Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry Surface Chemistry Chapter 5 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the Class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Surface Chemistry Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry
Question. The adsorption of a gas on a solid surface varies with pressure of the gas in which of the following manner
(a) Fast → slow → independent of the pressure
(b) Slow → fast → independent of the pressure
(c) Independent of the pressure → fast → slow
(d) Independent of the pressure → slow → fast
Answer
A
Question. Alloy is an example of
(a) gel
(b) solidified emulsion
(c) solid solution
(d) sol
Answer
C
Question. Pure water can be obtained from sea water by
(a) Centrifugation
(b) Plasmolysis
(c) Reverse osmosis
(d) Sedimentation
Answer
C
Question. How many layers are adsorbed in chemical adsorption ?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Many
(d) Zero
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following equation does not represent homogeneous catalysis?

Answer
B
Question. Hair cream is an example of
(a) gel
(b) sol
(c) aerosol
(d) foam
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following is correctly matched?
(a) Emulsion-smoke
(b) Gel-butter
(c) Aerosol-hair cream
(d) Sol-whipped cream
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is most effective in causing the coagulation of ferric hydroxide sol?
(a) KCl
(b) KNO3
(c) K2SO4
(d) K3[Fe(CN)6]
Answer
D
Question. Small liquid droplets dispersed in another liquid is called
(a) gel
(b) suspension
(c) emulsion
(d) true solution
Answer
C
Question. When dispersed phase is liquid and dispersion medium is gas then the colloidal system is called
(a) Smoke
(b) Clouds
(c) Jellies
(d) Emulsions
Answer
B
Question. Which is adsorbed in maximum amount by activated charcoal ?
(a) N2
(b) CO2
(c) Cl2
(d) O2
Answer
B
Question. Which one is a colloid?
(a) Sodium chloride
(b) Urea
(c) Cane sugar
(d) Blood
Answer
D
Question. The migration of dispersion medium under the influence of an electric potential is called :
(a) Cataphoresis
(b) Electroosmosis
(c) Electrophoresis
(d) Sedimentation
Answer
B
Question. A colloid always :
(a) Contains two phases
(b) Is a true solution
(c) Contains three phases
(d) Contains only water soluble particles
Answer
A
Question.Tyndall effect shown by colloids is due to :
(a) scattering of light by the particles
(b) movement of particles
(c) reflection of light by the particles
(d) coagulation of particles
Answer
A
Question.How non-polar and polar part in micelle are arranged ?
(a) Polar at outer surface and non-polar at inner surface
(b) Polar at inner surface and non-polar at outer surface
(c) Both polar and non-polar at inner surface
(d) Distributed all over the surface
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a lyophilic colloid ?
(a) Milk
(b) Gum
(c) Fog
(d) Blood
Answer
B
Question. Catalytic poisons act by :
(a) making the products chemically inactive.
(b) increasing the rate of the backward reaction.
(c) chemical combination with any one of the reactants.
(d) preferential adsorption on the catalyst surface.
Answer
D
Question. Freundlich equation for adsorption of gases (in amount of x g) on a solid (in amount of m g) at constant temperature can be expressed as
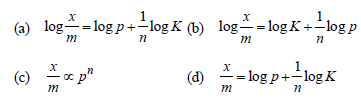
Answer
B
Question. In physical adsorption, gas molecules are bound on the solid surface by
(a) chemical forces
(b) electrostatic forces
(c) gravitational forces
(d) van der Waal’s forces
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct ?
(a) Physical adsorption is due to van der Waal’s forces
(b) Chemical adsorption first decreases with increase in temperature.
(c) Physical adsorption is reversible
(d) Adsorption energy for a chemical adsorption is generally greater than that of physical adsorption.
Answer
B
Question. Example of intrinsic colloid is
(a) glue
(b) sulphur
(c) Fe
(d) As2S3
Answer
A
Question. The ion that is more effective for the coagulation of As2S3 sol is
(a) Ba2+
(b) Na+
(c) PO43–
(d) AI3+
Answer
D
Question. If dispersed phase is a liquid and the dispersion medium is a solid, the colloid is known as
(a) a sol
(b) a gel
(c) an emulsion
(d) a foam
Answer
B
Question. The formation of micelles takes place only above
(a) inversion temperature
(b) Boyle temperature
(c) critical temperature
(d) Kraft temperature
Answer
D
Question. Butter is a colloid formed when
(a) Fat is dispersed in water
(b) Fat globules are dispersed in water
(c) Water is dispersed in fat
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. During dialysis
(a) only solvent molecules can diffuse
(b) solvent molecules, ions and colloidal particles can diffuse
(c) all kinds of particles can diffuse through the semipermeable membrane
(d) solvent molecules and ions can diffuse
Answer
D
Question. The electrolytic impurities of a sol can most easily be separated by
(a) dialysis
(b) electrosmosis
(c) electrophoresis
(d) electrodialysis
Answer
D
Question. The formation of colloid from suspension is
(a) Peptisation
(b) Condensation
(c) Sedimentation
(d) Fragmentation
Answer
A
Question. The separation of colloidal particles from particles of molecular dimensions is known as
(a) sedimentation
(b) dispersion
(c) pyrolysis
(d) dialysis
Answer
D
Question. Which one is an example of multimolecular colloid system
(a) Soap dispersed in water
(b) Protein dispersed in water
(c) Gold dispersed in water
(d) Gum dispersed in water
Answer
C
Question. The movement of colloidal particles towards their respective electrodes in the presence of an electric field is known as :
(a) electrolysis
(b) Brownian movement
(c) electrodialysis
(d) electrophoresis
Answer
D
Question. The action of enzymes in living system is to :
(a) supply energy to tissues
(b) enhance immunity
(c) circulate oxygen
(d) enhance the rate of biochemical reactions.
