Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry The p – Block Elements Chapter 7 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 7 The p – Block Elements have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the Class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
The p – Block Elements Worksheets Class 12 Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question. The basicity of pyrophosphorus acid is
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 5
Answer
A
Question. Number of sigma bonds in P4O10 is
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 17
(d) 16.
Answer
D
Question. Which acid has P – P linkage ?
(a) Hypophosphoric acid
(b) Pyrophosphoric acid
(c) Metaphosphoric acid
(d) Orthophosphoric acid
Answer
A
Question. In a cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid molecule, how many single and double bonds are present?
(a) 3 double bonds; 9 single bonds
(b) 6 double bonds; 6 single bonds
(c) 3 double bonds; 12 single bonds
(d) Zero double bonds; 12 single bonds
Answer
A
Question. Orthophosphoric acid is
(a) monobasic
(b) dibasic
(c) tribasic
(d) tetrabasic
Answer
C
Question. In solid state PCl5 is a ________.
(a) covalent solid
(b) octahedral structure
(c) ionic solid with [PCl6]+ octahedral and [PCl4]– tetrahedra
(d) ionic solid with [PCl4]+ tetrahedral and [PCl6]– octahedra
Answer
D
Question. The number of hydrogen atom(s) attached to phosphorus atom in hypophosphorous acid is
(a) three
(b) one
(c) two
(d) zero
Answer
C
Question. PCl3 reacts with water to form
(a) PH3
(b) H3PO4 and HCl
(c) POCl3
(d) H3PO4
Answer
B
Question. Which shows maximum catenation property ?
(a) S
(b) Se
(c) Te
(d) O
Answer
A
Question. The oxidation state of phosphorus in cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid is
(a) +3
(b) +5
(c) –3
(d) +2
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following hydrides has the lowest boiling point?
(a) H2O
(b) H2S
(c) H2Se
(d) H2Te
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following phosphorus is most reactive ?
(a) Red phosphorus
(b) White phosphorus
(c) Scarlet phosphorus
(d) Violet phosphorus
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following hydrides shows the highest boiling point ?
(a) H2O
(b) H2S
(c) H2Se
(d) H2Te
Answer
A
Question. Electron affinity of sulphur is
(a) more than O and Se
(b) more than O but less than Se
(c) less than O but more than Se
(d) equal to O and Se
Answer
A
Question. What is hybridization of P in PCl5 ?
(a) sp3
(b) sp3d2
(c) sp3d
(d) sp2
Answer
C
Assertion-Reason Questions
DIRECTION: Mark the option which is most suitable:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion: Fluorine has lower reactivity.
Reason: F—F bond has low bond dissociation energy.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion: PCl5 is covalent in gaseous state but ionic in solid state.
Reason: PCl5 exists as tetrahedral [PCl4]+ cation and octahedral [PCl6]– anion.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: At room temperature, oxygen exists as a diatomic gas whereas sulphur exists as a solid.
Reason: The catenated —O—O—O— chains are less stable as compared to O = O molecule.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Sulphuric Acid is more viscous than water.
Reason: Sulphuric Acid has a strong affinity for water.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: HI cannot be prepared by the reaction of KI with Concentrated H2SO4.
Reason: HI has lowest H-X bond strength among halogen acids.
Answer
B
The halogen elements show great resemblances to one another in their chemical behaviour and properties of their compounds with other elements. There is, however, a progressive change in properties from F through Cl, Br and I to At. F is most reactive among the halogens and infact, from all other elements and it has certain other properties that set it apart from the other halogens.
In the following questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices on the basis of the above passage.
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: Fluorine is strongest oxidising agent in halogens.
Reason: It displaces other halogens from its aqueous solution.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: The bond between F—F is weaker than between Cl—Cl.
Reason: Atomic size of F is smaller than that of Cl. Ans. (a) (i) Assertion: F2 has high reactivity.
Reason: F2 has low bond dissociation enthalpy.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion: Fluoride does not show oxidation number greater than zero.
Reason: The halogens chlorine, bromine and iodine can show positive oxidation state of +1, +3 and +7.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion: F atom has less negative electron affinity than Cl atom.
Reason: Additional electrons are repelled more effectively by 3p– electrons in Cl than by 2p– electrons in F atom.
