Students should refer to Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry Equilibrium Chapter 7 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 7 Equilibrium have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 11 Chemistry based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 11 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 11 Chemistry for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Equilibrium Worksheets Class 11 Chemistry
Question. pH value of which one of the following is NOT equal to one?
(a) 0.1 M CH3COOH
(b) 0.1 M HNO3
(c) 0.05 M H2SO4
(d) 50 cm³ 0.4 M HCl + 50 cm³ 0.2 M NaOH
Answer
A
Question. Equimolar solutions of the following were prepared in water separately. Which one of the solutions will record the highest pH?
(a) CaCl2
(b) SrCl2
(c) BaCl2
(d) MgCl2
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following fluoro-compounds is most likely to behave as a Lewis base?
(a) BF3
(b) PF3
(c) CF4
(d) SiF4
Answer
B
Question. Buffer solutions have constant acidity and alkalinity because
(a) They have large excess of H+ or OH– ions
(b) They have fixed value of pH
(c) These give unionised acid or base on reaction with added acid or alkali
(d) Acids and alkalies in these solutions are shielded from attack by other ions
Answer
C
Question. When two reactants, A and B are mixed to give products C and D, the reaction quotient, Q, at the initial stages of the reaction
(a) is zero
(b) Decreases With Time
(c) Is Independent Of Time
(d) Increases With Time
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following molecualr species has unpaired electrons?
(a) N2
(b) F2
(c) O–2
(d) O2-2
Answer
C
Question. An amount of solid NH4HS is placed in a flask already contaniing ammonia gas at a certain temperature and 0.50 atm pressure. Ammonium hydrogen sulphide decomposes to yield NH3 and H2S gases in the flask. When the decomposition reaction reaches equilibrium , the total pressure in the flask rises to 0.84 atm? The equilibrium constant for NH4HS decomposition at this temperature is
(a) 0.11
(b) 0.17
(c) 0.18
(d) 0.30
Answer
A
Question. The Ksp for Cr (OH)3 is 1.6 × 10-30. The molar solubility of this compound in water is:
(a) √ (1.6 × 10-30)
(b) (√(1.6 × 10-30))(1/4)
(c) (√(1.6 × 10-30)/(27)))(1/4)
(d) (1.6 × 10-30)/(27)
Answer
C
Question. 1 M NaCl and 1 M HCl are present in an aqueous solution. The solution is
(a) Not a buffer solution with pH < 7
(b) Not a buffer solution with pH > 7
(c) A buffer solution with pH < 7
(d) A buffer solution with pH > 7
Answer
A
Question. What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of barium hydroxide, Ba (OH)2?
(a) 11.31
(b) 11.7
(c) 13.30
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The value of ΔH for the reaction X2(g) + 4Y2(g) ⇌ 2XY4(g) is less than zero. Formation of XY4(g) will be favoured at
(a) high temperature and high pressure
(b) low pressure and low temperature
(c) high temperature and low pressure
(d) high pressure and low temperature.
Answer
D
Question. The dissociation constants for acetic acid and HCN at 25°C are 1.5 × 10–5 and 4.5 × 10–10 respectively. The equilibrium constant for the equilibrium, CN– + CH3COOH HCN + CH3COO– would be
(a) 3.0 × 10–5
(b) 3.0 × 10–4
(c) 3.0 × 104
(d) 3.0 × 105
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is a characteristic of reversible reaction?
(a) It never proceeds to completion.
(b) It can be influenced by a catalyst.
(c) It proceeds only in the forward direction.
(d) Number of moles of reactants and products are equal.
Answer
A
Question. For the reversible reaction,
A(s) + B(g) C(g) + D(g), ΔG° = –350 kJ,
which one of the following statements is true?
(a) The reaction is thermodynamically nonfeasible.
(b) The entropy change is negative.
(c) Equilibrium constant is greater than one.
(d) The reaction should be instantaneous.
Answer
C
Question. In a chemical equilibrium the rate constant of backward reaction is 3.2 × 10–2 and the equilibrium constant is 2–5. The rate constant of forward reaction is
(a) 1 × 10–3
(b) 2 × 10–2
(c) 8 × 10–2
(d) 4 × 10–2
Answer
A
Question. Which will make basic buffer?
(a) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 100 mL of
0.1 M NaOH
(b) 50 mL of 0.1 M NaOH + 25 mL of
0.1 M CH3COOH
(c) 100 mL of 0.1 M CH3COOH + 100 mL of
0.1 M NaOH
(d) 100 mL of 0.1 M HCl + 200 mL of
0.1 M NH4OH
Answer
D
Question. For the reaction,

if Kp = Kc(RT)x where the symbols have usual meaning then the value of x is (assuming ideality)
(a) 1
(b) – 1
(c) − 1/2
(d) 1/2
Answer
C
Question. The solubility product of aluminium sulphate is given by the expression
(a) 4s3
(b) 6912s7
(c) s2
(d) 108s5
Answer
D
Question. If K1 and K2 are the respective equilibrium constants for the two reactions,
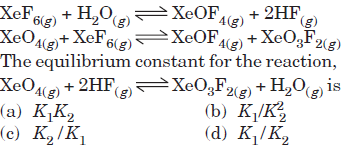
Answer
C
Question. When the rate of formation of reactants is equal to the rate of formation of products, this is known as,
(a) chemical reaction
(b) chemical equilibrium
(c) chemical kinetics
(d) none of these.
Answer
B
Question. For the system 3A + 2B ⇌ C,the expression for equilibrium constant K is

Answer
C
Question. In a reversible chemical reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of any one of the reactants is doubled, then the equilibrium constant will
(a) also be doubled
(b) be halved
(c) remain the same
(d) become one-fourth.