Answer
D
Question. An aerosol is a :
(a) dispersion of a solid or liquid in a gas
(b) dispersion of a solid in a liquid
(c) dispersion of a liquid in a liquid
(d) solid solution
Answer
A
Question. Colloidal gold is prepared by
(a) Mechanical dispersion
(b) Peptisation
(c) Bredig’s Arc method
(d) Hydrolysis
Answer
C
Question. Associated colloid among the following is
(a) enzymes
(b) proteins
(c) cellulose
(d) sodium stearate
Answer
D
Question. Hardy-Schulze rule explains the effect of electrolytes on the coagulation of colloidal solution. According to this rule,coagulation power of cations follow the order
(a) Ba+2 > Na+ > Al+3
(b) Al+3 > Na+ > Ba+2
(c) Al+3 > Ba+2 > Na+
(d) Ba+2 > Al+3 > Na+
Answer
C
Question. Tyndall effect is shown by
(a) sol
(b) solution
(c) plasma
(d) precipitate
Answer
A
Question. The cause of Brownian movement is
(a) heat changes in liquid state
(b) convectional currents
(c) the impact of molecules of the dispersion medium on the colloidal particles.
(d) attractive forces between the colloidal particles and molecules of dispersion medium.
Answer
C
Question. Peptization denotes
(a) Digestion of food
(b) Hydrolysis of proteins
(c) Breaking and dispersion into the colloidal state
(d) Precipitation of solid from colloidal dispersion
Answer
C
Question. The simplest way to check whether a system is colloidal or not is by
(a) Tyndall effect
(b) Brownian movement
(c) Electrodialysis
(d) Measuring particle size
Answer
A
Question. Surface tension of lyophilic sols is
(a) lower than that of H2O
(b) more than that of H2O
(c) equal to that of H2O
(d) either less or more than H2O depending upon the nature of disperse phase
Answer
A
Question. The ability of an ion to bring about coagulation of a given colloid depends upon
(a) its size
(b) the magnitude of its charge
(c) the sign of its charge
(d) both magnitude and sign of its charge
Answer
D
Question. Cheese is an example of
(a) solid sol
(b) emulsion
(c) gel
(d) foam
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following in not a colloidal solution?
(a) Smoke
(b) Ink
(c) Blood
(d) Air
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following acts as protective colloid?
(a) Silica gel
(b) Gelatin
(c) Sodium acetate
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Suspensions are
(a) Visible to naked eye
(b) Not visible by any means
(c) Invisible under electron microscope
(d) Invisible through microscope
Answer
A
Question. A precipitate is changed to colloidal solution by the following process :
(a) dialysis
(b) ultrafiltration
(c) peptization
(d) electrophoresis
Answer
C
Question. Lyophobic colloids are :
(a) gun proteins
(b) protective colloids
(c) irreversible colloids
(d) reversible colloids
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is used for neutralising charge on colloidal solution?
(a) Electrons
(b) Electrolytes
(c) Positively charged ions
(d) Compounds
Answer
B
Question. Cloud or fog is an example of colloidal system of
(a) Liquid dispersed in gas
(b) Gas dispersed in gas
(c) Solid dispersed in gas
(d) Solid dispersed in liquid
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following curves is in accordance with Freundlich adsorption isotherm ?

Answer
C
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) As2S3 sol (p) Bredig’s Arc method
(B) Fe(OH)3 sol (q) Double decomposition
(C) Colloidal sols of metals (r) Peptization
like Au, Ag, Pt, etc.
(D) Conversion of freshly (s) Hydrolysis
prepared precipitate
into a colloidal sol
(a) A – (q), B – (s), C – (r), D – (p)
(b) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(c) A – (s), B – (q), C – (p), D – (r)
(d) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
Answer
D
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(Catalyst) (Industrial product)
(A) V2O5 (p) High density poly-ethylene
(B) Ziegler-Natta (q) Polyacrylonitrile
(C) Peroxide (r) NH3
(D) Finely divided Fe (s) H2SO4
(a) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r)
(b) A – (s), B – (r), C – (q), D – (p)
(c) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)
(d) A – (s), B – (q), C – (p), D – (r)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Oil in water emulsion (p) Clouds
(B) Aerosols containing (q) Vanishing cream
small droplets of water
suspended in air
(C) When river water meets (r) Smoke
the sea water
(D) Colloidal solution of (s) Formation of delta
carbon, arsenic
compounds, dust etc.
in air
(a) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(b) A – (p), B – (q), C – (s), D – (r)
(c) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(d) A – (q), B – (p), C – (r), D – (s)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
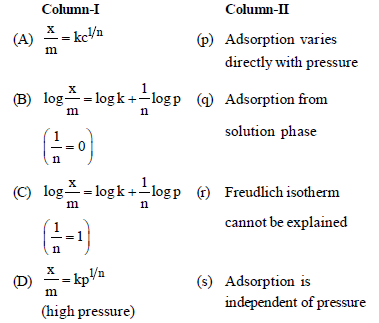
(a) A – (q), B – (s), C – (p), D – (r)
(b) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r)
(c) A – (r), B – (p), C – (s), D – (q)
(d) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Butter (p) dispersion of liquid in liquid
(B) Pumice stone (q) dispersion of solid in liquid
(C) Milk (r) dispersion of gas in solid
(D) Paints (s) dispersion of liquid in solid
(a) A – (r), B – (s), C – (p), D – (q)
(b) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
(c) A – (q), B – (r), C – (p), D – (s)
(d) A – (s), B – (r), C – (q), D – (p)
Answer
B
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) In this process molecules (p) Dialysis
and ions diffuse through
membrane outside and
pure colloidal solution
is left behind.
