Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry The Solid State Chapter 1 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 1 The Solid State have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the Class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
The Solid State Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions
Question. Pure silicon doped with phosphorus is a
(a) metallic conductor
(b) insulator
(c) n-type semiconductor
(d) p-type semiconductor
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a crystalline solid ?
(a) Definite and characteristic heat of fusion.
(b) Isotropic nature.
(c) A regular periodically repeated pattern of arrangement of constituent particles in the entire crystal.
(d) A true solid
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a crystalline solid?
(a) KCl
(b) CsCl
(c) Glass
(d) Rhombic S
Answer
C
Question. Iodine molecules are held in the crystals lattice by ______.
(a) london forces
(b) dipole-dipole interactions
(c) covalent bonds
(d) coulombic forces
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements about amorphous solids is incorrect ?
(a) They melt over a range of temperature
(b) They are anisotropic
(c) There is no orderly arrangement of particles
(d) They are rigid and incompressible
Answer
B
Question. If Germanium crystallises in the same way as diamond, then which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) Every atom in the structure is tetrahedrally bonded to 4 atoms.
(b) Unit cell consists of 8 Ge atoms and co-ordination number is 4.
(c) All the octahedral voids are occupied.
(d) All the octahedral voids and 50% tetrahedral voids remain unoccupied.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is an amorphous solid ?
(a) Graphite (C)
(b) Quartz glass (SiO2)
(c) Chrome alum
(d) Silicon carbide (SiC)
Answer
B
Question. Schottky defect defines imperfection in the lattice structure of
(a) solid
(b) gas
(c) liquid
(d) plasma
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statement is not true about amorphous solids ?
(a) On heating they may become crystalline at certain temperature.
(b) They may become crystalline on keeping for long time.
(c) Amorphous solids can be moulded by heating.
(d) They are anisotropic in nature.
Answer
D
Question. Why some glass objects from ancient civilisations are found to become milky in appearance?
(a) Glass is a crystalline solid, milky appearance is due to its crystalline nature.
(b) Glass is amorphous but on heating it become crystalline at some temperature.
(c) Because of reaction of glass with impurities present in the atmosphere.
(d) None of these.
Answer
B
Question. Equal number of atoms or ion missing from normal lattice point creating a vacancy due to
(a) Frenkel defect
(b) Mass defect
(c) Schottky defect
(d) Interstitial defect
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following amorphous solid is used as photovoltaic material for conversion of sunlight into electricity?
(a) Quartz glass
(b) Quartz
(c) Silicon
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
C
Question. The empty space in the body centred cubic lattice is
(a) 68%
(b) 52.4%
(c) 47.6%
(d) 32%
Answer
D
Question. Solid CH4 is
(a) ionic solid
(b) covalent solid
(c) molecular solid
(d) does not exist
Answer
C
Question. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of ______.
(a) lone pair of electrons
(b) free valence electrons
(c) cations
(d) anions
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following exists as covalent crystals in the solid state ?
(a) Iodine
(b) Silicon
(c) Sulphur
(d) Phosphorus
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following forms a molecular solid when solidified?
(a) Silicon carbide
(b) Calcium fluoride
(c) Rock salt
(d) Methane
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is a network solid ?
(a) SO2 (solid)
(b) I2
(c) Diamond
(d) H2O (Ice)
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following solids is not an electrical conductor?
(a) Mg (s)
(b) TiO (s)
(c) I2 (s)
(d) H2O (s)
Answer
C
Question. Graphite cannot be classified as ______.
(a) conducting solid
(b) network solid
(c) covalent solid
(d) ionic solid
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statement is not true about amorphous solids?
(a) On heating they may become crystalline at certain temperature.
(b) They may become crystalline on keeping for long time.
(c) Amorphous solids can be moulded by heating.
(d) They are anisotropic in nature.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not the characteristic of ionic solids?
(a) Very low value of electrical conductivity in the molten state.
(b) Brittle nature.
(c) Very strong forces of interactions.
(d) Anisotropic nature.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
(a) Graphite (C)
(b) Quartz glass (SiO2)
(c) Chrome alum
(d) Silicon carbide (SiC)
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following conditions favours the existence of a substance in the solid state?
(a) High temperature
(b) Low temperature
(c) High thermal energy
(d) Weak cohesive forces
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is true about the value
of refractive index of quartz glass?
(a) Same in all directions
(b) Different in different directions
(c) Cannot be measured
(d) Always zero
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following solids is not an electrical conductor?
I. Mg (s) II. TiO (s)
III. I2 (s) IV. H2O (s)
(a) (A) only
(b) (B) Only
(c) (C) and (D)
(d) (B), (C) and (D)
Answer
C
Question. The sharp melting point of crystalline solids is due to ……………. .
(a) a regular arrangement of constituent particles observed over a short distance in the crystal lattice:
(b) a regular arrangement of constituent particles observed over a long distance in the crystal lattice.
(c) same arrangement of constituent particles in different directions.
(d) different arrangement of constituent particles in different directions.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a network solid?
(a) SO2 (Solid)
(b) I2
(c) Diamond
(d) H2O (Ice)
Answer
C
Question. Iodine molecules are held in the crystals lattice by …………… .
(a) london forces
(b) dipole-dipole interactions
(c) covalent bonds
(d) coulombic forces
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a crystalline solid?
(a) Definite and characteristic heat of fusion.
(b) Isotropic nature.
(c) A regular periodically repeated pattern of arrangement of constituent particles in the entire crystal.
(d) A true solid
Answer
B
Assertion-Reason Questions
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements and Reason is correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements but Reason is not correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but Reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but Reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: The packing efficiency is maximum for the fcc structure.
Reason: The coordination number is 12 in fcc structures.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: In p-type semiconductor holes will appear to be moving towards the negatively charged plate.
Reason: Delocalised electrons increase the conductivity of doped silicon.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: Semiconductors are solids with conductivities in the intermediate range from 10–6 – 104 ohm–1m–1.
Reason: Intermediate conductivity in semiconductor is due to partially filled valence band.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: The total number of atoms present in a simple cubic unit cell is one.
Reason: Simple cubic unit cell has atoms at its corners, each of which is shared between eight adjacent unit cells.
Answer
A
Question.Assertion: Diamond and graphite do not have the same crystal structure.
Reason: Diamond is crystalline while graphite is amorphous.
Answer
C
Question.Assertion: The number of NaCl units per unit cell is 2.
Reason: There are four chloride ions per unit Cell of NaCl.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion: In caesium chloride crystal, Cs+ ion is present on the centre of cube of the unit cell.
Reason: For N-atoms adopting fcc arrangement, there are 2N tetrahedral voids.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: Valence band may remain partially filled.
Reason: The gap between valence band and conduction band cannot be determined.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: White ZnO becomes yellow upon heating.
Reason: On heating ZnO loses oxygen and free electrons go into exited stated and upon returning imparts yellow radiation.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Na+ and Al3+ are isoelectronic but the magnitude of ionic radius of Al3+ is less than that of Na+.
Reason: The magnitude of an effective nuclear charge on the outer shell electrons in Al3+ is greater than that of Na+.
Answer
A
Case Based Questions
1. The adjective, ‘crystalline’ when applied to solids, implies an ideal crystal in which the structural units, termed as unit cells, are repeated regularly and indefinitely in three dimensions in space. The unit cell, containing at least one molecule has definite orientation and shape defined by the translational vectors, a, b and c. The unit cell therefore has a definite volume, V that contains the atoms and molecules necessary for generating the crystal. Every crystal can be classified as a member of one of the seven possible crystal systems or crystal classes that are defined by the relationships between the individual dimensions, a, b and c of the unit cell and between the individual angles, α, β, and γ of the unit cell. The structure of the given crystal may be assigned to one of the 7 crystal systems, to one of the 14 Brevais lattices, and to one of the 230 space groups. These uniquely define the possible ways of rearranging atoms in a threedimensional solid. Based on these observations, seven crystal systems were identified: triclinic, monoclinic, trigonal or rhombohedral, tetragonal, hexagonal, rhombic or orthorhombic and cubic. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. An example of orthorhombic crystal system is
(a) SnO2
(b) KNO3
(c) ZnO
(d) K2Cr2O7
Answer
B
Question. The crystal system of a compound with unit cell dimensions, a = 0.387 nm, b = 0.387 nm and c = 0.504 nm and α = β = 90º and γ = 120° is.
(a) cubic
(b) hexagonal
(c) orthorhombic
(d) rhombohedral
Answer
B
Question. In a triclinic crystal
(a) a = b = c, α = β = γ ≠ 90°
(b) a ≠ b = c, α = β = γ = 90°
(c) a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°
(d) a ≠ b ≠ c, α = γ = 90°, β ≠ 90°
Answer
C
Question.(i) The unit cell with the structure given below represents ………… crystal system.
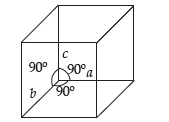
(a) cubic
(b) orthorhombic
(c) tetragonal
(d) trigonalAns.
Answer
A
Question. The unit cell with dimensions α = β = γ = 90°, a = b ≠ c is
(a) cubic
(b) triclinic
(c) hexagonal
(d) tetragonal
Answer
D
2. In contrast to the disorders of gases and liquids, there is translational order in crystals. However, disordered or amorphous solids also exist which lack such order, they are really highly viscous liquids. In translational order entire structure or lattice, can be generated by repeated replication of a small regular figure, termed as unit cell. The planes of any crystalline structure can be specified using Miller Indices, which is also serve to identify single crystal faces.The ordered structure or lattice, of a solid can be determined by X-ray or neutron diffraction studies, in which a beam of X-rays of neutrons is scattered from the sample to produce a diffraction pattern which can be analyzed to reveal the crystal structure of the sample. All crystal lattices can be classified into 14 Bravais lattices belonging to 7 systems. For example, the simple cubic, facecentred cubic and body-centred cubic lattices are the 3 lattices of the cubic system. Cubic and hexagonal close-packed structures have the structure of tightly packed spheres where each sphere touches 12 neighbours, 6 in the same plane and 3 above and 3 below. These two close-packed structures differ in the placement of successive planes or layers. For the hexagonal close packing, a third layer is laid down to reproduce the first layer, so the structure could be represented by ABABAB….. . For cubic close packing, third layer is again displaced, corresponding to ABCABC … .
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. Which of the following arrangements correctly represents hexagonal and cubic close packed structure?
(a) ABCABC… and ABAB…
(b) ABAB… and ABCABC…
(c) Both have ABAB… arrangement.
(d) Both have ABCABC… arrangement.
Answer
B
Question. The arrangement of the first two layers, one above the other in hcp and ccp arrangements is
(a) exactly same in both cases.
(b) partly same and partly different.
(c) different from each other.
(d) nothing definite.
Answer
A
Question. In hexagonal close packing, a sphere has coordination number of
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 12
Answer
D
Question.Which of the following statements about amorphous solids is incorrect?
(a) They melt over a range of temperature.
(b) There is no orderly arrangement of particles.
(c) They are anisotropic.
(d) They are rigid and incompressible.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) The amorphous solids have a random, disordered arrangement of constituents.
(b) The sime cubic, face-centred and bodycentred are the three lattices of the cubic system.
(c) The number of Bravais lattice in which a crystal can be categorized is 7.
(d) A metal that crystallizes in hcp structure has coordination number 12.
Answer
C
3. In an ideal crystal, there must be regular repeating arrangement of the constituting particles and its entropy must be zero at absolute zero temperature. However, it is impossible to obtain an ideal crystal and it suffers from certain defects called imperfections. In pure crystal, these defects arises either due to disorder or dislocation of the constituting particles from the normal positions or due to the movement of the particles even at absolute zero temperature. Such defects increase with rise in temperature. In addition to this certain defects arise due to the presence of some impurities. Such defects not only modify the existing properties of the crystalline solids but also impart certain new characteristics to them. Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. Which of the following gives both Frenkel and Schottky defect?
(a) AgCl
(b) CsCl
(c) KCl
(d) AgBrAns.
Answer
D
Question. Lattice defect per 1015 NaCl is 1. What is the number of lattice defects in a mole of NaCl?
(a) 6.02 × 1023
(b) 6.02 × 108
(c) 1014
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The ionic substances in which the cation and anion are of almost similar size shows
(a) non-stoichiometric defect
(b) Schottky defect
(c) Frenkel defect
(d) all of theseAns.
Answer
B
Question. AgCl is crystallized from molten AgCl containing a little CdCl2. The solid obtained will have
(a) cationic vacancies equal to number of Cd2+ ions incorporated.
(b) cationic vacancies equal to double the number of Cd2+ ions.
(c) anionic vacancies.
(d) neither cationic nor anionic vacancies.
Answer
A
Question. If Al3+ ions replace Na+ ions at the edge centres of NaCl lattice, then the number of vacancies in 1 mole of NaCl will be
(a) 3.01 × 1023
(b) 6.02 × 1023
(c) 9.03 × 1023
(d) 12.04 × 1023
Answer
A
4. In hexagonal system of crystals, a frequency encountered arrangement of atoms is described as a hexagonal prism. Here, the top and bottom of the cell are regular hexagons and three atoms are sandwiched in between them. A space-filling model of this structure, called hexagonal close packed (hcp), is constituted of a spheres on a flat surface surrounded in the same plane by six identical spheres as closely as possible. Three spheres are then placed over the first layer so that they touch each other and represent the second layer. Each one of these three sphere touches three spheres of the bottom layer. Finally, the second layer is covered with a third layer that is identical to the bottom layer in relative position.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. The number of atoms in this hcp unit cell is
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 12
(d) 17
Answer
B
Question. The volume of this hcp unit cell is

