Students should refer to Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry Thermodynamics Chapter 6 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 6 Thermodynamics have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 11 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 11 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Thermodynamics Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry
Question. An ideal gas is taken around the cycle ABCA as shown in P-V diagram The next work done by the gas during the cycle is equal to:
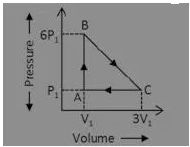
(a) 12P1V1
(b) 6P1V1
(c) 5P1V1
(d) P1V1
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following neutralisation reactions is most exothermic?
(a) HCl and NaOH
(b) HCN and NaOH
(c) HCl and NH4OH
(d) CH3COOH and NH4OH
Answer
A
Question. In a chemical reaction the bond energy of reactants is more than the bond energy of the products. Therefore, the reaction is
(a) Exothermic
(b) Athermic
(c) Endothermic
(d) Endergonic
Answer
C
Question. One mole of which of the following has the highest entropy?
(a) Liquid Nitrogen
(b) Hydrogen Gas
(c) Mercury
(d) Diamond
Answer
B
Question. In a reversible process the system absorbs 600 kJ heat and performs 250 kJ work on the surroundings. What is the increase in the internal energy of the system?
(a) 850 kJ
(b) 600 kJ
(c) 350 kJ
(d) 250 kJ
Answer
C
Question. 5 mole of an ideal gas expand isothermally and irreversibly from a pressure of 10 atm to 1 atm against a constant external pressure of 1 atm. Wirr at 300 K is:
(a) -15.921 kJ
(b) -11.224 kJ
(c) -110.83 kJ
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Entropy of the universe is
(a) Continuously Increasing
(b) Continuously Decreasing
(c) Zero
(d) Constant
Answer
A
Question. 2 mole of an ideal gas at 27° C expands isothermally and reversibly from a volume of 4 litres to 40 litre. The work done (in kJ) is:
(a) w = -28.72 kJ
(b) w = -11.488 kJ
(c) w = -5.736 kJ
(d) w = -4.988 kJ
Answer
B
Question. At absolute zero the entropy of a perfect crystal is zero. This statement corresponds to which law of thermodynamics?
(a) Zeroth Law
(b) First Law
(c) Second Law
(d) Third Law
Answer
D
Question. The latent heat of vapourization of ε liquid at 500 K and 1 atm pressure is 10.0 kcal/mol. What will be the change in internal energy (ΔU) of 3 moles of liquid at the same temperature
(a) 13.0 kcal/mol
(b) −13.0 kcal/mol
(c) 27.0 kcal
(d) −7.0 kcal/mol
Answer
C
Question. Work done in reversible isothermal process is given by

Answer
A
Question. Match the column I with column II and mark the appropriate choice.

(a) (A) → (iv), (B) → (iii), (C) → (i), (D) → (ii)
(b) (A) → (ii), (B) → (i), (C) → (iv), (D) → (iii)
(c) (A) → (i), (B) → (ii), (C) → (iii), (D) → (iv)
(d) (A) → (iii), (B) → (iv), (C) → (ii), (D) → (i)
Answer
D
Question. For which of the following reactions will ΔH be equal to ΔU?
(a) H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g)
(b) H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → H2O(l)
(c) 2SO3(g) → 2SO2(g) + O2(g)
(d) 2NO2(g) → N2O4(g)
Answer
A
Question. The standard heat of formation at 298 K for CCl4(g), H2O(g), CO2(g) and HCl(g) are –25.5, –57.8, –94.1 and –22.1 kcal per mole respectively. Then ΔH° at 298 K for the reaction
CCl4(g) + 2H2O(g) → CO2(g) + 4HCl(g) is
(a) – 32.9 kcal
(b) – 41.4 kcal
(c) – 99.2 kcal
(d) – 323.6 kcal
Answer
B
Question.
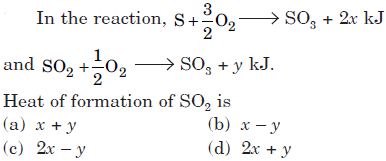
Heat of formation of SO2 is
(a) x + y
(b) x – y
(c) 2x – y
(d) 2x + y
Answer
C
Question. Calculate the resonance energy of N2O from the following data: ΔHf of N2O = 82 kJ mol–1. Bond energies of N ≡ N, N ≡ N, O ≡ O and N ≡ O bonds are 946, 418, 498 and 607 kJ mol–1 respectively.
