Please refer to Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper Set A with solutions below. The following CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Chemistry has been prepared as per the latest pattern and examination guidelines issued by CBSE. By practicing the Chemistry Sample Paper for Class 12 students will be able to improve their understanding of the subject and get more marks.
Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Hot conc. H2SO4 acts as moderately strong oxidising agent. It oxidises both metals and nonmetals.
Which of the following element is oxidised by conc. H2SO4 into two gaseous products?
(a) Cu
(b) S
(c) C
(d) Zn
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following are peroxoacids of sulphur?
(a) H2SO5 and H2S2O8
(b) H2SO5 and H2S2O7
(c) H2S2O7 and H2S2O8
(d) H2S2O6 and H2S2O7
Answer
A
B. Answer the following:
Question. Draw the structure of H2S2O8.
Answer.
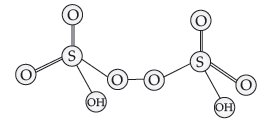
Question. Oxygen is a gas but sulphur a solid. Explain.
Answer. Oxygen being smallest in size is capable of forming pp – pp bond and exists as O=O(O2 molecule) while sulphur being larger in size is not able to form pp – pp bond.
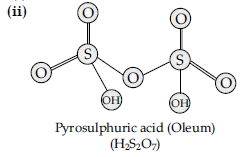
Question. Draw the structure of H2S2O7.
Answer. Pyrosulphuric acid (oleum) :
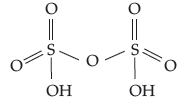
Question. Account for the following:
Oxygen shows catenation behaviour less than sulphur.
Answer. Bond energy of S—S bond (213 kJ mol–1) is greater than O – O bond (138 kJ mol–1). Due to small size of oxygen atom there is greater lp–bp repulsion in O – O, resulting in weakening of O – O bond more than in S–S bond. Therefore, the tendency of catenation in oxygen is lower than sulphur.
Question. Write the formula of the compound of sulphur which is obtained when conc. HNO3 oxidises S8.
Answer. H2SO4
Question. Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in the following case SO32– and the angle O—S—O.
Answer. Pyramidal :
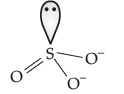
Angle : O—S—O more than 90°
Question. Write the formulae of any two oxoacids of sulphur.
Answer. H2SO3 (Sulphurous acid) and H2SO4 (Sulphuric acid).
Question. Arrange the following hydrides of Group-16 elements in the increasing order of their thermal stability : H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te.
Answer. H2Te<H2Se<H2S<H2O
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What happens when :
(i) Concentrated H2SO4 is added to calcium fluoride ?
(ii) SO3 is passed through water ?
Answer. (i) H2SO4 + CaF2 → 2HF + CaSO4
(conc.)
(ii) SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Question. Write the conditions to maximise the yield of H2SO4 by contact process.
Answer. The conditions used to maximise the yield of H2SO4 by contact process :
(i) High pressure
(ii) Low temperature
(iii) V2O5 is used as catalyst
Question. What happens when :
(i) conc. H2SO4 is added to Cu ?
(ii) SO3 is passed through water ?
Write the equations.
Answer. (i) Cu + 2H2SO4 → CuSO4 + SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Question. How is O3 estimated quantitatively?
Answer. When ozone reacts with potassium iodide (KI) solution buffered with a borate buffer (pH = 9.2) then iodine (I2) is liberated that can be titrated against a standard solution of sodium thiosulphate using starch as indicator.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. How is SO2 an air pollutant?
Answer. Sulphur dioxide causes harm to the environment in many ways :
(i) When it combines with water vapour it forms sulphuric acid (H2SO4). This causes acid rain. Acid rain damages soil, plants, and buildings, especially those made of marble.
(ii) Even in very low concentrations, SO2 causes irritation in the respiratory tract. It causes throat and eye irritation and can also affect the larynx to cause breathlessness.
