Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Chapter 3 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 3 Electrochemistry have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the Class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Electrochemistry Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry
Question. The e.m.f. of a Daniell cell at 298 K is E1.
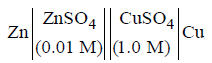
When the concentration of ZnSO4 is 1.0 M and that of CuSO4 is 0.01 M, the e.m.f. changed to E2. What is the relationship between E1 and E2?
(a) E2 = 0 ≠ E1
(b) E1 = E2
(c) E1 = E2
(d) E1 = E2
Answer
B
Question. The electrode potential E (Zn2+/Zn) of a zinc electrode at 25°C with an aqueous solution of 0.1 M ZnSO4 is [E0 (Zn2+/Zn)= –0.76 V. Assume 2.303RT/F = 0.06 at 298 K].
(a) + 0.73
(b) – 0.79
(c) – 0.82
(d) – 0.70
Answer
B
Question. The chemical reaction,
2AgCl(s) + H2 (g) → 2HCl(aq) + 2Ag(s) taking place in a galvanic cell is represented by the notation
(a) Pt(s) | H2 (g),1 bar |1MKCl(aq) | AgCl(s) | Ag(s)
(b) Pt(s) | H2(g),1 bar |1MHCl(aq) |1MAg+ (aq) | Ag(s)
(c) Pt(s) |H2 (g),1 bar |1MHCl(aq) | AgCl(s) |Ag(s)
(d) Pt(s) |H2 (g),1 bar |1MHCl(aq) | Ag(s) |AgCl(s)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements about galvanic cell is incorrect
(a) anode is positive
(b) oxidation occurs at the electrode with lower reduction potential
(c) cathode is positive
(d) reduction occurs at cathode
Answer
A
Question. In which of the following conditions salt bridge is not required in a galvanic cell?
(a) When galvanic cell is used in geyser.
(b) When distance between oxidation half cell and reduction half cell is negligible.
(c) Electrolytic solutions used in both the half cells are of same concentration.
(d) When both the electrodes are dipped in the same electrolytic solution.
Answer
D
Question Which one is not called a anode reaction from the following?

Answer
D
Question. The cell reaction Cu + 2Ag+ → Cu+2 + Ag is best represented by
(a) Cu(s) | Cu+2 (aq) | |Ag+ (aq) |Ag(s)
(b) Pt | Cu+2 || Ag+ (aq) | Ag(s)
(c) Cu+2 | Cu | | Pt | Ag
(d) None of the above representations
Answer
A
Question. Zn (s) | Zn 2+ (aq) | | Cu 2+ (aq) |Cu(s) is
anode cathode
(a) Weston cell
(b) Daniel cell
(c) Calomel cell
(d) Faraday cell
Answer
B
Question. The resistance of 0.01 N solution of an electrolyte was found to be 220 ohm at 298 K using a conductivity cell with a cell constant of 0.88cm–1. The value of equivalent conductance of solution is –
(a) 400 mho cm2 g eq–1
(b) 295 mho cm2 g eq–1
(c) 419 mho cm2 g eq–1
(d) 425 mho cmm2 g eq–1
Answer
A
Question. The tendency of an electrode to lose electrons is known as
(a) electrode potential
(b) reduction potential
(c) oxidation potential
(d) e.m.f.
Answer
C
Question. Given that the standard reduction potentials for M+/M and N+/N electrodes at 298 K are 0.52 V and 0.25 V respectively.Which of the following is correct in respect of the following electrochemical cell ?
M/M+ | | N+/N
(a) The overall cell reaction is a spontaneous reaction.
(b) The standard EMF of the cell is – 0.27 V.
(c) The standard EMF of the cell is 0.77 V.
(d) The standard EMF of the cell is – 0.77 V.
Answer
B
Question. For the given Nernst equation
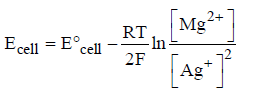
Which of the following representation is correct?
(a) Ag+|Ag||Mg2+|Mg
(b) Mg2+|Mg||Ag|Ag+
(c) Mg|Mg2+||Ag+|Ag
(d) Mg|Mg2+||Ag|Ag+
Answer
C
Question. The standard e.m.f. of a galvanic cell involving cell reaction with n = 2 is found to be 0.295 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction would be
(Given F = 96500 C mol–1; R = 8.314JK–1mol–1)
(a) 2.0×1011
(b) 4.0×1012
(c) 1.0×102
(d) 1.0×1010
Answer
D
Question. What will be the emf for the given cell
Pt | H2 (P1) | H+ (aq) | | H2 (P2) | Pt
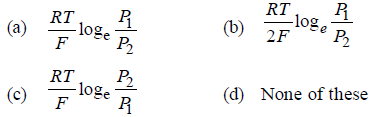
Answer
B
Question. For cell representation:
Cu(s)|Cu2+(aq)||Ag+(aq)|Ag(s)
Which of the following is correct?
