Please refer to Haloalkanes And Haloarenes MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Chemistry with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Haloalkanes And Haloarenes will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Haloalkanes And Haloarenes MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Haloalkanes And Haloarenes in Class 12 Chemistry. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on latest examination guidelines.
Question. CH3Br + Nu– → CH3 —Nu + Br– . The decreasing order of the rate of the above reaction with nucleophiles (Nu–) A to D is
[Nu– = (A) PhO–, (B) AcO– , ( C) HO– ],(D) CH3O– )
(a) D > C > A > B
(b) D > C > B > A
(c) A > B > C > D
(d) B > D > C > A
Answer
A
Question. An incorrect statement with respect to SN1 and SN2 mechanisms of alkyl halide is
(a) a strong nucleophile in an aprotic solvent increases the rate or favours SN2 reaction
(b) competing reaction for a SN2 reaction is rearrangement
(c) SN1 reactions can be catalysed by some Lewis acids
(d) a weak nucleophile and aprotic solvent increases the rate or favours SN1 reaction
Answer
B
Question. Reaction of trans-2-phenyl-l-bromo reaction with alcoholic KOH produces cyclopentane on
(a) 4-phenyl cyclopentene
(b) 2-phenyl cyclopentene
(c) 1-phenyl cyclopentene
(d) 3-phenyl cyclopentene
Answer
D
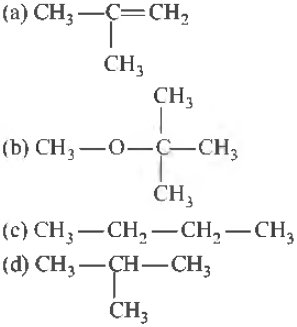
Question. Which of the following haloalkanes would undergo reaction faster?

(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Only III
(d) Only IV
Answer
A
Question. The molecular formula of diphenyl methane

How many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom?
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 7
Answer
B
Question. Of the five isomeric hexanes, the isomer which can give two monochlorinated compounds is
(a) 2-methy 1 pentane
(b) 2, 2-dimethy 1 butane
(c) 2, 3-dimethyl butane
(d) n-hexane
Answer
C
Question. In SN 2 reactions, the correct order of reactivity for the following compounds CH3 Cl, CH3CH2 Cl, (CH3)2 CHCI and (CH3)3 CCI is
(a) CH3CI > (CHH3)2 CHCI > CH2CH2CI > (CH3)3 CCI
(b) CH3Cl > CH3CH2Cl > (CH3)3 CHCI > (CH3)3CCI
(c) CH3CH2Cl > CH3Cl > (CH3 )2 CHCI >(CH3)3 CCI
(d) (CH3)2 CHCI > CH3CH2Cl > CH3Cl > (CH3)3 CCI
Answer
B
Question. What will be the product of the reaction,

Answer
A
Question. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points.