(iii) It is extremely harmful to plants. Plants exposed to sulphur dioxide for a long time lose colour from their leaves. This condition is known as chlorosis.
This happens because the formation of chlorophyll is affected by the presence of sulphur dioxide.
Question. Give reasons for the following :
(i) (CH3)3 P = O exists but (CH3)3 N = O does not.
(ii) Oxygen has less electron gain enthalpy with negative sign than sulphur.
(iii) H3PO2 is a stronger reducing agent than H3PO3.
Answer. (i) Because as N can’t form 5 covalent bonds as its maximum covalency is three. The octet cannot be extended as it doesn’t have d orbital, while P can extend its octet as it has empty d orbital.
(ii) This is due to very small size of oxygen atom,repulsion between electrons is large in relatively small 2p sub-shell.
(iii) In H3PO2 there are 2P – H bonds, whereas in H3PO3 there is 1 P-H bond.
Topic-2
Group-17 Elements, Properties and Some Important Compounds
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Affinity for hydrogen decreases in the group from fluorine to iodine. Which of the halogen acids should have highest bond dissociation enthalpy?
(a) HF
(b) HCl
(c) HBr
(d) HI
Answer
A
Question. Reduction potentials of some ions are given below.Arrange them in decreasing order of oxidising power.
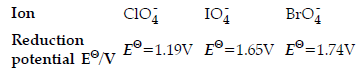
(a) ClO4– > IO4– > BrO4–
(b) IO4–> BrO4– > ClO4–
(c) BrO4–> IO4– > ClO4––
(d) BrO4– > ClO4– > IO4–
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is iso-electronic pair?
(a) ICl2, ClO2
(b) BrO2–, BrF2+
(c) ClO2, BrF
(d) CN–, O3
Answer
B
Question. A black compound of manganese reacts with a halogen acid to give greenish yellow gas. When excess of this gas reacts with NH3 an unstable trihalide is formed. In this process the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from :
(a) – 3 to +3.
(b) – 3 to 0.
(c) – 3 to +5.
(d) 0 to – 3.
Answer
A
B. Answer the following:
Question. HF is a weaker acid than HCl why ?
Answer. Since H—F bond is strongest with higher bond dissociation energy than HCl, hence it is weakest acid among all the halogen acids.
Question. Give reasons: Fluoride ion has higher hydration enthalpy than chloride ion.
Answer. Due to small size of fluoride ion/high charge density of fluoride ion/high charge size ratio of fluoride ion.
Question. Bond enthalpy of fluorine is lower than that of chlorine why ?
OR
Bond enthalpy of F2 is less than of Cl2.
Answer. Bond enthalpy of F—F is smaller due to greater repulsive interactions between the lone pair of one F atom with those of other. The repulsive interaction arise due to greater concentration of electron density on each F atom because of its extremely small size.
Question. Draw the structure of BrF3 molecule.
Answer.
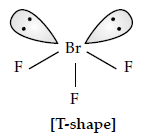
Question. Write the formula of the compound of iodine which is obtained when conc. HNO3 oxidises I2.
Answer. HIO3
Question. Give reason for the following :
F2 is more reactive than ClF3 but ClF3 is more reactive than Cl2.
Answer. Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds. But in case of fluorine due to the small size of fluorine, it has high electronegativity and low bond energy so it is more reactive than ClF3.Therefore ClF3 is more reactive than Cl2.
Question. Account for the following: Iron on reaction with HCl forms FeCl2 and not FeCl3.
Answer. Because HCl is a mild oxidising agent and formation of hydrogen gas prevents the formation of FeCl3.
Question. Give reason for the following :
PbCl4 is more covalent than PbCl2.
Answer. Due to high oxidising power, halogens combine directly with most metals to form their corresponding halides. But if the metal exhibit more than one oxidation state, the halide in higher oxidation state will be more covalent than the one in lower oxidation state. Therefore PbCl4 is more covalent than PbCl2, as Pb exhibits more than one oxidation states.
