Please refer to Haloalkanes and Haloarenes HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow:
The substitution reaction of alkyl halides occurs in SN1 or SN2 mechanism whatever mechanism alkyl halide follow for substitution reaction to occur, the polarity of the carbon-halogen bond is responsible for the substitution reaction. The rate of SN1 reactions are governed by the stability of carbocation where as for SN2 reactions steric factor is the deciding factor. If the starting material is a chiral compound, we may end up with an inverted product or racemic mixture depending upon the type of mechanism followed by alkyl halide. Cleavage of ethers with HI is also governed by steric factor and stability of carbocation which indicates that in organic chemistry, these two major factors help us in deciding the kind of product formed.
Question. The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for a SN2 reaction is
(a) CH3F > CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3I
(b) CH3F > CH3Br > CH3Cl > CH3-I
(c) CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3F > CH3I
(d) CH3I > CH3Br > CH3Cl > CH3F
Answer
D
Question. The stereochemistry of the product formed if optically active alkyl halide undergoes substitution reaction by SN1 mechanism is –
(a) Optically active inverted product
(b) Optically active retention product
(c) Racemic mixture
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction ?
(a) CH3 CH2 Br
(b) CH3CH(CH3 )Br
(c) (CH3)3CBr
(d) CH3Br
Answer
C
Question. n-propyl bromide on treatment with ethanolic potassium hydroxide produces
(a) propane
(b) propene
(c) propyne
(d) propanol
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following are secondary bromides?
(a) CH3CH2Br
(b) (CH3)3CCH2Br
(c) CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3
(d)(CH3)2CBr
Answer
C
Question. IUPAC name of (CH3)3CCl
(a) 3-Chlorobutane
(b) 2-Chloro-2-methylpropane
(c) t-butyl chloride
(d) n-butyl chloride
Answer
B
Question. C – X bond is strongest in
(a) CH3F
(b) CH3Cl
(c) CH3Br
(d) CH3I
Answer
A
Question. The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is by treating the alcohol with :
(a) PCl5
(b) dry HCl in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl2
(c) SOCl2 in presence of pyridine
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. A Grignard reagent may be made by reacting magnesium with
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH3 CH3
(c) CH3CH2 I
(d) CH3CH2OH
Answer
C
Question. Reaction used to prepare alkyl iodide from alkyl bromide by using NaI in acetone is
(a) Willamson’s reaction
(b) Swart reaction
(c) Finkelstein reaction
(d) Wurtz reaction
Answer
C
Question. Which of the reaction given below is an example of Swart Reaction
(a) C2H5Cl + KOH + H2O → C2H5OH
(b) C2H5Br + AgF → C2H5F
(c) C2H5Br + Na (dry ether) →n- butane
(d) CH3CH=CH2 + HBr → CH3CH(Br)CH3
Answer
B
Question. A hydrocarbon that does not gives only one monochloro product on photo chlorination is
(a) Propane
(b) Ethane
(c) Methane
(d) Cyclopentane
Answer
A
Assertion Reason Question
In these questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
b)Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
d)Assertion is wrong statement, but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: Iodoalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution more readily than bromoalkanes
Reason: Iodine is a better leaving group due to its larger size which makes the covalent bond weaker.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: SN2 reaction is a bimolecular reaction
Reason: Both alkyl halide and nucleophiles are involved in the slow step.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Haloalkanes react with KCN to form cyanoalkanes.
Reason: KCN completely ionises in solution.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Alkyl halides are polar molecule but immiscible in water.
Reason: Alkyl halides form hydrogen bonding with water.
Answer
A
Very short answer type Questions
Question. Out of CH2=CH—CH2Cl and CH3CH2CH2Cl which one undergoes SN1 mechanism faster?
Answer. CH2=CH—CH2Cl undergoes faster SN1 reaction because allyl carbocation gets stabilised by resonance
Question. Name the instrument used for measuring the angle by which the plane polarised light is rotated.
Answer. Polarimeter
Question. What is racemic mixture?
Answer. Mixture in which two enantiomers are present in equal proportion with net zero optical rotation.
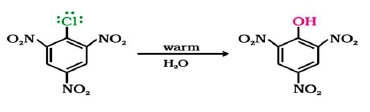
Question. Mention the product obtained by hydrolysis of 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene?
Answer. 2,4,6-trinitrophenol commonly known as picric acid is obtained
Short Answer type Questions :
Question. Write short notes on
(a) Fittig reaction
(b) Wurtz reaction
Answer. (a) Fittig reaction :

(b) Wurtz reaction

Question. Mention two difference between SN1 and SN2
Answer.