Answer
A
Question. The empty space in this hcp unit cell is
(a) 74%
(b) 47.6%
(c) 32%
(d) 26%Ans.
Answer
D
Question. In hexagonal close packing of spheres in threedimensions.
(a) In one unit cell there are 12 octahedral voids and all are completely inside the unit cell.
(b) In one unit cell there are six octahedral voids and all are completely inside the unit cell.
(c) In one unit cell there are six octahedral voids out of which three are completely inside the unit cell and other three are from contributions of octahedral voids which are partially inside the unit cell.
(d) In one cell unit there are 12 tetrahedral voids, all are completely inside the unit cell.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is correct about hexagonal close packing?
(a) In this arrangement, third layer is identical to the first layer.
(b) The coordination number in this arrangement is 6.
(c) It is as closely packed as body centered cubic packing
(d) It has 32% empty space.
Answer
A
5. In ideally ionic structures, the coordination numbers of the ions are determined by electrostatic considerations. Cations surround themselves with as many anions as possible and vice versa. This maximizes the attractions between neighbouring ions of opposite charge and hence maximizes the lattice energy of the crystal. This requirement led to the formulation of the radius ratio rule for ionic structures in which the ions and the structure adopted for a particular compound depend on the relative sizes of the ions. Thus, for the stable ionic crystalline structures, there is definite radius ratio limit for a cation to fit perfectly in the lattice of anions called radius ratio rule. This depends upon the ratio of radii of two types of ions, r+/r–.
This ratio for coordination numbers 3, 4, 6 and 8 respectively 0.155–0.225, 0.225–0.414, 0.414– 0.732 and 0.732–1.000. The coordination number of ionic solids also depends upon temperature and pressure. On applying high pressure, coordination number increases. On the other hand, on applying high temperature, it decreases.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. For a coordination number 4, the maximum limiting radius ratio is
(a) 0.414
(b) 0.732
(c) 0.225
(d) 0.155Ans.
Answer
A
Question. The ionic radii K+, Rb+ and Br– are 137, 148 and 195 pm. The coordination number of cation in RbBr and KBr structures are respectively.
(a) 8, 6
(b) 6, 4
(c) 6, 8
(d) 4, 6Ans.
Answer
A
Question. If the pressure of CsCl is increased, then its coordination number will
(a) increase
(b) remain the same
(c) decrease
(d) none of these
Answer
A
Question. If the radius of Na+ ion is 95 pm and that of Cl– ion is 181 pm, the coordination number of Na+ ion is
(a) 6
(b) 4
(c) 8
(d) 12
Answer
A
Question. Which is not the correct statement for ionic solids in which positive and negative ions are held by strong electrostatic attractive forces?
(a) The radius ratio r+/r– increases as coordination number increases.
(b) As the difference in size of ions increases, coordination number increases.
(c) When coordination number is eight, r+/r– ratio lies between 0.225 to 0.414.
(d) In ionic solid of the type AX(ZnS, wurtzite), the coordination number of Zn2+ and S2– respectively are 4 and 4.
Answer
C
6. The transition metals when exposed to oxygen at low and intermediate temperatures form thin, protective oxide films of up to some thousands of Angstroms in thickness. Transition metal oxides lie between the extremes of ionic and covalent binary compounds formed by elements from the left or right side of the periodic table. They range from metallic to semiconducting and deviate by both large and small degrees from stoichiometry. Since d-electron bonding levels are involved, the cations exist in various valence states and hence give rise to a large number of oxides. The crystal structures are often classified by considering a cubic or hexagonal close-packed lattice of one set of ions with the other set of ions filling the octahedral or tetrahedral interstices. The actual oxide structures, however, generally show departures from such regular arrays due in part to distortions caused by packing of ions of different size and to ligand field effects. These distortions depend not only on the number of d-electrons but also on the valence and the position of the transition metal in a period or group. (Source: Smeltzer, W. W., & Young, D. J. (1975). Oxidation properties of transition metals. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 10, 17-54.)
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given.Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: CrO crystallises in a hexagonal closepacked array of oxide ions with two out of every three octahedral holes occupied by chromium ions.
Reason: Transition metal oxide may be hexagonal close-packed lattice of oxide ions with metal ions filling the octahedral voids.
Answer
D
Question.Assertion: Crystal structure of oxides of transition metals often show defects.
Reason: Ligand field effect cause distortions in crystal structures.
Answer
A
Question.Assertion: Cations of transition elements occur in various valence states.
Reason: Large number of oxides of transition elements are possible.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: Transition metals form protective oxide films.
Reason: Oxides of transition metals are always stoichiometric.
Answer
C
Any deviation from orderly arrangement in crystal lattice leads to development of imperfections or defects in crystalline solids. These imperfections not only modify the properties but also sometimes impart new properties to the solids. These defects may be either of point nature or of line nature. Point defects may be classified as stoichiometric and nonstoichiometric. Due to stoichiometric defects formula of the compound remains same as the ideal formula whereas in case of nonstoichiometric defects it changes. In some cases, these defects are introduced in crystals to have the desired properties.
Question. Schottky defect mainly arises in ionic solids where
(a) Positive ion is bigger in size
(b) Negative ion is small in size
(c) Positive and negative ions are of similar sizes
(d) Positive ions are big and negative ions are small
Answer
C
Question. When electrons are trapped are crystal in anionic vacancy, the defect is known as
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Frankel defect
(c) Stoichiometric defect
(d) F- centres
Answer
D
Question. The appearance colour in solid alkali metal halides is mainly due to
(a) Frankel defect
(b) Interstitial defects
(c) F- centres
(d) Schottky defects
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following defects does not affect the density of the crystal?
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Interstitial defect
(c) Frankel defect
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
C
Question. Cations are present in interstitial sites in
(a) Frankel defects
(b) Schottky defects
(c) Vacancy defects
(d) Metal deficiency defects
Answer
D
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. In which of the following structures coordination number for cations and anions in the packed structure will be same?
(a) Cl– ion form fcc lattice and Na+ ions occupy all octahedral voids of the unit cell.
(b) Ca2+ ions form fcc lattice and F– ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
(c) O2– ions form fcc lattice and Na+ ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
(d) S2– ions form fcc lattice and Zn2+ ions go into alternate tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is true about the charge acquired by p-type semiconductors ?
(a) positive
(b) neutral
(c) negative
(d) depends on concentration of p impurity
Answer
B
Question. Packing efficiency by arrangement of atoms in two dimensional hexagonal close packing is
(a) 60.43
(b) 65.78
(c) 59.78
(d) 68.76
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) NaCl is a paramagnetic salt
(b) CuSO4 is a diamagnetic salt
(c) MnO is an example of ferromagnetic substance
(d) Ferrimagnetic substance like ZnFe2O4 becomes paramagentic on heating
Answer
D
Question. The edge length of unit cell of a metal having molecular weight 75 g/mol is 5Å which crystallizes in cubic lattice. If the density is 2g/cc then find the radius of metal atom.
(NA = 6 × 1023). Give the answer in pm.
(a) 217 pm
(b) 210 pm
(c) 220 pm
(d) 205 pm
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following represents correct order of conductivity in solids ?
(a) Kmetals > > Kinsulators < Ksemiconductors
(b) Kmetals < < Kinsulators < Ksemiconductors
(c) Kmetals ; Kinsulators > Ksemiconductors = zero
(d) Kmetals < Ksemiconductors > Kinsulators ≠ zero
Answer
A
Question. The number of atoms in 100 g of an fcc crystal with density,d = 10 g/cm3 and cell edge equal to 100 pm, is equal to
(a) 1 × 1025
(b) 2 × 1025
(c) 3 × 1025
(d) 4 × 1025
Answer
D
Question. Edge length of unit cell is 3.608 × 10–8 cm, which crystallizes in fcc and is determined to have a density of 8.92 g/cm3.
The mass of four atoms is
(a) 4.18 × 10–22
(b) 1.67 × 10–21
(c) 2.09 × 10–22
(d) 8.37 × 10–22
Answer
A
Question. A metal has a fcc lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 404 pm. The density of the metal is 2.72 g cm-3. The molar mass of the metal is :
(NA Avogadro’s constant = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
(a) 30 g mol–1
(b) 27 g mol–1
(c) 20 g mol–1
