Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 1 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 1 Solutions have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the Class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Solutions Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question. Which one of the following is not correct for an ideal solution?
(a) It must obey Raoult’s law
(b) ΔH = 0
(c) ΔH = ΔV ≠ 0
(d) All are correct
Answer
C
Question. The term homogenous mixtures signifies that
(a) its composition is uniform throughout the mixture.
(b) its properties are uniform throughout the mixture.
(c) both composition and properties are uniform throughout the mixture.
(d) neither composition nor properties are uniform throughout the mixture.
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a quantitative description of the solution?
(a) Dilute
(b) Concentrated
(c) Saturated
(d) Molar
Answer
D
Question. Mixtures of ethanol and acetone show positive deviation.The reason is
(a) In pure ethanol, molecules are hydrogen bonded.
(b) In pure acetone, molecules are hydrogen bonded
(c) In both molecules are hydrogen bonded
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The vapour pressure of pure benzene at 25°C is 640 mm Hg and that of solution of solute A is 630 mm Hg. The molality of solution is
(a) 0.2 m
(b) 0.4 m
(c) 0.5 m
(d) 0.1 m
Answer
A
Question. The statement “If 0.003 moles of a gas are dissolved in 900 g of water under a pressure of 1 atmosphere, 0.006 moles will be dissolved under a pressure of 2 atmospheres”, illustrates
(a) Dalton’s law of partial pressure
(b) Graham’s law
(c) Raoult’s law
(d) Henry’s law
Answer
D
Question. 4.0 g of NaOH is dissolved in 100 ml solution. The normality of the solution is
(a) 0.1 N
(b) 0.5 N
(c) 4.0 N
(d) 1.0 N
Answer
D
Question. The decrease in the vapour pressure of solvent depends on the
(a) quantity of non-volatile solute present in the solution
(b) nature of non-volatile solute present in the solution
(c) molar mass of non-volatile solute present in the solution
(d) physical state of non-volatile solute present in the solution
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure?
(a) mole fraction
(b) parts per million
(c) mass percentage
(d) molality
Answer
A
Question. 10 g of NaCl is dissolved in 106g of the solution. Its concentration is
(a) 100 ppm
(b) 0.1 ppm
(c) 1 ppm
(d) 10 ppm
Answer
D
Question. On adding a solute to a solvent having vapour pressure 0.80 atm, vapour pressure reduces to 0.60 atm. Mole fraction of solute is
(a) 0.25
(b) 0.75
(c) 0.50
(d) 0.33
Answer
A
Question. 2.5 litres of NaCl solution contain 5 moles of the solute. What is the molarity?
(a) 5 molar
(b) 2 molar
(c) 2.5 molar
(d) 12.5 molar
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following liquid pairs shows a positive deviation from Raoult’s law ?
(a) Water – Nitric acid
(b) Benzene – Methanol
(c) Water – Hydrochloric acid
(d) Acetone – Chloroform
Answer
B
Question. 25ml of a solution of barium hydroxide on titration with a 0.1 molar solution of hydrochloric acid gave a titre value of 35 ml. The molarity of barium hydroxide solution was
(a) 0.07
(b) 0.14
(c) 0.28
(d) 0.35
Answer
A
Question. Mole fraction of the solute in a 1.00 molal aqueous solution is
(a) 0.1770
(b) 0.0177
(c) 0.0344
(d) 1.7700
Answer
B
Question. All form ideal solution except
(a) C6H6 and C6H5CH3
(b) C2H6 and C2H5I
(c) C6H5Cl and C6H5B
(d) C2H5 I and C2H5OH.
Answer
D
Question. The volume of 4 N HCl and 10 N HCl required to make 1 litre of 6 N HCl are
(a) 0.75 litre of 10 N HCl and 0.25 litre of 4 N HCl
(b) 0.50 litre of 4 N HCl and 0.50 litre of 10 N HCl
(c) 0.67 litre of 4 N HCl and 0.33 litre of 10 N HCl
(d) 0.80 litre of 4 N HCl and 0.20 litre of 10 N HCl
Answer
C
Question. Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution. At 300 K, vapour pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y is 550 mm Hg. At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further added to this solution, vapour pressure of the solution increases by 10 mm Hg. Vapour pressure ( in mm Hg) of X and Y in their pure states will be, respectively
(a) 300 and 400
(b) 400 and 600
(c) 500 and 600
(d) 200 and 300
Answer
B
Question. 200 ml of water is added to 500 ml of 0.2 M solution. What is the molarity of this diluted solution ?
(a) 0.5010 M
(b) 0.2897 M
(c) 0.7093 M
(d) 0.1428 M
Answer
D
Question. For preparing 0.1 N solution of a compound from its impure sample of which the percentage purity is known, the weight of the substance required will be
(a) Less than the theoretical weight
(b) More than the theoretical weight
(c) Same as the theoretical weight
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. 5 ml of N HCl, 20 ml of N/2 H2SO4 and 30 ml of N/3 HNO3 are mixed together and volume made to one litre. The normality of the resulting solution is
(a) N/5
(b) N/10
(c) N/20
(d) N/40
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following concentration terms is/are independent of temperature?
(a) Molality only
(b) Molality and mole fraction
(c) Molarity and mole fraction
(d) Molality and normality
Answer
B
Question. A solution is prepared by dissolving 10 g NaOH in 1250 mL of a solvent of density 0.8 mL/g. The molality of the solution in mol kg–1 is
(a) 0.25
(b) 0.2
(c) 0.008
(d) 0.0064
Answer
A
Question. The azeotropic mixture of water (b.p.100°C) and HCl (b.p.85°C) boils at 108.5°C. When this mixture is distilled it is possible to obtain
(a) pure HCl
(b) pure water
(c) pure water as well as pure HCl
(d) neither HCl nor H2O in their pure states
Answer
D
Question. For mixture containing “four” components which of the following is correct in term of mole fraction?
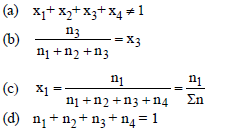
Answer
C
Question. When a solid solute is added to the solvent, some solute dissolves and its concentration increases in solution. This process is known as ______. Some solute particles in solution collide with the solid solute particles and get separated out of solution. This process is known as ______.
(a) Crystallization, dissolution.
(b) Dissolution, saturation.
(c) Saturation, crystallization.
(d) Dissolution, crystallization
Answer
D
Question. At the state of dynamic equilibrium, for solute + solvent ⇌ solution.
(a) Rate of dissolution = Rate of unsaturation.
(b) Rate of dissolution = Rate of unsaturation.
(c) Rate of dissolution = Rate of saturation
(d) Rate of crystallization = Rate of saturation.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) A solution in which no more solute can be dissolved at the same temperature and pressure is called a saturated solution.
(b) An unsaturated solution is one in which more solute can be dissolved at the same temperature.
(c) The solution which is in dynamic equilibrium with undissolved solute is the saturated solution.
(d) The minimum amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solvent is its solubility.
Answer
D
Question. On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature solution feels cool to touch. Under which of the following cases dissolution of sugar will be most rapid ?
(a) Sugar crystals in cold water.
(b) Sugar crystals in hot water.
(c) Powdered sugar in cold water.
(d) Powdered sugar in hot water.
Answer
D
Question. The solubility of a solid in a liquid is significantly affected by temperature changes.
Solute + Solvent ⇌ Solution.
The system being in a dynamic equilibrium must follow Le-chatelier’s principle. Considering the Le-chatelier’s principle which of the following is correct?

