Please refer to Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Chemistry with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Alcohols Phenols and Ethers will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Alcohols Phenols and Ethers MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Alcohols Phenols and Ethers in Class 12 Chemistry. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on latest examination guidelines.
Question. An oxygen containing organic compound upon oxidation forms a carboxylic acid as the only organic product with its molecular mass higher by 14 units. The organic compound is
(a) an aldehyde
(b) a primary alcohol
(c) a secondary alcohol
(d) a ketone
Answer
B
Question. The reaction of phenol with excess ofbromine water gives
(a) 11rbromophenol
(b) o-and p-bromophenol
(c) 2, 4-clibromophenol
(d) 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following properties is exhibited by phenol?
(a) It is soluble in aq. NaOH and evolves CO2 with aq. NaHCO3
(b) It is soluble is aq. NaOH and does not evolve CO, with aq. NaHCO3
(c) It is not soluble in aq. NaOH but evolves CO2 with aq. NaHCO3
(d) It is insoluble in aq. NaOH and does not evolve CO2 with aq. NaHCO3
Answer
B
Question. The reaction involved in the oil of winter green test is salicylic acid →Δ Cone. H2SO4 product. The product is treated with Na2CO3 solution. The missing reagent in the above reaction is
(a) phenol
(b) NaOH
(c) ethanol
(d) methanol
Answer
D
Question. The alcohol obtained by the hydrolysis of oils and fats is
(a) glycol
(b) glycerol
(c) propanol
(d) pentanol
Answer
B
Question. In the conversion of ethanol into methanol which of the following reagents will be used?
(a) K2Cr2O7 /H2SO4
(b) NaOH + CaO
(c) Cl2 + aq. KOH
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Reimer-Tiemann reaction involves
(a) carbonium ion intem1ediate
(b) carbene intermediate
(c) carbanion intermediate
(d) free radical intennediate
Answer
B
Question.
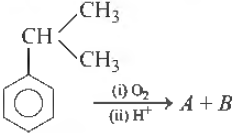
Identify A and B
(a) Phenol, acetone
(b) Phenol, acetaldehyde
(c) Benzoic acid, acetone
(d) Benzaldehyde, ethano
Answer
A
Question. Among the alkenes which one produces tertiary butyl alcohol on acid hydration?
(a) CH3CH2CH=CH2
(b) CH3CH=CH—CH3
(c) (CH3)2C=CH2
(d) CH3—CH=CH2
Answer
C
Question. The density of glycerol is higher than propanol due to
(a) van der Waals’ attraction
(b) hydrogen bonding
(c) ionic bonding
(d) more number of covalent bonds
Answer
B
Question. Argol, a brown cmst, formed during the fermentation of grape juice contains
(a) CO2
(b) fused oil
(c) potassium hydrogen tartarate
(d) lye
Answer
C
Question. Hydroboration oxidation of 4-methyl octene-1 would give
(a) 4-methyl octanol
(b) 2-methyl decane
(c) 4-methyl heptanol
(d) 4-methyl-2-octanone
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following combinations can be used to synthesise ethanol?
(a) CH3 Mgiand CH3COCH3
(b) CH3 Mgland C2H5OH
(c) CH3 Mgi and CH3COOC2H5
(d) CH3 Mgland HCHO
Answer
D
Question. The enzymes which are used to convert starch into ethyl alcohol are
(a) maltase, diastase
(b) diastase, maltase, zymase
(c) invertase, zymase
(d) invertase, diastase, maltase
Answer
B
Question. Ethanol is CH3CH2OH. Which species is formed when ethanol acts as a Bronsted base?
(a) CH3CH2O–
(c) CH3CH2O+H2
(b) CH3C+ H2
(d) H3O+
Answer
C
Question. Ethylene can be converted into alcohol by treatment of
(a) Aq. KOH
(b) H2SO4 as catalyst
(c) Moist silver oxide
(d) Zn/HCI
Answer
B
Question. Grignard reagent reacts with HCHO to produce
(a) secondary alcohol
(b) anhydride
(c) acid
(d) primary alcohol
Answer
D
Question. C6H5—CH=CHCHO—X C6H5CH= CHCH2OH
In the above sequence X can be
(a) H2 /Ni
(b) NaBH4
(c) K2Cr2O7 /H+
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
B
Question. Ethyl alcohol can be prepared from Grignard reagent by the reaction of
(a) HCHO
(b) R2CO
(c) RCN
(d) RCOCl
Answer
A
Question. The correct combination of names for isomeric alcohols with molecular formula C4 H10O is/are
(a) tert-butanol and 2-methyl propan-2-ol
(b) tert-butanol and 1, 1-dimethy 1 ethan-1-ol
(c) n-butanol and butan-1-ol
(d) iso-butyl alcohol and 2-methyl propan-1-ol
Answer
C
Question. The product X is
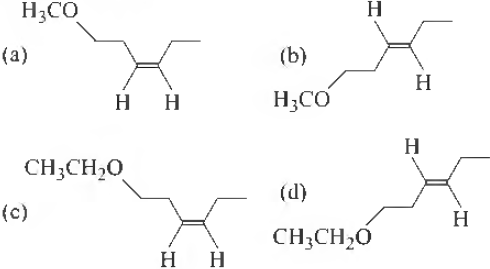
Answer
A
Question. The correct statement with respect to product Y is
(a) it gives a positi:i,e Tollen’s test and is a functional isomer of X
(b) it gives a positive Tollen’s test and is a geometrical isomer of X
(c) it gives a positive iodoform test and is a functional isomer of X
(d) it gives a positive iodoform test and is a geometrical isomer of X
Answer
C
Question. The correct statement regarding the following compounds is
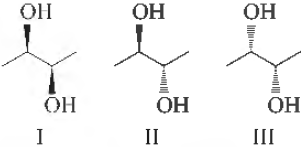
(a) all three compounds are chiral
(b) Only I and II are chiral
(c) I and III are diastereomers
(d) Only I and III are chiral
Answer
D
Question. For the sequence of reactions,
A →C2H5Mgl B → H2O/H+ tert-pentyl alcohol.
