Please see Chapter 1 Forms of Business Organisation Exam Questions Class 11 Business Studies below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 11 Business Studies Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 11 Business Studies. These solved problems for Business Trade and Commerce in Class 11 Business Studies will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Chapter 2 Forms of Business Organisation Class 11 Business Studies
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. In which form of business profits are not shared?
Answer : In a sole proprietorship all profits, losses, assets and liabilities are the direct and sole responsibility of the owner
Question. Write the names of systems which govern membership in Joint Hindu Family business
Answer : There are two Schools of Hindu Laws which govern the Hindu Undivided Family(HUF):
1. Mitakshara Law
The Mitakshara Law applies tothe whole of India except Bengal and Assam.
2. Dayabhaga Law
Dayabhaga Law applies to the communities like Bengalis and Assamese living in the States of Bengal and Assam and other parts of the world.
Question. What is the minimum no. of persons required to form a co-operative society
Answer : The minimum number of persons required to form a Co-operative is ten (10).
Question. Identify a company which has no restriction of on transfer of shares
Answer : Public company has no restriction of on transfer of shares
Question. Write the name of form of business organisation found only in India
Answer : Joint Hindu family form of business is the form of business which is only found in india
Short /Long Answer type Questions :
Question. Lakshay has set up a cement company on 10th January, 2017. He has got has company registered under Companies Act, 2013. From the day of its incorporation, it acquires an identity separate from its members. Like natural persons, it can own property, incur debts, borrow money and enter into contracts. The Board of Directors of the company will appoint top officials for running the business. Identify the four features of company form of organisation highlighted above by quoting the lines.
Answer. (a) Formation
‘He has got his company registered under Companies Act, 2013.’recipient of all profits.’
(b) Separate Legal Entity
‘From the day of its incorporation it acquires an identity separate from its members.’
(c) Artificial Person
‘Like natural persons, it can own property, incur debts, borrow money and enter into contracts.’
(d) Control
‘The Board of Directors of the company will appoint top officials for running the business.’
Question. Gurpreet, Agam, Shenoy, Dev and Lakshay are partners in a partnership firm. The firm has different types of partners. Gurpreet has contributed capital and participates in the management of firm. He shares profits & losses and is liable to an unlimited extent to the creditors of firm. Agam has contributed capital and shares its profits and losses. He also has unlimited liability but he does not take part in day to day activities of business. Shenoy is a partner, his association with the firm is unknown to general public but in all other respects he is like an active partner. Dev has allowed the firm to use his name as he enjoys good reputation among clients but he does not either contribute capital nor take part in the management. Lakshay, is 15 years of age, and is entitled to the benefits of partnership with mutual consent of all other members. He is not eligible to take part in management of firm and shares only profits and not losses.
(a) In the given case, how many types of partners are involved in the partnership firm?
(b) Who is working as an active partner and what is the nature of his liability?
(c) Who is working as sleeping partner and what is the nature of his liability?
(d) Who is working as secret partner and what is the nature of his liability?
(e) Who is working as nominal partner and what is the nature of his liability?
(f) Is Lakshay a legal partner? Can he be held for the losses of the business? What is the nature of his liability?
Answer. (a) Five
(b) Gurpreet-unlimited liability
(c) Agam-unlimited liability
(d) Shenoy-unlimited liability
(e) Dev-unlimited liability.
(f) Yes, he is a legal partner. No, he cannot be held liable for the losses of the business. His liability is limited to the extent of capital contributed by him.
Question. BSE Limited is the owner and operator of BSE Exchange (Bombay Stock Exchange), India’s largest stock exchange by number of companies listed. The Bombay Stock Exchange was established in year 1875 as the first stock exchange in Asia. Today, BSE has over 5000 companies listed on it, the highest in any exchange around the world.
(i) When and why is a company supposed to make an application to one or more recognised stock exchanges?
(ii) Can the stock exchange reject the application of a company for listing of securities? What are its consequences?
Answer. (i) A public company desirous to raise funds from the public by means of issue of shares and debentures has to make an application to one or more recognised stock exchanges for permission to deal in its shares or debentures.
(ii) Yes, the stock exchange may reject the application of a company for listing of securities if the required specifications are not being fulfilled.
If such permission is not granted within 10 weeks from the date of closure of subscription list, then the allotment will become void. Consequently, all money received from the applicants
will have to be returned to them within 8 days.
Question. Kapoor brothers formed a Joint Hindu Family business.There were three brothers and the eldest of them Ramesh Kapoor became the Karta. The business took a loan of ₹ 40 lakhs for three years but were unable to repay it due to poor financial condition of the business. They sold an ancestral property worth ₹ 25 lakhs and paid to bank. The bank filed a case of recovery for the balance amount. Ramesh Kapoor pleaded to the court that the loan was taken for the business purpose, so all member are liable to repay it. The court rejected the plea of Ramesh Kapoor.