(d) 40 g mol–1
Answer
B
Question. A compound is formed by elements A and B. The crystalline cubic structure has the A atoms at the corners of the cube and B atoms at the body centre. The simplest formula of the compound is
(a) AB
(b) A6B
(c) AB6
(d) A8B4
Answer
A
Question. What type of semiconductors respectively are formed when the group 14 are doped with the group 13 and group 15?
(a) p,n
(b) n,p
(c) p,p
(d) n,n
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is ferroelectric compound?
(a) BaTlO3
(b) K4[Fe(CN)6]
(c) Pb2O3
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is true about the value of refractive index of quartz glass ?
(a) Same in all directions
(b) Different in different directions
(c) Cannot be measured
(d) Always zero
Answer
A
Question. Substance which is weakly repelled by a magnetic field is
(a) O2
(b) H2O
(c) CrO2
(d) Fe3O4
(e) ZnFe2O4
Answer
B
Question. The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is :
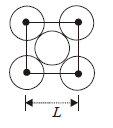
(a) 39.27%
(b) 68.02%
(c) 74.05%
(d) 78.54%
Answer
D
Question. A metallic element exists as cubic lattice. Each edge of the unit cell is 2.88 Å. The density of the metal is 7.20 g cm–3.How many unit cell will be present in 100 g of the metal?
(a) 6.85 × 102
(b) 5.82 × 1023
(c) 4.37 × 105
(d) 2.12 × 106
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What type of interactions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid? (All India)
Answer. Dipole-dipole forces of attractions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid.
Question. What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with arsenic? (All India)
Answer. n-type semiconductor.
Question. Which point defect in its crystal units increases the density of a solid? (Delhi)
Answer. Metal excess defect increases the density of a solid. It is due to presence of extra cations in the interstitial sites.
Question. Write a point of distinction between a metallic solid and an ionic solid other than metallic lustre. (Delhi)
Answer. Metallic solid conducts electricity in solid state but ionic solids do so only in molten state or in solution. Metals conduct electricity through electrons while ionic substances through ions.Metallic solids are malleable and ductile while ionic solids are hard and brittle.
Question. How can the conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor be increased? (All India)
Answer. The conductivity is increased by adding an appropriate amount of suitable impurity. This process is called as intrinsic doping.
Question. How do metallic and ionic substances differ in conducting electricity? (All India)
Answer. The electrical conductivity in metallic substances is due to free electrons while in ionic substances the conductivity is due to presence of ions.
Question. Which point defect in crystals does not alter the density of the relevant solid? (Delhi)
Answer. Frenkel defect.
Question. What is the number of atoms in a unit cell of a face-centred cubic crystal? (All India)
Answer. The number of atoms in a unit cell of fcc-crystal is 4 atoms.
Question. Write a feature which will distinguish a metallic solid from an ionic solid. (Delhi)
Answer. The electrical conductivity in metallic solid is due to free electrons while in ionic solid the conductivity is due to presence of ions.
Question. Which point defect in crystals of a solid does not change the density of the solid? (Delhi)
Answer. Frenkel defect.
Question. Which point defect in crystals of a solid decreases the density of the solid? (Delhi)
Answer. Schottky defect.
Question. Write a distinguishing feature of metallic solids. (All India)
Answer. Metallic solids possess high electrical and thermal conductivity due to presence of free electrons.
Question. ‘Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature.’What does this statement mean? (Delhi)
Answer. It means that crystalline solids show different values of some properties like electrical conductivity, refractive index, thermal expansion etc. in different directions.
Question. Which point defect of its crystals decreases the density of a solid? (Delhi & All India)
Answer. Schottky defect.
Question. Which stoichiometric defect in crystals increases the density of a solid? (Delhi)
Answer. Interstitial defect in crystals increases the density of a solid.
Question. Which stoichiometric defect increases the density of a solid? (All India)
Answer. Interstitial defect increases the density of a solid.
Question. What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by AgCl? (Delhi)
Answer. Frenkel defect is shown by AgCl.
Question. What are n-type semiconductors? (All India)
Answer. n-type semiconductor : They are obtained by doping silicon with an element of group15, like P, As etc.
Question. What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by AgBr and AgI ? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. AgBr shows both Frenkel defect and Schottky defect whereas AgI shows Frenkel defect.
Question. What type of defect can arise when a solid is heated ? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Vacancy defects can arise when a solid is heated.
Question. Which point defect in its crystal units alters the density of a solid? (Delhi)
Answer. Schottky defect.
Question. Why does LiCl acquire pink colour when heated in Li vapours? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. This is due to metal excess defect due to anionic vacancies in which the anionic sites are occupied by unpaired electrons (F-centres).
Question. How many atoms per unit cell (z) are present in bcc unit cell? (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. Number of atoms in a unit cell of a body centred cubic structure :Contribution by 8 atoms at the corners
= 1/8 × 8 = 1 Contribution by the atom presents within the body = 1
∴ Total number of atoms present in the unit cell = 1 + 1 = 2 atoms
Question. How many atoms constitute one unit cell of a face-centered cubic crystal? (Delhi)
Answer. 4 atoms constitute one unit cell of a fcc crystal.
Question. What type of Stoichiometric defect is shown by AgCl?
Answer. Frenkel defect.
Question.Calculate the number of atoms in a face centred cubic unit cell. (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. In face centered cubic arrangement, number of lattice points are : 8 + 6.
∴ Lattice points per unit cell = 8× 1/8 + 6×1/2 = 4
Question. What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by NaCl? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Schottky defect is shown by NaCl.
Question. Which ionic compound shows both Frenkel and Schottky defects? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Silver bromide (AgBr) shows both Schottky and Frenkel defect.
Question. On heating a crystal of KCl in potassium vapour, the crystal starts exhibiting a violet colour. What is this due to? (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. The Cl ions diffuse to the surface and combine with atoms which get ionized by losing electrons.These electrons are trapped in anions vacancies and act as F-centre which imparts violet colour to the crystal.
Question. What is meant by ‘doping’ in a semiconductor? (Delhi)
Answer. Addition of a suitable impurity to a semiconductor to increase its conductivity is called doping.
Question. Which type of ionic substances show Schottky defect in solids? (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. Highly ionic compounds with high coordination number and small difference in size of cations and anions show schottky defect.
Question.What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by NaCl? (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. Schottky defect is shown by NaCl.
Question. What is meant by ‘antiferromagnetism’? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Antiferromagnetism : These substances possess zero net magnetic moment because of presence of equal number of electrons with opposite spins.
Question. A metallic element crystallises into a lattice having a pattern of AB AB … and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What type of structure is formed by this arrangement?
Answer. Tetrahedral void is formed in AB AB … pattern.The hexagonal close packing (hcp) is formed in this arrangement.
Question. What is the formula of a compound in which the element Y forms ccp lattice and atoms of X occupy 1/3rd of tetrahedral voids? (Delhi)
Answer. Formula is X2Y3.
Question.What is the formula of a compound in which the element Y forms ccp lattice and atoms of X occupy 2/3rd of tetrahedral voids? (All India)
Answer. Y atoms are N (No. of tetrahedral voids are 2N),No. of tetrahedral voids occupied by X are
(2/3)× 2N = 4N/3
X : Y = 4N : 3N
Formula : X4Y3
Question. What is the no. of atoms per unit cell (z) in a body-centred cubic structure? (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. Contribution by the atoms present at eight
corners = 8 × 1/8 = 1
Contribution by the atoms present at centre = 1
Total number of atoms present in unit cell = 1 +
1 = 2
38. What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by
AgCl? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. AgCl shows Frenkel defect.
Question. What type of magnetism is shown by a substance if magnetic moments of domains are arranged in same direction? (Delhi)
Answer. Ferromagnetism is shown by a substance if magnetic moments of domains are arranged in same direction.