The compound A in the sequence is
(a) 2-butanone
(b) acetaldehyde
(c) acetone
(d) propanal
Answer
C
Question. Identify the product/s in the following reaction.
3CH3 CH=CH2 →BH3 X →H2O2/OH- products + H3BO3
(a) CH3CH2CH2OH
(b) CH3CHOHCH3
(c) CH3CH2CHO
(d) CH3CH2OH + CH3OH
(e) CH3CHO + CH3OH
Answer
A
Question. Which among the following compounds will give a secondary alcohol on reacting with Grignard’s reagent followed by acid hydrolysis ?
I. HCHO
II. C2H5CHO
III. CH3COCH3
IV. C2H5COOH
Select the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) Only II
(b) Only III
(c) I and IV
(d) II and IV
Answer
A
Question. The most suitable reagent for the conversion of
R—CH2—OH→ R—CHOis
(a) K.MnO4
(b) K2Cr2O7
(c) CrO3
(d) PCC (pyridiniurn chlorochromate)
Answer
D
Question. Ketone upon treatment with Grignard reagent gives
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary alcohol
(c) tertiary alcohol
(d) aldehyde
Answer
C
Question.

Answer
A
Question. In fermentation by zymase, alcohol and CO2 are obtained from
(a) invert sugar
(b) glucose
(c) fructose
(d) A.II of these
Answer
B
Question. The final product (IV) in the sequence of reactions
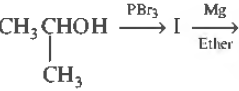

Answer
C
Question. 0.44 g of a monohydric alcohol when added to methylmagnesiurn iodide in ether liberates at STP, 112cm3 of methane. With PCC the same alcohol forms a carbonyl compound that answers silver mirror test. The monohydric alcohol is
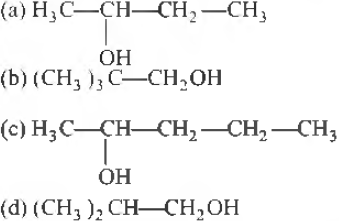
Answer
B
Question. Acid catalysed hydration of alkenes except ethene leads to the formation of
(a) mixture of secondary and tertiary alcohols
(b) mixture of primary and secondary alcohols
(c) secondary or tertiary alcohol
(d) primary alcohol
Answer
C
Question. Hydrogen bonding is maximum in
(a) diethyl ether
(b) triethyl amine
(c) ethanol
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The relative case of dehydration following order of alcohols follows
(a) tertiary > secondary > primary
(b) primary > secondary > tertiary
(c) secondary > tertiary > primary
(d) tertiary > primary > secondary
Answer
A
Question. An unknown alcohol is treated with the “Lucas reagent” to determine wheter the alcohol is primary, secondary or tertiary. Which alcohol reacts fastest and by what mechanism?
(a) Secondary alcohol by SN1
(b) Tertiary alcohol by SN2
(c) Secondary alcohol by SN2
(d) Tertiary alcohol by SN1
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following alcohol is unable to tum orange colour of chromic acid to green?