(B) This process is used (q) Ultrafilteration
if the dissolved substance
in the impure colloidal
solution is only an
electrolyte
(C) In this process ordinary (r) Electro-dialysis
filter paper is soaked into
collodion (4% solution of
nitrocellulose in a mixture
of alcohol and ether)
(a) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q)
(c) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r)
(d) A – (q), B – (r), C – (p)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Argyrol (p) Kalazar
(B) Antimony (q) Intramuscular injection
(C) Colloidal gold (r) Stomach disorders
(D) Milk of magnesia (s) Eye lotion
(a) A – (r), B – (p), C – (s), D – (q)
(b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)
(c) A – (s), B – (q), C – (p), D – (s)
(d) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r)
Answer
D
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Sulphur vapours passed (p) Normal electrolyte
through cold water solution
(B) Soap mixed with water (q) Molecular colloids
above critical micelle
concentration
(C) White of egg whipped (r) Associated colloid
with water
(D) Soap mixed with water (s) Macro molecular
below critical micelle colloids
concentration
(a) A – (q), B – (r), C – (s), D – (p)
(b) A – (r), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p)
(c) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
(d) A – (q), B – (s), C – (r), D – (p)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns

(a) A – (p), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s)
(b) A – (p), B – (q), C – (r), D – (s)
(c) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)
(d) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Dialysis (p) Cleansing action of soap
(B) Peptisation (q) Coagulation
(C) Emulsification (r) Colloidal sol formatioin
(D) Electrophoresis (s) Purification
(a) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q)
(b) A – (q), B – (r), C – (p), D – (s)
(c) A – (s), B – (p), C – (r), D – (q)
(d) A – (s), B – (r), C – (q), D – (p)
Answer
A
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II
(A) Protective colloid (p) FeCl3 + NaOH
(B) Liquid – liquid colloid (q) Lyophilic colloids
(C) Positively charged colloid (r) Emulsion
(D) Negatively charged colloid (s) FeCl3 + hot water
(a) A – (q), B – (r), C – (p), D – (s)
(b) A – (p), B – (r), C – (s), D – (q)
(c) A – (q), B – (r), C – (s), D – (p)
(d) A – (r), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p)
Answer
C
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contains two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : According to Freundlich: . x/m = k. p 1/ n
Reason : The isotherm shows variation of the amount of gas adsorbed by the adsorbent with temperature.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : The enthalpy of physisorption is greater than chemisorption.
Reason : Molecules of adsorbate and adsorbent are held by van der Waal’s forces in physisorption and by chemical bonds in chemisorption.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : The value of colligative properties are of small order for colloids as compared to true solution.
Reason : Number of particles in colloidal solution is comparatively smaller than true solutions.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : The relation x/m = k. p 1/ n is known as Freundlich adsorption isotherm, where x is the mass of gas adsorbed by m grams of adsorbate, p is the equilibrium pressure, k and n are constants for given system and temperature.
Reason : When several substances have same value of 1/n, the lines by which their adsorption isotherms can be represented will meet at a point.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: Detergents with low CMC are more economical to use.
Reason: Cleansing action of detergents involves the formation of micelles. These are formed when the concentration of detergents becomes equal to CMC.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: An ordinary filter paper impregnated with collodion solution stops the flow of colloidal particles.
Reason: Pore size of the filter paper becomes more than the size of colloidal particle.
Answer
C
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Quetion. In petrochemical industry alcohols are directly converted to gasoline by passing over heated
(a) Platinum
(b) ZSM-5
(c) Iron
(d) Nickel
Answer
B
Quetion. Methylene blue, from its aqueous solution, is adsorbed on activated charcoal at 25°C. For this process, which of the following statement is correct ?
(a) The adsorption requires activation at 25°C
(b) The adsorption is accompanied by a decrease in enthalpy
(c) The adsorption increases with increase of temperature
(d) The adsorption is irreversible
Answer
B
Quetion. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Colloidal gold is used for intramuscular injection.
(b) Colloidal solution of latex is used in preparation of rubber.
(c) Photographic films are prepared by coating an emulsion of AgBr in gelatin over glass plate.
(d) Tannin used in leather industry contains positively charged colloidal particles.
Answer
D
Quetion. Which of the following statements regarding difference between adsorption and absorption is incorrect?
(a) Adsorption is a surface whereas absorption is a bulk phenomena.
(b) Water vapours are absorbed by anhydrous CaCl2 but adsorbed by silica gel.
(c) Adsorption and absorption take place individually.They can not occur simultaneously.
(d) All of the above statements are correct.
Answer
C
Quetion. Which of the following statements regarding catalyst is not true ?
(a) A catalyst remains unchanged in composition and quantity at the end of the reaction
(b) A catalyst can initiate a reaction
(c) A catalyst does not alter the equilibrium in a reversible reaction
(d) Catalysts are sometimes very specific in respect of reaction
Answer
B
Quetion. Which of the following combinations of dispersed phase and dispersion medium will not form a colloid ?
(a) Dispersed phase – Solid, Dispersion medium – Solid.
(b) Dispersed phase – Solid, Dispersion medium – Gas.
(c) Dispersed phase – Gas, Dispersion medium – Gas.
(d) Dispersed phase – Liquid, Dispersion medium – Gas.
Answer
C
Quetion. Which of the following statements about a catalyst is true ?