(a) Why did court rejected the plea of Ramesh Kapoor?
(b) In this case who has unlimited and limited liability?
(c) Was the decision of court to claim only from Ramesh Kapoor justified?
Answer. (a) Because Ramesh Kapoor being karta has unlimited liability.
(b) Ramesh Kapoor-unlimited and all other members have limited liability.
(c) Yes as Ramesh Kapoor has unlimited liability.
Question. Compare the status of a minor in a Joint Hindu Family Business with that in a partnership firm.
Answer. A minor is a person who has not attained the age of 18 years (21 years in some case). In case of a Joint Hindu Family Business, membership is by birth. That is why, minors can also be members of the business. The liability of minor is limited to his share in the business. They have to share losses also. In case of a partnership firm, a minor cannot become a partner because he is not capable of entering into a valid contract but he can be admitted to the benefits of partnership firm with mutual consent of all other partners. He cannot be asked to bear the losses.
Question. Partners in affirm has different roles and liabilities, Identify and explain the type of partner in a firm from the given examples:
a) Rama is a partner in a business who has no actual interest in business trade or its profits but she is
Paid fee by the firm for lending its name to firm.
b) In Ram Hari & co. Ltd, Ram & Hari declare Gopal as a partner with knowing that Gopal remain silent
then Gopal will be liable to third parties for any loss.
c) What type of partner is Geeta if she only contribute capital, shar profit and loss if any?
d) What type of patner is Giri in Ram Hari & co. Where he is an outsider but represent himself as a
partner.
Answer : a) Rama is a partner in a business who has no actual interest in business trade or its profits but she is Paid fee by the firm for lending its name to firm- Nominal Partner
b) In Ram Hari & co. Ltd, Ram & Hari declare Gopal as a partner with knowing that Gopal remain silent
then Gopal will be liable to third parties for any loss- Partner by holding out
c) What type of partner is Geeta if she only contribute capital, shar profit and loss if any- Sleeping
Partner
d) What type of patner is Giri in Ram Hari & co. Where he is an outsider but represent himself as a
partner-Partner by Estoppel
Question. Explain the concept of mutual agency in partnership with suitable example
Answer : Mutual agency is the legal relationship between partners in a partnership where each partner has authorization powers and the ability enter the partnership into business contracts. In other words, each partner in the partnership is an agent in the business and the authority to make business decisions that commit or bind the partnership, as a whole, to a business agreement with a third party or entity.
For example, a partner of a grocery store who purchases a delivery truck creates a binding contract in the name of the partnership even if the partnership agreement denies this authority. On the other hand, if a partner in a law firm purchased a snowmobile for the partnership, such as act would not be binding on the partnership. The purchase is clearly outside the scope of partnership business.
Question. What is secret partner
Answer : Secret Partner is A person or partner who is not disclosed in a venture or enterprise. He contributes to the capital. He participates in the management but secretly. He also shares the profits and losses of business. His liability is unlimited as others.
Question. Explain a co-operative organisation in democratic setup.
Answer : The cooperative society is a voluntary association of persons, who join together with the motive of welfare of the members. The principle of ‘one man one vote’ governs the cooperative society. Each member is entitled to equal voting rights. Thus, cooperative society is run on democratic principles.
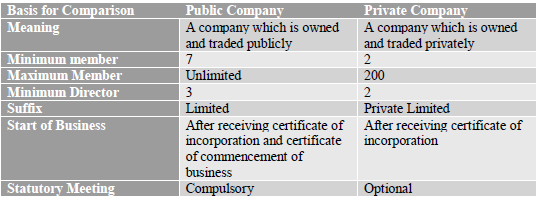
Question. Differentiate between private co. and public company
Answer :

Question. Explain limitations of Joint Stock Company
Answer : Limitations are as follows
• The formation of a company requires greater time, effort and extensive knowledge of legal requirements and the procedures involved
• Separation of ownership and management leads to lack of effort as well as personal involvement on the part of the officers of a company
• Information of company is provided to Registrar of companies time to time and hence information is available to general public
• The functioning of a company is subject to many legal provisions and compulsions. This reduces the freedom of operations of a company and takes away a lot of time, effort and money
• Communication as well as approval of various proposals to Top, middle and lower level management may cause delays not only in taking decisions but also in acting upon them.
• Board of Directors are representatives of the shareholders who are the owners. The owners have minimal influence in terms of controlling or running the business
• Various demands pose problems in managing the company as it often becomes difficult to satisfy such diverse interest
Question. If registration is optional, why do partnership firms willingly go through this legal formality? Explain the reason with procedure to get them registered.
