Style
Question. Name the parts A, B and C shown in the diagram and write their functions.
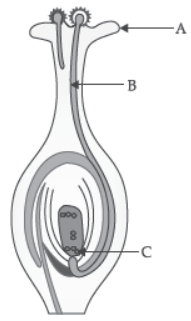
Answer: Part A is Stigma.
Function: It is the terminal part of carpel, which may be sticky and helps in receiving the pollen grains from the anther of stamen during pollination.
Part B is Pollen tube.
Function: The pollen tube grows out of the pollen grain through the style to reach the ovary. It carries male gametes into the embryo sac in ovule.
Part C is Female Germ Cell.
Function: It is a female gamete which fuses with male gamete to form a diploid cell known as zygote.
Question. What is reproduction? Explain two advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction.
Answer: Reproduction: It is a (biological) process by which new individuals of the same species are produced by the existing organisms.
Advantages of sexual reproduction:
(i) Leads to stability of population of species.
(ii) Results in variations useful for the survival of species over time.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? State two advantages and two disadvantages of this method.
Answer: Vegetative propagation is a mode of asexual reproduction in which new plants are formed from roots, stems, leaves and buds of the individual vegetative parts of the plants. e.g., eyes of potato.
Advantages:
(i) Offsprings are genetically identical and therefore useful traits can be preserved.
(ii) It is a rapid and economical method.
Disadvantages:
(i) New characters cannot be introduced.
(ii) The disease of the parent plant gets transferred to the offsprings.
Question. State the changes that take place in the uterus when:
(i) Implantation of embryo has occurred.
(ii) Female gamete/egg is not fertilised.
Answer: (a) When implantation of embryo has occurred, the uterine wall thickens and is richly supplied with blood to nourish the growing embryo.
(b) The thick and spongy lining of the uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus.
Question. Write the functions of the following parts of human female reproductive system:
(i) Ovary, (ii) Fallopian tube (iii) Uterus.
Answer: (i) Ovary: Produces egg or female gamete, female sex hormone/ estrogen and progesterone.
(ii) Fallopian tube: Transfer of ovum to the uterus, site for fertilization
(iii) Uterus: Site of implantation of zygote, development of embryo.
Question. What is placenta? Write any two major functions of placenta
Answer: Placenta: A disc shaped organ or special tissue in the uterus of pregnant mammal, nourishing and maintaining the foetus through the umbilical cord.
Functions of Placenta:
(i) Provides large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from mother to the embryo.
(ii) Removal of waste generated in the developing embryo into the mother‘s blood.
Question. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction? Write the importance of such reproductions in nature.
Answer: Formation of male and female gametes, fusion of gametes/syngamy. In Sexual reproduction, new individual is formed.
Importance: Combination of DNA from two different individuals lead to increase in genetic variation in the organism.
This leads to diversity in the population which helps in natural selection.
Question. State briefly the changes that take place in a fertilized egg till birth of the child in the human female reproductive system. What happens to the egg when it is not fertilized?
Answer: Changes in fertilized egg:
(a) Zygote/fertilized egg starts dividing.
(b) Implantation of zygote in the inner uterine wall.
(c) Embryo starts growing with the help of the placenta which results in the development of the child.
(d) Birth of a child as a result of rhythmic contraction of the muscles in the uterus.
When egg is not fertilized, the inner lining of the uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucous (Menstruation)
Question. What is contraception? Name any two methods.
How does the use of these methods have a direct effect on the health and prosperity of a family?
Answer: (i) Contraception: Any method which prevents conception/ pregnancy is called contraception.
(ii) Barrier Method, Chemical Method, Surgical Method.
(iii) Health of women (mother) is maintained, Parents can give more attention to their children/ family, More resources may be made available for improvement of standard of living. (or any other relevant point)
Question. Name the two types of mammalian gametes. How are these different from each other? Name the type of reproduction they are involved in. Write the advantage of this type of reproduction.
Answer: Male gamete: sperm
Female gamete: ovum/egg
Sperms are motile and produced by male individual, ova/eggs are non-motile and produced by female individual.
Type of reproduction is Sexual reproduction
Advantage: Generates more variations
Question. What are the functions of testis in the human male reproductive system? Why are these located outside the abdominal cavity? Who is responsible for bringing about changes in appearance seen in boys at the time of puberty?
Answer: Functions of testis:
(i) Produce sperms.
(ii) Produces male hormone/ testosterone.