Answer
B
Question. In a 0.2 molal aqueous solution of a weak acid HX the degree of ionization is 0.3. Taking kf for water as 1.85, the freezing point of the solution will be nearest to
(a) – 0.360ºC
(b) – 0.260ºC
(c) + 0.481ºC
(d) – 0.481ºC
Answer
D
Question.
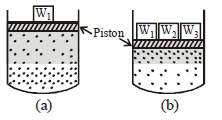
On the basis of the figure given above which of the following is not true?
(a) In figure (a) assuming the state of dynamic equilibrium rate of gaseous particles entering and leaving the solution phase is same.
(b) In figure (b) on compressing the gas number of gaseous particles per unit volume over the solution increases.
(c) Rate at which gaseous particles are striking the solution to enter it, decreases.
(d) Rate at which gaseous particles are striking the solution to enter it, increases.
Answer
C
Question. The vapour pressure of two liquids ‘P’ and ‘Q’ are 80 and 60 torr, respectively. The total vapour pressure of solution obtained by mixing 3 mole of P and 2 mole of Q would be
(a) 72 torr
(b) 140 torr
(c) 68 torr
(d) 20 torr
Answer
A
Question. According to Henry’s law, the amount of gas that will dissolve in blood plasma or any other liquid is determined by which of these factor?
(a) Solubility of the gas in the liquid.
(b) The total pressure of the gas mixture .
(c) pH of the liquid.
(d) The osmotic pressure of the gas mixture.
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following mixture is(are) called solution?
(i) water + ammonia (ii) water + acetone
(iii) acetone + alcohol (iv) hexane + water
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. Henry’s law constant of oxygen is 1.4 × 10–3 mol. lit–1. atm–1 at 298 K. How much of oxygen is dissolved in 100 ml at 298 K when the partial pressure of oxygen is 0.5 atm?
(a) 1.4 g
(b) 3.2 g
(c) 22.4 mg
(d) 2.24 mg
Answer
D
Question. At equillibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is ______.
(a) less than the rate of crystallisation.
(b) greater than the rate of crystallisation.
(c) equal to the rate of crystallisation.
(d) zero
Answer
C
Question.A beaker contains a solution of substance ‘A’. Precipitation of substance ‘A’ takes place when small amount of ‘A’ is added to the solution. The solution is ______.
(a) saturated
(b) supersaturated
(c) unsaturated
(d) concentrated
Answer
B
Question. The vapour pressure of pure benzene and toluene at a particular temperature are 100 mm and 50 mm respectively.Then the mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase in contact with equimolar solution of benzene and toluene is
(a) 0.67
(b) 0.75
(c) 0.33
(d) 0.50
Answer
A
Question. Value of Henry’s constant KH _______.
(a) increases with increase in temperature.
(b) decreases with increase in temperature.
(c) remains constant.
(d) first increases then decreases.
Answer
A
Question. What is the normality of a 1 M solution of H3PO4 ?
(a) 0.5 N
(b) 1.0 N
(c) 2.0 N
(d) 3.0 N
Answer
D
Question. Which of the followingfactor(s) affect the solubility of a gaseous solute in the fixed volume of liquid solvent ?
(i) Nature of solute (ii) Temperature (iii) Pressure
(a) (i) and (iii) at constant T
(b) (i) and (ii) at constant P
(c) (ii) and (iii) only
(d) (iii) only
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following graph is a correct representation of Henry’s law?
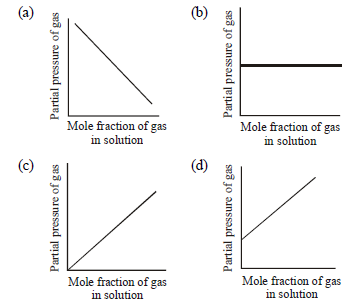
Answer
C
Question. People living at high attitudes often reported with a problem of feeling weak and inability to think clearly. The reason for this is.
(a) at high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is less than at the ground level.
(b) at high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is more than at the ground level.
(c) at high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is equal to at the ground level.
(d) None of these.
Answer
A
Question. ____ a contemporary of Henry concluded independently that solubility of a gas in a liquid solution is a function of ____ of the gas.
(a) Mosley, temperature
(b) Dalton, temperature
(c) Dalton, partial pressure
(d) Mosley, partial pressure
Answer
C
Question. Raoult’s law becomes a special case of Henry’s law when
(a) KH = p1°
(b) KH > p1°
(c) KH < p1°
(d) KH ≥ p1°
Answer
A
Question. “The importance of many pure substance in life depends on their composition.” Which of the following statement justify the above fact?
(a) 1 ppm of fluoride ions in water prevents tooth decay.
(b) 1.5 ppm of fluoride ions causes tooth decay.
(c) Concentration above 1.5 ppm can be poisonous.
(d) All of the above.
Answer
D
Question. Iodine and sulphur dissolve in
(a) water
(b) benzene
(c) carbon disulphide
(d) ethanol
Answer
C
Question. According to Raoult’s law, relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solution is equal to
(a) moles of solute
(b) moles of solvent
(c) mole fraction of solute
(d) mole fraction of solvent
Answer
C
Question. 1 M, 2.5 litre NaOH solution is mixed with another 0.5 M, 3 litre NaOH solution. Then find out the molarity of resultant nsolution
(a) 0.80 M
(b) 1.0 M
(c) 0.73 M
(d) 0.50 M
Answer
C
Question. The boiling point of an azeotropic mixture of water and ethanol is less than that of water and ethanol. The mixture shows
(a) no deviation from Raoult’s Law.
(b) positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
(c) negative deviation from Raoult’s Law.
(d) that the solution is unsaturated.
Answer
B
Question. Osmotic pressure of a solution is 0.0821 atm at a temperature of 300 K. The concentration in moles/litre will be
(a) 0.33
(b) 0.666
(c) 0.3×10–2
(d) 3
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following condition is not satisfied by an ideal solution?
(a) ΔHmixing = 0
(b) ΔVmixing = 0
(c) Raoult’s Law is obeyed
(d) Formation of an azeotropic mixture
Answer
D
Question. Mole fraction of glycerine C3H5(OH)3 in solution containing 36 g of water and 46 g of glycerine is
(a) 0.46
(b) 0.40
(c) 0.20
(d) 0.36
Answer
C
Question. The molal elevation constant depends upon
(a) nature of solute.
(b) nature of the solvent.
(c) vapour pressure of the solution.
(d) enthalpy change.
Answer
B
Question. The van’t Hoff factor (i) accounts for
(a) degree of solubilisation of solute.
(b) the extent of dissociation of solute.
(c) the extent of dissolution of solute.
(d) the degree of decomposition of solution.
Answer
B
Question. Which has the lowest boiling point at 1 atm pressure?
(a) 0.1 M KCl
(b) 0.1 M Urea
(c) 0.1 M CaCl2
(d) 0.1 M AlCl3
Answer
B
Question. Out of molality (m), molarity (M), formality (F) and mole fraction (x), those which are independent of temperature are
(a) M, m
(b) F, x
(c) m, x
(d) M, x
Answer
C
Question. People add sodium chloride to water while boiling eggs. This is to
(a) decrease the boiling point.
(b) increase the boiling point.
(c) prevent the breaking of eggs.
(d) make eggs tasty.
Answer
B
Question. Which relationship is not correct?
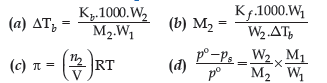
Answer
B
Assertion-Reason Type Questions
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements and Reason is correct explanation for Assertion.
(b) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements but Reason is not correct explanation for Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but Reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: 1 M glucose will have a higher boiling point than 2 M glucose.
Reason: Elevation in boiling point is a colligative property which depends upon the number of particles of solute in the solution.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion: An isotonic solution exerts same osmotic pressure under similar conditions.
Reason: Solute-solvent dipolar interactions exist in the pair of isotonic solution.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: An aqueous solution of NaCl freezes below 273 K.
Reason: Vapour pressure of the solution is less than that of the pure solvent.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Barium Chloride is more effective in causing coagulation than Potassium Chloride.
Reason: Ba2+ has greater valency of 2 than one valency of K+.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: On adding a non-volatile solute to a solvent, the vapour pressure of the solution get lowered.
Reason: A solution is said to be ideal if it strictly obeys Raoult’s law at all concentrations and temperatures.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: The Semipermeable membrane made of copper (II) ferrocyanide Cu2[Fe(CN)6] is not used for studying osmosis in a non-aqueous solution.
Reason: Copper (II) ferrocyanide is soluble in non-aqueous medium and insoluble in water.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: The boiling point of an azeotropic mixture of water and ethanol is less than that of water and ethanol.
Reason: Azeotropic mixture of water and ethanol show positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Molality is independent of temperature whereas molarity in a function of temperature.
Reason: Volume depends on temperature and mass does not depend on temperature.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Soft drink and soda water bottles are sealed under high pressure.
Reason: The dissolution of gas in liquid is an endothermic process.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: The aquatic species feel more comfortable in winter due to single space low temperature.
Reason: Solubility of gases increases with increase of temperature.
Answer
C
Case Based Questions
1. Fuel cells: Fuel cells are galvanic cells in which the chemical energy of fuel is directly converted into electrical energy. A type of fuel cell is a hydrogenoxygen fuel cell. It consists of two electrodes made up of two porous graphite impregnated with a catalyst (platinum, silver, or metal oxide).
The electrodes are placed in aqueous solution of NaOH. Oxygen and hydrogen are continuously fed into the cell. Hydrogen gets oxidized to H+ which is neutralized by OH, i.e., anodic reaction.
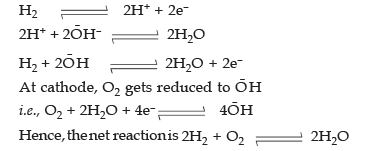
The overall reaction has ΔH = –285.6 KJ mol–1 and ΔG = –237.4 KJ mol–1 at 25˚C
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question. What is the value of ΔS– for the fuel cell at 25ºC?
(a) –1600 JK–1
(b) –160 JK–1
(c) 160 JK–1
(d) 1600 JK–1
Answer
B
Question. Suppose the concentration of hydroxide ion is doubled, then the cell voltage will be
(a) Reduced by half
(b) Increased by a factor of 2
(c) Increased by a factor of 4
(d) Unchanged
Answer
D
Question.(iv) A fuel cell is
I. A voltaic cell in which continuous supply of fuels are sent at anode to perform oxidation.
II. A voltaic cell in which fuels such as—Ch4, H2,and CO are used up at anode.
III. One which involves the reaction of H2—O2 fuel cell such as:

IV The efficiency of H2—O2 fuel cell is 70%–75%.
(a) I, III
(b) I, III, IV
(c) I, II, III, IV
(d) I, II, III
Answer
C
Question.(i) If the cell voltage is 1.23 V for the H2 — O2 fuel cell and for the half cell:
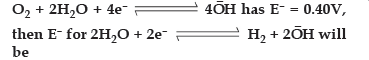
(a) 0.41V
(b) 0.83V
(c) –0.41V
(d) –0.83V
Answer
D
Question.(v) The reaction occurring at the cathode of hydrogen- oxygen fuel cell is

(c) H+ + OH– → H2O
(d) O2 + 2H2O + 4e– → 4OH–
Answer
D
2. The Properties of the solutions which depend only on the number of solute Particles but not on the nature of the solute are called colligative properties. Relative lowering in vapour pressure is also an example of colligative properties. For an experiment, sugar solution is prepared for which lowering in vapour pressure was found to be 0.061 mm of Hg. (Vabour pressure of water at 20ºC is 17.5 mm of Hg).
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. The vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of Solution will be
(a) 17.5
(b) 0.61
(c) 17.439
(d) 0.00348
Answer
C
Question. The vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of water at 293 K when 25 g of glucose is dissolved in 450 g of water is
(a) 17.2
(b) 17.4
(c) 17.120
(d) 17.02
Answer
B
Question. Mole fraction of sugar in the solution is
(a) 0.00348
(b) 0.9965
(c) 0.061
(d) 1.75
Answer
A
Question. Relative lowering of vapour pressure for the given solution is
(a) 0.00348
(b) 0.061
(c) 0.122
(d) 1.75
Answer
A
Question. If weight of sugar taken is 5 g in 108 g of water then molar mass of sugar will be
(a) 358
(b) 120
(c) 240
(d) 400
Answer
C
3. The concentration of a solute is very important in studying chemical reactions because it determines how often molecules collide in solution and thus indirectly determine the rate of reactions and the conditions at equilibrium.
There are several ways to express the amount of solute present in a solution. The concentration of a solution is a measure of the amount of solute that has been dissolved in a given amount of solvent or solution. Concentration can be expressed in terms of molarity, molality, parts per million, mass percentage, volume percentage etc.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question. Which of the following is true for an aqueous solution of the solute in term of concentration?
(a) 1 M = 1 m
(b) 1 M > 1 m
(c) 1 M < 1 m
(d) Cannot be predicted
Answer
B
Question. The molarity (in mol L–1) of the given solution will be
(a) 1.56
(b) 1.89
(c) 0.263
(d) 1.44
Answer
D
Question.(iii) Which of the following is correct relationship between mole fraction and molality?
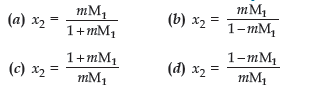
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is temperature dependent?
(a) Molarity
(b) Molality
(c) Mole fraction
(d) Mass percentage
Answer
A
Question. A solution is prepared using aqueous Kl which is turned out to be 20% w/w. Density of Kl is 1.202 g/mL. The molality of the given solution and mole fraction of solute are respectively.
(a) 1.95 m, 0.120
(b) 1.5 m, 0.0263
(c) 2.5 m, 0.0569
(d) 3.0 m, 0.0352
Answer
B
4. At 298 K, the vapour pressure of pure benzene, C6H6 is 0.256 bar and the vapour pressure of pure toluene C6H5CH3 is 0.0925 bar. Two mixtures were prepared as follows:
(I) 7.8 g of C6H6 + 9.2 g of toluene
(II) 3.9 g of C6H6 + 13.8 g of toluene
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question.Solution I is an example of a/an
(a) ideal solution
(b) non-ideal solution with positive deviation
(c) non-ideal solution with negative deviation
(d) cannot be predicted
Answer
A
Question. Which of the given solutions have higher vapour pressure?
(a) I
(b) II
(c) Both have equal vapour pressure
(d) Cannot be predicted
Answer
A
Question. The total vapour pressure (bar) of Solution I is
(a) 0.128
(b) 0.174
(c) 0.198
(d) 0.258
Answer
B
Question. Mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase in Solution I is
(a) 0.128
(b) 0.174
(c) 0.734
(d) 0.266
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements is/are correct?
I. Mole fraction of toluene in vapour phase is more in solution I.
II. Mole fraction of toluene in vapour phase is less in solution I.
III. Mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase is less in Solution I.
(a) Only II
(b) Only I
(c) I and III
(d) II and III
Answer
A
5. The solubility of gases increases with increase of pressure. William Henry made a systematic investigation of the solubility of a gas in a liquid. According to Henry’s law “the mass of a gas dissolved per unit volume of the solvent at constant temperature is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas in equilibrium with the solution”.
Dalton during the same period also concluded independently that the solubility of a gas in a liquid solution depends upon the partial pressure of the gas. If we use the mole fraction of gas in the solution as a measure of its solubility, then Henry’s law can be modified as “the partial pressure of the gas in the vapour phase is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution”.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. The partial pressure of ethane over a saturated solution containing 6.56 × 10–2 g of ethane is 1 bar. If the solution contains 5.00 × 10–2 g of ethane then what will be the partial pressure (in bar) of the gas?
(a) 0.762
(b) 1.312
(c) 3.81
(d) 5.0
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) KH increases with increase of temperature.
(b) KH decreases with increase of temperature.
(c) KH remains constant with increase of temperature.
(d) KH first increases then decreases, with increase of temperature.
Answer
A
Question. KH (K bar) values for Ar(g), CO2(g), HCHO(g) and CH4(g) are 40.39, 1.67, 1.83 × 10–5 and 0.413 respectively. Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility.
(a) HCHO < CH4 < CO2 < Ar
(b) HCHO < CO2 < CH4 < Ar
(c) Ar < CO2 < CH4 < HCHO
(d) Ar < CH4 < CO2 < HCHO
Answer
C
Question. Henry’s law constant for the solubility of methane in benzene at 298 K is 4.27 × 105 mm Hg. The solubility of methane in benzene at 298 K under 760 mm Hg is
(a) 4.27 × 10–5
(b) 1.78 × 10–3
(c) 4.27 × 10–3
(d) 1.78 × 10–5
Answer
B
Question. When a gas is bubbled through water at 298 K, a very dilute solution of the gas is obtained. Henry’s law constant for the gas at 298 K is 150 K bar. If the gas exerts a partial pressure of 2 bar, the number of millimoles of the gas dissolved in 1 L of water is
(a) 0.55
(b) 0.87
(c) 0.37
(d) 0.66
Answer
C
6. Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals. According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity.
(Source: Jayawardena, J. A. E. C., Vanniarachchi, M. P. G.,& Wansapala, M. A. J. (2017). Freezing point depression of different Sucrose solutions and coconut water.)
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. Identify which of the following is a colligative property?
(a) Freezing point
(b) Boiling point
(c) Osmotic pressure
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. Colligative properties are
(a) dependent only on the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s and solute’s identity.
(b) dependent only on the identity of the solute and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s identity.
(c) dependent on the identity of the solvent and solute and thus on the concentration of the solute.
(d) dependent only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solute’s identity.
Answer
D
Question. Assume three samples of juices A, B and C have glucose as the only sugar present in them. Th concentration of sample A, B and C are 0.1 M,0.5 M and 0.2 M respectively. Freezing point will be highest for the fruit juice
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) All have same freezing point
Answer
A
Question. When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will
(a) boil above 100ºC and freeze above 0ºC.
(b) boil below 100ºC and freeze above 0ºC.
(c) boil above 100ºC and freeze below 0ºC.
(d) boil below 100ºC and freeze below 0ºC.
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with arsenic?
Answer. n–type semiconductor.
Question. What is meant by ‘reverse osmosis’?
Answer. If a pressure higher than the osmotic pressure is applied on the solution, the solvent will flow from the solution into the pure solvent through semipermeable membrane. This process is called reverse osmosis (R.O.).
Question. What are isotonic solutions?
Answer. An isotonic solution is a kind of solution with the same salt concentration as blood and cells. Those solutions which are exerting same osmotic pressure under similar conditions (For example 0.9% NaCl solution by mass volume is Isotonic with human blood).
Question. Some liquids on mixing form ‘azeotropes’. What are ‘azeotropes’?
Answer. The liquid mixture having a definite composition and boiling like a pure liquid without change in composition is called as azeotrope.
Question. What type of intermolecular attractive interaction exists in the pair of methanol and acetone?
Answer. Solute-solvent dipolar interactions exist in the pair of methanol and acetone.
Question. Out of BaCl2 and KCl, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of a negatively charged colloidal Sol? Give reason.
Answer. BaCl2 is more effective in causing coagulation because it has double +ve charge than K+.
Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. Why do gases nearly always tend to be less soluble in liquids as the temperature is raised?
Answer. This is because the dissolution of gas in liquid is an exothermic process. The solubility should decrease with increase in temperature.
Question. Non-ideal solutions exhibit either positive or negative deviations from Raoult’s law. What are these deviations and why are they caused?
Explain with one example for each type.
Answer. Non-ideal solutions exhibit Negative deviation from Raoult’s law : For any composition of the non-ideal solution, the partial vapour pressure of each component and total vapour pressure of the solution is less than expected from Raoult’s law. Such solutions show negative deviation.
Example : Mixture of CHCl3 and acetone.