Answer : It is optional for partnership firm to get registered. But to avoid conflicts between partners it is preferred to have a written agreement.
The consequences of non-registration of a firm are as follows:
(a) A partner of an unregistered firm cannot file a suit against the firm or other partners,
(b) The firm cannot file a suit against third parties, and
(c) The firm cannot file a case against the partners.
The written agreement which specifies the terms and conditions that govern the partnership is called the partnership deed.
The partnership deed generally includes the following aspect:
• Name of firm
• Nature of business and location of business
• Duration of business
• Investment made by each partner
• Distribution of profits and losses
• Duties and obligations of the partners
• Salaries and withdrawals of the partners
• Terms governing admission, retirement and expulsion of a partner
• Interest on capital and interest on drawings
• Procedure for dissolution of the firm
• Preparation of accounts and their auditing
• Method of solving disputes
Procedure for firm registration:
1. Submission of application in the prescribed form to the Registrar of firms. The application should contain the following particulars:
• Name of the firm
• Location of the firm
• Names of other places where the firm carries on business
• The date when each partner joined the firm
• Names and addresses of the partners
• Duration of partnership
This application should be signed by all the partners.
2. Deposit of required fees with the Registrar of Firms.
3. The Registrar after approval will make an entry in the register of firms and will subsequently issue a certificate of registration.
Question. Why cooperative forms of organisation are formed? Explain various types of cooperative societies
Answer : The cooperative society is a voluntary association of persons, who join together with the motive of welfare of the members. They are driven by the need to protect their economic interests in the face of possible exploitation at the hands of middlemen obsessed with the desire to earn greater profits. The process of setting up a cooperative society is simple enough and at the most what is required is the consent of at least ten adult persons to form a society. The capital of a society is raised from its members through issue of shares. The society acquires a distinct legal identity after its registration
Types of Cooperative Societies
♦ Consumer’s Cooperative Societies
It is formed to protect the interests of consumers
• Society aims at eliminating middlemen to achieve economy in operations
• It purchases goods in bulk directly from the wholesalers and sells goods to the members
• Profits are distributed on the basis of either their capital contributions to the society or purchases made by individual members.
♦ Producer’s Cooperative Societies
• It is set up to protect the interest of small producer
• The members comprise of producers desirous of procuring inputs for production of goods to meet the demands of consumers
• Profits are distributed on the basis of their contributions to the total pool of goods produced or sold by the society.
• Marketing Cooperative Societies
• It is established to help small producers in selling their products.
• The members consist of producers who wish to obtain reasonable prices for their output
• It pools the output of individual members and performs marketing functions like transportation, warehousing, packaging, etc., to sell the output at the best possible price.
• Profits are distributed according to each member’s contribution
♦ Farmer’s Cooperative Societies
• It is formed to protect the interests of farmers by providing better inputs at a reasonable cost
• The members comprise farmers who wish to jointly take up farming activities
• The aim is to gain the benefits of large scale farming and increase the productivity.
• Improves the yield and returns to the farmers, but also solves the problems associated with the farming on fragmented land holdings
♦ Credit Cooperative Societies
• It is established for providing easy credit on reasonable terms to the members.
• The members comprise of persons who seek financial help in the form of loans.
• The aim of such societies is to protect the members from the exploitation of lenders who charge high rates of interest on loans.
♦ Cooperative Housing Societies
• It is established to help people with limited income to construct houses at reasonable costs.
• The members of these societies consist of people who are desirous of procuring residential accommodation at lower costs.
• The aim is to solve the housing problems of the members by constructing houses and giving the option of paying in instalments
Question. ‘Reva Chemicals’ is a partnership firm. Sona and Mona one two partners in this firm. It is recorded in the Partnership Deed that Sona’s liability is unlimited, whereas Mona’s is limited. Sona wants to set up the Anti-Pollution plant in his factory, but Mona does not let him do so. Almost all the transactions of this firm are done through the internet. The firm Sells its goods to other Business units only. The firm gets its Research and Development work done by another firm, who is a specialist of such work.
i. Describe the type of partnership.
ii. ldentify the two values being overlooked.
iii. Name the type-business being done by the firm
Answer : i. It is a limited partnership where the liability of at least one partner is unlimited whereas the rest may have limited liability. The limited partners do not enjoy the right of management and their acts do not bind the firm or the other partners. Registration of such partnership is compulsory.
ii. The two values which are overlooked are:
• Violation of government rules
• Social responsibility clause is not fulfilled
iii. It is a Business to Business Commerce. B2B e-commerce (also written as e-Commerce, eCommerce or similar variants), short for business-to-business, electronic commerce, is selling products or services between businesses through the internet via an online sales portal. In general, it is used to improve efficiency for companies. Instead of processing orders manually – by telephone or e-mail – with ecommerce orders can be processed digitally.