(a) A catalyst accelerates the reaction by bringing down the free energy of activation
(b) A catalyst also takes part in the reaction mechanism
(c) A catalyst makes the reaction more feasible by making the ΔGº more negative
(d) A catalyst makes the equilibrium constant of the reaction more favourable for the forward reaction
Answer
A
Quetion. Flocculation value of BaCl2 is much less than that of KCl for sol A and flocculation value of Na2SO4 is much less than that of NaBr for sol B. The correct statement among the following is :
(a) Both the sols A and B are negatively charged.
(b) Sol A is positively charged arid Sol B is negatively charged.
(c) Both the sols A and B are positively charged.
(d) Sol A is negatively charged and sol B is positively charged.
Answer
B
Quetion. Which one of the following, statements is incorrect about enzyme catalysis?
(a) Enzymes are mostly protenious in nature.
(b) Enzyme action is specific.
(c) Enzymes are denaturated by ultraviolet rays and at high temperature.
(d) Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature.
Answer
D
Quetion. Which of the following is not correctly matched ?
(a) Sulphur sol – Oxidation
(b) Gold sol – Double decomposition
(c) Fe(OH)3 sol – Hydrolysis
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
B
Quetion. How does a delta form at the meeting place of sea and river water?
(a) The electrolyte present in sea water coagulate the clay
(b) the electrolyte present in sea water has no role
(c) the electrolyte present in river water coagulate the clay
(d) Both (a) and (c) are correct
Answer
A
Quetion. Which one of the following statements is incorrect in the case of heterogeneous catalysis ?
(a) The catalyst lowers the energy of activation
(b) The catalyst actually forms a compound with the reactant
(c) The surface of the catalyst plays a very important role
(d) There is no change in the energy of activation.
Answer
C
Quetion. Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding physisorptions?
(a) More easily liquefiable gases are adsorbed readily.
(b) Under high pressure it results into multimolecular layer on adsorbent surface.
(c) Enthalpy of adsorption ( ΔHadsorption) is low and positive.
(d) It occurs because of van der Waal’s forces.
Answer
C
Quetion. Which of the following feature of catalysts is described in reactions given below?
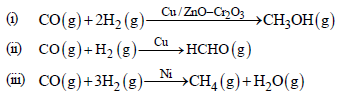
(a) Activity
(b) Selectivity
(c) Catalytic promoter
(d) Catalytic poison
Answer
B
Quetion. Which is correct about physical adsorption?
(a) High temperature and high pressure favour adsorption
(b) High temperature and low pressure favour adsorption
(c) Low temperature and high pressure favour adsorption
(d) Low temperature and low pressure favour adsorption
Answer
C
Quetion. The dispersed phase and dispersion medium in soap lather are respectively
(a) gas and liquid
(b) liquid and gas
(c) solid and gas
(d) solid and liquid
Answer
A
Quetion. On the basis of data given below predict which of the following gases shows least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?
Gas CO2 SO2 CH4 H2
Critical temp./K 304 630 190 33
(a) CO2
(b) SO2
(c) CH4
(d) H2
Answer
D
Quetion. Which of the following forms a colloidal solution in water ?
(a) NaCl
(b) Glucose
(c) Starch
(d) Barium nitrate
Answer
C
Quetion. Which one of the following is not applicable to the phenomenon of adsorption ?
(a) ΔH > 0
(b) ΔG < 0
(c) ΔS < 0
(d) ΔH < 0
Answer
A
Quetion. Which of the following forms cationic micelles above certain concentration?
(a) Sodium dodecyl sulphate
(b) Sodium acetate
(c) Urea
(d) Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
Answer
D
Quetion. Given below, catalyst and corresponding process/reaction are matched. The one with mismatch is
(a) [RhCl(PPh3)2] : Hydrogenation
(b) TiCl4 + Al (C2H5)3 : Polymerization
(c) V2O5 : Haber-Bosch process
(d) Nickel : Hydrogenation
Answer
C
Quetion. Which of the following does not contain a hydrophobic structure ?
(a) Linseed oil
(b) Lanolin
(c) Glycogen
(d) Rubber
Answer
D
Quetion. In the adsorption of a gas on solid, Freundlich isotherm is obeyed. The slope of the plot is zero. Then the extent of adsorption is
(a) directly proportional to the pressure of the gas
(b) inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas
(c) directly proportional to the square root of the pressure of the gas
(d) independent of the pressure of the gas
Answer
D
Quetion. Bredig arc method cannot be used to prepare colloidal solution of which of the following
(a) Pt
(b) Fe
(c) Ag
(d) Au
Answer
B
Quetion. Colloid of which one of the following can be prepared by electrical dispersion method as well as reduction method ?
(a) Sulphur
(b) Ferric hydroxide
(c) Arsenious sulphide
(d) Gold
Answer
D
Quetion. Which one of the following is an example for multimolecular colloid?
(a) Aqueous starch sol
(b) Aqueous enzyme sol
(c) Alcoholic polystyrene sol
(d) Aqueous sol of sodium laurylsulphate
Answer
A
Quetion. Which of the following will be most effective in the coagulation of Al(OH)3 sol ?
(a) KCN
(b) BaCl2
(c) NaCl
(d) Mg3(PO4)2
Answer
D
Quetion. Which of the following is not a colloid ?
(a) Chlorophyll
(b) Smoke
(c) Ruby glass
(d) Milk
Answer
A
Quetion. The disperse phase in colloidal iron (III) hydroxide and colloidal gold is positively and negatively charged,respectively. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
(a) Coagulation in both sols can be brought about by electrophoresis
(b) Mixing the sols has no effect
(c) Sodium sulphate solution causes coagulation in both sols
(d) Magnesium chloride solution coagulates, the gold sol more readily than the iron (III) hydroxide sol.
