Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Chapter 11 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principles and Processes have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Biology based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Biology for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Biotechnology Principles and Processes Worksheets Class 12 Biology
Question. A restriction endonucleases which always cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising a specific sequence of six base pairs is :
(a) Hind-II
(b) Psu I
(c) Hae-III
(d) All of these
Answer
A
Question. The first letter of the name of Restriction endonuclease came from the
(a) Genus of organism
(b) Species of organism
(c) Family of organism
(d) Class of organism
Answer
A
Question. Father of genetic engineering is :
(a) Paul Berg
(b) Nathans
(c) Herbert Boyer
(d) Stanley Cohen
Answer
A
Question. A definition of biotechnology that encompasses both traditional view and modern view are given by :
(a) European forum on Biotechnology
(b) European focus on Biotechnology
(c) European Federation of Biotechnology
(d) European Centre of Biotechnology
Answer
C
Question. In a chromosome there is a specific DNA sequence which is responsible for initiating replication is :
(a) Ori
(b) Palindromic sequence
(b) Initiation sequence
(d) Promoter sequence
Answer
A
Question. To make cell competent to take up DNA, heat shock is given to cells, the temperature of shock is :
(a) 30°C
(b) 42°C
(c) 60°C
(d) 90°C
Answer
B
Question. In gel electrophoresis technique the DNA fragments are forced to move through a medium towards :
(a) Anode
(b) Cathode
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. First recombinant DNA was made by Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer in :
(a) 1968
(b) 1970
(c) 1972
(d) 1974
Answer
C
Question. The first restriction endonuclease discovered, was
(a) Eco RI
(b) Sam I
(c) Bam HI
(d) Hind II
Answer
D
Question. In the vector pBR322 there is
(a) One selectable marker
(b) Two selectable markers
(c) Three selectable markers
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. When the isolation of genetic material is done the RNA can be removed by treatment with :
(a) Protease
(b) Chitinase
(c) Ribonuclease
(d) Deoxyribonuclease
Answer
C
Question. If DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of b-galactosidase enzyme then
(a) Non-recombinants will give blue coloured colonies in presence of chromogenic substrate
(b) Recombinant will give blue coloured colonies in presence of chromogenic substrate
(c) Both recombinants and non-recombinants give blue colour
(d) Non-recombinants do not produce colour due to insertional inactivation.
Answer
A
Question. Knife of DNA :
(a) DNA – ligase
(b) Restriction endonuclease
(c) Exonuclease
(d) Peptidase
Answer
B
Question. Insertional inactivation results into inactivation of which enzyme ?
(a) Transacetylase
(b) Permease
(c) Taq polymerase
(d) b-galactosidase
Answer
D
Question. If the bacterium does not have any insert, then the presence of chromogenic substrate, it gives :
(a) Red coloured colonies
(b) Colourless colonies
(c) Blue colonies
(d) Green colonies
Answer
C
Question. Large vessel in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products, individual enzymes etc using microbial plant, animal or human cell is:
(a) Biotank
(b) Biovessel
(c) Bioreactor
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. The enzymes, which remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA are :
(a) Exonuclease
(b) Endonuclease
(c) Cellulase
(d) Hydrolase
Answer
A
Question. When a recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme b-galatosidase, it results into inactivation of the enzyme gene this is called :
(a) Insert inactivation
(b) Insertional inactivation
(c) Insertional activation
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Group of letters that form the same words when read both forward and backward is called :
(a) Palindrome
(b) Same words
(c) Opposite words
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. Which type of ends are produced by EcoRI ?
(a) Blunt ends
(b) Sticky ends
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. The sequence which is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA is :
(a) Coding sequence
(b) Promoter sequence
(c) Terminator sequence
(d) Ori
Answer
D
Question. In gel electrophoresis the DNA fragments separate according to size (smaller the fragment size, the faster it moves) this effect is called :
(a) Sieving effect
(b) Movement effect
(c) Size effect
(d) Spooling
Answer
A
Question. Extraction, purification and packaging of products is collectively known as :
(a) Upstream processing
(b) Distillation
(c) Downstream processing
(d) Genetic engineering
Answer
C
Question. EcoRI recognises palindromic sequence
(a) 5’GGGCCC3′
3’CCCGGG
(b) 5′-GAATTC-3′
3-CTTAAG-5′
(c) 5-AAGCTT3′
3-TTCGAA-5
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. The enzymes responsible for restricting the growth of bacteriophage in E-coli were isolated in 1963, these enzyme are :
(a) DNA ligases
(b) Alkaline phosphatases
(c) DNA polymerases
(d) Restriction endonuclease
Answer
D
Question. DNA cannot pass through cell membrane as it is :
(a) hydrophilic
(b) hydrophobic
(c) lipophilic
(d) All the above
Answer
A
Question. Which type of bioreactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the contents?
