Students should refer to Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry Hydrocarbons Chapter 13 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 11 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 11 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Hydrocarbons Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry
Question. Which branched chain isomer of the hydrocarbon with molecular mass 72u gives only one isomer of mono substituted alkyl halide?
(a) Neopentane
(b) Carbon
(c) Isohexane
(d) Neohexane
Answer
A
Question. Hydrocarbon containing following bond is most reactive
(a) C ≡ C
(b) C = C
(c) C – C
(d) All of these
Answer
C
Question. Which one of these is NOT TRUE for benzene?
(a) Heat of hydrogenation of benzene is less than the theoretical value
(b) There are three carbon-carbon single bonds and three carbon-carbon double bonds
(c) It forms only one type of monosubstituted product
(d) The bond angle between carbon-carbon bonds is 120o
Answer
B
Question. A gas decolourised by KMno4 solution but gives no precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride is
(a) Ethene
(b) Propane
(c) Propene
(d) Methane
Answer
A
Question. When cyclohexane is poured on water, it floats because
(a) Cyclohexane is in boat form
(b) Cyclohexane is in chair form
(c) Cyclohexane is in crown fromorm
(d) Cyclohexane is less dense than water.
Answer
D
Question. Among the following compounds the one that is most reactive towards electrophilic nitration is
(a) Toluene
(b) Benzene
(c) Benzoic Acid
(d) Nitrobenzene
Answer
A
Question. A gas decolourised by KMnO4 solution but gives no precipitate with ammoniacal cuprous chloride is
(a) Ethane
(b) Methane
(c) Ethene
(d) Acetylene
Answer
C
Question. A dibromo derivative of an alkane reacts with sodium metal to form an alicyclic hydrocarbon. The derivative is _______
(a) 1, 4-dibromobutane
(b) 1, 2-dibromoethane
(c) carbon
(d) none of the above
Answer
A
Question. HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to give
(a) CH3CHO and CH3Br
(b) BrCH2CHO and CH3OH
(c) BrCH2 – CH2 – OCH3
(d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3
Answer
D
Question. A dibromo derivative of an alkane reacts with sodium metal to form an alicyclic hydrocarbon. The derivative is ______.
(a) 2, 2-dibromobutane
(b) 1, 1-dibromopropane
(c) 1, 4-dibromobutane
(d) 1, 2-dibromoethane
Answer
C
Question. During ozonolysis of CH2 == CH2 if hydrolysis is made in absence of Zn dust the products formed are
(a) HCHO
(b) HCOOH
(c) CH2OHCH2OH
(d) CH3OH
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds reacts with sodium to liberate hydrogen gas?
(a) Ethane
(b) Propene
(c) Acetylene
(d) Benzene
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion?
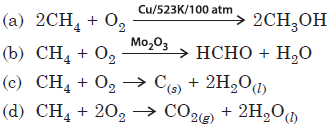
Answer
C
Question. Which among the following is very strong o-, p-directing group ?
(a) Cl
(b) OR
(c) NH2
(d) NHR
Answer
D
Question. In the following sequence of reactions, the compound B is
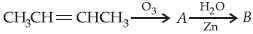
(a) CH3CHO
(b) CH3CH2CHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) CH3CH2COCH3
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds will not undergo Friedal-Crafts reaction easily?
(a) Nitrobenzene
(b) Toluene
(c) Cumene
(d) Xylene
Answer
A
Question. The IUPAC name of the given compound is
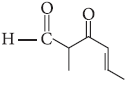
(a) 5-formylhex-2-en-3-one
(b) 5-methyl-4-oxohex-2-en-5-al
(c) 3-keto-2-methylhex-5-enal
(d) 3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal
Answer
D
Question. The reaction, RC ≡ CR →H2Lindlar’s catalyst gives the main product as
(a) cis-alkene
(b) trans-alkene
(c) alkane
(d) none of these.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following species is most stable?
(a) p-O2N — C6H4 — C+H2
(b) C6H5 — C+H2
(c) p-Cl — C6H4 — C+H2
(d) p-CH3O — C6H4 — C+H2
Answer
D
Question. Meta-directing and deactivating group in aromatic electrophilic substitution is
(a) – CH3
(b) – OH
(c) – NO2
(d) – Cl
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is Baeyer’s reagent?