Non-ideal solutions show positive deviations from Raoult’s law on mixing of two volatile components of the solution.Example : Mixture of acetone and benzene solutions show positive deviation.
Question. A 1.00 molal aqueous solution of trichloroacetic acid (CCl3COOH) is heated to its boiling point.The solution has the boiling point of 100.18°C.
Determine the van’t Hoff factor for trichloroacetic acid. (Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol–1)
Answer. As ΔTb = iKbm
(100.18 – 100) °C = i × 0.512 K kg mol–1 × 1 m
0.18 K = i × 0.512 K kg mol–1 × 1 m
∴ i = 0.35
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (ii) Isotonic solutions
(iii) van’t Hoff factor (iv) Ideal solution
Answer. (i) Mole fraction : Mole fraction is the ratio of number of moles of one component to the total number of moles in a mixture.
(ii) Isotonic solution : Two solutions having same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called Isotonic solutions.
(iii) van’t Hoff factor : van’t Hoff factor is expressed as :
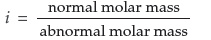
(iv) Ideal solution : The solution which obeys Raoult’s law under all conditions is known as an ideal solution.
Question. Explain why aquatic species are more comfortable in cold water rather than in warm water.
Answer. Aquatic species need dissolved oxygen for breathing. As solubility of gases decreases with increase of temperature, less oxygen is available in summer in the lake. Hence the aquatic species feel more comfortable in winter (low temperature) when the solubility of oxygen is higher.
Question. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan.At what temperature will this solution boil?
(Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol–1, boiling point of pure water = 373.15 K)
Answer. We know that :
Elevation of boiling point ΔTb
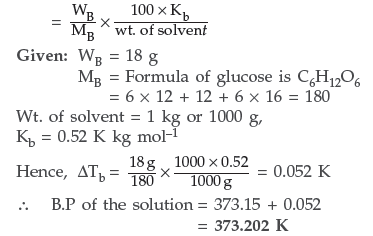
Question.Differentiate between molality and molarity of a solution. What is the effect of change in temperature of a solution on its molality and molarity?
Answer. Distinction between molarity and molality.
Molarity : It is the number of moles of solute dissolved in 1 litre of solution. It is temperature dependent.

Molarity is temperature dependent while molarity is not.
For very dilute solution, the factor MM2/1000 can be neglected in comparison to 1.
Hence molality will be same to molarity when density d = 1. Molality is independent of temperature, whereas molarity is a function of temperature because volume depends on temperature and mass does not.
Question. State Raoult’s law. How is it formulated for solutions of non-volatile solutes?
Answer. Raoult’s Law : Raoult’s Law states that “for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour of each component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction”.

Question. State Henry’s law and mention two of its important applications.
Answer. Henry’s law : Henry’s law states that “The partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution”.
Applications of Henry’s law :
(i) To increase the solubility of CO2 in soft drinks and soda water, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
(ii) To avoid a dangerous medical condition called bends, scuba divers use oxygen diluted with less soluble helium gas.
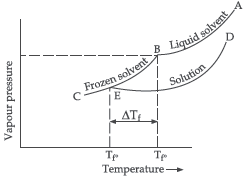
Question. An aqueous solution of sodium chloride freezes below 273 K. Explain the lowering in freezing points of water with the help of a suitable diagram.
Answer. An aqueous solution of sodium chloride freezes below 273 K because vapour pressure of the solution is less than that of the pure solvent.
Question. Derive expression for Raoult’s law when the solute is non-volatile.
Answer. Raoult’s law : Raoult’s law states that “for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction”.