These are located outside the human body, as sperms need lower temperature than the normal body temperature to mature.
Testosterone.
Question. Mention the total number of chromosomes along with the sex chromosomes that are present in a human female and a human male. Explain how in sexually producing organisms the number of chromosomes in the progeny remains the same as that of the parents.
Answer: Total number of chromosomes is 46. In human male, two sex chromosomes i.e., X or Y are present, while in human female, both sex chromosomes are X.
During sexual reproduction, a female gamete or egg cell fuses with a male gamete or sperm cell which are haploid to form zygote. Zygote is diploid (2n) which contains 46 chromosomes, 23 chromosomes from mother and 23 from father. In this way, an equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny.
Question. (a) Mention the role of the following organs of human male reproductive system:
(i) Testis; (ii) Scrotum; (iii) Vas deferens;
(iv) Prostate glands.
(b) What are the two roles of testosterone?
Answer: (a) (i) Testis: To produce male gametes / sperm or male hormone / testosterone.
(ii) Scrotum: To provide optimal temperature to testis for the formation of sperms.
(iii) Vas deferens: To deliver the sperms to the urinary bladder.
(iv) Prostrate glands: To secrete the fluid which provides nutrition and medium for transport of sperms.
(b) (i) Regulates formation of sperms, (ii) Brings about the changes in boys during adolescence.
Long Answer Type Questions :
Question. What is vegetative propagation? List with brief explanation three advantages of practising this process for growing same types of plants. Select two plants from the following which are grown by this process:
Banana, Wheat, Mustard, Jasmine, Gram.
Answer: (a) Vegetative propagation is the development
of a new plant from the vegetative parts / roots, stem and leaves of a plant.
(b) Advantages: (i) Such plants can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
(ii) Allows propagation of plants (banana, orange
etc) that have lost capacity to produce seeds.
(iii) All plants produced are genetically similar to the parent plant and hence have all its characters.
Jasmine, banana.
Question. (i) Describe the role of prostate gland, seminal vesicle and testes in the human male reproductive system.
(ii) How is the surgical removal of unwanted pregnancies misused?
(iii) Explain the role of oral contraceptive pills in preventing conception.
Answer: (i) Prostate and the seminal vesicles produce fluid that nourishes the sperm. This fluid provides most of the volume of semen, the fluid in which the sperm is expelled during ejaculation.
Testes secrete testosterone which brings about changes in the appearances in the boys at the time of puberty.
(ii) Female foeticides/illegal sex selected abortion of female foeticide.
(iii) Interfere in release of egg and eggs are not released.
Question. Define pollination. Explain the different types of pollination. List two agents of pollination. How does suitable pollination lead to fertilization?
Answer: Pollination: Transfer of pollen from anther / stamen to stigma of the flower Types of Pollination:
(a) Self pollination: Transfer of pollen from anther/ stamen to stigma occurs in the same flower.
(b) Cross pollination: Pollen is transferred from anther stamen of one flower to stigma of another flower.
Agents of pollination: Wind, Water, Insects and Animals
A tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style, to reach the female germ cell in the ovary to cause fertilization.
Question. (a) Identify the given diagram. Name the parts 1 to 5.
(b) What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
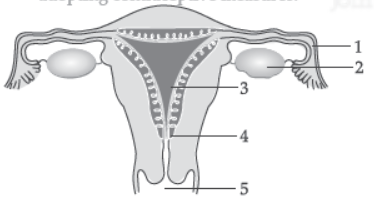
Answer: (a) Female reproductive system
Name of parts –
1: Fallopian tube/Oviduct
2: Ovary
3: Uterus
4: Cervix
5: Vagina
(b) Contraception: Method to avoid pregnancy
Advantages:
(i) Proper gap between two pregnancies
(ii) Avoiding unwanted pregnancy
(iii) Keeping population under control
Question. Different organisms reproduce by different methods suitable to their body designs.
(i) Justify the above statement using examples of three different organisms which reproduce by different methods of asexual reproduction.
(ii) Differentiate between sexual and asexual modes of reproduction.
Answer: (i) Amoeba: Binary fission
Plasmodium: Multiple fission
Hydra: Budding
Planaria: Regeneration (Any three + Explain)
(ii) Sexual two parents; Asexual single parent.
Question. (a) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower and mark on it the following organs/parts:
(i) Pollen grain (ii) Pollen tube (iii) Stigma (iv) Female germ cell
(b) State the significance of pollen tube.