(a) alkaline KMnO4
(b) acidic K2Cr2O7
(c) alkaline Na2Cr2O7
(d) MnO2
Answer
A
Question. Among the three conformations of ethane, the order of stability follows the sequence :
(a) eclipsed > gauche > staggered
(b) eclipsed > staggered > gauche
(c) staggered > gauche > eclipsed
(d) gauche > staggered > eclipsed
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following reaction is not correct?
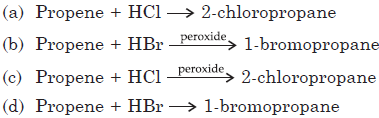
Answer
D
Question. The function of anhydrous AlCl3 in Friedel–Crafts reaction is
(a) to absorb water
(b) to absorb HCl
(c) to produce attacking electrophile
(d) to produce nucleophile.
Answer
C
Question. The correct order of reactivity towards electrophilic substitution is
(a) phenol > benzene > chlorobenzene > benzoic acid
(b) benzoic acid > chlorobenzene > benzene > phenol
(c) phenol > chlorobenzene > benzene > benzoic acid
(d) benzoic acid > phenol > benzene > chlorobenzene
Answer
A
Question. Benzene easily shows
(a) ring fission reactions since it is unstable
(b) addition reactions since it is unsaturated
(c) electrophilic substitution reactions due to stable ring and high p electron density
(d) nucleophilic substitution reactions due to stable ring and minimum electron density.
Answer
C
Question. Which is the correct IUPAC name of the following compound?

(a) 5-(2′, 2′-Dimethylpropyl)decane
(b) 4-Butyl-2,2-dimethylnonane
(c) 2,2-Dimethyl- 4-pentyloctane
(d) 2,2-Dimethyl- 4-butylnonane
Answer
A
Question. An alkene on ozonolysis gave 2-pentanone and acetaldehyde. The alkene was

Answer
A
Case Based MCQs :
Compound (A) is an important industrial feed stocks, but it’s largest use as the fuel for the oxyacetylene torch. It is a colourless, foul smelling gas that burns in air with a yellow, sooty flame.
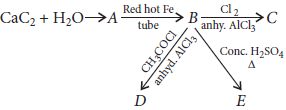
Question. Identify the product A.
(a) ethane
(b) ethyne
(c) ethene
(d) methane
Answer
B
Question. The reaction B →Cl2 Anhy.AlCl3 follows
(a) nucleophilic substitution mechanism
(b) electrophilic addition mechanism
(c) electrophilic subsituition mechanism
(d) elimination reaction mechanism.
Answer
C
Question. The product E is
(a) nitrobenzene
(b) benzene sulphonic acid
(c) both (a) and b
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
Question. The compound (B) formed is
(a) cyclohexane
(b) benzene
(c) hexane
(d) cyclopentane.
Answer
C
Question. Identify the product ‘D’.
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Bromobenzene
(c) Toluene
(d) Acetophenonone
Answer
D
Compound ‘A’ is the simplest and ideal aromatic compound. It is also one of the most basic petrochemi-cals which is mainly used to prepare a number of important chemicals such as toluene, phenol, aniline, biphenyl etc, which are used in manufacture of dyes, detergents, drugs, explosives, pesticides etc. But it is carcinogenic.
In the given sequence of reaction, compound A undergoes a number of changes
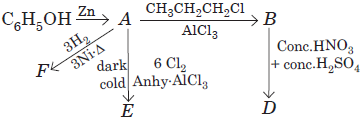
Question. The name of compound A is
(a) cyclohexane
(b) benzene
(b) cyclohexene
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
Question. The name of product F is
(a) benzene
(b) cyclohexene
(c) cyclohexane
(d) cyclohex-1 4-diene
Answer
C
Question. The major product when ‘A’ reacts with propyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3 is
(a) propyl benzene
(b) isopropyl benzene
(c) chloro benzene
(d) ethyl benzene.
Answer
B
Question. The reaction A →CH3CH2CH2ClAlCl3 B is an example of
(a) elimination reaction
(b) addition reaction
(c) electrophilic substitution reaction
(d) nucleophilic substitutional reaction.
Answer
C
Question. The major product ‘D’ in the given series of reaction is
(a) 4-nitro isopropyl benzene
(b) 2-nitro isopropyl benzene
(c) 3-nitro propyl benzene
(d) none of these.
Answer
A