Question. Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
Answer. Phosgene (COCl2), tear gas (CCl3NO2), mustard gas [C4H8Cl2S].
Question. Arrange the following in the order of property indicated against each set:
(a) F2, Cl2, Br2, l2 (increasing bond dissociation enthalpy)
(b) H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te (increasing acidic character)
OR
Answer the following questions :
(i) Write the formula of the neutral molecule which is isoelectronic with ClO.
(ii) Draw the shape of H2S2O7.
Answer. (a) I2 < F2< Br2 < Cl2
(b) H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te
OR
(i) CIF
Question. Fluorine exhibits only –1 oxidation state whereas other halogens exhibit +1, +3, +5 and +7 oxidation states also. Why is it so ?
Answer. Fluorine has no d-orbital for excitation of electrons and it is most electronegative element. Hence, it shows oxidation state of –1 only.
Question. Give reasons: ICl is more reactive than I2.
Answer. Inter halogen compound ICl are more reactive than halogens Cl2 because X–X (I–Cl) bond in inter halogens is weaker than Cl–Cl bond in halogens except F–F bond.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Arrange the following in order of property indicated for each set :
(i) F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 – increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
(ii) PH3, AsH3, BiH3, SbH3, NH3 – increasing base strength.
Answer. (i) I2 < F2 < Br2 < Cl2
(ii) BiH3 <SbH3 < AsH3 < PH3 < NH3
Question. Complete the following chemical equations :
(i) Ca3P2 + H2O →
(ii) 3Cu + H2SO4 (conc.) →
OR
Arrange the following in the order of property indicated against each set :
(i) HF, HCl, HBr, HI – increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
(ii) H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te – increasing acidic character.
Answer. (i) Ca3P2 + 6H2O → 3Ca(OH)2 + 2PH3
(ii) Cu + 2H2SO4 (conc.) → CuSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
OR
(i) H—I < H—Br < H—Cl < H—F
(ii) H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te
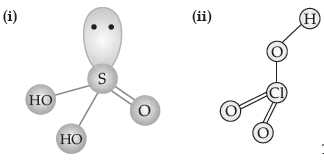
Question. Draw the structures of the following:
(i) H2SO3
(ii) HClO3
Answer.
Question. What happens when
(i) HCl is added to MnO2?
(ii) PCl5 is heated ?
Write the equation involved.
Answer. (i) MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
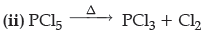
Question. Draw the structures of the following:
(i) H2S2O8
(ii) ClF3
Answer.
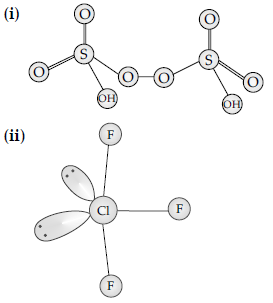
Question. Account for the following:
(i) Two S-O bond lengths in SO2 are equal.
(ii) Fluorine shows only -1 oxidation state in its compounds.
Answer. (i) Due to resonance the two S-O bond lengths are identical.
(ii) Absence of d-orbitals and most electronegative element.
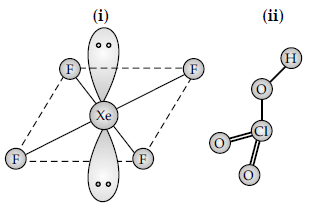
Question. Draw the structures of the following :
(i) XeF4
(ii) HClO3
Answer.
Question. Account for the following:
(i) The two oxygen-oxygen bond lengths in ozone molecule are identical.
(ii) Most of the reactions of fluorine are exothermic.
Answer. (i) Due to resonance the two O-O bond lengths are identical.
(ii) Due to strong bond formed by it with other elements.
Question. Give reasons :
(i) When Cl2 reacts with excess of F2, ClF3 is formed and not FCl3.
(ii) Dioxygen is a gas while Sulphur is a solid at room temperature.
Answer. (ii) F cannot show positive oxidation state as it has highest electronegativity/Because Fluorine cannot expand its covalency / As Fluorine is a small sized atom, it cannot pack three large sized Cl atoms around it.