(i) Cu is reducing agent.
(ii) Overall cell reaction is

(iii) Cu is cathode
(iv) Ag is anode
(a) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer
D
Question. The reference electrode is made by using
(a) ZnCl2
(b) CuSO4
(c) HgCl2
(d) Hg2Cl2
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding electrochemistry?
(a) It is the study of production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions.
(b) NaOH, Cl2, alkali and alkaline earth metals are prepared by electrochemical methods.
(c) The demerit associated with electrochemical methods is that they are more polluting. Thus they are ecodestructive.
(d) Electrochemical reactions are more energy efficient and less polluting.
Answer
C
Question. The standard hydrogen electrode potential is zero, because
(a) hydrogen oxidized easily
(b) electrode potential is considered as zero
(c) hydrogen atom has only one electron
(d) hydrogen is a very light element
Answer
B
Question. Without losing its concentration ZnCl2 solution cannot be kept in contact with
(a) Au
(b) Al
(c) Pb
(d) Ag
Answer
B
Question. On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing agent is :
[Fe(CN)6]4– →[Fe(CN)6]3– + e– ; E° = – 0.35 V
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e–; E° = – 0.77 V
(a) [Fe(CN)6]4–
(b) Fe2+
(c) Fe3+
(d) [Fe(CN)6]3–
Answer
C
Question. The unit of specific conductivity is
(a) ohm cm–1
(b) ohm cm–2
(c) ohm–1 cm
(d) ohm–1 cm–1
Answer
D
Question. Standard electrode potential for Sn4+ / Sn2+ couple is + 0.15 V and that for the Cr3+ / Cr couple is – 0.74 V. These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be
(a) + 1.19 V
(b) + 0.89 V
(c) + 0.18 V
(d) + 1.83 V
Answer
B
Question. What flows in the internal circuit of a galvanic cell?
(a) Ions
(b) Electrons
(c) Electricity
(d) Atoms
Answer
A
Question. Standard reduction potentials of the half reactions are given below :
F2(g) + 2e– → 2F– (aq); E° = + 2.85 V
Cl2(g) + 2e– → 2Cl–(aq); E° = + 1.36 V
Br2(l) + 2e– → 2Br–(aq); E° = + 1.06 V
I2(s) + 2e– → 2I–(aq); E° = + 0.53 V
The strongest oxidising and reducing agents respectively are
(a) F2 and I–
(b) Br2 and Cl–
(c) Cl2 and Br–
(d) Cl2 and I2
Answer
A
Question. A button cell used in watches functions as following
Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ 2Ag(s) + Zn2+(aq) + 2OH–(aq)
If half cell potentials are :
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– → Zn(s); Eo = – 0.76 V
Ag2O(s) + H2O (l) + 2e– → 2Ag(s) + 2OH–(aq); Eo = 0.34 V
The cell potential will be :
(a) 0.42 V
(b) 0.84 V
(c) 1.34 V
(d) 1.10 V
Answer
D
Question. Specific conductance of a 0.1 N KCl solution at 23ºC is 0.012 ohm–1 cm–1. Resistance of cell containing the solution at same temperature was found to be 55 ohm. The cell constant is
(a) 0.0616 cm–1
(b) 0.66 cm–1
(c) 6.60 cm–1
(d) 660 cm–1
Answer
B
Question. The oxidation potentials of A and B are +2.37 and +1.66 V respectively. In chemical reactions
(a) A will be replaced by B
(b) A will replace B
(c) A will not replace B
(d) A and B will not replace each other
Answer
B
Question. Which cell will measure standard electrode potential of copper electrode ?
(a) Pt (s) |H2 (g, 0.1 bar) |H+ (aq., 1 M) ||Cu2+ (aq., 1 M) | Cu
(b) Pt (s) |H2 (g, 1 bar) |H+ (aq., 1 M) ||Cu2+ (aq., 2 M) | Cu
(c) Pt (s) |H2 (g, 1 bar) |H+ (aq., 1 M) ||Cu2+ (aq., 1 M) | Cu
(d) Pt (s) |H2 (g, 1 bar) |H+ (aq., 0.1 M) ||Cu2+ (aq., 1 M) | Cu
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell ?
(a) It does not participate in the cell reaction.
(b) It provides surface either for oxidation or for reduction reaction.
(c) It provides surface for conduction of electrons.
(d) It provides surface for redox reaction.
Answer
D
Question. In the electrochemical reaction
2Fe3+ Zn → Zn2+ + 2Fe2+ ,on increasing the concentration of Fe2+
(a) increases cell emf
(b) increases the current flow
(c) decreases the cell emf
(d) alters the pH of the solution
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following solutions of KCl will have the highest value of specific conductance?
(a) 1.0 N
(b) 0.1 N
(c) 1.0 ×10–2N
(d) 1.0 ×10–3N
Answer
A
Question.The cell constant of a conductivity cell ___________.