Answer
C
Under the normal conditions, noble gases are monoatomic and have closed shell electronic configuration. Lighter noble gases have low boiling points due to weak dispersion forces between the atoms and the absence of other interatomic interactions. Xenon, one of the important noble gas, forms a series of compounds with fluorine with oxidation number +2, +4 and +6. All xenon fluorides are strong oxidising agents. XeF4 reacts violently with water to give XeO3. The geometry of xenon compounds can be deduced by considering the total number of electron pairs in their valence shell.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate options:
Question. Among the noble gases (from He to Xe) only xenon reacts with fluorine to form stable xenon fluorides because xenon
(a) as the largest size.
(b) has the lowest ionisation enthalpy.
(c) has the highest heat of vapourisation.
(d) is the most readily available noble gas.
Answer
B
Question. The structure of XeO3 is
(a) square planar
(b) Pyramidal
(c) linear
(d) T-shaped
Answer
B
Question. The oxidation state of xenon in XeO3 is
(a) +4
(b) +2
(c) +8
(d) +6
Answer
D
Question. In the preparation of compound of xenon, Bartlett had taken O2+P F6 t − as a base compound. This is because
(a) both O2 and Xe have same size.
(b) both Xe and O2 have same electron gain enthalpy.
(c) both have almost same ionisation enthalpy.
(d) both Xe and O2 are gases.
Answer
C
Question. XeF6 is expected to be
(a) oxidising agent.
(b) reducing agent.
(c) unreactive.
(b) strongly basic.
Answer
A
p-block Elements (page 30-36)
Group-15
Question. Why is BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the Hydrides of Group-15 elements.
Answer. Down the group, the size of element increases and so the length of E—-H bond decreases. Thus Bi—–H bond is weakest and easily evolves H2 gas, which is a reducing agent.
Question. What happens when Sodium Azide is heated?
Answer. It gives off Dinitrogen gas. 2NaN3 ————–> 2Na + 3N2
Question. What is the Covalency of Nitrogen in N2O5?
Answer. 4
Question. PH3 has lower boiling point than NH3. Why?
Answer. Unlike NH3, PH3 cannot form Hydrogen bond, so its boiling point is less than NH3.
2 marks questions
Question.2. Give the reaction of dilute Nitric acid with Copper and Zinc.
Answer. 3Cu +8HNO3 (dil) —————>3Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO + 4H2O
4Zn + 10HNO3 (dil) ——————–>4Zn(NO3)2 + N2O + 5H2O
Question. Name the industrial method of preparation of nitric acid and give the reactions involved in it.
Answer. Ostwald process.
Reactions-
4NH3 + 5O2—Pt/Pd——–> 4NO + 6H2O
2NO + O2—————-> 2NO2
3NO2 + H2O————–> 2HNO3 + NO
Question.Arrange the following in increasing order of the properties indicated within the brackets.
a. AsH3, BiH3, NH3, SbH3, PH3 (Basic Strength)
b. AsH3, NH3, PH3, BiH3, SbH3 (Thermal stability)
Answer.
a. BiH3< SbH3< AsH3< PH3< NH3
b. BiH3< SbH3< AsH3< PH3< NH3
Group-16
1 Mark Questions-
Question. How is the presence of SO2 detected?
Answer. SO2 decolorizes pink color of KMnO4.
Question. Why SF4 can be hydrolyzed but SF6 cannot?
Answer. It is because SF6 has a stable octahedral structure and steric effect due to which it cannot be hydrolyzed.
Question. What happens when Sulphur Trioxide is passed through water?
Answer. Hydrogen Sulphate is formed.
SO3 + H2O——————–> H2SO4
Question. List the important sources of Sulphur.
Answer. Epsom salt(MgSO4.7H2O), Gypsum(CaSO4.2H2O),Baryte(BaSO4)
Question. Mention 3 uses of H2SO4.
Answer. a. As a laboratory reagent.
b. In manufacturing dyes, paints, etc.
c. In manufacturing fertilizers.
Question. What happens when conc.H2SO4 is added to Calcium Fluoride?
Answer. It forms Calcium Sulphate and Hydrogen Fluoride.
CaF2 + H2SO4—————-> CaSO4 + 2HF
2 Marks questions-
Question. Compare the bleaching action of SO2 and Cl2.
Answer. SO2 does temporary bleaching, while Cl2 does permanent bleaching.
SO2 bleaches via reduction and Cl2 bleaches via oxidation.
Question. How Ozone is estimated?
Answer. When Ozone reacts with an excess of potassium iodide solution, with a borate buffer (pH=9.2), Iodine is liberated which can be titrated against a standard solution of sodium thiosulphate. This is used for estimation of Ozone.
Question. What happens when (a) Sulphuric acid reacts with sugar?
Answer. It forms Carbon black (dehydration of sugar).