(iii) Oxygen has multiple bonding whereas sulphur shows catenation / Due to pπ-pπ bonding in oxygen whereas sulphur does not / Oxygen is diatomic therefore held by weak intermolecular force while sulphur is polyatomic held by strong intermolecular forces.
Question. Account for the following:
(i) Bond angle in NH4+ is higher than that in NH3.
(ii) ICl is more reactive than I2.
Answer. (i) In NH4+, all are bond pairs whereas in ammonia the lone pair of electron on nitrogen repels the bond pairs and reduces the bond angle.
(ii) I-Cl bond is weaker than I-I bond / low bond dissociation enthalpy in I-Cl.
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidizing power of F2 and Cl2.
Answer. F2 is a stronger agent than Cl2 because
(i) Bond dissociation enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine.
(ii) Electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine.
(iii) F– has high hydration enthalpy.
Question. Explain why the stability of oxoacids of chlorine increases in the order given below : HClO < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4
Answer. Oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine;therefore, dispersal of negative charge present on chlorine increases from ClO to ClO4 ion because numbers of oxygen atoms are attached to chlorine increases. Therefore, stability of ions will increase in the order given below :
ClO < ClO2 < ClO3 < ClO5
Thus due to increase in stability of conjugate base,acidic strength of corresponding acid increases in the following order :
HClO < HClO2 < HClO5 < HClO4
Topic-3
Group-18 Elements, Properties and Some Important Compounds
Very Short Answer-Objective Type Questions
A. Multiple choice Questions:
Question. Which one of the following does not exist?
(a) XeOF4
(b) NeF2
(c) XeF2
(d) XeF6
Answer
B
Question. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken O2+PtF6– as a base compound. This is because
(a) both O2 and Xe have same size.
(b) bothO2 and Xe have same electron gain enthalpy.
(c) both O2 and Xe have same ionisation enthalpy.
(d) both Xe and O2 are gases.
Answer
C
B. Match the following :
Question. Match the species given in Column I with those mentioned in Column II.
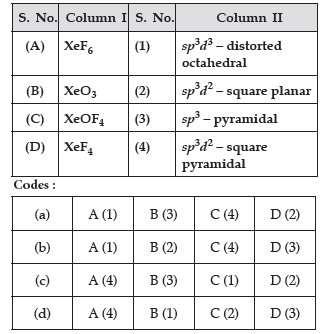
Answer
A
C. Answer the following:
Question. XeF6 undergoes complete hydrolysis?
Answer. When XeF6 undergoes complete hydrolysis, it forms
XeF6 + 3H2O → 6HF + XeO3
Question. Complete the following chemical equation :
XeF4 + SbF5 →
Answer. XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3]+[SbF6]–
Question. Helium is used in diving equipment.
Answer. Helium is used as a diluent for oxygen in modern diving apparatus because of its very low solubility in blood.
Question. What inspired N. Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6 ?
Answer. First ionisation enthalpy of molecular oxygen was almost similar with that of Xenon. Thus, after preparing red coloured compound O2+ [PtF6 ] −,
Bartlett got inspired for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6 and made efforts to prepare Xe+[PtF6]– by mixing Xe and PtF6.
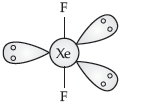
Question. Draw the structure of XeF2 molecule.
Answer. XeF2 :
Question. Draw the structures of the following :
XeF4
Answer.
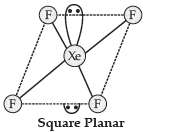
Question. Draw the structures of the following :
(i) XeF4 (ii) BrF5
Answer.
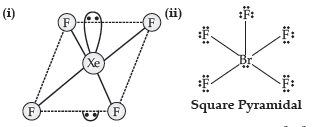
Question. Draw the structures of the following :
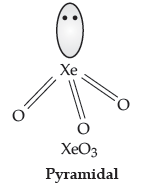
(i) XeO3 (ii) H2SO4
Answer.
