Students should refer to Worksheets Class 10 Science How do the Organisms Reproduce Chapter 8 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 10 Science based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 10 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 10 Science for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
How do the Organisms Reproduce Worksheets Class 10 Science
Question. The simple animals like Planaria can be cut into a number of pieces and each piece grows into a complex organism. What is the process known as?
(a) Budding
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Spore formation
(d) Regeneration
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a sexually transmitted disease?
(a) Warts
(b) Kala azar
(c) Syphilis
(d) Gonorrhoea
Answer
B
Question. Where does fertilisation occur in human females?
(a) Uterus
(b) Cervix
(c) Oviduct
(d) None of these
Answer
D
Question. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba.
(b) yeast.
(c) plasmodium.
(d) leishmania.
Answer
B
Question. What are the functions performed by the testis in human males?
(a) Production of gametes–eggs and secretion of sex hormones–estrogen
(b) Production of gametes–sperms and secretion of sex hormones–testosterone
(c) Production of gametes–sperms and secretion of sex hormones–estrogen
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer
C
Question. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba.
(b) yeast.
(c) plasmodium.
(d) leishmania.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer
C
Question. The anther contains
(a) sepals.
(b) ovules.
(c) carpel.
(d) pollen grains.
Answer
D
Question. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba.
(b) yeast.
(c) plasmodium.
(d) leishmania.
Answer
B
Question. The anther contains
(a) sepals.
(b) ovules.
(c) carpel.
(d) pollen grains.
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer
C
Question. The anther contains
(a) sepals
(b) ovules
(c) carpel
(d) pollen grains
Answer
D
Question. Growing foetus derive nutrition from mother’s blood through
(a) uterus
(b) fallopian tube
(c) placenta
(d) cervix
Answer
C
Question. The two oviducts in a human female unite into an elastic bag like structure known as
(a) Vagina
(b) Uterus
(c) Fallopian tube
(d) Cervix
Answer
B
Question. Fruit is formed from
(a) Stamen
(b) Stigma
(c) Ovary
(d) Ovule
Answer
C
Question. Which of these is not the function of the seminal vesicles present in human males?
(a) To covert the sperms in a fluid medium.
(b) To provide nutrition.
(c) To make their transport easier.
(d) To make them sticky.
Answer
D
Question. What is the surgical method of contraception in female and male respectively?
(a) Tubectomy and Vasectomy
(b) Vasectomy and Copper-T
(c) Tubectomy and Copper-T
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The female reproductive part of the flower consists of
(a) Stigma, Anther, Filament
(b) Style, Ovary, Thalamus
(c) Stigma, Ovary, Style
(d) Anther, Corolla, Filament
Answer
C
Question. The common passage meant for transporting urine and sperms in males is
(a) Ureter
(b) Vas deferens
(c) Urethra
(d) Anus
Answer
C
Question. In which of the following plant bud in notches of leaves help in its propagation?
(a) Radish
(b) Bryophyllum
(c) Bougainvillea
(d) Jasmine
Answer
B
Question. Identify the type of cell division taking place
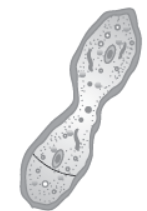
(a) Longitudinal cell division taking place
(b) Transversal cell division in Paramecium
(c) Longitudinal cell division in Paramecium
(d) Transversal cell division in Amoeba
Answer
B
Question. The process of the transfer of pollen grains from the flower of one plant to the stigma of the flower of another plant of the same species is known as
(a) Cross pollination
(b) Fertilisation
(c) Self pollination
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. ___________ is the portion on which grafting is done and it provides the roots?
(a) Stock
(b) Scion
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Why are the testes located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum?
(a) Because sperm formation requires more spaces.
(b) Because sperm formation requires a lower temperature.
(c) Because sperm formation requires a higher temperature.
(d) None of the above.
Answer
B
Question. IUCD is for
(a) Vegetative propagation
(b) Contraception
(c) Increasing fertility
(d) Avoiding miscarriage
Answer
B
Question. Union of male and female gametes forms
(a) Egg
(b) Embryo
(c) Zygote
(d) Spore
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following disease is transmitted sexually?
