Please refer to Determinants MCQ Questions Class 12 Mathematics below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Mathematics with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books, and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Determinants will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Determinants MCQ Questions Class 12 Mathematics
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Determinants in Class 12 Mathematics. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on the latest examination guidelines.
MCQ Questions Class 12 Mathematics Determinants
Question. If the system of linear equations x + 2ay + az = 0 x + 3by + bz = 0, x +3cy + cz = 0 has a non-zero solution, then a,b,c ?
(a) Are in AP.
(b) Are in G.P.
(c) Are in H.P.
(d) Satisfy
Answer
C
Question: If α β, and Y are the roots of the equation x3 +px +q= 0, then the value of the determinant

(a) 0
(b) – 2
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer
A
Question: if
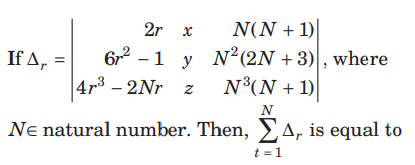
(a) N
(b) N2
(c) zero
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question: If the system of equations x+ ay= 0, az+y = 0 and ax+ z + = 0 has infinite solutions, then the value of a is
(a) 0
(b) – 1
(c) 1
(d) no real values
Answer
C
Question: If a b, and c are pth, qth , and rth terms of an HP, then

(a) term containing a, b, c, p, q and r
(b) a constant
(c) zero
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question:
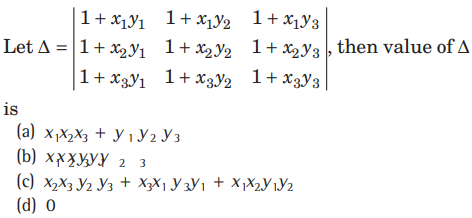
Answer
D
Question: Let px4 +qx3+ rx2 +sx+t =
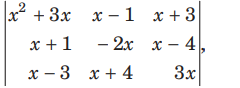
where p, q, r, s and t are constants, then tis equal to
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) –1
Answer
A
Question:
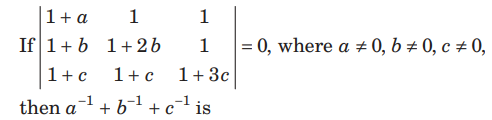
(a) 4
(b) – 3
(c) – 2
(d) – 1
Answer
B
Question: If [ ] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to the real number under consideration and – 1≤ x<0; 0 ≤ y<1;1≤ z <2, then the value of the determinant
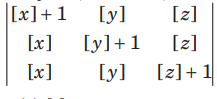
(a) [x]
(b) [y]
(c) [z]
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question:
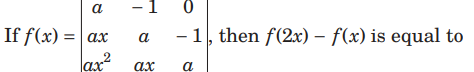
(a) ax
(b) ax (2a+3x)
(c) ax(2+3x)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If a ≠ b ≠ c , the value of x which satisfies the equation
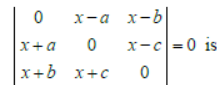
(a) x = 0
(b) x = a
(c) x = b
(d) x = c
Answer
A
Question. If ω is a cube root of unity and △ (Image 80) then △2 is equal to:
(a) −ω
(b) ω
(c) 1
(d) ω2
Answer
B
Question.
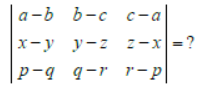
(a) a(x + y + z) + b( p + q + r) + c
(b) 0
(c) abc + xyz + pqr
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question.
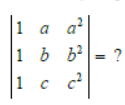
(a) a2 + b2 + c2
(b) (a + b) (b + c) (c + a)
(c) (a − b)(b − c)(c − a)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If a + b + c = 0 , then the solution of the equation
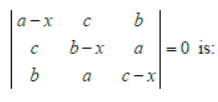
(a) 0
(b) ± 3/2 (a2 + b2 + c2)
(c) 0± √3/2(a2 + b2 + c2)
(d) 0± (a2 + b2 + c2)
Answer
C
Question. If