(a) Sparged tank bioreactor
(b) Stirred tank bioreactor
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. In PCR-technology primer is a :
(a) Small chemically synthesized oligonucleotide that are complementary to region of DNA
(b) Large chemically synthesized oligonucleotide that are identical to region of DNA
(c) Small segment of RNA
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. In gel electrophoresis the DNA fragment separate according to their size through sieving effect, which is provided by :
(a) Agarose gel
(b) Nylone membrane
(c) Polyethylene glycol
(d) Ethidium Bromide
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following method of vectorless gene transfer is suitable for plants ?
(a) Biolistics method
(b) Micro injection
(c) Liposome mediated
(d) Electroporation
Answer
A
Question. The linking of antibiotic resistant gene in the plasmid vector become possible with the enzyme :
(a) Restriction endonuclease
(b) DNA ligase
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) RNA polymerase
Answer
B
Question. In gel electrophoresis, separated bands of DNA are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel pieces, This step is known as :
(a) Blotting
(b) Elution
(c) Cloning
(d) Tagging
Answer
B
Question. If the plasmid in the bacteria dose not have any insert then the colonies produce :
(a) Blue colour in the presence of X-gal
(b) No colour in the presence of X-gal
(c) Blue colour in the absence of X-gal
(d) None of the above
Answer
A
Question. The normal E-coli cell carries resistance gene against:
(a) Ampicillin
(b) Chloramphenicol
(c) Tetracycline
(d) None of the above
Answer
D
Question. Ti plasmid is present in :
(a) E.coli
(b) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(c) Agrobacterium orifaciens
(d) Vibrio cholerae
Answer
B
Question. Apart from DNA in the bacterial nucleoid, there is a circular extrachromosomal DNA in a bacterial cell called :
(a) Plasmid
(b) Mesosomes
(c) Chromosome
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the following passage and answer any four questions given below:
Rama lives in a society where a robbery occurred last night. Robbers came into the flat and murdered the old lady residing there. Police came and restricted the entry into the flat. They took samples from the room, where the dead body was found. While examining, they found that there is some blood and tissue in the nails of old lady.
According to their observation, police filtered out their inspection to three suspects viz. servant, cook and milkman. Finally after two days of robbery, police caught the criminal. It was the old lady’s cook. Rama was amazed to see that how quickly police completed and shut the case. She asked the inspector that how they did it? The police man told her that it become possible due to the sample collected from the victim, that lead them to the criminal. The sample taken from nail scraping was amplified using PCR and then tested.
Question. What technique was used by the police to identify the criminal?
(a) DNA fingerprinting
(b) Gel electrophoresis
(c) Molecular diagnosis
(d) Cloning
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements regarding PCR is correct?
(a) Taq polymerase, which is isolated from bacterium Thermus aquaticus is stable at low temperature only.
(b) Wi th the help of DNA l igase, the complementary sticky ends of the DNA are joined to produce a rDNA.
(c) Since the sequence of primers are complementary to 5′ end of the template DNA, they anneal to it.
(d) DNA purified from the cell is precipitated by adding hot ethanol.
Answer
B
Question. Given below are steps of polymerase chain reaction.
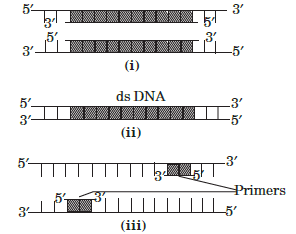
Select the option that correctly mention the sequence in which they occur.
(a) (ii) → (iii) → (i)
(b) (i) → (ii) → (iii)
(c) (iii) → (i) → (ii)
(d) (ii) → (i) → (iii)
Answer
A
Case II : Read the following passage and answer any four questions given below:
The DNA, which is transferred from one organism into another by joining it with the vehicle DNA is called passenger or foreign DNA. Generally three types of passenger DNAs are used. These are complementary DNA (cDNA), synthetic DNA (sDNA) and random DNA. Complementary DNA (cDNA) is synthesized on RNA template (usually mRNA) with the help of reverse transcriptase.
Synthetic DNA (sDNA) is synthesized on DNA template or without a template. Random DNA are small fragments formed by breaking a chromosome of an organism in the presence of restriction endonucleases.