(a) Kala azar
(b) Jaundice
(c) Elephantiasis
(d) Syphilis
Answer
D
Question. Identify the organism
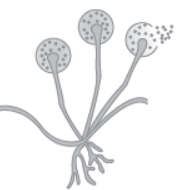
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Rhizopus
(c) Rhizoid
(d) Mushroom
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is a contraceptive?
(a) Copper-T
(b) Condom
(c) Diaphragm
(d) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the options is incorrect?
Vegetative propagation is practised because
(a) Plants which produce non viable seeds can be grown.
(b) It is a easier method than sowing seeds.
(c) Such plants produce seeds and fruits much earlier than other methods
(d) For obtaining better species of plants.
Answer
C
Question. The process where the unfertilised egg is released out of the body with the blood used to nourish the embryo is known as
(a) Menstruation
(b) Fertilisation
(c) Germination
(d) Pollination
Answer
A
Question. After fertilisation name the part which develops into the seeds
(a) Ovary
(b) Ovule
(c) Pollen grain
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. The process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells is known as?
(a) Karyokinesis
(b) Cytokinesis
(c) Meiosis
(d) Mitosis
Answer
D
Question. What is the puberty age in human males?
(a) 8-10
(b) 10-12
(c) 12-14
(d) 14-16
Answer
C
Question. Unicellular organisms reproduce by
(a) Mitotic cell division
(b) Meiotic cell division
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. What is the surgical method of contraception used in human males?
(a) Vasectomy
(b) Condoms
(c) Contraceptive pills
(d) Tubectomy
Answer
A
Question. Unisexual flowers contain
(a) Both stamen and carpel
(b) Only stamen
(c) Only carpel
(d) Either stamen or carpel
Answer
D
Question. Vegetative propagation in potato takes place through
(a) Stem
(b) Root
(c) Leaves
(d) Seeds
Answer
A
Question. The type of reproduction taking place is
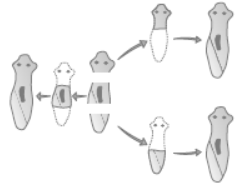
(a) Budding
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Regeneration
(d) Fission
Answer
C
Question. Spirogyra reproduces by
(a) Fission
(b) Regeneration
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Budding
Answer
C
Question. The anther contains
(a) Sepals
(b) Ovules
(c) Carpel
(d) Pollen grains
Answer
D
Question. The full form of AIDS is
(a) Acquired Immune Deficiency System
(b) Acquired Immune Disease Syndrome
(c) Acquired Immediate Deficiency Syndrome
(d) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
Answer
D
Question. The number of chromosomes in human ovum is
(a) 21
(b) 22
(c) 23
(d) 24
Answer
C
Question.
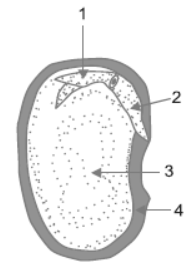
Choose the correct option (Table 95)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| (a) Plumule | Radicle | Cotyledon | Seed coat |
| (b) Radicle | Plumule | Seed coat | Cotyledon |
| (c) Cotyledon | Seed coat | Radicle | Plumule |
| (d) Radicle | Plumule | Cotyledon | Seed coat |
Answer
A
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. What is fertilization?
Answer : Fertilization is the process of fusion of the male and the female gametes.
Question. Name two plants whose flowers are unisexual.
Answer : Papaya, watermelon.
Question. Why do organisms reproduce?
Answer : Organisms reproduce to perpetuate their race and maintain their species.
Question. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer : DNA copying during reproduction is important for the transfer of parental characters to the offsprings.
Question. Name two plants whose flowers are bisexual.
Answer : Mustard, chinarose.
Question. What happens during copying of DNA?
Answer : Copies of DNA are formed and hereditary information is passed on from one generation to the next.
Question. How is pollination different from fertilization?
Answer: Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther lobe to the stigma of the flower, while fertilization is the process of fusion of malegamete and female gamete to form the zygote.
Question. Name the plant in which vegetative propagation takes place by leaves.
Answer: Bryophyllum.