Answer
B
Quetion. Which of the following is not an application of adsorption?
(a) In metallurgy for concentration of sulphide ores.
(b) In heterogeneous catalysis involving solid catalyst.
(c) In homogeneous catalysis.
(d) Separation of inert gas.
Answer
C
Quetion. In Brownian movement or motion, the paths of the particles are
(a) Linear
(b) Zig-zag
(c) Uncertain
(d) Curve
Answer
B
Quetion. Point out the false statement :
(a) The colloidal solution of a liquid in liquid is called gel
(b) Hardy Schulze rule is related with coagulation
(c) Brownian movement and Tyndall effect are shown by colloidal system
(d) Gold number is a measure of the protective power of lyophilic colloid
Answer
A
Quetion. ………. is a silver sol used as an eye lotion. Fill in the blank with an appropriate answer.
(a) Amytol
(b) Argyrol
(c) Ciprofloxacin
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
A
Quetion. Colloidal solutions are not purified by
(a) Dialysis
(b) Electrodialysis
(c) Ultrafiltration
(d) Electrophoresis
Answer
D
Quetion. Which of the following will show Tyndall effect?
(a) Aqueous solution of soap below critical micelle concentration.
(b) Aqueous solution of soap above critical micelle concentration.
(c) Aqueous solution of sodium chloride.
(d) Aqueous solution of sugar.
Answer
B
Quetion. Which of the following ions can cause coagulation of proteins ?
(a) Ag+
(b) Na+
(c) Mg2+
(d) Ca2+
Answer
A
Quetion. A colloidal solution is subjected to an electric field. The particles move towards anode. The coagulation of same sol is studied using NaCl, BaCl2 and AlCl3 solutions. The order of their coagulation power should be –
(a) NaCl > BaCl2 > AlCl3
(b) BaCl2 > AlCl3 > NaCl
(c) AlCl3 > BaCl2 > NaCl
(d) BaCl2 > NaCl > AlCl3
Answer
C
Question. Why is adsorption always exothermic in nature?
Answer.When a gas is adsorbed on the surface of a solid, its entropy decreases and S becomes negative. Now G = H- TΔ S and for the process to be spontaneous, free energy
change must be negative. As TΔ S is negative i.e. -TΔ S is positive and for free energy change to be negative enthalpy change should be negative hence reaction should be exothermic always.
Question. Differentiate between lyophilic and lyophobic colloids.
Answer.a) Lyophilic sols are easily prepared by directly mixing with the liquid dispersion medium but lyophobic sols cannot be prepared directly by mixing with liquid.
lyophilic sols are stable and are not easily coagulated but lyophobic sols can be easily precipitated by the addition of suitable electrolyte.
Question.What is demulsification? Name two demulsifying agent.
Answer.The process of separation of constituent liquid of an emulsion is called demulsification. It can be done by either centrifuging or boiling.
Question. Why is the ester hydrolysis slow in the beginning and becomes faster after some time?
Answer.RCOOR’ + H2O ———————→RCOOH + R’OH
The acid produced in above reaction act as auto catalyst for the reaction. Hence the reaction becomes faster after some time.
Question. Comment on the statement that “colloid is not a substance but state of a substance.”
Answer.The given statement is true. This is because the same substance may exist as colloid under certain conditions and as a crystalloid under certain conditions for e.g. NaCl in water behave as crystalloid but in benzene as a colloid. It is the size of solute particle which matters i.e. the state in which the substance exists. If it lies in the range of 1nm to 1000nm its a colloid.
Question. Why is it essential to wash the precipitate with water before estimating it quantitatively?
Answer.Some amount of the electrolytes mixed to form the precipitate remains adsorbed on the surface of the particles of the precipitate. Hence, it is essential to wash the precipitate with water to remove the sticking electrolytes or any other impurity before estimating it
quantitatively.
Question. Explain the terms coagulation, dialysis and Tyndall effect.
Answer.Coagulation is the process of aggregation of colloidal particles so as to change them into large sized particles which ultimately settles as precipitate.
Dialysis is the process of separating the particles of colloids from those of crystalloids by diffusion of the mixture through parchment membrane.
Scattering of light through colloidal solution by the colloid particles is called Tyndall effect
Question. What is the difference between multimolecular and macromolecular colloids? Give one example of each.
Answer.Multimolecular colloids are formed by the aggregation of large number of molecules (for e.g. S8). Macromolecular colloids are due to large size of molecule themselves (e.g. starch) so large that their size lies in the colloidal range.
Question. Give specific term to show the effect of the following process.
a) Ferric hydroxide is mixed with arsenic sulphide sol
b) Ferric chloride solution is mixed with freshly prepared precipitate of ferric hydroxide.
c) H2S is passed through arsenic oxide solution.
Answer.a) Coagulation b) Peptization c) Double decomposition
Question. Explain the following terms alcosol, aerosol and hydrosol.
Answer.Alcosol is colloidal dispersion having alcohol as dispersion medium e.g. collodion. Aerosol is colloidal dispersion of a liquid in gas for e.g. fog. Hydrosol is colloidal dispersion of a solid in liquid e.g. starch sol or egg albumin sol.
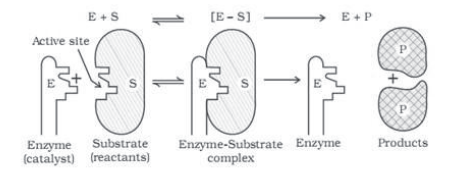
Question. What are enzymes? Write in brief the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
Answer.