(a) changes with change of electrolyte.
(b) changes with change of concentration of electrolyte.
(c) changes with temperature of electrolyte.
(d) remains constant for a cell.
Answer
D
Question. The value of electrode potential (10–4 M) H+ | H2(1 atm) | Pt at 298 K would be
(a) – 0.236 V
(b) + 0.404 V
(c) + 0.236 V
(d) – 0.476 V
Answer
A
Question. According to Nernst equation, which is not correct if Q = Kc :
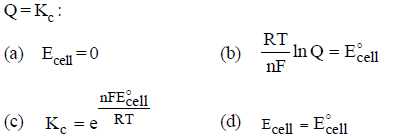
Answer
D
Question. The standard emf of a cell, involving one electron change is found to be 0.591 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is (F = 96500 C mol–1)
(a) 1.0 × 101
(b) 1.0 × 105
(c) 1.0 × 1010
(d) 1.0 ×1030
Answer
C
Question. For the galvanic cell
Zn | Zn2+ (0.1M) || Cu2+ (1.0M)|Cu the cell potential increase if:
(a) [Zn2+] is increased
(b) [Cu2+] is increased
(c) [Cu2+] is decreased
(d) surface area of anode is increased
Answer
B
Question. Reaction that takes place at graphite anode in dry cell is

Answer
B
Question. Consider the following cell reaction:
2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+ (aq) → 2Fe2+ (aq) + 2H2O(l);E 1.67V
At [Fe2+] = 10–3 M, p(O2) = 0.1 atm and pH = 3, the cell potential at 25ºC is
(a) 1.47 V
(b) 1.77 V
(c) 1.87 V
(d) 1.57 V
Answer
D
Question. E° of a cell aA + bB → cC + dD is
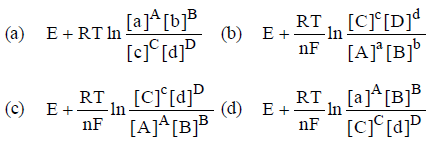
Answer
B
Question. E° for the cell,
Zn | Zn2+ (aq) | | Cu2+ (aq)| Cu is 1.10 V at 25°C. The equilibrium constant for the cell reaction
Zn + Cu2+ (aq) ⇌ Cu+ Zn2+ (aq) is of the order of
(a) 10–37
(b) 1037
(c) 10–17
(d) 1017
Answer
B
Question. What is the standard cell potential E° for an electrochemical cell in which the following reaction takes place spontaneously ?
Cl2(g) + 2Br– → Br2(aq)+ 2Cl– ΔG°=-50.6 kJ
(a) 1.2 V
(b) 0.53 V
(c) 0.26 V
(d) –0.53 V
Answer
C
Question. If 0.01 M solution of an electrolyte has a resistance of 40 ohms in a cell having a cell constant of 0.4 cm–1, then its molar conductance in ohm–1 cm2 mol–1 is
(a) 102
(b) 104
(c) 10
(d) 103
Answer
D
Question.The difference between the electrode potentials of two electrodes when no current is drawn through the cell is called _________.
(a) Cell potentials
(b) Cell emf
(c) Potential difference
(d) Cell voltage
Answer
B
Question. The unit of equivalent conductivity is
(a) ohm cm
(b) ohm–1 cm2 (g equivalent)–1
(c) ohm cm2 (g equivalent)
(d) S cm–2
Answer
B
Question. Which device converts chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy?
(a) Galvanic cell
(b) Electrolytic cell
(c) Daniell cell
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Specific conductance of 0.1 M HNO3 is 6.3×10–2 ohm–1 cm–1.The molar conductance of the solution is
(a) 100 ohm–1 m2
(b) 515 ohm–1 cm2
(c) 630 ohm–1 cm2
(d) 6300 ohm–1 cm2
Answer
C
Question. Standard electrode potential of three metals X, Y and Z are – 1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V, respectively. The reducing power of these metals will be :
(a) Y > Z > X
(b) X > Y > Z
(c) Z > X > Y
(d) X > Y > Z
Answer
C
Question. The specific conductance of a 0.1 N KCl solution at 23°C is 0.012 ohm–1cm–1. The resistance of cell containing the solution at the same temperature was found to be 55 ohm.The cell constant will be
(a) 0.142 cm–1
(b) 0.66 cm–1
(c) 0.918 cm–1
(d) 1.12 cm–1
Answer
B
Question. A smuggler could not carry gold by depositing iron on the gold surface since
(a) gold is denser
(b) iron rusts
(c) gold has higher reduction potential than iron
(d) gold has lower reduction potential than iron
Answer
C
Question. In the cell reaction
Cu(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) → Cu2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) ,
Eocell = 0.46 V. By doubling the concentration of Cu2+, Eocell will become
(a) doubled
(b) halved
(c) increases but less than double
(d) decreases by a small fraction
Answer
D