Question. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer: DNA copying is essential for transferring genetic material from one generation to another.
Question. What is the role of seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer: Seminal vesicle and prostate gland help in nutrition and mobility of sperms.
Question. What are the advantages of vegetative propagation?
Answer: Quick/easy/economical method/can creates exact copies of the parent/only method for the propagation of seedless plants.
Question. Writescientific term for the following:
a) Release of ovum from ovary.
b) Onset of menstrual cycle in a female.
Answer: a) Ovulation
b) Menarche.
Question. Where does fertilization takes place in human female?
Answer: Oviduct (fallopian tube)
Question. How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer: the embryo gets nutrition, oxygen and gets rid of waste materials throughPlacenta.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Enumerate the various methods of asexual reproduction in living organisms.
Answer : The various methods of asexual reproduction are fission (binary and multiple), fragmentation, regeneration, budding, vegetative propagation, spore formation and tissue culture.
Question. What is binary and multiple fission? Name the organisms in which they occur.
Answer : Binary fission is the division of one parent cell into two identical daughter cells. It takes place in Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena and other protozoa.
In multiple fission one single celled organism divides into many daughter cells within a cyst. These are released when the cyst breaks. This takes place in Plasmodium
(malarial parasite).
Question. What is budding? Name two organisms that reproduce asexually by budding.
Answer : In budding a small part of the parents body grows out as a bud which then detachesand becomes a new organism. Hydra and yeast reproduce by budding.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? What are its advantages?
Answer : The process by which some plants can reproduce asexually by their vegetative parts like roots, stem and leaves is called vegetative propagation. It has many advantages.
Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds. Plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds like banana, rose and jasmine can be propagated by this method. All plants produced by this method are genetically similar to the parent plant.
Question. How is the amount of DNA maintained in each generation?
Answer : The amount of DNA is maintained in each generation by a specialized mode of cell division called meiosis which produces specialized male and female germ cells called gametes which are haploid. One male and female gamete fertilize to give rise to a diploid zygote which has the same chromosome number as the parent. This process maintains the chromosome number and the amount of DNA in each generation.
Question. How do potato and Bryophyllum plants reproduce vegetatively?
Answer : Potato tuber has depressions called ‘‘eyes’’ on its surface. These eyes have vegetative buds in them which germinate to produce a new potato plant. Similarly the fleshy leaves
of Bryophyllum bear vegetative buds in the notches along the leaf margin. These buds germinate to form small plantlets which form new plants on being detached.
Question. a) What is AIDS?
b) Name the causative organism?
c) List the important modes of transmission of the disease.
Answer: a)Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome.
b) HIV (Virus)
c) i) Through infected blood transfusion
ii) Contaminated syringes.
iii) Infected mother to child.
iv) Sexual contact
Question. What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer: a) Barrier method: condoms used by males /vaginal diaphragm used by females.
b) Chemical method: e.g. oral pills /vaginal pills used by females
c) Surgical method: vasectomy in males /tubectomy in females
Question. Explain the process of fertilization in plants with the help of neat labeled diagram
Answer: Hints: Formation of pollen tube, movement of male gametes towards the ovule.
Fertilization: Fusion of male and female gamete.
Question. Describe the different methods of asexual reproduction seen in animals with the help of neat labelled diagrams.
Answer: Description for the following:
1. Fission : binary and multiple fission
2. Regeneration
3. Bud formation
Question. Name two plants that can reproduce asexually by formation of spores.
Answer : Bread mould (Rhizopus) and ferns reproduce asexually by formation of spores.
Question.What are the limitations of asexual mode of reproduction?
Answer : In asexual mode of reproduction there are no genetic variation so there is less adaptability in the offspring.
Q11.What is the significance of sexual reproduction?
Answer : (a) A sexual reproduction results in new combination of characters and increases genetic variations.
(b) It promotes diversity of characters in the offspring.
(c) It speeds up the process of making variations in the population.