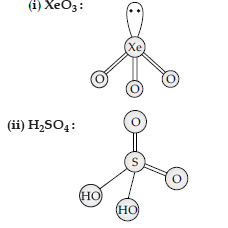
Question. Write the structures of the following :
(i) BrF3 (ii) XeF4
OR
What happens when :
(i) SO2 gas is passed through an aqueous solution Fe3+ salt ?
(ii) XeF4 reacts with SbF5 ?
Answer.
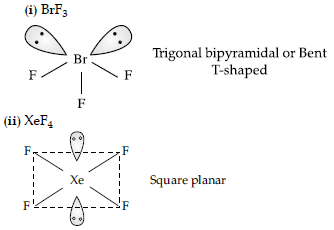
OR
(i) When SO2 gas is passed through an aqueous solution of Fe3+ salt, SO2 acts as a reducing agent and reduces Fe3+ to Fe2+. The brown colour of iron
(III) solution turns into green.
2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2++ SO42– + 4H+
(ii) When XeF4 reacts with strong Lewis acids like SbF5 it forms complexes (addition compounds).
XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3]+[SbF6]–
Question. Draw the structures of the following:
(i) XeF2 (ii) BrF5
Answer.
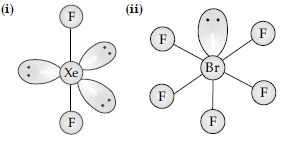
Question. Complete the following reactions:
(i) NH3 + 3Cl2 (excess) →
(ii) XeF6 + 2H2O →
Answer. (i) NH3 + 3Cl2 (excess) → NCl3 + 3HCl
(ii) XeF6 + 2H2O → XeO2F2
Question. Draw the molecular structure of XeF6.
Answer. XeF6 :
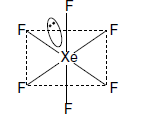
Question. Explain the following giving an appropriate reason in each case :
(i) O2 and F2 both stabilize higher oxidation states of metals but O2 exceeds F2 in doing so.
(ii) Structures of Xenon fluoride cannot be explained by Valence Bond approach.
Answer. (i) This is due to the ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds with metals. Oxygen has -2 charge for each atom while F2 bears -1 for each atoms. Thus the force of attraction between the metal atom and O2– ion is greater than the force between same metal atom and F–. Hence O2 gets higher oxidation state of metals.
(ii) This is because the energy required for the promotion of electrons in Xenon is very high.Energy factor does not favour VB approach.
Question. Complete the following chemical equation :
(i) F2+2Cl- →
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O →
Answer. (i) F2 + 2Cl- → 2F- + Cl2
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O → 2Xe + 4HF + O2
Question. Account for the following :
(a) Cl2 acts as a bleaching agent.
(b) Noble gases have very low boiling points.
OR
(a) What happens when F2 reacts with water ?
(b) Write the formula of a noble gas species which is isostructural with IBr2.
Answer. (a) Because Cl2 in presence of moisture liberates nascent oxygen.
(b) Interatomic interactions are weak.
OR
(a) 2F2+2H2O → 4HF + O2
HF and O2 are produced.
(b) XeF2
Question. Complete the following equations :
(i) C + conc. H2SO4 →
(ii) XeF2 + H2O →
Answer. (i) C + 2H2SO4(conc.) → CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O → 2Xe + 4HF + O2
Question. Draw the structures of the following :
(i) H2SO4 (ii) XeF2
Answer.
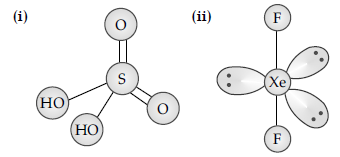
Question. Complete the following equations :
(i) P4 + H2O →
(ii) XeF4 + O2F2 →
Answer. (i) P4 + H2O → no reaction or if attempted in any form, award one mark.