Question. Give an example each of a molecular solid and an ionic solid. (All India)
Answer. Molecular solid ⎯⎯→ Iodine (I2)
Ionic solid ⎯⎯→ Sodium chloride (NaCl)
Question. A metallic element crystallises into a lattice having a ABC ABC … pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What type of structure is formed by this arrangement?
Answer. Octahedral voids are formed in ABC ABC … pattern. The cubic close packing (ccp) is formed in this arrangement.
Question. What type of substances would make better Permanent Magnets: Ferromagnetic or Ferrimagnetic? (Delhi)
Answer. Ferromagnetic substances would make better permanent magnets
Example : Fe, Co, Ni etc.
Question. Write a distinguishing feature between a metallic solid and an ionic solid. (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. The electrical conductivity in metallic substances is due to free electrons while in ionic substances the conductivity is due to presence of ions.
Question. Why are crystalline solids anisotropic? (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Crystalline solids show different values of their some properties like electrical conductivity,refractive index, thermal expansion etc. in different directions.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain the following terms with suitable examples :
Ferromagnetism and Ferrimagnetism
Answer. Ferromagnetic solids : The solids which are strongly attracted by external magnetic field and do not lose their magnetism when the external field is removed are called ferromagnetic solids. The property, thus exhibited, is termed as ferromagnetism.
Example : Fe, Co and Ni show ferromagnetism at room temperature.
Ferrimagnetic solids : The solids which are expected to show large magnetism due to the presence of unpaired electrons but in fact have small net magnetic moment, are called ferrimagnetic solids.
Example : Fe3O4 and ferrites.
Question. Explain how you can determine the atomic mass of an unknown metal if you know its mass density and the dimensions of unit cell of its crystal. (All India)
Answer. Suppose edge of the unit cell = a pm
Number of atoms present per unit cell = Z
∴ Volume of unit cell = (a pm)3
= (a × 10–10 cm)3 = a3 × 10–30 cm3
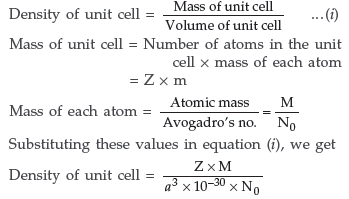
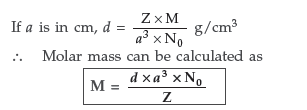
Question. Define the following terms in relation to crystalline solids :
(i) Unit cell (ii) Coordination number
Give one example in each case. (All India)
Answer. (i) Unit cell : The smallest three dimensional portion of a complete space lattice which when repeated over and again in different directions produces the complete space lattice is called the unit cell.
Example : Cubic unit cell, Hexagonal unit cell etc.
(ii) Coordination number : The number of nearest spheres with which a particular sphere is in contact is called co-ordination number.
Example : Co-ordination number of hexagonal (hcp) structures is 12.
Question. The unit cell of an element of atomic mass 108 u and density 10.5 g cm–3 is a cube with edge length, 409 pm. Find the type of unit cell of the crystal.[Given : Avogadro’s constant = 6.023 × 1023 mol–1]
Answer.
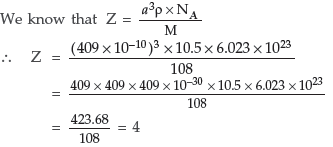
So it forms cubic- closed packed (ccp) lattice or fcc structure.
Question. Calculate the packing efficiency of a metal crystal for a simple cubic lattice.
Answer. Percentage efficiency of packing of simple cubic lattice = 52.4%.
Question. An element X crystallizes in f.c.c structure. 208 g of it has 4.2832 × 1024 atoms. Calculate the edge of the unit cell, if density of X is 7.2 g cm–3.
Answer. Z = 4(fcc) d = 7.2 g/cm3 a = ?
4.2832 × 1024 atoms have mass = 208 g
6.022 × 1023 atoms have mass