(b) SO2 reacts with Chlorine.
Answer. It forms Sulphuryl Chloride.
SO2 + Cl2————> SO2Cl2.
Group-17
1 Mark questions-
Question. Why Halogens have maximum negative electron gain enthalpy in their respective periods of periodic table?
Answer. It is due to the smallest size and highest effective nuclear charge of the Halogens, the readily accept one electron to acquire Nobel gas configuration.
Question. Sea is the greatest source of Halogen. Comment.
Answer. Sea water contains Chlorides, Bromides and Iodides of Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium and Calcium. Mainly it contains 2.5% NaCl by mass. Thus, sea is the greatest source of Halogens.
Question. Why are Halogens colored?
Answer. It is because Halogens absorb radiation in visible region which results in excitation of outer shell electrons to higher energy level so, they display different colors.
Question.Arrange the following in increasing order of their acidic strength.
HOCl, HClO4, HClO2, HClO3
Answer. HOCl<HClO2<HClO3<HClO4
Question. Why HF is liquid and HCl is a gas.
Answer. It is due to the presence of Hydrogen bond in HF.
Question. Which oxide of Iodine is used in estimation of Carbon Monoxide?
Answer. I2O5
Question. Why I—Cl is more reactive than I2.
Answer. I—-Cl bond is weaker than I—–I bond. Consequently, I—–Cl bond breaks easily. Hence it is more reactive.
2 Marks questions-
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of bond dissociation enthalpy.
a. Cl2, I2, Br2, F2
b. HF, HCl, HI, HBr
Answer.
a. I2<F2<Br2<Cl2
b. HI<HBr<HCl<HF
Question. Arrange the following in increasing order of the properties indicated within the brackets.
a. HF, HCl, HI, HBr (Acidic strength)b. HOCl, HOF, HOI, HOBr (Acidic strength)
Answer.
a. HF<HCl<HBr<HI
b. HOI<HOBr<HOCl<HOF
Question. What happens when-
a. Chlorine reacts with cold and dilute NaOH.
b. Chlorine reacts with hot and concentrated NaOH.
Answer.
a. Cl2 +2NaOH(dil.)—————> NaCl + NaOCl+ H2O
b. 3Cl2 + 6NaOH(conc.)————–> 5NaCl + NaClO3 + 3H2O
Group-18
1 Mark questions-
Question. Nobel gases have very low boiling point. Why?
Answer. Nobel gases being monoatomic, they do not have any intermolecular forces of attraction, except weak Dispersion/ London forces. So, they liquefy as well as boil at a very low temperature.
Question. Why are the elements of Group-18, known as noble gases?
Answer. As they have stable, fully filled configuration, they react with very few elements so, they are known as noble gases.
Question. Give the equations for the Hydrolysis of-
a. XeF2
b. XeF4
c. XeF6
Answer.
a. 2XeF2 + 2H2O ————–> 2Xe + 4HF + O2
b.6XeF4 + 12H2O —————-> 4Xe + 2XeO3 + 24HF + 3O2
c. XeF6 + 3H2O ——————–> XeO3 + 6HF
Question. Why Helium is used in scuba divers apparatus?
Answer. It is because it is less soluble in blood/ has very low solubility in blood.
Question. Give the equations for partial hydrolysis of XeO6.
Answer.
XeF6 + H2O —————-> XeOF4 + 2HF
XeF6 + 2H2O —————> XeO2F2 + 4HF
Question. Why is it difficult to study the chemistry of Radon?
Answer. It is because, Radon is Radioactive in nature.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Bond enthalpy of fluorine is lower than that of chlorine. Why?
Answer. Because F2 is very small and its interelectronic repulsions between the lone pairs of electrons are very large.
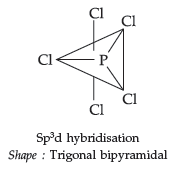
Question. Write the structural formula of PCl5(s).
Answer. PCl5 (s)
Question. HF is a weaker acid than HCl. Why?
Answer. Because of higher bond dissociation energy and strong H-bonding in HF.
Question. What is the basicity of H3PO3?
Answer. Basicity of H3PO3 = 2
Because basicity is the number of replaceable H+ ions in an acid and H3PO3 is a Dibasic acid.
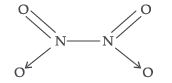
Question. Why does NO2 dimerise?
Answer. NO2 contains 7 + 2 × 8 i.e. 23 odd electrons. In the valence shell N has seven electrons and hence less stable. To acquire stability it dimerizes to form N2O4.