(a) 1° alcohol
(b) 2° alcohol
(c) 3° alcohol
(d) Allyl alcohol
Answer
C
Question. Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are clistinguished from one another by
(a) Ninhydrin test
(b) Tollen’s reagent
(c) Lucas test
(d) Wittig reaction
Answer
C
Question. Catalytic dehydrogenation of a primary alcohol gives a
(a) secondary alcohol
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) ester
Answer
B
Question. In the reaction, CH3OH →Oxidation A →NH3 B; A and B are
(a) HCHO, HCOONH4
(b) HCOOH, HCOONH4
(c) HCOOH, HCONH2
(d) HCHO, HCONH2
Answer
B
Question. When compound X is oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate, compound Y is formed. Compound Y on reduction with LiAIH4 gives X. X and Y respectively are
(a) C2H5OH, CH3COOH
(b) CH3COCH3 , CH3COOH
(c) C2H5OH, CH3COCH3
(d) CH3CHO, CH3COCH3
Answer
A
Question. The compound on dehydrogenation gives a ketone. The original compound is
(a) primary alcohol
(b) secondary alcohol
(c) tertiary alcohol
(d) carboxylic acid
Answer
B
Question. RCH2CH2OH can be converted to RCH2CH2COOH by the following sequence of steps
(a) PBr3 , KCN, H3O+
(b) PBr3 , KCN, H2 /P+
(c) KCN, H3O+
(d) HCN, PBr3 , H3O+
Answer
A
Question. In Lucas test an alcohol reacts immediately and gives insoluble chloride. The alcohol is
(a) CH3OH
(b) CH3CH2OH
(c) (CH3)2 CHOH
(d) (CH3)3 COH
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following will most reaclily be dehydrated in aciclic conclitions ?
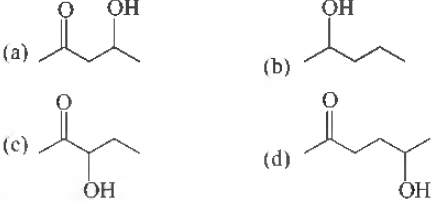
Answer
A
Question. From amongst the following alcohols the one that would react fastest with cone. HCl and anhydrous ZnCI2 is
(a) 2-butanol
(b) 2-methyl propan-2-ol
(c) 2-methylpropanol
(d) 1 butanol
Answer
B
Question. The main product of the following reaction is

Answer
A
Question. Which compound will have highest boiling point?
(a) CH4
(b) CH3OH
(c) C2H5OH
(d) HCHO
Answer
C
Question. In the following sequence of reactions,
CH3CH2OH→P+I2 A→Mgether B→HCHO C→H2OD the compound ‘D’ is
(a) butanal
(b) n-butyl alcohol
(c) n-propyl alcohol
(d) propanal
Answer
C
Question. The—OH group of an alcohol or the—COOH group of a carboxylic acid can be replaced by—Cl using
(a) phosphorus pentachloride
(b) hypochlorous acid
(c) chlorine
(d) hydrochloric acid
Answer
A
Question. Power alcohol is a mixture of
(a) 80% petrol + 20% ethanol + small quantity of benzene
(b) 80% ethanol + 20% benzene + small quantity of petrol
(c) 50% petrol + 50%ethanol + small quantity ofbenzene
(d) 80% petrol + 20% benzene + small quantity of ethanol
Answer
A
Question. When ethylene glycol is heated with acidified potassium permanganate, the main organic compound obtained is
(a) oxalic acid
(b) glyoxal
(c) formic acid
(d) acetaldehyde
(e) 2-hydroxy ethanol
Answer
C
Question. Upon treatment with I2 and aqueous NaOH, which of the following compounds will fotm iodoform?
(a) CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO
(b) CH3CH2COCH2CH3
(c) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2OH
(d) CH3CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3
Answer
D
Question. Ethylene glycol gives oxalic acid on oxidation with
(a) acidified K2Cr2O7
(b) acidified KMnO4
(c) alkaline KMnO4
(d) periodic acid
Answer
C
Question. An organic compound’ X’ on treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate in dichloromethane gives compound ‘Y’. Compound ‘Y’, reacts with I2 and alkali to form triiodomethane. The compound ‘ X’ is
(a) C2H5OH
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3COCH3
(d) CH3COOH
Answer
A
Question. Pinacol is
(a) 3-methylbutan-2-ol
(b) 2, 3-dimethyl-2, 3-butaned:iol
(c) 2, 3-dimethyl-2-propanone
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. The best method to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol is by using
(a) cone. HCl + ZnCI2
(b) cone. H3PO4
(c) HBr
(d) cone. HCl
Answer
B
Question. The compound which gives turbidity immediately with Lucas reagent at room temperature is
(a) butan-1-ol
(b) butan-2-ol
(c) 2-methyl propan-2-ol
(d) 2-methyl propan-1 -ol
Answer
C
Question. Lucas test is associated with
(a) aldehydes
(b) phenols
(c) carboxylic acids
(d) alcohols
Answer
D
Question. The function of ZnCl2 in Lucas test for alcohols is
(a) to act as acid catalyst and react with HCl to form H2 ZnCI4
(b) to act as base catalyst and react with NaOH to form Na2Zn(OH)4
(c) to act as amphoteric catalyst
(d) to act as neutral catalyst
Answer
A
Question. Salicyl aldehyde is obtained when phenol is heated with CHCl3 and aqueous NaOH. This reaction is known by which name?
(a) Carbyl amine reaction
(b) Hofmann’s reaction
(c) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(d) Kolbe-Schmidt reaction
Answer
C