Question. What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors.
Answer. Semiconductor : The solid materials whose electrical conductivity lies between those of the typical metallic conductors and insulators are termed as semiconductors. The semiconductors possess conductivity in the range of 102 to 10 –9 ohm–1 cm–1.
These are of two types :
(a) n-type semiconductors : Doping of higher group element impurity forms n-type semiconductors. e.g. when ‘As’ is doped in ‘Ge’.
(b) p-type semicondctors : Impurity of lower groups forms electron deficient bond in the structure. Electron deficiency develops to p-hole.
Question. Account for the following:
(i) Schottky defects lower the density of related solids.
(ii) Conductivity of silicon increases on doping it with phosphorus. (All India)
Answer. (i) Schottky defect produced due to missing of equal number of cation and anion from lattice as a result of which the density of the lattice solid decreases.
(ii) The conductivity of silicon increases due to negatively charged extra electron of doped pentavalent phosphorus.
Question. Aluminium crystallizes in an fcc structure.Atomic radius of the metal is 125 pm. What is the length of the side of the unit cell of the metal? (All India)
Answer. For fcc, Formula : r = a/2√2
Given: r = 125 pm
∴ a = 2√2 r÷ a = 2√2 × 125
⇒ a = 2 × 1.414 × 125 = 353.5 pm
Question. If NaCl is doped with 10–3 mole percent SrCl2, what will be the concentration of cation vacancies? (NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
Answer. 10–3 mol percent means 100 moles of NaCl are doped with 10–3 moles of SrCl2
∴ 1 mole of NaCl is doped with SrCl2
= 10–3 /100
= 10–5 mole
Since each Sr2+ ion introduces one cation vacancy
∴ Concentration of cation vacancies
= 10–5 mol/mol of NaCl
= 10–5 × 6.02 × 1023 mol–1
= 6.02 × 1018 mol–1
Question. What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism. (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Semiconductor : The solids which have intermediate conductivities between metals and non-metals i.e. between 10 –6 to 104 π –1 m–1 are called semiconductors.
Example : Germanium and Silicon.
Main types of semiconductors are of two types :
(i) Intrinsic semiconductor : These are insulators at room temperature and become semiconductors when temperature is raised
(ii) Extrinsic semiconductor
p-type semiconductor
n-type semiconductor
These are formed by dopping impurity of lower or higher group.
These are subdivided into two types :
p-type semiconductor : When a silicon crystal is doped with atoms of group-13 elements like B, Al, Ga etc., the atom forms only 3 covalent bonds with the Si atom and 4th missing electron creates a hole which conducts electricity.
n-type semiconductor : When a silicon crystal is doped with atoms of group-15 elements like P, As etc., then only four of the five valence electrons of each impurity atom participate in 4 covalent bond formation and 5th e– conducts electricity.
Question. Define the following terms: (Comptt. Delhi)
(i) n-type semiconductor
(ii) Ferrimagnetism
Answer. (i) n-type semiconductor : When Si/Ge is doped with group 15 element.
(ii) Ferrimagnetism : When magnetic domains are aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers.
Question. A compound forms hcp structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mol of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids?
Answer. No. of atoms in the hcp = 0.5 × 6.022 × 1023
= 3.011 × 1023
No. of octahedral voids
= No. of atoms in packing = 3.011 × 1023
No. of tetrahedral voids
= 2 × No. of atoms in packing
= 2 × 3.011 × 1023 = 6.022 × 1023
∴ Total no. of voids
= 3.011 × 1023 + 6.022 × 1023 = 9.033 × 1023
Question. An element crystallizes in a structure having fcc unit cell of an edge 200 pm. Calculate the density if 200 g of this element contains 24 × 1023 atoms.
Answer. 24 × 1023 atoms of an element have mass = 200 g
∴ 6.022 × 1023 atoms of an element have mass
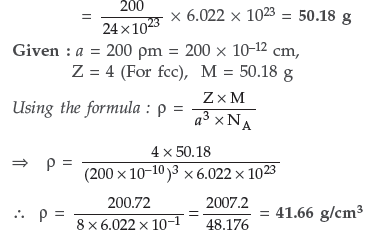
Question. (i) Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moments are oppositively aligned and cancel out each other.
(ii) Which stoichiometric defect does not change the density of the crystal?
Answer. (i) Diamagnetism is observed when the magnetic moments are oppositively aligned and cancel out each other.
(ii) Frenkel defect does not change the density of the crystal.
Question.An element with density 11.2 g cm–3 forms a f.c.c. lattice with edge length of 4 × 10–8 cm.Calculate the atomic mass of the element.
(Given : NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol–1) (Delhi)
Answer. Given : ρ = 11.2 g cm–3, a = 4 × 10–8 cm
For fcc lattice, Z = 4
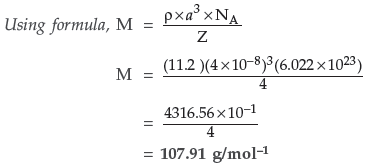
Question. (a) Why does presence of excess of lithium makes LiCl crystals pink?
(b) A solid with cubic crystal is made of two elements P and Q. Atoms of Q are at the corners of the cube and P at the body-centre. What is the formula of the compound?
Answer. (a) This is due to metal excess defect due to anionic vacancies in which the anionic sites are occupied by unpaired electrons (F-centres).
(b) As atoms of Q are present at the 8 centres of the cube, therefore, number of atoms of Q in the unit cell = 1/8 × 8 = 1
The atom P is at the body centre
∴ Number of atoms = 1
Ratio of atoms P : Q = 1 : 1
Hence, the formula of the compound is PQ.
Question. Examine the given defective crystal