(a) II < I < III
(b) I < II < III
(c) III < I < II
(d) III < II < I
Answer
C
Question. Which reagents would you use to carry out the reaction Ethyl benzene → 2 and 4-chloro- 1 -ethyl benzene?
(a) Cl2, light and heat
(b) Cl2, FeCl3
(c) SOCl2
(d) C2H5CI, AICl3
Answer
B
Question. 9.65 C of electric current is passed through fused anhydrous magnesium chloride. The magnesium metal thus, obtained is completely converted into a Grignard reagent. The number of moles of the Grignard reagent obtained is
(a) 5 x 10-4
(b) 1 x 10-4
(c) 5 x 10-5
(d) 1 x 10-5
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following forms propane nitrile as the major product?
(a) Ethyl bromide + alcoholic KCN
(b) Propyl bromide + alcoholic KCN
(c) Propyl bromide + alcoholic AgCN
(d) Ethyl bromide + alcoholic AgCN
Answer
A
Question. Tertiary butyl alcohol gives tertiary butyl chloride on treatment with
(a) cone. HCl/anhy. ZnCl2
(b) KCN
(c) NaOCI
(d) Cl2
Answer
A
Question. The product of reaction between alcoholic silver nitrite with ethyl bromide is
(a) ethene
(b) ethane
(c) ethyl nitrile
(d) nitro ethane
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not true for the hydrolysis of t-butyl bromide with aqueous NaOH?
(a) Reaction occurs through the SN1 mechanism
(b) The intermediate formed is a carbocation
(c) Rate of the reaction doubles when the concentration of alkali is doubled
(d) Rate of the reaction doubles when the concentration of t-butyl bromide is doubled
Answer
C
Question. Grignard reagent is not prepared in aqueous medium but prepared in either medium, because
(a) the reagent is highly reactive in ether
(b) the reagent does not react with water
(c) the reagent becomes inactive in water
(d) the reagent reacts with water
Answer
D
Question. Ethyl iodide when heated with sodium in dry ether gives pure
(a) C4H10
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H8
(d) C2H5OH
Answer
A
Question. 2-bromopentane with ale. KOH yields a mixture of three alkenes. Which of the following alkene is predominant?
(a) 1-pentene
(b) Cis-2-pentene
(c) Trans-2-pentene
(d) Cis-1-pentene
Answer
C
Question. Number of monochloro derivatives obtained when neo-pentane is chlorinated, is
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer
A
Question. The catalyst used in the preparation of an alkyl chloride by the action of dry HCI on an alcohol is
(a) anhy. AlCl3
(b) FeCl3
(c) anhy. ZnCl2
(d) Cu
Answer
C
Question. t-butyl chloride preferably undergo hydrolysis by
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) SN2 mechanism
(c) Any of(a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. In the following sequence of reactions,
C2H5Br →AgCN X →Reduction Y , Y IS
(a) n-propylamine
(b) iso-propylamine
(c) ethylamine Reduction
(d) ethyl methyl amine
Answer
D
Question. Alkyl halides are less soluble in water because
(a) they ionise in water
(b) they do not form H-bonds with water
(c) they are highly viscous
(d) they have very strong C—X bond
Answer
B
Question. Predict the product,

Answer
A
Question. X + KCN → CH3CN →2H2/Ni CH3CH2NH2 What is X ?
(a) CH3CH2Cl
(b) CH3CI
(c) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(d) (CH3)2CHCl
Answer
B
Question. 1-chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives
(a) 1-butene
(b) 1-butanol
(c) 2-butene
(d) 2-butanol
Answer
A
Question. The organic chloro compound, which shows complete stereochemical inversion during an SN2 reaction is
(a) (C2H5)2CHCl
(b) (CH3)3CCl
(c) (CH3)2CHCl
(d) CH3Cl
Answer
D
Question. On treating a mixture of two alkyl halides with sodium metal in dry ether, 2-methyl propane was obtained. The alkyl halides are
(a) 2-chloropropane and chloromethane
(b) 2-chloropropane and chloroethane
(c) chloromethane and chloroethane
(d) chloromethane and 1-chloropropane
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
(a) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(b) CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl
(c) CH3CH(CH3)CH2Cl
(d) (CH3)3 CCI
Answer
B
Question. 1 , 2-dibromoethane reacts with alcoholic KOH to yield a productX. The hybridisation state of the carbons present in X respectively, are
(a) sp ,sp
(b) sp3 , sp3
(c) sp3 , sp2
(d) sp3 , sp2
Answer
A
Question. In the reaction, 2A + dry silver oxide →Δ ether+ 2Ag X A is a /an
(a) primary alcohol
(b) acid
(c) alkyl halide
(d) alcohol
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following haloalkanes is most reactive?
(a) 1-chloropropane
(b) 1-bromopropane
(c) 2-chloropropane
(d) 2-bromopropane
Answer
D
Question. 1-chlorobutane on reaction with alcoholic potash gives
(a) but-1-ene
(b) butane-1-ol
(c) but-2-ene
(d) butane-2-ol
Answer
A
Question. An alkyl halide reacts with alcoholic ammonia in a sealed tube, the product formed will be
(a) a primary amine
(b) a secondary amine
(c) a tertiary amine
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Anti-Markownikoff’s addition of HBr is observed in
(a) propane
(b) but-2-ene
(c) pent-2-ene
(d) All of the above
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following alkyl halides is used as a methylating agent?
(a) C2H5Br
(b) C6H5Cl
(c) CH3CI
(d) C2H5Cl
Answer
C
Question. CH3Br + KCN (ale. ) → X Reduction→Na +C2H5 OH Y. What is Y in the series ?
(a) CH3CN
(b) C2H5CN
(c) C2H5NH2
(d) CH3NH2
Answer
C
Question. In a group of isomeric alkyl halides, the order of boiling points is
(a) primary < secondary < tertiary
(b) primary > secondary < tertiary
(c) primary < secondary > tertiary
(d) primary > secondary > tertiary
Answer
D
Question. The order ofreactivities of methyl halides in the formation of Grignard reagent is
(a) CH3l > CH3Br > CH3CI
(b) CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3I
(c) CH3Br > CH3CI > CH3I
(d) CH3Br > CH3l > CH3Cl
Answer
A
Question. Alkyl halide is converted into alcohol. This is an example of …… reaction.
(a) addition
(b) displacement
(c) substitution
(d) complex
Answer
C
Question. Maximum number of molecules of CH3l that can react with a molecule of CH3NH2 are
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer
A
Question. Match the following columns.