and A1,B1,C1 denote the cofactors of a1, b1, c1 respectively, then the value of the determinant
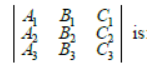
(a) △
(b) △2
(c) △3
(d) 0
Answer
B
Question. The determinant
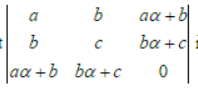
is equal to zero, then:
(a) a, b, c are in AP
(b) a, b, c are in GP
(c) a, b, c are in HP
(d) (x – α) is a factor of ax2 + 2bx + c
Answer
A,D
Question. For 3 × 3 matrices M and N, which of the following statement(s) is (are) not correct ?
(a) T N M N is symmetric or skew-symmetric, according as M is symmetric or skew-symmetric
(b) MN – NM is is symmetric for all symmetric matrices M and N
(c) M N is symmetric for all symmetric matrices M and N
(d) (adj M) (adj N) = adj (MN) for all invertible matrices M and N
Answer
C,D
Question.
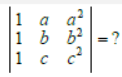
(a) a2 + b2 + c2
(b) (a + b)(b + c)(c + a)
(c) (a − b)(b − c)(c − a)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. If the value of a third order determinant is 11, then the value of the square of the determinant formed by the cofactors will be:
(a) 11
(b) 121
(c) 1331
(d) 14641
Answer
D
Question. If n ≠ 3k ≠ and 1, ω, ω2 are the cube roots of unity, then
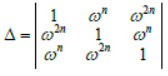
has the value:
(a) 0
(b) ω
(c) ω2
(d) 1
Answer
A
Question. For all values of A, B, C and P, Q, R the value of
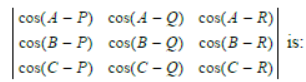
(a) 0
(b) cos A cos B cosC
(c) sin A sin B sin C
(d) cos P cosQ cos R
Answer
A
Question. If x, y, z are integers in AP. lying between 1 and 9 and x51, y41 and z31 are three digit numbers then the value of
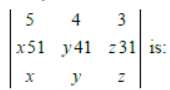
(a) x + y + z
(b) x − y + z
(c) 0
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The cofactor of the element ‘4’ in the determinant
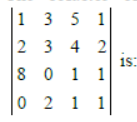
(a) 4
(b) 10
(c) – 10
(d) – 4
Answer
B
Question. The minors of – 4 and 9 and the co-factors of – 4 and 9 in determinant
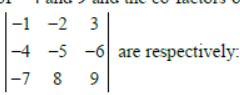
(a) 42, 3 ; – 42, 3
(b) –42, –3 ; 42, –3
(c) 42, 3 ; – 42, – 3
(d) 42, 3; 42, 3
Answer
B
Question. The value of
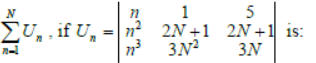
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) –1
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question. If

are the given determinants, then:
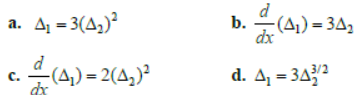
Answer
B
Question.

, then ∫0π/2 △(x)dx is equal to:
(a) 1/4
(b) 1/2
(c) 0
(d) –1/2
Answer
D
Question. The roots of the equation
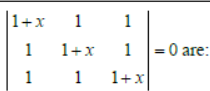
(a) 0, – 3
(b) 0, 0, – 3
(c) 0, 0, 0, – 3
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Let M be a 2 × 2 symmetric matrix with integer entries. Then, M is invertible, if:
(a) the first column of M is the transpose of the second row of M
(b) the second row of M is the transpose of the first column of M
(c) M is a diagonal matrix with non-zero entries in the main diagonal
(d) the product of entries in the main diagonal of M is not the square of an integer.
Answer
C,D
Question. If the system of equations x + 2y − 3z =1, (k + 3)z = 3, (2k +1)x + z = 0 is inconsistent, then the value of k is:
(a) –3
(b) 1/2
(c) 0
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question.
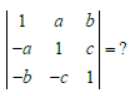
(a) 1+a2 + b2 + c2
(b) 1–a2 + b2 + c2
(c) 1+a2 + b2 – c2
(d) 1+a2 – b2 + c2
Answer
A
Question. The equations x+ y + z = 6, x + 2y +3z =10, x+2y +mz = n give infinite number of values of the triplet (x, y, z) if:
(a) m = 3, n ∈ R
(b) m = 3, n ≠ 10
(c) m = 3, n = 10
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The three lines ax + by + c = 0, bx + cy + a = 0, cx + ay + b = 0 are concurrent only when:
(a) a + b + c = 0
(b) a2 + b2 + c2 = ab + bc + ca
(c) a3 + b3 + c3 = ab + bc + ca
(d) None of these
Answer
A,B
Assertion and Reason
Note: Read the Assertion (A) and Reason (R) carefully to mark the correct option out of the options given below:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If the assertion and reason both are false.
e. If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Let A be a 2×2 matrix with non-zero entries and let A2 =I
where I is 2×2 identity matrix. Define Tr (A) = sum of diagonal elements of A and |A| = determinant of matrix A:
Assertion: Tr (A) =0
Reason: |A|=1.
Answer
B
Question. Let
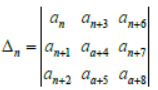
Assertion: If ak > ∀k ≥ and a1,a2,a3,… are in G.P. then △n = 0∀n≥1.
Reason: If a1,a2,a3, . . . . are in (a)P. then n △n =0∀n≥1.
Answer
B
Question. Suppose
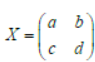
satisfies the equation X2 – 4X + 3I = O
Assertion: If a + d ≠ 4, then there are just two such matrices X.
Reason: There is infinite number of matrices X, satisfying
X2 – 4X + 3I = 0.
Answer
B
Question. Let A be a 2×2matrix
Assertion: adj(adjA) = A
Reason: |adjA| = |A|
Answer
B
Question. Assertion:
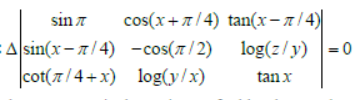
Reason: A skew symmetric determinant of odd order equals 0.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Let 0 p < and α1 , α2,… α9 be the nine roots x9= p, of then
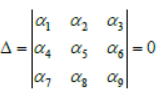
Reason: If two rows of a determinant are identical, then determinant equals zero.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion: If A∈Mn(R), A ≠ O with det (A) = 0, then det
(Adj A) = 0
Reason: For (R), A∈Mn det (Adj A) = (det 1 )n An-1
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: If a1 , b1 ∈ N for i = 1,2,3 and

