Please see Chapter 10 Internal Trade Exam Questions Class 11 Business Studies below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 11 Business Studies Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 11 Business Studies. These solved problems for Internal Trade in Class 11 Business Studies will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Chapter 10 Internal Trade Class 11 Business Studies
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Identify the type of itinerant trader from the following:
a) Traders who open their shop on fixed day.
b) Petty retailer who have temporary independent shops.
c) Traders commonly found in populated area.
Answer :
a) Traders who open their shop on fixed day:
Market traders: The small retailers who open their shops at different places on fixed days or dates. They are mainly catering to lower-income group of customers and deal in low-priced consumer items of daily use
b) Petty retailer who have temporary independent shops:
Cheap jacks: Retailers who have independent shops of a temporary nature in a business locality. They keep on changing their business from one locality to another, depending upon the potentiality of the area. They deal in consumer items as well as services such as repair of watches, shoes, buckets etc.
c) Traders commonly found in populated area:
Street traders: Retailers who are commonly found at places where huge floating population gathers, for example, near railway stations and bus stands, and sell consumer items of common use, such as stationery items, eatables, readymade garments, newspapers and magazines
Question. Identify the types of retailers in the following statements:
(a) Rohan displays his goods on bus-stands or pavements.
(b) Mangal sells goods from one street to another, from one locality to another.
(c) Rajkumar sells only school uniforms.
(d) Deepanshu deals only in second hand books.
Answer :
(a) Rohan displays his goods on bus-stands or pavements:
Street traders: Retailers who are commonly found at places where huge floating population gathers, for example, near railway stations and bus stands, and sell consumer items of common use, such as stationery items, eatables, readymade garments, newspapers and magazines
(b) Mangal sells goods from one street to another, from one locality to another:
Peddlers and hawkers: They are small producers or petty traders who carry the products on a bicycle, a hand cart, a cycle-rickshaw or on their heads, and move from place to place to sell their merchandise at the doorstep of the customers. They generally deal in non-standardised and low-value products
(c) Rajkumar sells only school uniforms:
Speciality shops: Instead of selling a variety of products of different types, these retail stores specialise in the sale of a specific line of product. The speciality shops are generally located in a central place where a large number of customers can be attracted, and they provide a wide choice to the customers in the selection of goods
(d) Deepanshu deals only in second hand books:
Second-hand goods shop: These shops deal in second-hand or used goods, like books, clothes, automobiles, furniture and other household goods. The shops, selling second-hand goods may be located at street crossings or in busy streets in the form of a stall having very little structure — a table or a temporary platform to display the books or may have reasonably good infrastructure, as in the case of those selling furniture or used cars or scooters or motorcycles
Question. Vishal buys goods in larger quantities and sells them to small businessmen.
(a) Which type of trader in Vishal?
(b) State services to Consumer of this type of trade.
Answer :
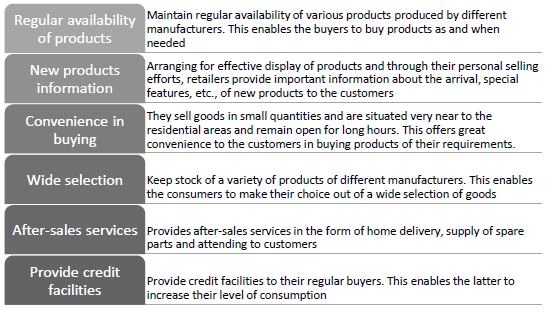
(a) Vishal is a Retail trader. A retailer is a business enterprise that is engaged in the sale of goods and services directly to the ultimate consumers. The retailer normally buys goods in large quantities from the wholesalers and sells them in small quantities to the ultimate consumers. Arranges for proper storage of goods, sells the goods in small quantities, bears business risks, grades the products, collects market information, extends credit to the buyers and promotes the sale of products through displays, participation in various schemes, etc. The retails represents the final stage in the distribution where goods are transferred from the hands of the manufacturers or wholesalers to the final consumers or users
(b)
Question. Explain the features of Departmental store
Answer :
• Provide maximum service to higher class of customers for whom price is of secondary
importance
• Located at a central place in the heart of a city, which caters to a large number of customers.
• As the size of these stores is very large, they are generally formed as a joint stock company
managed by a board of directors
• A departmental store combines both the functions of retailing as well as warehousing
• They have centralised purchasing arrangements and sales are decentralised in different
departments
Question. Explain two features, merits and limitations of super market
Answer : Features
• Generally carries a complete line of food items and groceries, in addition to non-food
convenience goods
• Different products as per their requirements under one roof
Merits
• Sales are made on cash basis, there are no bad debts
• Benefits of large scale buying and selling because of which its operating costs are lower
Limitations
• No credit facilities restricts the purchasing power of buyers
• The principle of selfservice is followed therefore, do not get any personal attention
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Why are consumer cooperative stores considered to be less expensive? What are their relative advantages over other large scale retailer?