Enzymes are basically protein molecules of high molecular masses. These form colloidal solutions when dissolved in water. These are complex, nitrogenous organic compounds
produced by living plants and animals. Enzymes are also called ‘biochemical catalysts’.
Mechanism of enzyme catalysis:
On the surface of the enzymes, various cavities are present with characteristic shapes. These cavities possess active groups such as -NH2,-COOH etc. The reactant molecules having a complementary shape fit into the cavities just like a key fits into a lock. This leads to the formation of an activated complex. This complex then decomposes to give the product. Hence,
Step 1: E+S → ES+
(Activated complex)
Step 2: ES → E+P
Question. Explain the mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
Answer. Mechanism of enzyme catalysed reactions-
There are active centres or cavities on the surface of enzyme particles. The molecules of the reaction or substrate which have complementary shape fit into these just like a key fits into a lock. This forms an activated complex which decomposes to yield products. The reactions proceed in two steps –
Step 1: Binding of enzymes to substrate to form activated complex.
E+S → ES
Step 2 : Decomposition of complex to form products.
ES → E+P
Question. What are the factors which influence the adsorption of a gas on a solid?
Answer. There are various factors that affect the rate of adsorption of a gas on a solid surface.
(1) Nature of the gas:
Easily liquefiable gases such as NH3 , HCl etc. are adsorbed to a great extent in comparison to gases such as H2,O2 etc. This is because Van der Waal’s forces are stronger in easily liquefiable gases.
(2) Surface area of the solid
The greater the surface area of the adsorbent, the greater is the adsorption of a gas on the solid surface.
(3) Effect of pressure
Adsorption is a reversible process and is accompanied by a decrease in pressure. Therefore,
adsorption increases with an increase in pressure.
(4) Effect of temperature
Adsorption is an exothermic process. Thus, in accordance with Le-Chatelier’s principle, the magnitude of adsorption decreases with an increase in temperature.
Question. Explain the following terms:
(i) Electrophoresis (ii) Coagulation
(iii) Dialysis (iv) Tyndall effect.
Answer. (i) Electrophoresis:
The movement of colloidal particles under the influence of an applied electric field is known as electrophoresis. Positively charged particles move to the cathode, while negatively charged particles move towards the anode. As the particles reach oppositely charged electrodes, they become neutral and get coagulated.
(ii) Coagulation:
The process of settling down of colloidal particles i.e., conversion of a colloid into a precipitate is called coagulation.
(iii) Dialysis
The process of removing a dissolved substance from a colloidal solution by the means of diffusion through a membrane is known as dialysis. This process is based on the principle that ions and small molecules can pass through animal membranes unlike colloidal particles.
(iv) Tyndall effect:
When a beam of light is allowed to pass through a colloidal solution, it becomes visible like a column of light. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This phenomenon takes place as particles of colloidal dimensions scatter light in all directions.
Question. Give four examples of heterogeneous catalysis.
Answer. (i) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide to form sulphur trioxide. In this reaction, Pt acts as a catalyst.

(ii) Formation of ammonia by the combination of dinitrogen and dihydrogen in the presence of finely divided iron.
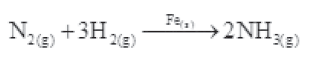
This process is called the Haber’s process.
(iii) Oswald’s process: Oxidation of ammonia to nitric oxide in the presence of platinum.

(iv) Hydrogenation of vegetable oils in the presence of Ni.

Question. What is an adsorption isotherm? Describe Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Answer. The plot between the extent of adsorption (x/m)against the pressure of gas (P) at constant temperature (T) is called the adsorption isotherm.
Freundlich adsorption isotherm:
Freundlich adsorption isotherm gives an empirical relationship between the quantity of gas adsorbed by the unit mass of solid adsorbent and pressure at a specific temperature.
From the given plot it is clear that at pressure PS, (x/m) reaches the maximum valve. Ps is called the saturation pressure. Three cases arise from the graph now.
Case I- At low pressure:
The plot is straight and sloping, indicating that the pressure in directly proportional to (x/m)
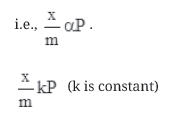
Case II- At high pressure:
When pressure exceeds the saturated pressure, (x/m) becomes independent of P values.
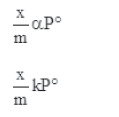
At intermediate pressure, (x/m) depends on P raised to the powers between 0 and 1. This relationship is known as the Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
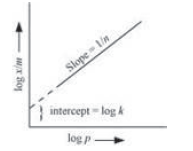
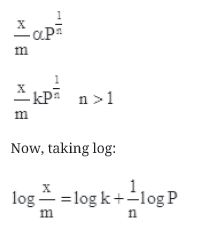
On plotting the graph between log (x/m) and log P, a straight line is obtained with the slope equal to 1/n and the intercept equal to log k.
Question. Explain Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
Answer. Freundlich adsorption isotherm gives an empirical relationship between the quantity of gas adsorbed by unit mass of solid adsorbent and pressure at a particular temperature The
relationship is
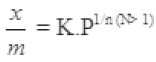
Where x is a mass of gas adsorbed on mass m of adsorbent at pressure P, K &n are constant that depend on the nature of adsorbent and adsorbate – The Relationship can be represented by plotting curves between x/m and P. They show that at a fix pressure, the physical adsorption decreases with increase in temperature.