(a) – 88 kJ mol–1
(b) –170 kJ mol–1
(c) – 82 kJ mol–1
(d) –258 kJ mol–1
Answer
A
Question. The temperature of the system increases during an
(a) isothermal expansion
(b) adiabatic compression
(c) adiabatic expansion
(d) isothermal compression.
Answer
B
Question. One word answer is given for the following definitions. Mark the one which is incorrect.
(a) The process in which temperature remains constant : Isobaric
(b) The process in which volume remains constant : Isochoric
(c) The relation between ΔH and ΔU when all the reactants and products are solid : ΔH = ΔU
(d) The relation between ΔG, ΔH and ΔS : ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Answer
A
Question. In endothermic reactions,
(a) reactants have more energy than products
(b) reactants have less energy than products
(c) reactants and products have same energy
(d) reactants have lower temperature than products.
Answer
B
Question. When 1 M H2SO4 is completely neutralised by sodium hydroxide, the heat liberated is 114.64 kJ. What is the enthalpy of neutralisation?
(a) +114.64 kJ
(b) –114.64 kJ
(c) –57.32 kJ
(d) +57.32 kJ
Answer
C
Case Based MCQs :
Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation This law was presented by Hess in 1840. According to the law, if a chemical reaction can be made to take place in a number of ways in one or in several steps, the total enthalpy change is always the same.
Thus, the total enthalpy change of a chemical reaction depends on the initial and final stages only.
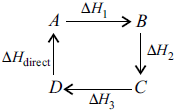
Total enthalpy change from A to D,
∆Htotal = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3
∆Htotal + ∆Hdirect = 0
i.e., ∆Htotal = –∆Hdirect
For example, formation of CO2 from C in two different manners involves a total heat change of –393.5 kJ/ mol
Single step process :
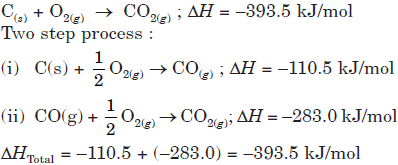
Question. A hypothetical reaction, A → 2B, proceeds through following sequence of steps :
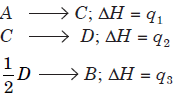
The heat of reaction is
(a) q1 – q2 + 2q3
(b) q1 + q2 – 2q3
(c) q1 + q2 + 2q3
(d) q1 + 2q2 – 2q3
Answer
C
Question. Given :
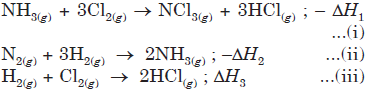
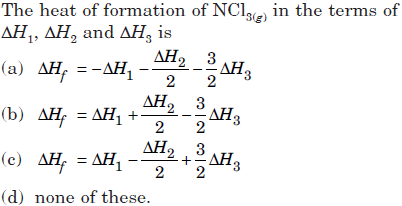
Answer
A
Question. In which of the enlisted cases, Hess’s law is not applicable?
(a) Determination of lattice energy
(b) Determination of resonance energy
(c) Determination of enthalpy of transformation of one allotropic form to another
(d) Determination of entropy
Answer
D
Question. For the given reactions,
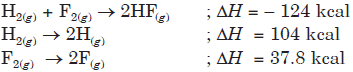
then the value of ∆H° for H(g) + F(g) → HF(g) is
(a) 142 kcal
(b) – 132.9 kcal
(c) 132 kcal
(d) 134 kcal.
Answer
B
Question. Use the bond energy data and calculate the enthalpy change for

The bond energies of C — H and C — Cl are 413 and 328 kJ mol–1 respectively.
(a) –1465 kJ/mol
(b) 1465 kJ/mol
(c) –1482 kJ/mol
(d) 1482 kJ/mol
Answer
C
A thermodynamically irreversible process is always accompanied by an increase in the entropy of the system and its surroundings taken together while in a thermodynamically reversible process, the entropy of the system and its surrounding taken together remain unchanged i.e. for reversible process
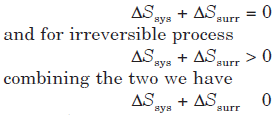
where ‘equal’ to sign refers to a reversible process while the ‘greater than’ sign refers to an irreversible process.
Change in entropy for an ideal gas under different conditions may be calculated as

Question. The entropy of the universe
(a) increasing and tending towards maximum value
(b) decreasing and tending to be zero
(c) remains constant
(d) decreasing and increasing with a periodic rate.