Question. Calculate the mass of compound (molar mass = 256 g mol–1) to be dissolved in 75 g of benzene to lower its freezing point by 0.48 K (Kf = 5.12 K kg mol–1).
Answer.
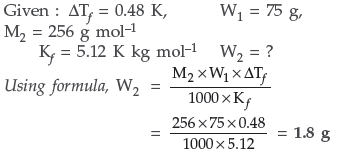
Question. Define an ideal solution and write one of its characteristics.
Answer. Those solutions which are obeying Raoult’s law are called ideal solutions. An ideal solution is a solution in which no volume change and no enthalpy change takes place on mixing the solute and the solvent in any proportion.
Characteristic of an ideal solution :
There will be no change in enthalpy ΔHmixing = 0,
ΔVmix = 0, ΔPmix = 0
Question. Define the terms, ‘osmosis’ and ‘osmotic pressure’.What is the advantage of using osmotic pressure as compared to other colligative properties for the determination of molar masses of solutes in solutions?
Answer. Osmosis : The net spontaneous flow of the solvent molecules from the solvent to the solution or from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution through a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
Osmotic pressure : The minimum excess pressure that has to be applied on the solution to prevent the entry of the solvent into the solution through the semipermeable membrane is called the osmotic pressure.
The osmotic pressure method has the advantage that it uses molarities instead of molalities and it can be measured at room temperature.
Question. State Raoult’s law for the solution containing volatile components. What is the similarity between Raoult’s law and Henry’s law?
Answer. Raoult’s law : “In a solution, the vapour pressure of a component at a given temperature is equal to the mole fraction of that component in the solution multiplied by the vapour pressure of that component in pure state.”
Similarity between Raoult’s law and Henry’s law is that the partial pressure or vapour pressure of the volatile component (gas) is directly proportional to the mole fraction of that component in the solution.
Question. (i) Gas (A) is more soluble in water than Gas
(B) at the same temperature. Which one of the two gases will have the higher value of KH (Henry’s constant) and why?
(ii) In non-ideal solution, what type of deviation shows the formation of maximum boiling azeotropes?
Answer. (i) Gas (B) will have higher value of KH
(Henry’s constant) than Gas (A) at the same temperature because lesser the solubility of a gas in a given solvent, higher will be the value of KH for a gas.
KH = Partial pressure of gas/Mole fraction of gas in the solution
(ii) Negative deviations from Raoult’s law show the formation of maximum boiling azeotropes.
Question. How is the vapour pressure of a solvent affected when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it?
Answer. The vapour pressure of a solvent decreases when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it because some solvent molecules are replaced by the molecules of solute.
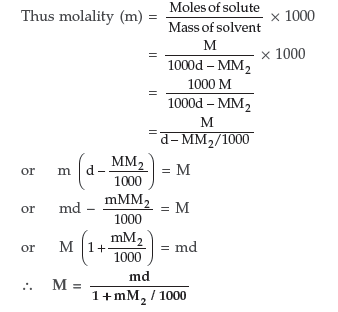
Question. Differentiate between molarity and molality of a solution. How can we change molality value of a solution into molarity value?
Answer.
Molarity (M) and Molality (m) relationship : Q Molarity is M moles of solute present in 1000 mL solution
If density of solution is d g mL–1, then
Mass of solution = 1000 d g Mass of solute = MM2
(M2 is molar mass of solute)
∴ Mass of solvent = 1000 d – MM2g
Question. What is meant by positive deviations from Raoult’s law? Give an example. What is the sign of ΔmixH for positive deviation?
Answer. In positive deviations, the partial vapour pressure of each component A and B of a solution and the total pressure of the solution is higher than the vapour pressure calculated from Raoult’s law.
For example, Water and Ethanol.
In case of positive deviations, ΔmixH > 0 (Positive)
Question. Define osmotic pressure. How is osmotic pressure related to the concentration of a solute in a solution?
Answer. Osmotic pressure is the measure of excess pressure applied on solution side to stop the process of osmosis. Osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the conentration of solute in solution π ∝ C
Question. Define osmotic pressure of a solution. How is the osmotic pressure related to the concentration of a solute in a solution?
Answer. Osmotic pressure : It is the external pressure which is applied on the side solution which is sufficient to prevent the entry of the solvent through semi-permeable membrane.
According to the Boyle-van’t Hoff Law, the osmotic pressure (π) of a dilute solution is directly proportional to its molar concentration provided temperature is constant.
π ∝ C (At constant temperature)
π ∝ CT (At constant concentration)
π = CRT (R = Solution constant)
or, π = (n/v) RT
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Ideal solution
(ii) Molarity (M)
Answer. (i) Ideal solution. The solution that obeys Raoults Law over the entire range of concentration.
(ii) Molarity is the number of moles of solute dissolved per litre of solution or
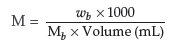
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (x)
(ii) Molality of a solution (m)
Answer. (i) Mole fraction : Mole fraction of a constituent is the fraction obtained by dividing number of moles of that constituent by the total number of moles of all the constituents
present in the solution. It is denoted by ‘x’.

(ii) Molality of a solution : Molality of a solution is defined as the number of moles of the solute dissolved in 1000 grams (1 kg) of the solvent. It is denoted by ‘m’.
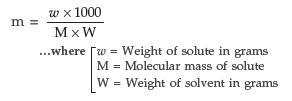
Question. What is osmotic pressure? Why it is a colligative property? (Comptt. Delhi)
Answer. The excess pressure applied on solution side to stop the process of osmosis. Because it depends upon the number of solute particles but not on their nature.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Colligative properties
(ii) Molality (m)
Answer. (i) Colligative properties. All those properties which depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of the nature of solute are called as colligative properties.
(ii) Molality (m). Number of moles of solute dissolved per kg of the solvent.
Question. (i) On mixing liquid X and liquid Y, volume of the resulting solution decreases. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is shown by the resulting solution? What change in temperature would you observe after mixing liquids X and Y?
(ii) What happens when we place the blood cell in water (hypotonic solution)? Give reason.
Answer. (i) Volume decreases by mixing X and Y. It
shows negative deviations from Raoult’s law. There will be rise in temperature.
(ΔHmix < 0)
(ii) Blood cell will swell due to osmosis as water enters the cell.
Question. State Henry’s law. What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas in a liquid?
Answer. Henry’s law : Henry’s law states that, “The solubility of a gas in a liquid at a particular temperature is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas in equilibrium with the liquid at that temperature.”
Solubility of gas decreases with increase of temperature at the same pressure.
Question. Define the following terms:
(i) Abnormal molar mass
(ii) van’t Hoff factor (i)
Answer. (i) Abnormal molar mass. If the molar mass calculated by using any of colligative properties tends to be different than theoretically expected molar mass, it is called abnormal molar mass.
(ii) van’t Hoff factor (i). Extent of dissociation or association or ratio of the observed colligative property to calculated colligative property.
i = Observed colligative property/Theoretical colligative property
Question.Define azeotropes. What type of azeotrope is formed by positive deviation from Raoult’s law? Given an example.
Answer. Azeotropes : Liquid mixture which distills without change in compositions are called azeotropic mixtures or Azeotropes.
In positive deviations from Raoult’s law,minimum boiling point azeotropic mixture is formed. For example, 95% ethanol + 5% water.
Short Answer Type Questions-II
Question. Calculate the freezing point depression expected for 0.0711 m aqueous solution of Na2SO4. If this solution actually freezes at – 0.320°C, what would be the value of Van’t Hoff factor? (Kf for water is 1.86°C mol–1)
Answer. Given : Molality, m = 0.0711 m
ΔTf = – 0.320°C Kf = 1.86°C i = ?
Substituting these values in the formula, we get

Question. A solution prepared by dissolving 1.25 g of oil of winter green (methyl salicylate) in 99.0 g of benzene has a boiling point of 80.31°C.Determine the molar mass of this compound. (B.P. of pure benzene = 80.10°C and Kb for benzene = 2.53°C kg mol–1).
Answer. Given : w2 = 1.25 g,w1 = 99 g
ΔTb = 80.31 – 80.10°C = 0.21°C
Kb = 2.53°C kg mol–1
According to the formula :
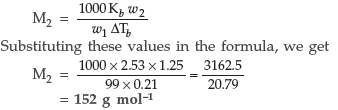
Question. An aqueous solution of 2 percent non-volatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.004 bar at the boiling point of the solvent. What is the molecular mass of the solute? [Vapour pressure of water = 1.013 bar]
Answer.


Question. A 10% solution (by mass) of sucrose in water has freezing point of 269.15 K. Calculate the freezing point of 10% glucose in water, if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K.
Given: (Molar mass of sucrose = 342 g mol–1) (Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol–1)
Answer.

Question. What mass of NaCl (molar mass = 58.5 g mol–1) must be dissolved in 65 g of water to lower the freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87.
Answer. Given : M2 = 58.5 g mol–1 w1 = 65 g
ΔTf = 7.5 °C Kf = 1.86 K kg mol–1 i = 1.87
Substituting these values in the formula
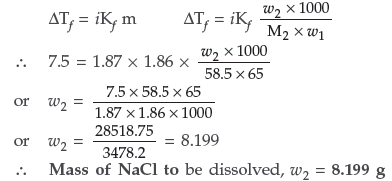
Question. What mass of ethylene glycol (molar mass = 62.0 g mol–1) must be added to 5.50 kg of water to lower the freezing point of water from 0° C to – 10.0° C? (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)?
Answer. According to the formula :
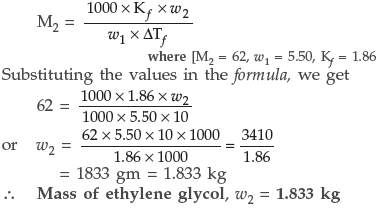
Question. 15 g of an unknown molecular substance was dissolved in 450 g of water. The resulting solution freezes at – 0.34° C. What is the molar mass of the substance?
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer. Given : w2 = 15 g, w1 = 450 g
ΔTf = – 0.34° CKf = 1.86 K kg mol–1 M2 = ?
Substituting these values in the formula,
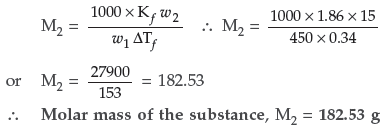
Question. 100 mg of a protein is dissolved in just enough water to make 10.0 mL of solution. If this solution has an osmotic pressure of 13.3 mm Hg at 25°C,what is the molar mass of the protein? (R = 0.0821 L atm mol–1 K–1 and 760 mm Hg = 1 atm.)
Answer. Given :
w = 100 mg = 0.100 = 0.1 g,
V = 10.0 mL = 0.01 L
π = 13.3 mm Hg = 13.3/760 atm,
T = 25°C = 25 + 273 = 298 K
R = 0.0821 L atm mol–1 K–1, M = ?