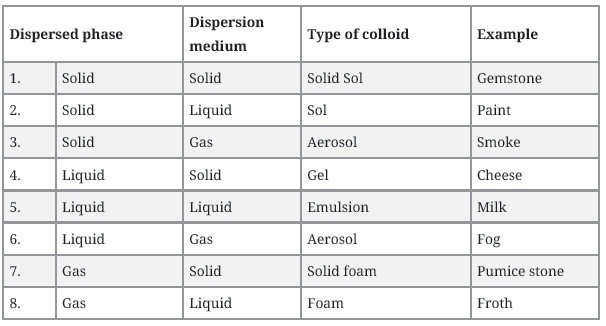
Question. How are the colloidal solutions classified on the basis of physical states of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
Answer. One criterion for classifying colloids is the physical state of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium. Depending upon the type of the dispersed phase and dispersion medium (solid, liquid, or gas), there can be eight types of colloidal systems.
Question. What are homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis? Give example.
Answer. Homogeneous catalysis –
When reactant and catalyst are in the same phase, the process is said to be homogeneous catalysis.
Examples –
(1) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide in the presence of oxygen gas and nitric oxide gas as catalyst.

(2) Hydrolysis of methyl acetate catalysed by H+ ions.
(3) Hydrolysis of sugar catalysed by H2SO4. .
Hetrogeneous Catalysis –
The catalytic process in which the reactant and catalyst are in different phases is known as heterogeneous catalysis.
Examples:-
(1) Oxidation of sulphur dioxide in presence of platinum.
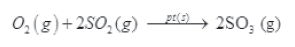
(2) Preparation of ammonia by Haber’s process
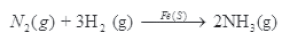
(3) Oxidation of ammonia in Ostwald’s process.

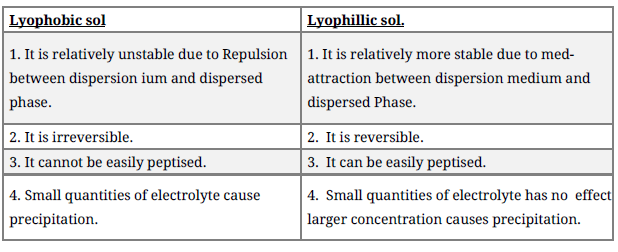
Question. What are lyophilic and lyophobic sols? Give one example of each type. Why are hydrophobic sols easily coagulated?
Answer. (i) Lyophilic sols:
Colloidal sols that are formed by mixing substances such as gum, gelatin, starch, etc. with a suitable liquid (dispersion medium) are called lyophilic sols. These sols are reversible in nature i.e., if two constituents of the sol are separated by any means (such as evaporation), then the sol can be prepared again by simply mixing the dispersion medium with the dispersion phase and shaking the mixture.
(ii) Lyophobic sols:
When substances such as metals and their sulphides etc. are mixed with the dispersion medium, they do not form colloidal sols. Their colloidal sols can be prepared only by special methods. Such sols are called lyophobic sols. These sols are irreversible in nature. For example: sols of metals.
Now, the stability of hydrophilic sols depends on two things- the presence of a charge and the salvation of colloidal particles. On the other hand, the stability of hydrophobic sols is only
because of the presence of a charge. Therefore, the latter are much less stable than the former. If the charge of hydrophobic sols is removed (by addition of electrolytes), then the particles present in them come closer and form aggregates, leading to precipitation.
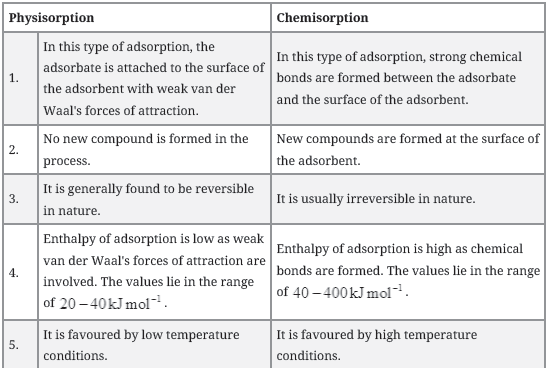
Question. What is the difference between physisorption and chemisorption?
Answer.

Question. What is the difference between multimolecular and macromolecular colloids? Give one example of each. How are associated colloids different from these two types of colloids?
Answer. (i) In multi-molecular colloids, the colloidal particles are an aggregate of atoms or small molecules with a diameter of less than 1 nm. The molecules in the aggregate are held
together by van der Waal’s forces of attraction. Examples of such colloids include gold sol and sulphur sol.
(ii) In macro-molecular colloids, the colloidal particles are large molecules having colloidal dimensions. These particles have a high molecular mass. When these particles are dissolved in a liquid, sol is obtained. For example: starch, nylon, cellulose, etc.
(iii) Certain substances tend to behave like normal electrolytes at lower concentrations.
However, at higher concentrations, these substances behave as colloidal solutions due to the formation of aggregated particles. Such colloids are called aggregated colloids.
Question. What role does adsorption play in heterogeneous catalysis?
Answer. Heterogeneous catalysis:
A catalytic process in which the catalyst and the reactants are present in different phases is known as a heterogeneous catalysis. This heterogeneous catalytic action can be explained in terms of the adsorption theory. The mechanism of catalysis involves the following steps:
(i) Adsorption of reactant molecules on the catalyst surface.
(ii) Occurrence of a chemical reaction through the formation of an intermediate.
(iii) De-sorption of products from the catalyst surface
(iv) Diffusion of products away from the catalyst surface.
In this process, the reactants are usually present in the gaseous state and the catalyst is present in the solid state. Gaseous molecules are then adsorbed on the surface of the catalyst.