Answer
C
Question. For the following three reactions (i), (ii) and (iii), equilibrium constants are given
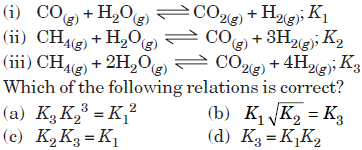
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a characteristic of equilibrium?
(a) Rate is equal in both directions.
(b) Measurable quantities are constant at equilibrium.
(c) Equilibrium occurs in reversible condition.
(d) Equilibrium occurs only in an open vessel at constant temperature
Answer
D
Question. Equilibrium constants are given for the following reactions. Out of the following, which is farthest towards completion?
(a) K = 100
(b) K = 0.1
(c) K = 0.01
(d) K = 1
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following options will be correct for the stage of half completion of the reaction X Y.
(a) ΔG° = 0
(b) ΔG° > 0
(c) ΔG° < 0
(d) ΔG° = –RT ln2
Answer
A
Question. It is not possible to attain equilibrium in
(a) closed system
(b) isolated system
(c) open system
(d) none of these.
Answer
C
Question. Kp/Kc for following reaction will be
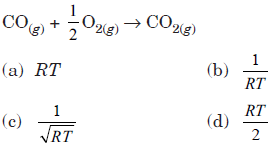
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following solutions will have pH close to 1.0?
(a) 100 mL of M/10 HCl + 100 mL of M/10 NaOH
(b) 55 mL of M/10 HCl + 45 mL of M/10 NaOH
(c) 10 mL of M/10 HCl + 90 mL of M/10 NaOH
(d) 75 mL of M/10 HCl + 25 mL of M/10 NaOH
Answer
D
Question. Conjugate base for Bronsted acids H2O and HF are
(a) H3O+ and H2F+, respectively
(b) OH– and H2F+, respectively
(c) H3O+ and F–, respectively
(d) OH– and F–, respectively.
Answer
D
Case Based MCQs :
Le Chatelier’s principle is also known as the equilibrium law, used to predict the effect of change on a system at chemical equilibrium. This principle states that equilibrium adjust the forward and backward reactions in such a way as to accept the change affecting the equilibrium condition. When factor like concentration, pressure, temperature, inert gas that affect equilibrium are changed, the equilibrium will shift in that direction where the effects that caused by these changes are nullified. This principle is also used to manipulate reversible reaction in order to obtain suitable outcomes.
Question. For the reversible reaction,
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) + heat
The equilibrium shifts in forward direction
(a) by increasing the concentration of NH3(g)
(b) by decreasing the pressure
(c) by decreasing the concentrations of N2(g) and H2(g)
(d) by increasing pressure and decreasing temperature.
Answer
D
Question. X + Y ⇌ P + Q
For the above equilibrium, the reactant concentration is doubled, what would happen then to equilibrium constant?
(a) Remains constant
(b) Be doubled
(c) Be halved
(d) Cannot be predicted
Answer
A
Question. Favourable conditions for manufacture of ammonia by the reaction,
N2 + 3H2 ⇌ 2NH3; ΔH = – 21.9 kcal are
(a) low temperature, low pressure and catalyst
(b) low temperature, high pressure and catalyst
(c) high temperature, low pressure and catalyst
(d) high temperature, high pressure and catalyst.
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following conditions will favour maximum formation of the product in the reaction
A2(g) + B2(g) X2(g), Δr H = –X kJ ?
(a) Low temperature and high pressure
(b) Low temperature and low pressure
(c) High temperature and high pressure
(d) High temperature and low pressure
Answer
A
Question. In which one of the following equilibria will the point of equilibrium shift to left when the pressure of the system is increased?
(a) H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
(b) 2NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3H2(g)
(c) C(s) + O2(g) ⇌ CO2(g)
(d) 2H2(g) + ⇌ O2(g) 2H2O(g)
Answer
B
Reactants and products coexist at equilibrium, so that the conversion of reactant to products is always less than 100%. Equilibrium reaction may involve the decomposition of a covalent (nonpolar) reactant or ionization of ionic compound into their ions in polar solvents. Ostwald dilution law is the application of the law of mass action to
the weak electrolytes in solution.
A binary electrolyte AB which dissociates into A+ and B– ions i.e.
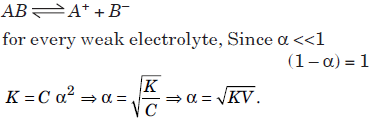
Question. If a is the fraction of HI dissociated at equilibrium in the reaction :
2HI ⇌ H2 + I2
then starting with 2 mol of HI, the total number of moles of reactants and products at equilibrium are
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 1 + a
(d) 2 + 2a
Answer
B
Question. Calculate ionisation constant for pyridinium hydrogen chloride. (Given that H+ ion concent-ration is 3.6 × 10–4 M and its concentration is 0.02 M.)
(a) 6.48 × 10–2
(b) 6 × 10–6
(c) 1.5 × 10–9
(d) 12 × 10–8
Answer
C
Question. Ostwald dilution law is applicable to
(a) weak electrolytes
(b) non-electrolyte
(c) strong electrolyte
(d) all type of electrolyte.
Answer
A
Question. The hydrogen ion concentration of a 10–8 M HCl aqueous solution at 298 K(Kw = 10–14) is
(a) 9.525 × 10–8 M
(b) 1.0 × 10–8 M
(c) 1.0 × 10–6 M
(d) 1.0525 × 10–7 M D
Question. A monobasic weak acid solution has a molarity of 0.005 M and pH of 5. What is its percentage ionization in this solution?
(a) 2.0
(b) 0.2
(c) 0.5
(d) 0.25
Answer
B