Question. Differentiate between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Answer :
| Asexual | Sexual |
| 1. Asexual reproduction involves a single parent. | 1. Sexual reproduction involves two parents (male and female). |
| 2. No gametes are formed during asexual reproduction. | 2. Gamete formation takes place in sexual reproduction. |
| 3. No or little variations occur during asexual reproduction. | 3. Many variations occur during sexual reproduction. |
Question. Explain the process of sexual reproduction in plants.
Answer : After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma it germinates to form the pollen tube. The pollen tube grows through the style and carries the male germ cells in it. The pollen tube enters the ovule and the male germ cells fuse with the egg cell to form the zygote. This process is called fertilisation.
Question. State the advantages of seed formation in plants.
Answer : The seed contains the future plant or embryo which can develop into a seedling under appropriate conditions. The seed is in a state of dormancy and can be kept in secure state for long period of time.
Question. What is germination of seed?
Answer : When the seed gets the right conditions the embryo within it starts growing to form the shoot and the root. When the embryo emerges out of the seed to form a new seedling it is called the germination of seed.
Question. Draw a well labelled diagram of a bisexual flower.
Answer :

Question. Reproduction is one of the most important characteristics of the living beings. Give three reasons in support of your answer.
or
Define reproduction. How does it help in providing stability to the population of species?
Answer :
a. Reproduction is the process of producing individuals of its own kind. Through reproduction, the continuity is maintained.
b. Members of population are eliminated due to old age, disease, accidents and other reason. They have to be replaced by new members in order to maintain a stable population.
c. Reproduction brings variation so that population may adapt better and evolution in species takes place. Ultimately new species originate from preexisting ones.
d. Reproduction is not essential for an individual as its survival is not dependent upon it but is essential for a species for its survival.
Question. Mention the total number of chromosome along with sex chromosome. Explain how in a sexually reproducing organism chromosome number of parents and their offsprings is the same.
Answer : Total number chromosomes is 23 pairs. The last pair is called sex chromosome. If they are similar, they are termed as XX chromosome. They are present in the females. If they are dissimilar, they are called XY.
They are present in the males. DNA doubling is always followed by cell division. But multicellular organisms have special linkages of cells in specialised organs which have only half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA. Thus, when these germcells from two individuals combine during sexual reproduction to form a new individual, it results in
re-establishment of number of chromosome and DNA content.
Question. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction.
Write the importance of such reproduction in nature.
Answer : Sexual reproduction takes place in multicellular organisms with complex body design. There are specialized (sex) organs in which through a special type of cell division, number of chromosome is reduced to half and male and female germ cells/gametes form.
These gamete fuse to form zygote on fertilization, thus the characteristic number of chromosome and the normal DNA content for a cell is regained.
Sexual reproduction gives rise to more variations which are essential for evolution as well as survival of species under unfavorable conditions. Species reproducing sexually have better chances of survival.
Question. What happens when:
a. Accidentally Planaria is cut into three different pieces.
b. Bryophyllum leaf fall on the wet soil.
c. On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus burst.
Answer :
a. Three new Planaria will form due to regeneration.
b. New plantlets will form from these buds helping the plant to propagate vegetatively.
c. Spores are released which upon finding suitable substratum germinates to form new individual.
Question. List four steps in sexual reproduction. Write two of its advantages.
Answer :
a. Four steps in sexual reproduction :
b. Formation of gametes in the sex organs.
c. Transfer of male gamete to female gamete which involves release of both types of gametes in the medium outside.
d. Fusion of gametes, either inside or outside the female parents body.
e. Development of zygote to embryo and then complete individual.
Advantages:
a. Variations are produced among the progeny.
b. Such populations are able to adapt well to
changing environment and thus evolves faster.
Question. Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria. How is this process different from reproduction?
Answer : Regeneration is the ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual e.g., Hydra and Planaria, if their bodies get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of re-growing into a complete individual. (Image 92)
In some organism regeneration occurs but only to regain lost body parts like in tail of lizard, arm of a star fish. In the case of Planaria, it is a way of reproduction that is producing organisms of its own kind.
Question. In the process of reproduction as used by Spirogyra, the organism splits itself into small pieces.
a. What is this process of reproduction called?
b. Is this type of reproduction sexual or asexual? Answer with reason.
c. Is this process same as regeneration?