Answer : A consumer cooperative store is an organisation owned, managed and controlled by consumers themselves. The objective of such stores is to reduce the number of middlemen who increase the cost of produce, and thereby provide service to the members. The cooperative stores generally buy in large quantity, directly from manufacturers or wholesalers and sell them to the consumers at reasonable prices. The profits earned by consumer cooperative stores during a year are utilised for declaring bonus to members and for strengthening the general reserves and general welfare funds or similar funds for social and educational benefits of the members. This is why consumer cooperative stores considered to be less expensive
Advantages of Consumer cooperative stores over large scale retailers are as below:
• Easy to form a consumer cooperative society
• The liability of the members in a cooperative store is limited to the extent of the capital contributed by them
• It has democratic management. Each member has one vote, irrespective of the number of shares held by him/her
• Elimination of middlemen results in lower prices for the consumer goods to the members
• The consumer cooperative stores normally sell goods on cash basis
• The consumer cooperative stores are generally opened at convenient public places where the members and others can easily buy the product
Question. Discuss the features of Mail order houses? State their merits and limitations?
Answer :
• Mail order houses are the retail outlets that sell their merchandise through mail.
• There is generally no direct personal contact between the buyers and the sellers in this type of trading.
• For obtaining orders, potential customers are approached through advertisements in newspapers or magazines, circulars, catalogues, samples and bills, and price lists sent to them by post
• On receiving the orders, the items are carefully scrutinised with respect to the specifications asked for by the buyers and are complied with through the post office
• There can be different alternatives for receiving payments.
o First, the customers may be asked to make full payment in advance.
o Second, the goods may be sent by Value Payable Post (VPP). Under this arrangement, the goods are sent through post and are delivered to the customers only on making full payment for the same.
o Third, the goods may be sent through a bank, which is instructed to deliver the articles to the customers. In this arrangement there is no risk of bad debt
• Only the goods that can be (i) graded and standardised, (ii) easily transported at low cost, (iii) have ready demand in the market, (iv) are available in large quantity throughout the year, (v) involve least possible competition in the market and (vi) can be described through pictures etc., are suitable for this type of trading
Question. Nirmala orders a mixer on the basis of an advertisement in a newspaper specifying the features, price, delivery terms. It specified that the terms of payment will be VPP only.
(i) Identify this type of retail business.
(ii) Explain two advantages and two limitations of them.
Answer :
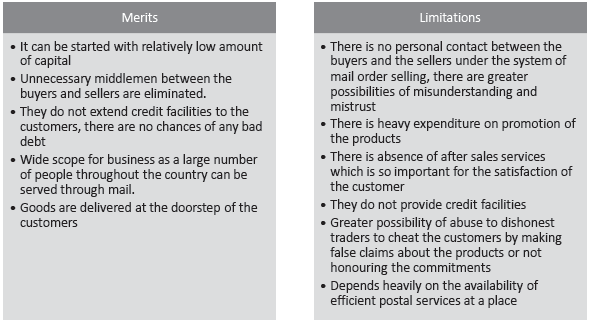
(i) Mail order houses are the retail outlets that sell their merchandise through mail. There is generally no direct personal contact between the buyers and the sellers in this type of trading. For obtaining orders, potential customers are approached through advertisements in newspapers or magazines, circulars, catalogues, samples and bills, and price lists sent to them by post. On receiving the orders, the items are carefully scrutinised with respect to the specifications asked for by the buyers and are complied with through the post office. The goods may be sent by Value Payable Post (VPP). Under this arrangement, the goods are sent through post and are delivered to the customers only on making full payment for the same.
(ii) Advantages:
• It can be started with relatively low amount of capital
• Unnecessary middlemen between the buyers and sellers are eliminated.
Disadvantages:
• There is no personal contact between the buyers and the sellers under the system of mail order selling, there are greater possibilities of misunderstanding and mistrust
• Depends heavily on the availability of efficient postal services at a place
Question. Briefly explain the role of commerce in promoting internal trade?
Answer :
| Interstate movement of goods | The Chambers of Commerce and Industry help in many activities concerning inter state movement of goods which include registration of vehicles, surface transport policies, construction of highways and roads |
| Octroi and other local levies | These are collected on the goods and from people entering the state or the municipal limits. The Chambers of Commerce try to ensure that their imposition is not at the cost of smooth transportation and local trade |
| Harmonisation of sales tax structure and Value Added Tax | The sales tax is an important part of the state revenue. A rational structure of the sales tax and its uniform rates across states, are important for promoting a balance in trade |
| Marketing of agro products and related issues | Streamlining of local subsidies and marketing policies of organisations selling agro products are some of the areas where the Chambers of Commerce and Industry can really intervene and interact with concerned agencies like farming cooperatives |
| Weights and Measures and prevention of duplication brands | Laws relating to weights and measures and protection of brands are necessary to protect the interest of the consumers as well as the traders. These need to be enforced strictly |
| Excise duty | Central excise is the chief source of the government revenue levied across states by the central government. The excise policy plays an important role in pricing mechanism |
| Promoting sound infrastructure | The Chambers of Commerce and Industry hold discussions with government agencies for investments into infrastructure projects |
| Labour legislation | A simple and flexible labour legislation is helpful in running industries maximising production and generating employment. The Chambers of Commerce and Industry and the government are constantly interacting on issues with government |