Answer the following questions :
(i) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by the crystal?
(ii) How is the density of the crystal affected by this defect?
(iii) What type of ionic substances show such defect? (Delhi)
Answer. (i) Schottky defect
(ii) Density of the crystal decreases
(iii) NaCl (Ionic solids having approximate equal size of cations and anions)
Question. Calculate the number of unit cells in 8.1 g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a face-centered cubic (f.c.c.) structure. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol–1) (Comptt. All India)
Answer. 1 mole of Aluminium = 27 g = 6.022 × 1023
Hence, No. of atoms present in 27 g of Al
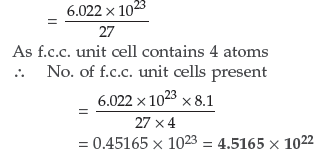
Question.(i) What type of non-stoichiometric point defect is responsible for the pink colour of LiCl?
(ii) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by NaCl? (All India)
Answer. (i) This is due to metal excess defect due to anionic vacancies in which the anionic sites are occupied by unpaired electrons (F-centres).
(ii) Schottky defect is shown by NaCl.
Question. How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms :
(i) Tetrahedral and octahedral voids
(ii) Crystal lattice and unit cell (All India)
Answer.

(ii) A regular arrangement of the constituent particles of a crystal in a three dimensional space is called crystal lattice.
The smallest three dimensional portion of a complete crystal lattice, which when repeated over and again in different directions produces the complete crystal lattice is called the unit cell.
Question. (a) What change occurs when AgCl is doped with CdCl2?
(b) What type of semiconductor is produced when silicon is doped with boron?
Answer. (a) Impurity defect of ionic solids is produced when AgCl is doped with CdCl2. Due to this defect vacancies are created that result in higher electrical conductivity of the solid.
(b) p-type semi-conductor is obtained when silicon is doped with boron.
Question. (i) Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moments are aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers.
(ii) Which stoichiometric defect decreases the density of the crystal? (All India)
Answer. (i) Ferrimagnetism is observed.
(ii) Schottky defect decreases the density of the crystal.
Question. Explain the following terms with suitable examples : (Comptt. All India)
(i) Frenkel defect (ii) F-centres
Answer. (i) Frenkel defect : The defect in which the smaller ion/cation is dislocated to a nearby interstitial site.
Example : Silver halides, ZnS.
(ii) F-centres : The anion vacancy occupied by an electron is called F-centre in Alkali metal halides.
Example : NaCl, KCl, LiCl.
Question. An element with density 2.8 g cm–3 forms a f.c.c. unit cell with edge length 4 × 10–8 cm. Calculate the molar mass of the element.
(Given : NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol–1) (All India)
Answer.

Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell edge of 286.65 pm. The density of iron is 7.87 g cm–3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number (At. mass of Fe = 56 g mol–1).
Answer. Given :
a = 286.65 pm = 286.65 × 10–10,
d = 7.87 g cm–3, M = 56 g mol–1
Z = 2 NA = ?

∴ Avogadro’s number NA = 6.022 × 1023
Question. Silver crystallises with face-centred cubic unit cells. Each side of the unit cell has a length of 409 pm. What is the radius of an atom of silver? (Assume that each face atom is touching the four corner atoms.)
Answer. Given : a = 409 pm r = ?
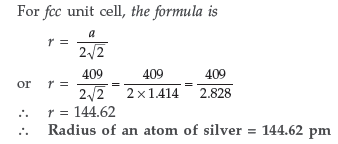
Question. Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell dimension of 286.65 pm. The density of iron is 7.874 g cm–3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number.
(Atomic mass of Fe = 55.84 g mol–1)
Answer. Given :
a = 286.65 pm = 286.65 × 10–10,d = 7.87 g cm–3, M = 56 g mol–1 Z = 2 NA = ?

Question. Silver crystallizes in face-centered cubic unit cell. Each side of this unit cell has a length of 400 pm. Calculate the radius of the silver atom. (Assume the atoms just touch each other on the diagonal across the face of the unit cell. That is each face atom is touching the four corner atoms.)
Answer. Given : a = 400 pm, r = ?
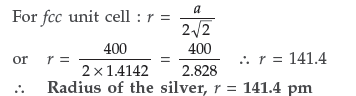
Question. The density of lead is 11.35 g cm–3 and the metal crystallizes with fcc unit cell. Estimate the radius of lead atom.(At. Mass of lead = 207 g mol–1 and NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
Answer. Given : d = 11.35 g cm–3
According to the formula

Question. Tungsten crystallizes in body centred cubic unit cell. If the edge of the unit cell is 316.5 pm, what is the radius of tungsten atom?
Answer.