Codes
A B C D
(a) 5 3 4 1
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 3 4 1 2
(d) 4 1 4 2
Answer
C
Question. The conversion of ethyl chloride into diethyl ether takes place by
(a) Williamson’s synthesis
(b) Perkin’s reaction
(c) Wurtz reaction
(d) Grignard reaction
Answer
A
Question. The structure of the major product formed in the following reaction is

Answer
D
Question. CH3Br + OH → CH3OH + Br– reaction proceeds by SN2 mechanism. Its rate is dependent on the concentration of
(a) CH3Br, OH
(b) Only CH3Br
(c) Only OH
(d) CH3Br, CH3OH
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following is not fom1ed when a mixture of methyl bromide and bromobenzene is heated with sodium metal in the presence of dry ether?
(a) Diphenyl
(b) Propane
(c) Toluene
(d) Ethane
Answer
B
Question. RX+ A → RNC,A is
(a) AgCN
(b) KCN
(c) NaCN
(d) HCN
Answer
A
Question. Ethyl chloride on heating with AgCN forms a compound X. The functional isomer of X is
(a) C2H5NC
(b) C2H5NH2
(c) C2H5CN
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements regarding the SN1 reaction shown by alkyl halide is not correct?
(a) The added nucleophile plays no kinetic role in SN1 reaction
(b) The SN1 reaction involves the inversion of configuration of the optically active substrate
(c) The SN1 reaction on the chiral starting material ends up with racemisation of the product
(d) The more stable the carbocation intermediate the faster the SN1 reaction
(e) Polar pro tic solvent increases the rate of SN1 reaction.
Answer
B
Question. The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is by treating the alcohol with
(a) PCl3
(b) PCl5
(c) SOCl2 in the presence of pyridine
(d) dry HCl in the presence of anhydrous ZnCI2
Answer
C
Question. The final product, in the below reaction, is