then coefficient of x in expansion of △(x̅) is 0.
Reason: If P(x) = (1+ x)n ,n∈N then coefficient of x in the expansion of P(x) is P'(0).
Answer
A
Question. Consider the system of equations x − 2y + 3z = −1,
x − 3y + 4z =1 and −x + y − 2z = k
Answer
A
Assertion: The system of equation has no solution for k ≠ 0 and
Reason: The determinant
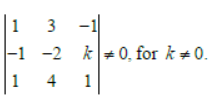
Answer
C
Paragraph
Let p be an odd prime number and Tp be the following set of 2 × 2 matrices
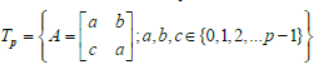
Question. The number of A in Tp such that A is either symmetric or skew-symmetric or both, and det (A) is divisible by p is
(a) (p – 1)2
(b) 2(p – 1)
(c) (p – 1)2+1
(d) 2p – 1
Answer
D
Question. The number of A in p T such that the trace of A is not divisible by p but det(A) is divisible by p is:
[Note: The trace of a matrix is the sum of its diagonal entries.]
(a) (p – 1) (p2 – p + 1)
(b) p3 – (p – 1)2
(c) (p – 1)2
(d) (p – 1) (p2 – 2)
Answer
C
Question. The number of A in Tp such that det(A) is not divisible by p is:
(a) 2p2
(b) p3 – 5p
(c) p3 – 3p
(d) p3 – p2
Answer
D
Let A and B are two matrices of same order 3×3 where
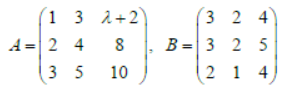
Question. If A is singular matrix, then tr(A + B)is equal to:
(a) 6
(b) 12
(c) 24
(d) 17
Answer
C
Question. If matrix 2A + 3B is singular, then the value of 2λ is:
(a) 11
(b) 13
(c) 15
(d) 17
Answer
D
Question. If λ = 3, then 1/7 (tr(AB) + tr (BA) is equal to:
(a) 34
(b) 42
(c) 84
(d) 63
Answer
A
Question. If
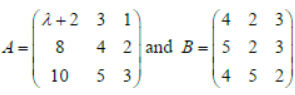
if tr(A –2B) = 0, then the value of λ is:
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 9
Answer
C
Question. The correct statement is:
(a) (A + B)(A − B) = A2 + B2 − 2AB
(b) (A+ B)2 = A2 + B2 + AB + BA
(c) (A + B)2 = A2 + B2 + 2AB
(d) none of above
Answer
B
Question. Suppose a, b, c ∈ R and abc = 1 If
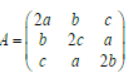
is such that AA’ = 4I and |A|>0, then the value of (a3 + b3 + c3)4 must be:
Answer
256
Question. Suppose a matrix A satisfied A2 – 5A + 7I = O. If A5 =aA + bI, then the value of 2a – 3b must be:
Answer
1453
Question.

then the value of A2 must be:
Answer
576
Question. If
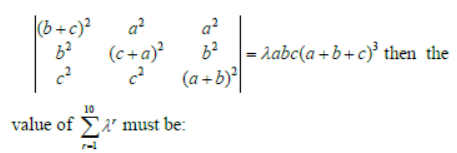
Answer
2046
Question. If a2 + b2 + c2 = –2 and then f(x) is a polynomial of degree:
Answer
2
Question. The value of
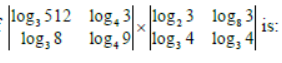
Answer
10
Question. If
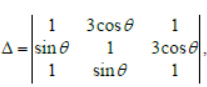
then the |Maximum value of △– Minimum value of △|3 is equal to:
Answer
1000