Question. Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with a cell dimension of 286.65 pm. The density of iron is 7.874 g cm–3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number.(At. mass of Fe = 55.845 u)
Answer.

Question. Copper crystallises with face centred cubic unit cell. If the radius of copper atom is 127.8 pm, calculate the density of copper metal. (Atomic mass of Cu = 63.55 u and Avogadro’s
number NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
Answer.
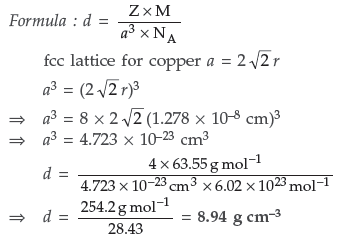
Question. (a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids: Silicon carbide, Argon
(b) ZnO turns yellow on heating. Why?
(c) What is meant by groups 12-16 compounds? Give an example. (All India)
Answer. (a) Silicon carbide is a covalent or network solid while Argon is a non-polar molecular solid.
(b) ZnO shows metal excess defect due to presence of extra cations, i.e., Zn2+ ions in interstitial sites which on heating changes into yellow due to loss of oxygen.

(c) Group 12-16 compounds are imperfect covalent compounds in which the ionic character depends on the electronegativities of the two elements, e.g., ZnS, CdS, etc.
Question. (a) What are intrinsic semi-conductors? Give an example.
(b) What is the distance between Na+ and Cl– ions in NaCl crystal if its density is 2.165 g cm–3? [Atomic Mass of Na = 23u, Cl = 35.5u; Avogadro’s number = 6.023×1023]
Answer. (a) Intrinsic semi-conductors : These are insulators at room temperature and become semi-conductors when temperature is raised,Example : silicon and germanium.
(b) Applying the formula
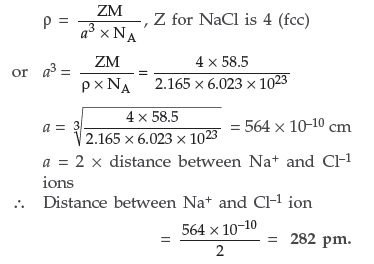
Question. Define the following :
(i) Schottky defect (ii) Frenkel defect
(iii) F-centre (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer.(i) Schottky defect : If in an ionic crystal of type A+ B–, equal number of cations and anions are missing from their lattice sites so that the electrical neutrality is maintained, it is called Schottky defect.

(ii) Frenkel defect : If an ion leaves its site from its lattice site and occupies the interstitial site and maintains electrical neutrality, then it is called Frenkel defect.

(iii) F-centre : The centres which are created by trapping of electrons in anionic vacancies and which are responsible for imparting colour to the crystals are called F-centres.(F = Fabre)

Question. (a) What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with boron?
(b) What type of magnetism is shown in the following alignment of magnetic moments?

(c) What type of point defect is produced when AgCl is doped with CdCl2?
Answer. (a) p-type semi-conductor is obtained when silicon is doped with boron.
(b) Ferromagnetism is shown when the alignment of magnetic movements will be

(c) Impurity defect of inonic solids is produced when AgCl is doped with CdCl2. Due to this defect vacancies are created that result in higher electrical conductivity of the solid.
Question. The density of copper metal is 8.95 g cm–3. If the radius of copper atom is 127.8 pm, is the copper unit cell a simple cubic, a body-centred cubic or a face centred cubic structure? (Given : At. mass of Cu = 63.54 g mol–1 and NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
Answer. If copper atom were simple cubic :
a = 2 × r = 2 × 127.8 pm
= 255.6 pm = 255.6 ×10–10 cm
Z = 1


Question. An element occurs in bcc structure. It has a cell edge length of 250 pm. Calculate the molar mass if its density is 8.0 g cm–3. Also calculate the radius of an atom of this element.
Answer. Given : For bcc structure, Z = 2
Edge of the unit cell, a = 250 ρm
Density of the element, ρ = 8.0 g/cm3
M = ? r = ?
Using the formula
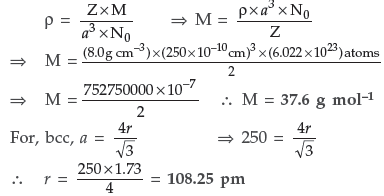
Question. Iron (II) oxide has a cubic structure and each unit cell has a size of 5 Å. If density of this oxide is 4 g cm–3, calculate the number of Fe2+ and O2– ions present in each unit cell.(Atomic mass of Fe = 56, O = 16, NA = 6.023 × 1023 and 1 Å = 10–8 cm)
Answer. Given : ρ = 4g cm–3
a = 5Å = 5 × 10–8 cm M = 72 g/mol, Z = ?
Using the formula for cubic crystals
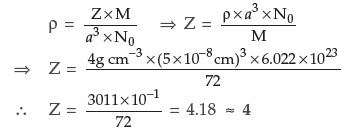
There are four formula units of FeO present per unit cell. Hence it has face-centred cubic lattice where each Fe2+ and O2– are four in number.
Question. The well known mineral fluorite is chemically calcium fluoride. It is known that in one unit cell of this mineral there are 4 Ca2+ ions and 8 F– ions and that Ca2+ ions are arranged in a fcc lattice. The F– ions fill all the tetrahedral holes in the face centred cubic lattice of Ca2+ ions. The edge of the unit cell is 5.46 × 10 –8 cm in length. The density of the solid is 3.18 g cm–3. Use this information to calculate Avogadro’s number (Molar mass of CaF2 = 78.08 g mol–1).
Answer. Given :
Edge of the unit cell (a) = 5.46 × 10 –8 cm
Density (P) = 3.18 g cm–3
According to the formula :
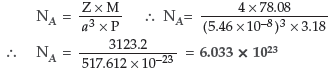
Question. (a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids: Benzene, Silver
(b) AgCl shows Frenkel defect while NaCl does not. Give reason.
(c) What type of semiconductor is formed when Ge is doped with Al? (All India)
Answer. (a) Benzene — Molecular solid (non-polar)
Silver — Metallic solid
(b) Due to intermediate radius of AgCl, the size of Ag+ is smaller than larger Na+ ion of NaCl so it can easily occupy interstitial spaces and shows Frenkel defect.
(c) p-type semiconductor is formed when Ge is doped with Al.
Question. Niobium crystallizes in body-centred cubic structure. If its density is 8.55 g cm–3, calculate atomic radius of niobium, given its atomic mass 93u. (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer.


Question. Examine the given defective crystal :
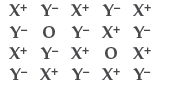
Answer the following questions :
(i) Is the above defect stoichiometric or nonstoichiometric?
(ii) Write the term used for this type of defect. Give an example of the compound which shows this type of defect.
(iii) How does this defect affect the density of the crystal? (All India)
Answer. (i) It is stoichiometric defect.
(ii) Schottky defect, e.g. NaCl.
(iii) Density of crystal decreases.
Question. (a) Some of the glass objects recovered from ancient monuments look milky instead of being transparent. Why?
(b) Iron (ΙΙ) oxide has a cubic structure and each side of the unit cell is 5Å. If density of the oxide is 4 g cm–3, calculate the number of Fe2+ and O2– ions present in each unit cell. [Atomic mass : Fe = 56 u, O = 16 u; Avagadro’s number = 6.023 × 1023 mol–1]
Answer. (a) Some of the glass objects found from ancient monuments look to be milky in appearance because of crystallisation of glass.
(b) Volume of unit cell = a3 = (5Å) = (5 × 10–8)3 = 1.25 × 10–22 cm
Density of FeO = 4g cm–3
Mass of unit cell = Volume × Density
= 1.25 × 10–22 × 4 g
= 5 × 10–22 g
Mass of FeO molecule per unit cell
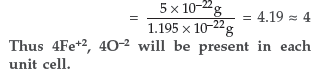
Question. An element crystallizes in a f.c.c. lattice with cell edge of 250 pm. Calculate the density if 300 g of this element contains 2 × 1024 atoms.
Answer. Given: a = 250 pm = 250 × 10–10 cm
z = 4 (for fcc)
M = ? d = ?