Question. (a) Arrange the following compounds in the decreasing order of rate of reaction towards SN1 reaction
C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
(b) In the following pair of halogen compounds, which would undergo SN2 reaction faster?
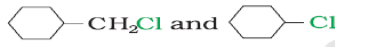
Answer. (a)

(b)

Short Answer type Question:
Question. Among the isomeric alkyl bromide of molecular formula C4H9Br
(i) Write the compound which is optically active
(ii) Write the compound which is more reactive towards SN2 reaction
(iii) Write the compounds which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction.
Answer: (i) CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 , Contains a chiral centre at carbon containing Br
(ii) CH3CH2CH2CH2Br , Primary alkyl halide
(iii) (CH3)3CBr , Tertiary alkyl halide
Question. Give reasons
a. C―Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C-Cl bond length in CH3―Cl
b. Boiling point of n-butyl chloride is more than t-butyl chloride
c. Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions
Answer.
a) In chlorobenzene, there is partial double bond character b/w carbon and halogen due to+ resonance effect.
b) Strong Van-der-waal interaction due to more surface area in n-butyl chloride compared to t-butyl chloride.
c) Grignard reagent is highly reactive and its forms alkane in presence of moisture.
Question. Account for the following .
(a) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(b) Alkyl halides though polar immiscible in water
(c) Sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI
Answer.
(a) Due to resonance chlorine gets partial positive charge in chlorobenzene resulting in lowering of dipole moment
(b) The force of interaction between alkyl halide and water is less compared to dipole interaction between alkyl halide and hydrogen bonding in water.
(c) HI formed will get oxidized to I2 by concentrated Sulphuric acid which is an oxidizing agent.
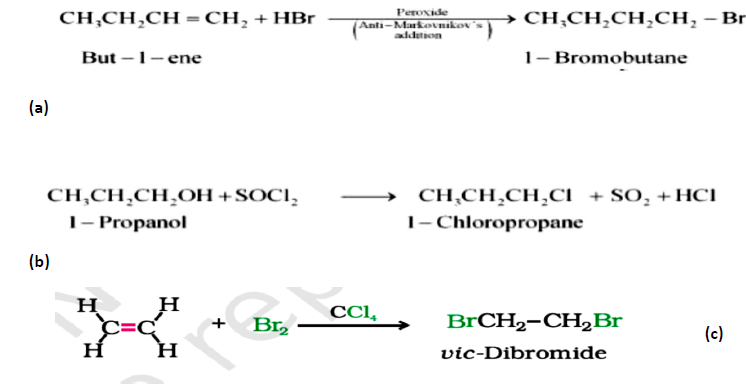
Question. Write the major product in the following reaction :
Answer.
Question. Write the product when
a) Chlorobenzene is treated with Cl2 and AlCl3
b) Chloroethane is treated with magnesium in dry ether
c) Methyl bromide is treated with AgNO2
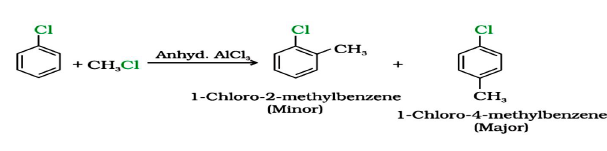
Answer.
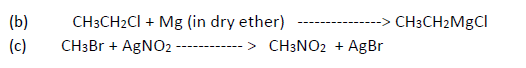
Long Answer type Question
Question. (a) Identify A,B,C,D

(b) Carry out the following conversion
(i) Ethanol to butane
(ii) Propene to propan-1-ol
(iii) Toluene to benzyl iodide
Answer. (a) A ➔ H2C=CH2 B ➔ CH3CH2OH C ➔ CH3CH2NC D ➔ CH3CH2CN
(b) (i) CH3CH2OH +SOCl2 —-> CH3CH2Cl +Na (dry ether) —-> CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3
(ii) CH3-CH=CH2 + HBr + H2O2 —– > CH3-CH2CH2-Br +KOH +H2O ——-> CH3-CH2CH2-OH
(iii) C6H5-CH3 + Br2 + UV radiation ——- > C6H5-CH2-Br +NaI + Acetone ——-> C6H5-CH2-I