Question. Why does NH3 act as a Lewis base?
Answer. Due to presence of lone pair on nitrogen NH3 acts as a Lewis base.
Question. Write the formulae of any two oxoacids of sulphur.
Answer. H2SO3 and H2SO4
Question. On adding NaOH to ammonium sulphate, a colourless gas with pungent odour is evolved which forms a blue coloured complex with Cu2+ ion. Identify the gas.
Answer. The gas with a pungent odour is Ammonia (NH3) and the blue coloured complex is Tetra-ammine copper (II) sulphate monohydrate.
Question.Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
Answer. (i) Phosgene gas (COCl2) and (ii) Chloropicrin or tear gas (CCl3NO2).
Question. Pb(NO3)2 on heating gives a brown gas which undergoes dimerization on cooling. Identify the gas.
Answer. The brown gas is nitrogen dioxide (NO2) which can dimerize to N2O4
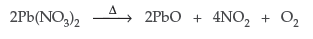
Question.What is the covalency of nitrogen in N2O5?
Answer. The covalency of nitrogen in N2O5 is 4 because each nitrogen atom has four shared pairs of electrons.
Question. What inspired N.Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6?
Answer. Since PtF6 oxidises O2 to O2+, Bartlett thought that PtF6 should also oxidise Xe to Xe+ because the ionization enthalpies of O2 (1175 kJ mol–1) and Xe (1170 kJ mol–1) are quite close.
Question. Why is F2 a stronger oxidising agent than Cl2?
Answer. Due to low bond dissociation enthalpy and high electronegativity of Fluorine, it has strong tendency to accept electrons and thus get reduced.
F + e– → F–
Therefore F2 acts as strong oxidising agent, while Cl2 is weak oxidising agent due to low electronegativity
Question. What is the basicity of H3PO4?
Answer. Since there are 3 OH groups present in H3PO4, its basicity is 3.

Short Answer Type Questions-I
Question. What happens when
(i) conc. H2SO4 is added to Cu?
(ii) SO3 is passed through water?
Write the equations.
Answer. (i) Cu + 2H2SO4 (conc.) → CuSO4 + 2H2O + SO2
(ii) SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Question. Complete the following chemical equations:
(i) F2 + 2Cl– →
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O ⎯ →
Answer. (i) F2 + 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2F–
(ii) 2XeF2 + 2H2O ⎯ → 2Xe + 4HF + O2
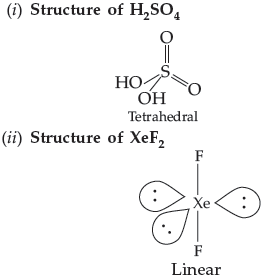
Question. Draw the structures of the following :
(i) H2SO4 (ii) XeF2
Answer.
Question. What happens when
(i) HCl is added to MnO2?
(ii) PCl5 is heated?
Write the equations involved.
Answer. (i) When HCl is added to MnO2, chlorine gas is formed, along with other products.
MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
(ii) PCl5 Δ → PCl3 + Cl2
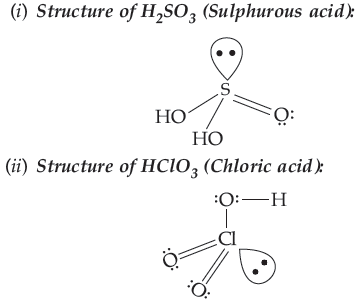
Question. Draw the structures of the following:
(i) H2SO3 (ii) HClO3
Answer.
Long Answer Type Questions
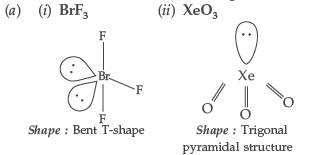
Question. (a) Draw the structure of the following :
(i) BrF3 (ii) XeO3
(b) Answer the following :
(i) Why is NH3 more basic than PH3?
(ii) Why are halogens strong oxidising agents?
(iii) Draw the structure of XeOF4.
Answer.
(b) (i) Both P and N contains lone pairs of electrons but due to small size and high electronegativity of nitrogen in NH3 , the electron density is much higher than PH3, therefore it can easily donate electrons and acts as a strong Lewis base than PH3.
(ii) Halogens have strong tendency to accept an electron due to high negative electron gain enthalpies. Hence halogens act as strong oxidising agents.
Question. (a) Account for the following:
(i) Ozone is thermodynamically unstable.
(ii) Solid PCl5 is ionic in nature.
(iii) Fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF.