Answer
A
Question. Compound ‘A’ reacts with alcoholic KOH to yield compound ‘B ‘, which on ozonolysis followed by reaction with Zn /H2O gives methanal and propanal. Compound ‘A’ is
(a) 1-propanol
(b) 1-butanol
(c) 1-chlorobutane
(d) 1-chloropentane
Answer
C
Question. Identify A and B in the following reactions
A →Aq. NaOH C2H5 OH AgOH← B
(a) A = C2H2, B = C2H6
(b) A = C2H5 Cl,B = C2H4
(c) A = C2H4 , B = C2H5 Cl
(d) A = C2H5 Cl,B = C2H5 Cl
Answer
D
Question. The order of reactivities of methyl halides in the formation of Grignard reagent is
(a) CH3I > CH3Br > CH3CI
(b) CH3CI > CH3Br > CH3I
(c) CH3Br > CH3CI > CH3I
(d) CH3Br > CH3I > CH3CI
Answer
A
Question. Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of
(a) steric hindrance
(b) inductive effect
(c) instability
(d) insolubility
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following applies in the reaction,
CH3CHBrCH2CH3 →Ale. KOH
I. CH3CH = CHCH3 (major product)
II. CH2 = CHCH2CH3 (minor product)
(a) Markownikoff’s rule
(b) Saytzeff’s rule
(c) Kharasch effect
(d) Hofrnann’s rule
Answer
B
Question. Identify X and Y in the following sequence :
C2H5 Br → product → C3H7NH2
(a) X = KCN,Y = LiAIH4
(b) X = KCN,Y = H3O+
(c) X = CH3Cl,Y = AlCl3 / HCI
(d) X = CH3NH2 ,Y = HNO2
Answer
A
Question. Elimination of bromine from 2-bromobutane results in the formation of
(a) predominantly 2-butyne
(b) predominantly 1-butene
(c) predominantly 2-butene
(d) equimolar mixture of 1 and 2-butene
Answer
C
Question. When 32.25 g of ethyl chloride is subjected to dehydrohalogenation reaction the yield of the alkene formed is 50%. The mass of the product formed is (atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5)
(a) 14 g
(b) 28 g
(c) 64.5 g
(d) 56 g
(e) 7 g
Answer
E
Question. Which halide does not get hydrolysed by sodium hydroxide?
(a) Vinyl chloride
(b) Methyl chloride
(c) Ethyl chloride
(d) Iso-propyl chloride
Answer
A
Question. An alkyl halide (RX) reacts with Na to form 4, 5-diethyloctane. Compound RX is
(a) CH3 (CH2)3 Br
(b) CH3 (CH2)2CH(Br)CH2CH3
(c) CH3 (CH2)3CH(Br)CH3
(d) CH3 (CH2)5 Br
(e) CH3Br
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following is more readily hydrolysed by SN1 mechanism?
(a) (C6H5)2 C(CH3)2
(b) C6H5CH2Br
(c) C6H5CH(CH3) Br
(d) (C6H5)2 CHBr
Answer
A
Question. Alkyl iodide reacts with NaCN to give alkyl cyanide and small amount of alkyl isocyanide. Fom1ation of these two products is due to the
(a) ionic character of NaCN
(b) nucleophilic character of CN–
(c) ambidentate character of CN–
(d) electrophilic character of CN–
Answer
C
Question. The following compound on hydrolysis in aqueous acetone will give

(a) mixture of(K) and (L)
(b) mixture of(K) and (M)
(c) Only (M)
(d) Only (K)
Answer
A
Question. Of the isomeric hexanes, the isomers that give the minimum and maximun number of monochloro derivatives are respectively
(a) 3-methyl pentane and 2, 3-dimethyl butane
(b) 2, 3-dimethy 1 butane and n-hexane
(c) 2, 2-dimethye 1 butane and 2-methy 1 pentane
(d) 2, 3-dimethy 1 butane and 2-methy 1 pentane
(e) 2-methyl pentane and 2, 2-dimethylbutane
Answer
D
Question. Following is the substitution reaction in which —CN replaces —CL
R—Cl + KCNAlcoholic →Δ R—CN + KCl
To obtain propane nitrile, R—Cl should be
(a) chloroethane
(b) 1-chloropropane
(c) chloromethane
(d) 2-chloropropane
Answer
A