(c) Name the parts of flower that develop after fertilization into: (i) Seed (ii) Fruit.
Answer: (a)
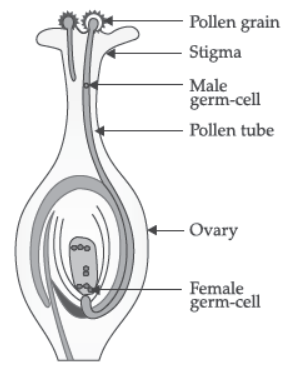
(b) Pollen tube carries male gametes to ovule present inside the ovary leading to fertilization.
(c) After fertilization, ovary develops into fruit whereas ovules into the seed.
Question. (i) Describe the various steps involved in the process of binary fission with the help of a diagram.
(ii) Why do multicellular organisms use complex way of reproduction?
Answer: (i)
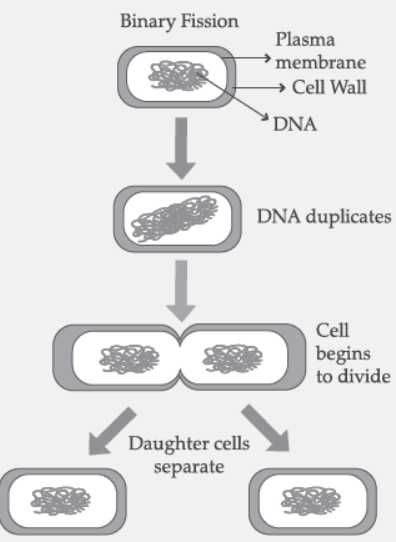
(ii) Multicellular organisms cannot reproduce by cell because they are not simple random collection of cells. In them, specialized cells are organized as tissues which are organized into organs. Cell-bycell division would be impractical. Multicellular organisms, therefore, require to use more complex ways of reproduction.
Question. (a) “Use of a condom is beneficial for both the sexes involved in a sexual act.” Justify this statement giving two reasons.
(b) How do oral contraceptive help in avoiding pregnancies?
(c) What is sex selective abortion? How does it affect a healthy society? (State any one consequence)
Answer: (a) (i) Prevents meeting of sperm and ova
(ii) Protects against sexually transmitted diseases (b) Oral pills contain hormones which prevent the ovaries from releasing ovum into the oviduct.
(c) Selective abortion means abortion (termination) of pregnancy, especially female foeticide.
Effect: Society will have imbalance in the male female ratio.
Question. (a) Write the functions of following parts in human female reproduction system:
(i) Ovary, (ii) Oviduct, (iii) Uterus
(b) Describe in brief the structure and function of placenta.
Answer: (a) (i) Ovary: Releases egg / female gamete/ovum, Releases oestrogen/female hormones.
(ii) Oviduct: Transportation of ovum/egg/ from ovary to the uterus/Site of fertilization.
(iii) Uterus: Development of embryo/foetus.
(b) Placenta: It is disc like tissue embedded in uterine wall which contains villi on the embryo side of the tissue and blood space on mother side.
Function of placenta: Provides nourishment to embryo from mother’s blood / Removal of waste from embryo to mother’s blood.
Question. (a) Name the organ that produces sperms as well as secretes a hormone in human males. Name the hormone it secretes and write its functions.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs.
(c) Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Answer: (a) Testes
Testosterone
Functions of Testosterone:
(i) Formation of sperms
(ii) Development of secondary sexual
characters
(b) Fallopian Tubes/Oviduct
(c) Placenta, a special disc-like tissue embedded in the mother’s uterine wall and is connected to the foetus/embryo.
Placenta provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen/nutrients to pass from the mother’s blood to the developing embryo/foetus.
Question. (a) Suggest any two categories of contraceptive methods to control the size of human population which is essential for the prosperity of a country.
Also explain about each method briefly.
(b) Name two bacterial and two viral infections each that can get sexually transmitted.
(c) List two advantages of using condom during sexual act.
Answer: (a) Methods of contraception:
(i) Barrier method or mechanical method/ Condom/ Diaphragm, to prevent the meeting of sperms and ova.
(ii) Chemical method/ Oral pills: Changes the hormonal balance of the female partner so that the eggs are not released.
(iii) Surgical method: To block the vas deferens in males/ vasectomy or the fallopian tube (oviduct) in females/ tubectomy, to prevent the transfer of sperms or egg and hence no fertilization takes place.
