Please refer to Structure of the Atom MCQ Questions Class 9 Science below. These MCQ questions for Class 9 Science with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books, and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Structure of the Atom will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Structure of the Atom MCQ Questions Class 9 Science
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Structure of the Atom in Class 9 Science. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 9 based on the latest examination guidelines.
MCQ Questions Class 9 Science Structure of the Atom
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Question. Na+ ion is isoelectronic with
(a) Li+
(b) Mg2+
(c) Ca2+
(d) Ba2+
Answer
B
Question. The valency of an element is
(a) the mass of the element displacing 1 part by the mass of hydrogen
(b) the mass of the element combining with 8 parts by the mass of oxygen
(c) the number of atoms of hydrogen combining with 1 atom of the given element
(d) the number of atoms in 1 molecule of the given statement.
Answer
C
Question. Maximum number of electrons which can be filled in the third shell of an atom is
(a) 8
(b) 18
(c) 10
(d) 32
Answer
B
Question. Cathode rays are made up of
(a) positively charged particles
(b) negatively charged particles
(c) neutral particles
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question. Rutherford’s alpha particle scattering experiment eventually led to the conclusion that
(a) mass and energy are related
(b) nucleus is present in the centre of the atom
(c) neutrons are buried deep in the nucleus
(d) the point of impact with matter can be precisely determined.
Answer
B
Question. Neutrons are present in the nucleus of all atoms, except
(a) hydrogen
(b) helium
(c) lithium
(d) boron
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following particles is not deflected by a magnetic field?
(a) Proton
(b) Neutron
(c) Electron
(d) All of these
Answer
B
Question. MgCl2 is the formula for an ionic compound of magnesium and chlorine. If the charge on Cl is -1, then the charge on Mg must be
(a) +2
(b) +3
(c) -2
(d) -3
Answer
A
Question. A cation has a positive charge because
(a) there are more protons than neutrons
(b) the neutrons in the nucleus are charged
(c) there are fewer electrons than protons
(d) there are more electrons than protons
Answer
C
Question. The element with the atomic number 3 is likely to have similar chemical properties to the element with the atomic number
(a) 5
(b) 11
(c) 8
(d) 20
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following has the same number of electrons as an oxide ion (O2-)?
(a) K+
(b) Mg2+
(c) Cl–
(d) S2-
Answer
B
Question. Mass of proton is
(a) equal to the mass of hydrogen atom
(b) less than the mass of hydrogen atom
(c) negligible
(d) more than the mass of hydrogen atom
Answer
A
Question. The number of neutrons in the element 94Be is
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 9
(d) 13
Answer
B
Question. Atom X and atom Y have similar chemical properties. If the proton number of atom X is 12, What is the likely proton number of atom Y ?
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 14
(d) 20
Answer
D
Question. A neutral atom (atomic number > 1) has
(a) electron and proton
(b) neutron and electron
(c) neutron, electron and proton
(d) neutron and proton
Answer
C
Question. Maximum number of electrons in any orbit is
(a) n2
(b) 2n2
(c) 1/2n2
(d) none of these
Answer
B
Question. The part of an atom where nearly whole mass is concentrated is called
(a) extra-nuclear part
(b) nucleus
(c) atom
(d) neutron
Answer
B
Question. In the nucleus of 4020Ca , there are
(a) 40 protons and 20 electrons
(b) 20 protons and 40 electrons
(c) 20 protons and 20 neutrons
(d) 20 protons and 40 neutrons
Answer
C
Question. The electronic structure of an ion Z2- is 2, 8. The number of neutrons is 11. The nucleon number of Z is
(a) 16
(b) 19
(c) 20
(d) 21
Answer
B
Question. In 1932. J. Chadwick discovered another sub-atomic particle which had no charge and a mass nearly equal to that of a proton. It was eventually named as
(a) proton
(b) neutron
(c) electron
(d) a -particle
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a property of isotopes?
(a) They have the same number of electrons.
(b) They have different numbers of protons.
(c) They have different chemical properties.
(d) They have the same mass number.
Answer
A
Question. X and Y are the two atomic species:
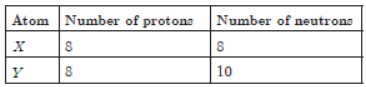
Select the correct statement about X and Y .
(a) X and Y are isobars
(b) X and Y have different chemical properties
(c) X and Y have different physical properties
(d) X and Y are the atoms of different elements
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following shows the electronic configuration of Ca2+?
(a) He
(b) Ne
(c) Ar
(d) F—
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following do not represent Bohr’s model of an atom correctly?

(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
Answer
C
FILL IN THE BLANK
Question. An atom of an element has 11 protons, 11 electrons and 12 neutrons. The atomic mass of the atom is ………
Answer
23
Question. Isotopes are the atoms of ……… element, having same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Answer
same
Question. According to Maharishi Kanad, the tiniest to tiny particle of a pure substance is called ……….
Answer
anu
Question. Cathode rays are a beam of fast moving ……….
Answer
electrons
Question. The K-shell of any atom cannot have more than ………. electrons.
Answer
two
TRUE/FALSE
Question. An electron has a mass that is much less than a proton.
Answer
True
Question. a -particles are same thing as helium atoms.
Answer
True
Question. The innermost atomic shell can hold a maximum of 18 electrons.
Answer
False
Question. Atoms of an element may have more or less neutrons or electrons than other atoms of the same element.
Answer
True
MATCHING QUESTIONS
2.
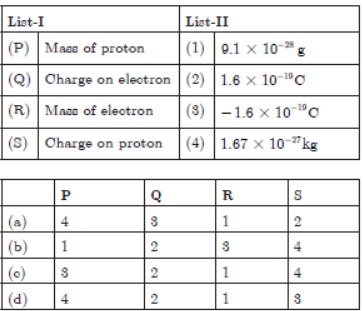
Answer
(a) P – 4, Q – 3, R – 1, S – 2
4.
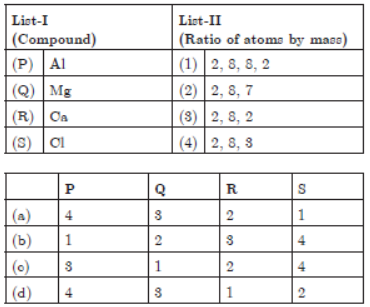
Answer
(d) P – 4, Q – 3, R – 1, S – 2
ASSERTION AND REASON
Question. Assertion : Isobars are identical in chemical properties.
Reason : Isobars have same atomic number.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Thomson’s atomic model is known as ‘raisin pudding’ model.
Reason : The atom is visualized as a pudding of positive charge with electrons (raisins) embedded in it.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Anions are larger in size than the parent atom.
Reason : In an anion, the number of protons in the nucleus is less than the number of electrons moving around it.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The mass of the total number of protons and neutrons is a measure of the approximate mass of an atom.
Reason : The mass of an electron is negligible.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The atoms of different elements having same mass number but different atomic numbers are known as isobars.
Reason : The sum of protons and neutrons, in the isobars is always different.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom.
Reason : The electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Cathode rays travel in straight lines.
Reason : Cathode rays do not penetrate through thin sheets.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Isotopes of an element show different valencies.
Reason : Isotopes have different atomic numbers.
Options:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
Answer
D