Question. A solution of glycerol (C3H8O3) in water was prepared by dissolving some glycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point of 100.42°C while pure water boils at 100 °C. What mass of glycerol was dissolved to make the solution?
Answer.
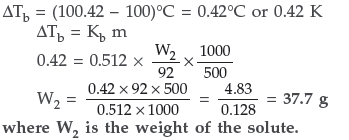
Question. A solution of glycerol (C3H8O3 ; molar mass = 92 g mol–1) in water was prepared by dissolving some glycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point of 100.42 °C. What mass of glycerol was dissolved to make this solution? Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol–1.
Answer. Given : M2 = 92 g mol–1 w1 = 500 g
ΔTb = 100.42 °C – 100 °C = 0.42 °C,
Kb = 0.512 K kg mol–1
Substituting above values in the formula
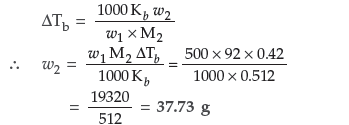
Question. 15.0 g of an unknown molecular material was dissolved in 450 g of water. The resulting solution was found to freeze at – 0.34 °C. What is the molar mass of this material? (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer.
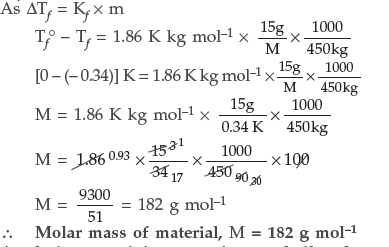
Question. The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B at 400 K are 450 and 700 mmHg respectively. Find out the composition of liquid mixture if total vapour pressure at this temperature is 600 mmHg.
Answer.
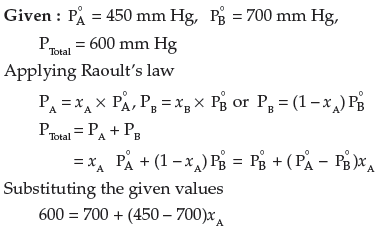

Question. A solution containing 30 g of non-volatile solute exactly in 90 g of water has a vapour pressure of 2.8 kPa at 298 K. Further 18 g of water is added to this solution. The new vapour pressure becomes 2.9 kPa at 298 K. Calculate
(i) the molecular mass of solute and
(ii) vapour pressure of water at 298 K.
Answer. For a very dilute solution
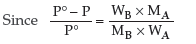
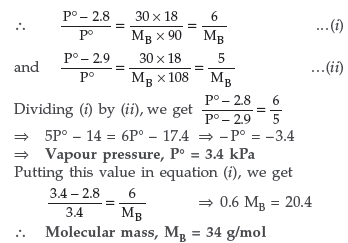
Question. The partial pressure of ethane over a saturated solution containing 6.56 × 10-2 g of ethane is 1 bar. If the solution contains 5.0 × 10–2 g of ethane, then what will be the partial pressure of the gas?
Answer. Applying the Henry’s law, m = KH × p
In first case, 6.56×10–2 = KH×1
KH = 6.56 × 10–2 g bar–1
Putting the value of KH in the second case, we get
5 × 10–2 g = 6.56 × 10–2 g bar–1 × p
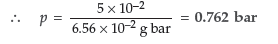
Question. Calculate the amount of KCl which must be added to 1 kg of water so that the freezing point is depressed by 2K. (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer.

Question. Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 2.5 × 10–2 g of K2SO4 in 2L of water at 25° C, assuming that it is completely dissociated.
(R = 0.0821 L atm K–1 mol–1, Molar mass of K2SO4 = 174 g mol–1).
Answer.

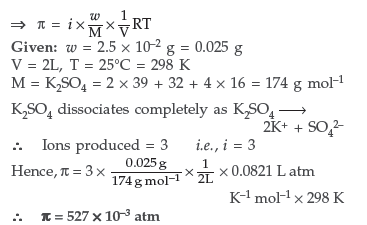
Question. Some ethylene glycol, HOCH2CH2OH, is added to your car’s cooling system along with 5 kg of water. If the freezing point of water-glycol solution is –15.0°C, what is the boiling point of the solution?
(Kb = 0.52 K kg mol–1 and Kf = 1.86 K kg mol–1 for water)
Answer.
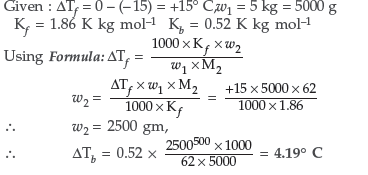
Question. A solution is prepared by dissolving 10 g of non-volatile solute in 200 g of water. It has a vapour pressure of 31.84 mm Hg at 308 K.Calculate the molar mass of the solute. (Vapour pressure of pure water at 308 K = 32 mm Hg)
Answer.

Question. 45 g of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) is mixed with 600 g of water. Calculate
(i) the freezing point depression and
(ii) the freezing point of the solution
(Given : Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer.

Question. A 5 percent solution (by mass) of cane-sugar (M.W. 342) is isotonic with 0.877% solution of substance X. Find the molecular weight of X.
Answer. Given : W (mass) of cane-sugar = 5% means 5 g
Molar mass of cane-sugar (M) = 342 g mol–1
Mass of isotonic substance X = 0.877% means 0.877 g
Molar mass of X = ?
Using formula,
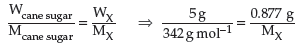

Question. Calculate the boiling point of solution when 4 g of MgSO4 (M =120 g mol–1) was dissolved in 100 g of water, assuming MgSO4 undergoes complete ionization.
(Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol–1)
Answer. Since MgSO4 is an ionic compound, so undergoes complete ionisation in the following way:
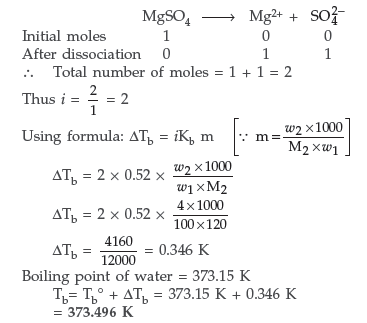
Question. If N2 gas is bubbled through water at 293K, how many millimoles of N2 gas would dissolve in 1 litre of water? Assume that N2 exerts a partial pressure of 0.987 bar. Given that Henry’s law constant for N2 at 293K is 76.48 k bar.
Answer.

Question. Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molecular mass 40) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce the vapour pressure to 80%.
Answer.

Question. 3.9 g of benzoic acid dissolved in 49 g of benzene shows a depression in freezing point of 1.62 K. Calculate the Van’t Hoff factor and predict the nature of solute (associated or dissociated). (Given : Molar mass of benzoic acid = 122 g mol–1, Kf for benzene = 4.9 K kg mol–1)
Answer.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question. (a) Explain why on addition of 1 mol glucose to 1 litre water the boiling point of water increases.
(b) Henry’s law constant for CO2 in water is 1.67 × 108 Pa at 298 K. Calculate the number of moles of CO2 in 500 ml of soda water
when packed under 2.53 × 105 Pa at the same temperature.
Answer. (a) Glucose is a non-volatile solute, therefore, addition of glucose to water lowers the vapour pressure of water as a result of which boiling point of water increases.

Question. (a) What is meant by :
(i) Colligative properties
(ii) Molality of a solution
(b) What concentration of nitrogen should be present in a glass of water at room temperature? Assume a temperature of 25° C, a total pressure of 1 atmosphere and mole fraction of nitrogen in air of 0.78.[KH for nitrogen = 8.42 × 10–7 M/mm Hg]
Answer. (a) (i) Colligative properties : Those properties of ideal solutions which depend only on the number of particles of the solute dissolved in a definite amount of the solvent and do not depend on the nature of solute are called colligative properties. (ii) Molality of a solution : Molality of a solution is defined as the number of moles of the solute dissolved in 1000 grams (1 kg) of the solvent. It is denoted by ‘m’.