(b) Bacterial infections: Syphilis and Gonorrhea Viral infections: Human papilloma virus (HPV), HIV
(c) (i) Prevents meeting of sperm and ova
(ii) Protects against sexually transmitted diseases
Question. What is sexual reproduction? Explain how this mode of reproduction give rise to more viable variations than asexual reproduction? How does this affect the evolution?
Answer: When male and female organisms are involved in producing young ones, is known as sexual reproduction / Gametes from two organisms of opposite sex must fuse to produce young ones.
Gametes (germs cells) produced are the products of meiosis / due to combining of DNA from two individuals, this results in mixing of characters and causes variations.
In asexual reproduction, single parent produces young ones. There is no mixing of characters.
More variations help in the process of evolution.
Helpful variations accumulate over time and produce new species and result in evolution.
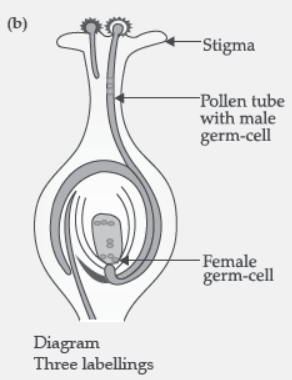
Question. (a) What is pollination? Give its two types.
(b) Draw a longitudinal section of female reproductive part of a flower showing germination of pollen grain. Label on it the following:
(i) Stigma;
(ii) Pollen tube with a male germ cell;
(iii) Female germ cell.
Answer: (a) Pollination: Process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the flower.
Two types: Self-pollination and Cross pollination
(b)
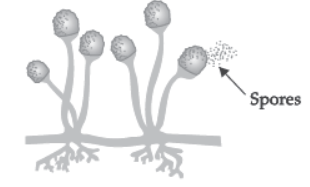
Question. (a) Draw a diagram to show spore formation in Rhizopus.
(b) With the help of an example differentiate between the process of Budding and Fragmentation.
(c) Why is vegetative propagation practiced for growing some type of plants?
Answer: (a) Spore formation in Rhizopus:
(b) Differences between Budding and Fermentation:
(c) Vegetative propagation is practiced for growing some type of plants because:
(i) Only one parent is required for reproduction; this eliminates the need of special mechanisms (pollination) and fusion of gametes i.e., fertilization.
(ii) Many plants are able to tide over unfavourable conditions because of the presence of vegetative reproductive parts like tubers, corns and bulbs.
(iii) Plants that do not produce seeds can be propagated by this method, e.g., sugarcane and potato.
(iv) Vegetative propagation is a cheaper, easier and rapid method of reproduction in plants than growing plants from seeds. For examplelilies grow very slowly and take up to seven years to develop flowers when their seeds are grown, but when grown vegetatively, flowers are produced only after a year or two.
(v) The trait (character) of the parent plant is preserved and the offsprings are genetically identical.
Question. (a) Draw the diagram of female reproductive system and match and mark the part(s):
(i) Where block is created surgically to prevent fertilization.
(ii) Where CuT is inserted?
(iii) Inside which condom can be placed.
(b) Why do more and more people prefer to use condoms? What is the principle behind use of condoms?
Answer: (a)
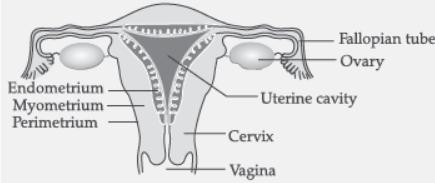
Correct diagram with correct labelling, correctly matched with the following parts:
(i) Fallopian Tube/Oviduct
(ii) Uterus
(iii) Vagina
(b) People prefer use of condoms as it prevents STDs/ gives privacy to the user. Condoms help create a mechanical barrier preventing meeting of sperms and ovum.
Question. Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers. Differentiate between the two types of pollination that occur in flowers. What happens when a pollen lands on a suitable stigma? Write about the events that occur till the seed formation in the ovary.
Answer: Unisexual Flower: Papaya/Water-melon
Bisexual Flower: Hibiscus/Rose/
Self pollination: The pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or to the flower of the same plant.
Cross pollination: The pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of a flower of a different plant.
♦ After pollen lands on a suitable stigma, a pollen tube grows out of pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary.
♦ The male germ cell fuses with the female germ cell to form a zygote.
♦ Zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
♦ The ovule develops tough coat and gradually gets converted into a seed.