(ii) XeF4 + O2F2 → XeF6 + O2
Question. Draw the structures of the following molecules :
(a) H2S2O7
(b) XeOF4
Answer.
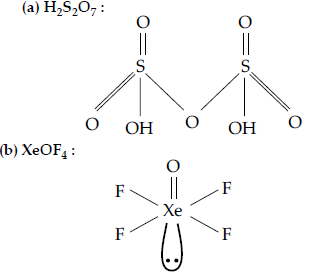
Question. Account for the following :
(i) Acidic character increases from HF to HI.
(ii) There is a large difference between the melting and boiling points of oxygen and sulphur.
Answer. (a) Acidic character increases from HF to HI due to increase in size as a result attraction force decreases and acidity increase.
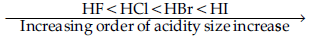
(ii) There is large difference between the melting point and boiling point of oxygen and sulphur due to small size and high electronegativity of oxygen.
Question. Complete the following reactions:
(i) Cl2 + H2O →
(ii) XeF6 + 3H2O →
Answer. (i) Cl2 + H2O → 2HCl + [O] / HCl +HOCl
(ii) XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
Question. (i) Complete the following chemical equations :
(a) NaOH + Cl2 →
(hot and conc.)
(b) XeF4 + O2F2 →
Answer. (i) (a) 6NaOH + 3Cl2 → 5NaCl + NaClO3 + 3H2O
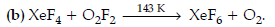
Long Answer Type Questions-I
Question. (i) F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than Cl2. Why ?
(ii) Which noble gas is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations ?
(ii) Complete the following equation :
XeF2 + PF5 →
Answer. (i) F2 has lower bond dissociation energy than Cl2 because the size of F2 is much smaller than Cl2 as a result interelectronic repulsion works and make F2 weak.
(ii) Helium is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations.
(iii) XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+ [PF6]–
Question. (i) What happens when :
(a) chlorine gas reacts with cold and dilute solution of NaOH ?
(b) XeF2 undergoes hydrolysis ?
(ii) Assign suitable reasons for the following :
(a) Out of noble gases only Xenon is known to form established chemical compounds.
Answer. (i) (a) 2NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaOCl + H2O
(b) 2XeF2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2Xe(g) + 4HF(aq) + O2(g)
(ii) Xe has least ionization energy among the noble gases and hence it forms chemical compounds particularly with O2 and F2.
Question. (i) Draw the structure of a noble gas species which is isostructural with BrO3–.
(ii) Considering the parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy, compare the oxidising power of F2 and Cl2.
(iii) Why is Ka2<< Ka1 for H2SO4 in water ?
OR
Explain the following :
(i) Hydrogen fluoride is a weaker acid than hydrogen chloride in aqueous solution.
(ii) SF6 is inert towards hydrolysis.
(iii) Out of noble gases only Xenon is known to form established chemical compounds.
Answer. (i) XeO3 is isostructural with BrO3–. (pyramidal structure)
(ii) The bond dissociation enthalpy of F—F bond is lower than that of Cl—Cl bond and hydration enthalpy of F– ion is much higher than that of Cl– ion.These two factors more than compensate the less negative electron gain enthalpy of F2. Thus, F2 is a stronger oxidizing agent than Cl2.
(iii) H2SO4 ionises in two stages and hence has two dissociation constants. Ka2 << Ka1.
This is because the negatively charged HSO4– ion resonance stabilized which has much less tendency to donate a proton to H2O as compared to neutral H2SO4.
OR
(i) Due to stronger H-F bond than HCl bond, HF ionises less readily than HCl in aqueous solution to give H+ ions. Therefore, HF is a weaker acid than HCl.
(ii) In SF6, S is sterically protected by six F atoms and hence does not allow H2O molecules to attack the S molecule. Also, F does not have d-orbitals to accept the electrons donated by H2O molecules.
(iii) Except radon which is radioactive, Xenon has least ionisation energy among noble gases and hence it readily forms chemical compounds particularly with O2 and F2.