Question. An element crystallizes in a b.c.c. lattice with cell edge of 500pm. The density of the element is 7.5g cm–3. How many atoms are present in 300 g of the element?
Answer. Given: For b.c.c. structure, z = 2
Edge of the unit cell, a = 500 pm = 500 × 10–10 cm
Density d = 7.5 g cm–3
Using the formula,


Question. If NaCl is doped with 10–3 mol % of SrCl2, what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
Answer. Concentration of SrCl2 = 10–3 mol% = 10–3/100
mol = 10–5 mol
1 mol of NaCl on doping procuces = 6.022 × 1023 cation vacancies
Therefore, 10–5 mol of NaCl on doping produces = 6.022 × 1023 × 10–5 = 6.022 × 1018 cation vacancies
Question.98. Silver crystallises in f.c.c. lattice. If edge length of the cell is 4.07 × 10–8 cm and density is 10.5 g cm–3, calculate the atomic mass of silver.
Answer.

Question. Iron has a body centred cubic unit cell with the cell dimension of 286.65 pm. Density of iron is 7.87 g cm–3. Use this information to calculat Avogadro’s number. (Atomic mass of Fe = 56.0 u)
Answer.

Question. Silver crystallises in fcc lattice. If edge length of the unit cell is 4.077 × 10–8 cm, then calculate the radius of silver atom.
Answer. Given : a = 4.077 × 10–8 cm r = ? for fcc lattice Using formula,
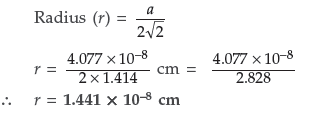
Question. The density of copper is 8.95 g cm–3. It has a face centred cubic structure. What is the radius of copper atom? (Atomic mass Cu = 63.5 g mol–1,NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1)
Answer.
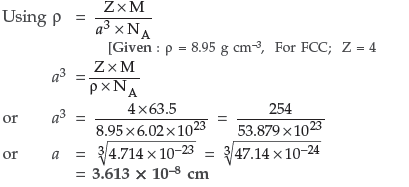
Question. An element crystallises in b.c.c. lattice with cell edge of 400 pm. Calculate its density if 500 g of this element contains 2.5 × 1024 atoms.
Answer. Given : a = 400 pm = 400 × 10–10 cm
Z = 2 (for bcc) M = ? d = ?

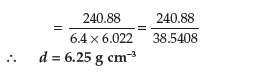
Question.105. An element exists in bcc lattice with a cell edge of 288 pm. Calculate its molar mass if its density is 7.2 g/cm3. (Comptt. All India)
Answer. Given : Cell edge, a = 288 pm = 288 × 10–10 cm
Density, d = 7.2 g/cm3
For bcc formula, units per cell Z = 2, M = ?
Using formula and substituting values,

Question. An element crystallises in fcc lattice with cell edge of 400 pm. Calculate its density if 250 g of this element contain 2.5 × 1024 atoms.
Answer. Given : a = 400 pm = 400 × 10–10 cm
Z = 4 (for fcc), M = ?, d = ?

Question. (a) Based on the nature of intermolecular forces, classify the following solids: Sodium sulphate, Hydrogen
(b) What happens when CdCl2 is doped with AgCl?
(c) Why do ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances? (All India)
Answer. (a) Sodium sulphate — Ionic solid Hydrogen — Molecular solid (non-polar)
(b) Cd2+ ion is dipositive and therefore addition of one Cd2+ ion results in the loss of two Ag+ ions from the lattice. But out of 2 holes obtained, one is occupied by Cd2+ ion and one left empty. Hence, addition of CdCl2 results in an impurity defect with cation vacancy.
(c) In ferrimagnetism, domains/magnetic moments are aligned in opposite direction in unequal numbers while in antiferromagnetic substances, the domains align in opposite direction in equal numbers so they cancel magnetic moments completely, i.e., net magnetism is zero.
Question. An element crystallises in bcc lattice with cell edge of 400 pm. Calculate its density if 250 g of this element contains 2.5 × 1024 atoms.
Answer. Given : a = 400 pm = 400 × 10–10 cm
Z = 2 (for bcc), M = ?, d = ?

Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Calculate the number of unit cells in 8.1 g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a f.c.c. structure. (Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol–1)
(b) Give reasons:
(i) In stoichiometric defects, NaCl exhibits Schottky defect and not Frenkel defect.
(ii) Silicon on doping with Phosphorus form n-type semiconductor.
(iii) Ferrimagnetic substances show better magnetism than antiferromagnetic substances.
Answer. (a) Given:
Mass of Al = 8.1,
Atomic mass of Al = 27 g mol–1
No. of atoms = η × 6.022 × 1023
= 8.1/27 × 6.022 × 1023
= 0.3 × 6.022 × 1023
= 1.8066 × 1023
Since one f.c.c. unit cell has 4 atoms
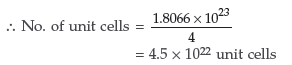
(b) (i) Schottky defect is shown by the ionic solids having very small difference in their cationic and anionic radius whereas Frenkel defect is shown by ionic solids having large difference in their cationic and anionic radius. NaCl exhibits Schottky defect because radius of both Na+ and Cl– have very small difference.
(ii) Phosphorus is pentavalent that is it has 5 valence electrons, an extra electron results in the formation of n-type semi conductors on doping with Silicon.The conductivity is due to presence of extra electrons
(iii) In antiferromagnetic substances the magnetic moments of domains are half aligned in one direction and remaining half in opposite direction in the presence of magnetic field so magnetic moment will be zero while in ferrimagnetic substances the magnetic moments of domains are aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers, hence shows some value of magnetic moment.
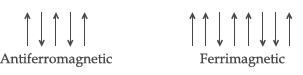
Question.106. (a) An element has an atomic mass 93 g mol–1 and density 11.5 g cm–3. If the edge length of its unit cell is 300 pm, identify the type of unit cell.
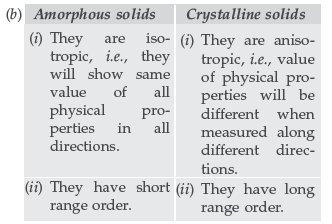
(b) Write any two differences between amorphous solids and crystalline solids.
Answer. (a) Given:
M = 93 g mol–1; ρ = 11.5 g cm–3;
a = 300 pm = 300 × 10–10 cm = 3 × 10–8 cm
Using formula,

As the number of atoms present in given unit cells are coming nearly equal to 2, hence the given units cell is body centered cubic unit cell (BCC).