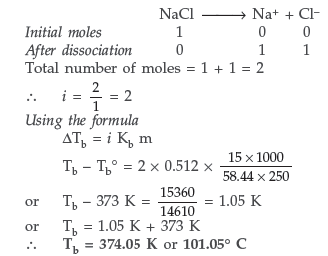
Question. (a) Define the terms osmosis and osmotic pressure. Is the osmotic pressure of a solution a colligative property? Explain.
(b) Calculate the boiling point of a solution prepared by adding 15.00 g of NaCl to 250.0 g of water.
(Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol–1, Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g)
Answer. Yes, osmotic pressure is the colligative property because it depends upon the number of particles of the solute.
(b) Since NaCl is an ionic compound so undergoes complete dissociation.
Question. (a) The vapour pressures of benzene and toluene at 293 K are 75 mm Hg and 22 mm Hg respectively. 23.4 g of benzene and 64.4 g of toluene are mixed. If the two form an ideal solution, calculate the mole fraction of benzene in the vapour phase assuming that the vapour pressures are in equilibrium with the liquid mixture at this temperature. (b) What is meant by +ve and –ve deviations from Raoult’s law and how is the sign of ΔH solution related to +ve and –ve deviations from Raoult’s law?
Answer.

(b) +ve and –ve deviations :
If it is higher, the solution exhibits positive deviation and if it is low, it exhibits negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
For positive deviation ΔmixH = +ve
For negative devation ΔmixH = –ve
Question. (a) State the following :
(i) Henry’s law about partial pressure of a gas in a mixture.
(ii) Raoult’s law in its general form in reference to solutions.
(b) A solution prepared by dissolving 8.95 mg of a gene fragment in 35.0 mL of water has an osmotic pressure of 0.335 torr at 25°C.
Assuming the gene fragment is a nonelectrolyte, determine its molar mass.
Answer. (a) (i) Henry’s law : “The solubility of a gas in a liquid at a particular temperature is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas in equilibrium with the liquid at that temperature.”
Applications of Henry’s law :
• In the production of carbonated beverages which are prepared under high pressure.
• Deep sea divers depend upon compressed air for their oxygen supply.
(ii) Raoult’s law : For a solution of volatile liquids the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution.
P = P°x
Non-ideal solution shows positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law.
• Positive deviation from Raoult’s law : The total vapour pressure for any solution is greater than the corresponding ideal solution of same
composition. Such behaviour is called positive deviation.
Example : Mixtures of ethanol + cyclohexane
Mixture of acetone + carbon disulphide
• Negative deviation from Raoult’s law : When the total vapour pressure will be less than corresponding vapour pressure, then it is termed as negative deviation.
Example : Chloroform + Benzene
Chloroform + Diethylether
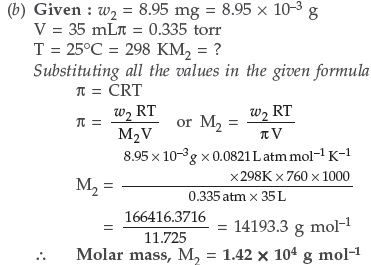
Question. (a) Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (ii) Van’t Hoff factor
(b) 100 mg of a protein is dissolved in enough water to make 10.0 mL of a solution. If this solution has an osmotic pressure of 13.3 mm Hg at 25°C,what is the molar mass of protein? (R = 0.0821 L atm mol–1 K–1 and 760 mm Hg = 1 atm)
Answer. (a) (i) Mole fraction : Mole fraction of a constituent is the fraction obtained by dividing number of moles of that constituent by the total number of moles of all the constituents present in the solution. It is denoted by ‘x’.
Example :

Question. (a) Differentiate between molarity and molality in a solution. What is the effect of temperature change on molarity and molality in a solution?
(b) What would be the molar mass of a compound if 6.21 g of it dissolved in 24.0 g of chloroform form a solution that has a boiling point of 68.04°C. The boiling point of pure chloroform is 61.7°C and the boiling point elevation constant, Kb for chloroform is 3.63°C/m.
Answer.

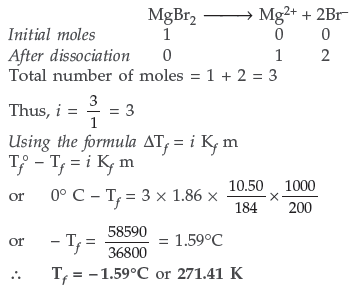
Question. (a) Differentiate between molarity and molality for a solution.How does a change in temperature influence their values?
(b) Calculate the freezing point of an aqueous solution containing 10.50 g of MgBr2 in 200 g of water. (Molar mass of MgBr2 = 184 g) (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer.
(b) Since MgBr2 is an ionic compound, so undergoes complete dissociation
Question. (a) Define the following terms :
(i) Mole fraction (ii) Ideal solution
(b) 15.0 g of an unknown molecular material is dissolved in 450 g of water. The resulting solution freezes at – 0.34°C. What is the molar mass of the material?
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Answer. (a) (i) Mole fraction : Mole fraction is the ratio of number of moles of one component to the total number of moles in a mixture.
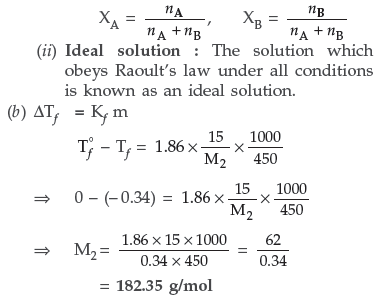
Question. (a) Define the following terms :
(i) Ideal solution
(ii) Osmotic pressure
(b) Calculate the boiling point elevation for a solution prepared by adding 10 g CaCl2 to 200 g of water, assuming that CaCl2 is completely dissociated.
(Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol–1; Molar mass of CaCl2 = 111 g mol–1)
Answer. (a) (i) Ideal solution : The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
(ii) The minimum excess pressure that has to be applied on the solution to prevent the entry of the solvent into the solution through the semipermeable membrane is called the osmotic pressure.
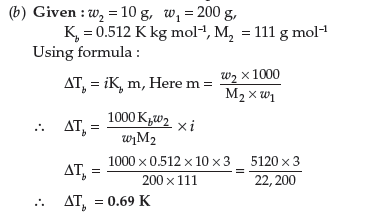
Question. (a) State Raoult’s law for a solution containing volatile components. How does Raoult’s law become a special case of Henry’s law? (b) 1.00 g of a non-electrolyte solute dissolved in 50 g of benzene lowered the freezing point of benzene by 0.40 K. Find the molar mass of the solute. (Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol–1)
Answer. Raoult’s law : For a solution of volatile liquids the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution.
P = P°x
Non-ideal solution shows positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law.
(i) Positive deviation from Raoult’s law : The total vapour pressure for any solution is greater than the corresponding ideal solution of same composition. Such behaviour is called positive deviation.
Example : Mixtures of ethanol + cyclohexane
Mixture of acetone + carbon disulphide
(ii) Negative deviation from Raoult’s law : When the total vapour pressure will be less than corresponding vapour pressure, then it is termed as negative deviation.
Example : Chloroform + Benzene
Chloroform + Diethylether
According to Raoult’s law PA = PAº × xA
According to Henry’s law PA = KH × xA
Thus both laws are identical and differ by their proportionality constants.

Question. (a) Define the following terms :
(i) Ideal solution (ii) Azeotrope
(iii) Osmotic pressure
(b) A solution of glucose (C6H12O6) in water is labelled as 10% by weight. What would be the molality of the solution?
(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol–1)
Answer. (a) (i) Ideal solution : An ideal solution is that which obeys Raoult’s law and in which the intermolecular interactions between the different components are of same magnitude as that is found in pure components.
(ii) Azeotrope : It is a type of liquid mixture having a definite composition and boiling like a pure liquid. (distills without change in compositions)
(iii) Osmotic pressure : The minimum excess pressure that has to be applied on the solution to prevent the entry of the solvent into the solution through semipermeable membrane is called osmotic pressure.
(b) 10% of glucose means 10 g of solute in 100 g of solvent
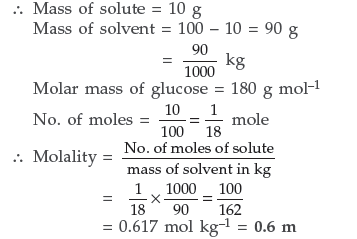
Question. (a) Define the following terms :
(i) Molarity
(ii) Molal elevation constant (Kb)
(b) A solution containing 15 g urea (molar mass = 60 g mol–1) per litre of solution in water has the same osmotic pressure (isotonic) as a solution of glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol–1) in water. Calculate the mass of glucose present in one litre of its solution.
Answer. (a) (i) Molarity is the number of moles of solute dissolved in one litre of solution.
(ii) Molal elevation constant may be defined as the elevation in boiling point when the molality of solution is unity i.e. 1 mole of solute is dissolved in 1 kg of the solvent.