Answer :
a. Fragmentation.
b. Asexual as only one parent is involved,
c. In fragmentation, the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks down into many ‘fragments’. All cells undergo division and the organism develops from each fragment.
In regeneration, body of a multicellular organism get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of re-growing into a complete individual.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer :
| Sexual reproduction | Asexual reproduction | |
| 1. | It involves two parents and causes genetic variation. | It involves only one parent and does not causes genetic variation. |
| 2. | Fertilization/zygote formation is observed. | No fertilization/zygote formation is observed. |
The species having sexual mode of reproduction have better chances of survival because sexual reproduction leads to variations which give better survival advantage to the species over time.
Question. Explain the term “Regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Answer :
The ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual is called regeneration, e.g., Hydra and Planaria, if their bodies get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of re-growing into a complete individual.
Question. Compare the following:
a. Unisexual and bisexual flower.
b. Self-pollination and cross pollination.
c. Style and filament.
Answer :
a. Unisexual flowers have either stamens or carpels, e.g., Papaya and Watermelon. Bisexual Flowers have both stamens and carpels, e.g., Mustard and Hibiscus.
b. Self-Pollination is transfer of pollen grains from the stamen to the stigma of same flower. Cross Pollination is transfer of pollen grains to another flower by agents like wind, water or animals.
c. Style is the middle elongated part of the carpel.
It acts as a passage for pollen to reach ovary for the fertilization. Filaments is the elongated part of stamen.
Question. a. Trace the path of sperms from where they are produced in human body to the exterior.
b. Write the functions of secretions of prostate gland and seminal vesicles in humans.
Answer :
a. The formation of sperms takes place in testes and delivered through the vas deferens which unites with a tube coming from urinary bladder to form urethra from where they are excreted out of the body.
b. Prostate gland and seminal vesicles add their secretions to make the sperms motile in a fluid which makes their transport easier and provides nutrition.
Question. Give two examples each of the following:
a. Plants having unisexual flowers
b. Agents of pollination
c. Physical changes on puberty that are common to both boys and girls.
Answer :
a. Papaya, watermelon
b. Insects, air, water, etc.
c. (i) Appearance of pubic hair.
(ii) Skin becomes oily and may develop pimples.
Question. “Regeneration is not same as reproduction”.
a. Justify the statement.
b. What is meant by regeneration?
c. How is this process different from fragmentation?
Answer :
a. Regeneration is not the same as reproduction, since most organisms would not normally depend on being cut up to be able to reproduce.
b. The ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual is called regeneration.
c. In fragmentation, the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks down onto many ‘fragments’. All cells undergo division and the organism develops from each fragment. Regeneration occurs only through some specialised cells.
Question. Why are the testes located outside the abdominal cavity? Mention the endocrine and exocrine function of testes.
Answer :
Sperm formation requires a lower temperature than the normal body temperature. This temperature is 1-3°C lower than the temperature of the body. Testes are thus located outside so that scrotum provides an optimal temperature for the formation of the sperms.
Endocrine function:
Production of male hormone (testosterone).
Exocrine function:
Production of male gametes (sperms).
Question. What is placenta? Explain its function in human female.
or
State the role of placenta in the development of embryo.
or
What is placenta? Describe its structure. State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Answer :
Placenta is a specialized tissue embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side and blood spaces on the mother’s side.
Function:
a. Helps in passing of nutrients from mother to foetus.
b. Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide gases.
c. Passing of waste materials from embryo to the mother.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival- the one reproducing sexually or the one reproducing asexually? Justify your answer.
or
How is sexual reproduction better than asexual reproduction?
Answer :
a. Asexual reproduction does not involve genetic fusion while sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
b. Species reproducing sexually have better chances of survival.
Reason :
Sexual reproduction gives rise to more variations which are essential for evolution as well as survival of species under unfavorable conditions.
Question. What are chromosomes? Explain how in sexually reproducing organisms, the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained?
Answer : Chromosomes are thread like structures made-up of DNA found in the nucleus. The original number of chromosomes becomes half during gamete formation.
Hence, when the gametes combine, the original number of chromosome gets restored in the progeny.