Answer
A
Question. Entropy changes for the process,
H2O(l) → H2O(s),
at normal pressure and 274 K are given below
ΔSsystem = – 22.13, ΔSsurr = + 22.05,
the process is non-spontaneous because (‘surr’ stands for surrounding and ‘u’ stands for universe)
(a) ΔSsystem is – ve
(b) ΔSsurr is +ve
(c) ΔSu is – ve
(d) ΔSsystem ≠ ΔSsurr
Answer
C
Question. Calculate entropy change when 5 moles of an ideal gas expands reversibly and isothermally from an initial volume of 5 litre to 50 litre at 27°C.
(a) 190.15 JK–1
(b) 95.74 JK–1
(c) 87.25 JK–1
(d) 90.13 JK–1.
Answer
B
Question. ΔS is positive for the change
(a) mixing of two gases
(b) boiling of liquid
(c) melting of solid
(d) all of these.
Answer
D
Question. The total entropy change for a system and its surroundings increases, if the process is
(a) reversible
(b) irreversible
(c) exothermic
(d) endothermic.
Answer
B
The enthalpy of a system is defined as the sum of the internal energy of the system and the energy that arises due to its pressure and volume. Mathematically, the enthalpy is defined by the equation,
H = U + PV
Enthalpy change (ΔH) of a system is the heat absorbed or evolved by the system at constant pressure.
ΔH = qp, ΔH = ΔU + PΔV
Question. In which of the following thermochemical changes ΔH° is always negative?
(a) Enthalpy of solution
(b) Enthalpy of hydrogenation
(c) Enthalpy of reaction
(d) Enthalpy of transition
Answer
B
Question. The heat of a chemical reaction is given by the following expression
(a) ΔH = ∑HR – ∑HP
(b) ΔH = ∑HR
(c) ΔH = ∑HP – ∑HR
(d) ΔH = ∑HP
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following reactions will ΔU be equal to ΔH?
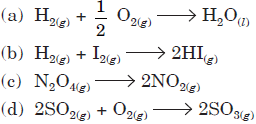
Answer
B
Question. Lattice enthalpies are determined by
(a) Born-Haber cycle
(b) Hess’s law
(c) lattice cycle
(d) none of these.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not correct about enthalpy?
(a) It is an extensive property.
(b) It is not a state function.
(c) Its absolute value cannot be determined.
(d) Enthalpy of a compound is equal to enthalpy of formation of that compound.
Answer
B
In chemical thermodynamics, the type of work involved is mostly pressure-volume work that is the work done when a system (gas) expands or contracts against an external opposing pressure. Hence, work is also defined as the transfer of energy that can be used to change the height of a mass in the surroundings.
Pressure-volume work : The work W, that is done due to the expansion or compression of a gas against an external opposing pressure P is called pressure-volume work.
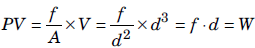
Question. Which of the following is correct match as far as the thermodynamic processes are involved?
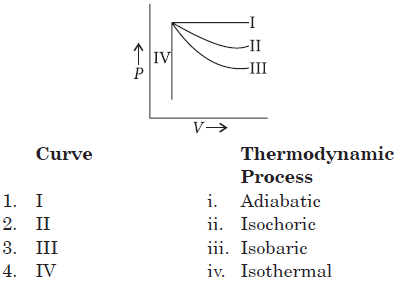
The correct match is
1 2 3 4
(a) i ii iii iv
(b) iii iv i ii
(c) ii i iv iii
(d) iii iv ii i
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) ΔU = Wadiabatic
(b) Wad = + ve, when work is done on the system
(c) Wad = – ve, when work is done by the system
(d) All of the above.
Answer
D
Question. A gas expands in vacuum. The work done by the gas is
(a) zero
(b) minimum
(c) maximum
(d) cannot be predicted.
Answer
A
Question. A process in which the system does not exchange heat with the surroundings is known as
(a) isothermal
(b) isobaric
(c) isochoric
(d) adiabatic.
Answer
D
Question. 3 moles of an ideal gas are expanded isothermally and reversibly from 10 m3 to 20 m3 at 300 K. The work done is (R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1).
(a) +5.187 kJ
(b) –5.187 kJ
(c) –2.175 kJ
(d) +3.750 kJ
Answer
B