Question. (a) When 2.56 g of sulphur was dissolved in 100 g of CS2, the freezing point lowered by 0.383 K. Calculate the formula of sulphur (SX).
(Kf for CS2 = 3.83 K kg mol–1, Atomic mass of Sulphur = 32 g mol–1)
(b) Blood cells are isotonic with 0.9% sodium chloride solution. What happens if we place blood cells in a solution containing
(i) 1.2% sodium chloride solution?
(ii) 0.4% sodium chloride solution?
Answer.
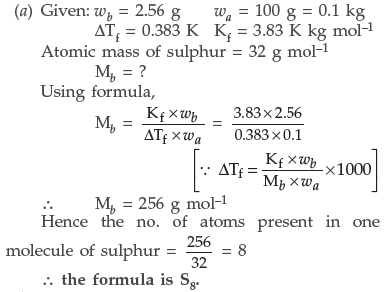
(b) (i) If RBCs are placed in contact with 1.2% NaCl solution, then the osmotic pressure of 1.2% NaCl becomes higher than that of RBCs due to which water present inside the cells moves into the NaCl solution which results in shrinkage of RBCs.
(ii) Reverse process will take place if RBCs are kept in contact with 0.4% NaCl solution which has less osmotic pressure due to which water moves into RBCs and they will swell.
Question. (a) What type of deviation is shown by a mixture of ethanol and acetone? Give reason.
(b) A solution of glucose (molar mass = 180 g mol–1) in water is labelled as 10% (by mass).What would be the molality and molarity of the solution?
(Density of solution = 1.2 g mL–1)
Answer. (a) Since acetone is nearly non-polar in nature and ethanol is polar in nature therefore, no interaction occurs between acetone and ethanol, the number of molecules increases,
which shows positive deviation.
(b) 10% glucose means 10 g in 100 g solution or, 90 g of water = 0.090 kg of water
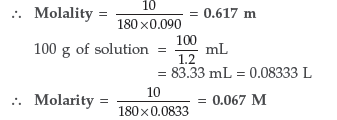
Question. (a) What is van’t Hoff factor? What types of values can it have if in forming the solution, the solute molecules undergo
(i) Dissociation? (ii) Association?
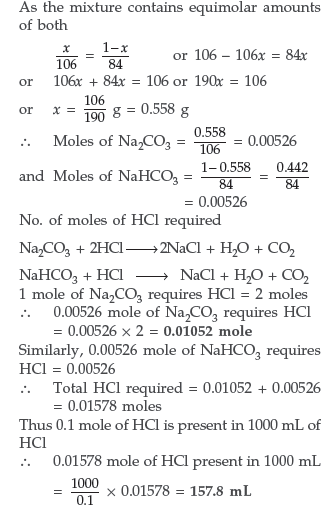
(b) How many mL of a 0.1 M HCl solution are required to react completely with 1 g of a mixture of Na2CO3 and NaHCO3 containing equimolar amounts of both?
(Molar mass : Na2CO3 = 106 g,
NaHCO3 = 84 g)
Answer. (a) (i) Van’t Hoff factor : It is defined as the ratio of the experimental value of the colligative property to the calculated value of the colligative property
i = Experimental value / Calculated value
If there is dissociation of the solute in the solution, the Van’t Hoff factor ‘i’ will be greater than one i.e. i > 1.
It means observed colligative property will be greater than calculated value.
(ii) Association : If there is association of solute in the solution, the Van’t Hoff factor ‘i’ will be less than one i.e. i < 1.
Thus, observed colligative property will be less than the calculated value.
(b) Calculation of no. of moles of the components in the mixture Suppose Na2CO3 in the mixture = x g
∴ NaHCO3 in the mixture = (1 – x) g
Molar mass of Na2CO3 = 106 g mol–1
Molar mass of NaHCO3 = 84 g mol–1
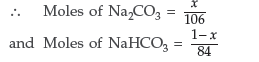
Question. (a) Calculate the freezing point of solution when 1.9 g of MgCl2 (M = 95 g mol–1) was dissolved in 50 g of water, assuming MgCl2 undergoes complete ionization.
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
(b) (i) Out of 1 M glucose and 2 M glucose, which one has a higher boiling point and why?
(ii) What happens when the external pressure applied becomes more than the osmotic pressure of solution?
Answer. (a) Since MgCl2 is an ionic compound, so it undergoes complete dissociation.
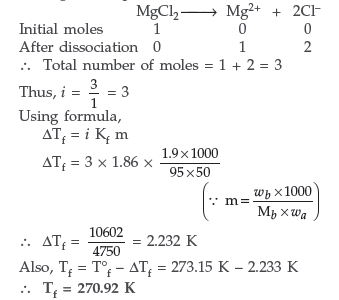
(b) (i) 2M glucose will have a higher boiling point than 1M glucose because elevation in boiling point is a colligative property which depends upon the number of particles in the solution which is more in the case of 2M glucose solution.
(ii) When the external pressure applied becomes more than the osmotic pressure of the solution, then the solvent will flow from the solution into the pure solvent through the semi-permeable membrane. The process is called reverse osmosis (RO).
Question. (a) Explain the following :
(i) Henry’s law about dissolution of a gas in a liquid
(ii) Boiling point elevation constant for a solvent
(b) A solution of glycerol (C3H8O3) in water was prepared by dissolving some glycerol in 500 g of water. This solution has a boiling point of 100.42°C. What mass of glycerol was dissolved to make this solution?
(Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mol–1)
Answer. (a) (i) Henry’s law : The law states “that at a constant temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas.”
(ii) Boiling point elevation constant for a solvent or molal elevation constant may be defined as the elevation in the boiling point when the molality of the solution is unity.
Question. (a) A 10% solution (by mass) of sucrose in water has a freezing point of 269.15 K.Calculate the freezing point of 10% glucose in water if the freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K.
Given: (Molar mass of sucrose = 342 g mol–1)
(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol–1)
(b) Define the following terms:
(i) Molality (m)
(ii) Abnormal molar mass (All India)
Answer.
(b) (i) Molality (m). Number of moles of solute dissolved per kg of the solvent.
(ii) Abnormal molar mass. If the molar mass calculated by using any of the colligative properties comes to be different than theoretically expected molar mass.
Question. (a) 30 g of urea (M = 60 g mol–1) is dissolved in 846 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution if vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg.
(b) Write two differences between ideal solutions and non-ideal solutions.
Answer. (a) Given:
Urea (W) = 30 g; H2O (W) = 846 g

Question. (a) A 5% solution (by mass) of cane-sugar in water has freezing point of 271 K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% solution (by mass) of glucose in water if the freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K. [Molecular masses : Glucose C6H12O6 : 180 amu; Cane-sugar C12H22O11 : 342 amu]
(b) State Henry’s law and mention two of its important applications. (Comptt. All India)
Answer. (a) Molality of sugar solution
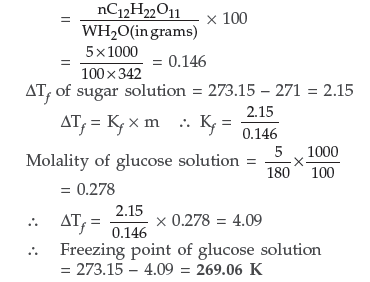
(b) Henry’s law : Henry’s law : Henry’s law states that, “The solubility of a gas in a liquid at a particular temperature is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas in equilibrium with the liquid at that temperature.”Solubility of gas decreases with increase of temperature at the same pressure.