Question. (i) Arrange the hybrids of group 16 in increasing order of their acidic character. Justify your answer.
(ii) Draw structure of XeOF4.
Answer. (i) H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te, because of decrease in bond dissociation enthalpy.
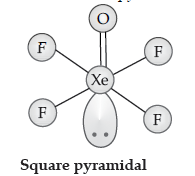
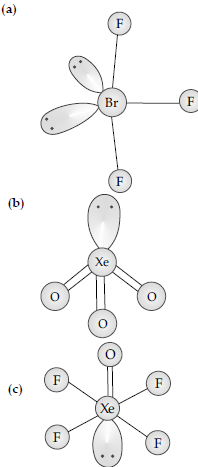
Question. (i) Draw the structure of the following
(a) BrF3 (b) XeO3
(c) XeOF4
Answer.
Question. (i) Compare the oxidizing action of F2 and Cl2 by considering parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy.
(ii) Write the conditions to maximize the yield of H2SO4 by contact process.
Answer. (i) F2 is the stronger oxidising agent than chlorine :
(a) Low enthalpy of dissociation of F-F bond.
(b) Less negative electron gain enthalpy of F.
(c) High hydration enthalpy of F– ion.
(ii) The main reaction in contact process is 2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3 ↑
This reaction is reversible and conditions to increase the yield of SO3 are :
(a) High pressure
(b) Low temperature (optimum temperature 720 K) should be maintained and
(c) V2O5 as catalyst.
Long Answer Type Questions-II
Question. (i) Write balanced equations for the following reactions :
(a) Chlorine reacts with dry slaked lime.
(b) Carbon reacts with concentrated H2SO4.
(ii) Describe the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid with special reference to the reaction conditions, catalysts used and the yield in the process.
Answer. (i) (a) 2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 → Ca(OCl)2 + CaCl2 + 2H2O
(b) C + 2H2SO4(conc.) → CO2 + 2SO2 + 2H2O
(ii) It is manufactured by Contact Process which involves following steps :
(a) burning of sulphur or sulphide ores in air to generate SO2.
(b) conversion of SO2 to SO3 by the reaction with oxygen in the presence of a catalyst (V2O5).
(c) absorption of SO3 in H2SO4 to give Oleum (H2S2O7). The oleum obtained is diluted to give sulphuric acid.
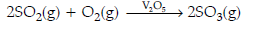
Reaction condition – pressure of 2 bar and temperature of 720 K.
Catalyst used is V2O5.
Yield – 96 – 98% pure.
Question. (i) Account for the following:
(a) Reducing character decreases from SO2 to TeO2.
(b) HClO3 is a stronger acid than HClO.
(c) Xenon forms compounds with fluorine and oxygen only.
(ii) Complete the following equations:
(a) 4NaCl + MnO2 + 4H2SO4 →
(b) 6XeF4 + 12H2O →
Answer. (i) (a) Stability of higher oxidation state decreases down the group from S to Te/Stability of lower oxidation state increases down the group from S to Te.
(b) ClO3 is more stable than ClO–/ClO3– is a weak conjugate base than ClO-/Due to higher oxidation state of chlorine in HClO3
(c) Fluorine and oxygen are most electronegative and very reactive.
(ii)
(a) 4NaCl + MnO2 + 4H2SO4 → MnCl2 + 4NaHSO4 + 2H2O + Cl2
(b) 6XeF4+ 12H2O → 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
Question. (i) Complete the following chemical reaction equations :
(a) P4 + SO2Cl2 →
(b) XeF6 + H2O →
(ii) Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in each of the following cases :
(a) SO32– and the angle O—S—O
(b) ClF3 and the angle F—Cl—F
(c) XeF2 and the angle F—Xe—F
Answer. (i) (a) P4 + 10SO2Cl2 → 4PCl5 + 10SO2.
(b) XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
or
XeF6 + 2H2O → XeO2F2 + 4HF
or
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
(ii) (a) Pyramidal or