As the concentration of reactants on the surface of the catalyst increases, the rate of reaction also increases. In such reactions, the products have very less affinity for the catalyst and are quickly desorbed, thereby making the surface free for other reactants.
Question. How are colloids classified on the basis of
(i) Physical states of components
(ii) Nature of dispersion medium and
(iii) Interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
Answer. Colloids can be classified on various bases:
(i) On the basis of the physical state of the components (by components we mean the
dispersed phase and dispersion medium). Depending on whether the components are solids,
liquids, or gases, we can have eight types of colloids.
(ii) On the basis of the dispersion medium, sols can be divided as:
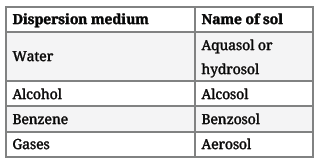
(iii) On the basis of the nature of the interaction between the dispersed phase and dispersion medium, the colloids can be classified as lyophilic (solvent attracting) and lyophobic (solvent repelling).
Question. Distinguish between the meaning of the terms adsorption and absorption.
Give one example of each.
Answer. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon of accumulation of molecules of a substance at the surface rather than in the bulk of a solid or liquid. The substance that gets adsorbed is called the ‘adsorbate’ and the substance on whose surface the adsorption takes place is called the ‘adsorbent’. Here, the concentration of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent increases. In adsorption, the substance gets concentrated at the surface only. It does not penetrate through the surface to the bulk of the solid or liquid. For example, when we dip a chalk stick into an ink solution, only its surface becomes coloured. If we break the chalk stick, it will be found to be white from inside.
On the other hand, the process of absorption is a bulk phenomenon. In absorption, the substance gets uniformly distributed throughout the bulk of the solid or liquid.
Question. What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts?
Answer. (a) Activity of a catalyst:
The activity of a catalyst is its ability to increase the rate of a particular reaction.Chemisorption is the main factor in deciding the activity of a catalyst. The adsorption of reactants on the catalyst surface should be neither too strong nor too weak. It should just be strong enough to make the catalyst active.
(b) Selectivity of the catalyst:
The ability of the catalyst to direct a reaction to yield a particular product is referred to as the selectivity of the catalyst. For example, by using different catalysts, we can get different products for the reaction between H2 and CO.

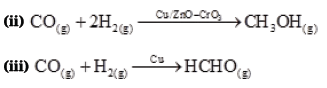
Question. Why is adsorption always exothermic?
Answer. Adsorption is always exothermic. This statement can be explained in two ways.
(i) Adsorption leads to a decrease in the residual forces on the surface of the adsorbent. This causes a decrease in the surface energy of the adsorbent. Therefore, adsorption is always
exothermic.
(ii) ΔH of adsorption is always negative. When a gas is adsorbed on a solid surface, its movement is restricted leading to a decrease in the entropy of the gas i.e., ΔS is negative.
Now for a process to be spontaneous, ΔG should be negative.
Therefore, ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Since ΔS is negative,ΔH has to be negative to make ΔG negative. Hence, adsorption is always exothermic.
Question. Explain modern theory of heterogeneous catalysis.
Answer. According to modern theory of catalysis, the mechanism of heterogeneous catalysis involves following steps –
(i) Diffusion of reactants on the surface of catalyst.
(ii) Adsorption of reactant molecules on the surface.
(iii) Occurrence of reaction on the catalysts surface through formation of an intermediate.
(iv) Desorption of products from surface.
(v) Diffusion of products away from surface.
Question. Explain the terms with suitable examples: (i) Alcosol (ii) Aerosol (iii) Hydrosol
Answer. (i) Alcosol:
A colloidal solution having alcohol as the dispersion medium and a solid substance as the dispersed phase is called an alcosol.
For example: colloidal sol of cellulose nitrate in ethyl alcohol is an alcosol.
(ii) Aerosol:
A colloidal solution having a gas as the dispersion medium and a solid as the dispersed phase is called an aerosol.
For example: fog
(iii) Hydrosol
A colloidal solution having water as the dispersion medium and a solid as the dispersed phase is called a hydrosol. For example: starch sol or gold sol.
Question. Explain what is observed
(i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol.
(ii) An electrolyte, NaCl is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol.
(iii) Electric current is passed through a colloidal sol?
Answer. (i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal solution, then scattering of light is observed. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This scattering of light illuminates the path of the beam in the colloidal solution.
(ii) When NaCl is added to ferric oxide sol, it dissociates to give Na+ and Cl– ions. Particles of ferric oxide sol are positively charged. Thus, they get coagulated in the presence of negatively charged Cl– ions.
(iii) The colloidal particles are charged and carry either a positive or negative charge. The dispersion medium carries an equal and opposite charge. This makes the whole system
neutral. Under the influence of an electric current, the colloidal particles move towards the oppositely charged electrode. When they come in contact with the electrode, they lose their
charge and coagulate.
Question. Differentiate between lyophobic and lyophillic sol?
Answer.
Question. Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment.
Answer. The cleansing action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Soaps are basically sodium and potassium salts of long chain fatty acids,R- COO-Aa+ . The end of the molecule to which the sodium is attached is polar in nature, while the alkyl-end is nonpolar.
Thus, a soap molecule contains a hydrophilic (polar) and a hydrophobic (non-polar) part.
When soap is added to water containing dirt, the soap molecules surround the dirt particles in such a manner that their hydrophobic parts get attached to the dirt molecule and the
hydrophilic parts point away from the dirt molecule. This is known as micelle formation.
Thus, we can say that the polar group dissolves in water while the non-polar group dissolves in the dirt particle. Now, as these micelles are negatively charged, they do not coalesce and a stable emulsion is formed.