(b) Draw the structure of (i) BrF5 (ii) XeF4
Answer. (a) (i) Ozone is thermodynamically very unstable because:
• The decomposition of ozone into oxygen is exothermic in nature. (ΔH = –ve)
• There is also increase in entropy which in turn makes ΔG –ve and reaction spontaneous.
(ii) In solid state, PCl5 exists as [PCl4]+ [PCl6]– in which the cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral. Because of the presence of strong attractive forces, it is a solid.
(iii) Due to absence of d-orbitals in fluorine, it can only form one oxoacid i.e., HOF.
(b) (i) Structure of BrF5

Question. (i) Compare the oxidizing action of F2 and Cl2 by considering parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy.
(ii) Write the conditions to maximize the yield of H2SO4 by contact process.
(iii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of property mentioned:
(a) H3PO3, H3PO4, H3PO2 (Reducing character)
(b) NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3 (Base strength)
Answer. (i) Since the standard reduction potential value of fluorine is more than that of chlorine, so fluorine is a stronger oxidising agent.
• Bond dissociation enthalpy of F2 is less as compared to that of chlorine.
• The negative electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is slightly less than that of chlorine.
• The hydration enthalpy of flouride ion is much higher than that of Cl– ion due to smaller size.
(ii) Favourable conditions for manufacturing sulphuric acid by contact process are:
• high pressure of about 2 bars
• low temperature 720 K
• presence of V2O5 catalyst
(iii) (a) H3PO4 < H3PO3 < H3PO2 (Reducing character)
(b) BiH3 < SbH3 < AsH3 < PH3 < NH3 (Basic strength)
Question. (a) Write balanced equations for the following reactions :
(i) Chlorine reacts with dry slaked lime.
(ii) Carbon reacts with concentrated H2SO4
(b) Describe the contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid with special reference to the reaction conditions, catalysts used and the yield in the process.
Answer. (a) (i) Chlorine reacts with dry slaked lime

(b) Contact process of sulphuric acid :It involves the following steps :
(i) Formation of sulphur dioxide by burning either sulphur or iron pyrites in excess of air.
S + O2 → SO2
4FeS2 + 11O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 8SO2
(ii) Catalytic oxidation of SO2 into SO3 by using V2O5 as catalyst
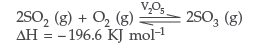
According to Le-Chatelier’s principle the reaction conditions are :
(a) High concentration of reactants
(b) Low temperature (623-723 K)
(c) High pressure (2 bar)
By obeying above conditions the yield of H2SO4 will be 96-98%
(iii) Absorption of SO3 in 98% H2SO4 to give Oleum (H2S2O7)
SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
Oleum
(iv) Dilution of Oleum to give sulphuric acid
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
Question. (a) Complete the following equations :
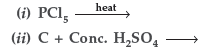
(b) Explain giving reason in each case :
(i) Halogens are strong oxidising agents
(ii) Fluorine form only one oxoacid, HOF
(iii) Helium is used in diving apparatus
Answer.
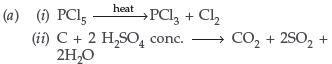
(b) (i) Due to their high electron affinity. As they have seven electrons, they accept one electron readily.
(ii) Due to high electronegativity and small size of fluorine.
(iii) Due to low solubility in blood.
Question. (a) Complete the following chemical equations :
(i) Cu + HNO3 (dilute) ⎯ →
(ii) P4 + NaOH + H2O ⎯ →
(b) (i) Why does R3P = O exist but R3N = O does not? (R = alkyl group)
(ii) Why is dioxygen a gas but sulphur a solid?
(iii) Why are halogens coloured?
Answer.
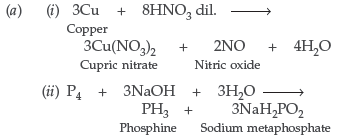
(b) (i) Nitrogen in R3N = O cannot form pπ – dπ multiple bonds because it cannot expand its covalency beyond 4 due to absence of d-orbital, so it will not exist.
But R3P = O can do so due to presence of d-orbitals and formation of pπ – dπ multiple bonds which can expand its covalency up to 5.
(ii) Because of bigger size and the strong forces of attraction holding 8 atoms, their bonds cannot be broken easily and hence sulphur exists as solid while oxygen due to high electro-negativity and tendency to form pπ – dπ multiple bonds through Vander-waals forces of attraction can be broken easily and hence exists as gas.
(iii) All halogens are coloured due to absorption of light in the visible region as a result of which their electrons get excited to higher energy levels and while returning to lower level transmit energy of corresponding colour.