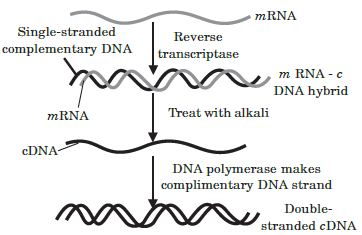
Question. During cDNA formation, what would happen if DNA formed by reverse transcriptase is not treated with the alkali?
(a) cDNA will not be digested
(b) mRNA will not be digested
(c) Hydrogen bonds will not form between base pairs
(d) mRNA will not be formed.
Answer
B
Question. DNA polymerase can be obtained form
(a) retrovirus
(b) Agrobacterium
(c) tobacco mosaic virus
(d) Thermus aquaticus.
Answer
D
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Bacterial cells are made competent by treating them with specific concentration of a divalent cation.
Reason : Treatment of bacterial cell with a divalent cation increases the efficiency with which DNA enters the bacterium through pores in its cell wall.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Vector DNA and foreign DNA are cut by same restriction endonuclease.
Reason : Digestion of vector DNA and foreign DNA with same enzyme produces complementary sticky ends.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : In recombinant DNA technology, human genes are often transferred into bacteria (prokaryotes) or yeast (eukaryote).
Reason : Both bacteria and yeast multiply very fast to form huge populations which express the desired gene.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in specific regions of DNA sequence.
Reason : DNA fingerprinting is the basis of paternity testing.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Soil inhabiting bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is called a natural plant genetic engineer.
Reason : Agrobacterium tumefaciens produce crown galls in several dicot plants.
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Who is considered as the “father of genetic engineering”?
Answer : Genetic engineering was started by Paul Berg (1972) when he was able to introduce a gene of SV-40 into a bacterium. He is often considered as “father of genetic engineering”.
Question. What is the role of sterile air bubbles in the sparged stirred-tank bioreactor?
Answer : The sterile air bubbles in the sparged stirred-tank bioreactor increases the surface area for oxygen transfer.
Question. Name the material used as matrix in gelelectrophoresis and mention its role.
Answer : Most commonly used matrix in DNA gel electrophoresis is agarose. It provides sieving effect for separation of DNA fragments according to their size.
Question. State what happens when an alien gene is ligated at SalI site of pBR322 plasmid.
Answer : When an alien gene is ligated at SalI site of pBR322, the gene tetR becomes non functional and plasmid loses its tetracycline resistance. Hence, the cell possessing such recombinant pBR322 will not be able to grow on tetracycline.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why is ‘plasmid’ an important tool in biotechnology experiments?
Answer : Plasmid have the ability to replicate within bacterial cells independent of the control of chromosomal DNA and have high copy number, therefore any alien DNA ligated to it, also multiplies to equal the copy number of plasmids. So, it is used as a vector in gene cloning experiments and thus, plays a role of an important tool in biotechnology.
Question. Name the natural source of agarose. Mention one role of agarose in biotechnology.
Answer : Agarose is commonly used as matrix in agarose gel electrophoresis. It is extracted from sea weeds. In recombinant DNA technology, agarose is used to separate DNA fragments according to their sizes.
Question. A recombinant DNA is formed when sticky ends of vector DNA and foreign DNA join.
Explain how the sticky ends are formed and get joined.
Answer : When restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, between the same two bases on the opposite strands, it leaves single stranded portions at the ends. This forms overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand. They are called sticky as they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. The stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Question. Explain any two methods of vectorless gene transfer.
Answer : Vectorless gene transfer is a method to introduce recombinant DNA into recipient cells of host without involving carrier molecule.
Two methods of vectorless gene transfer are:
(i) Microinjection : It is the introduction of foreign gene into plant cell or animal cell by using microneedles or micropipettes.
(ii) Electroporation : In this method, electrical impulses induce transient pores in the plant cell membrane through which the DNA molecules are incorporated into the plant cells.
Question. Rearrange the following in the correct sequence to accomplish an important biotechnological reaction :
(i) Denaturation of ds-DNA
(ii) Chemically synthesised oligonucleotides
(iii) Primers
(iv) Complementary region of DNA
(v) Thermostable DNA polymerase (from Thermus aquaticus)
(vi) Nucleotides provided
(vii) Genomic DNA template
(viii) In vitro synthesis of copies of DNA of interest
(ix) Enzyme DNA-polymerase.
Answer : The correct sequence to accomplish biotechnological reaction is :
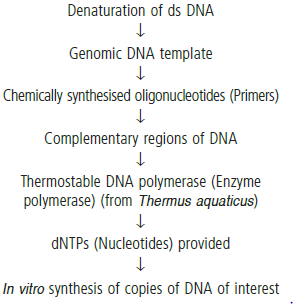
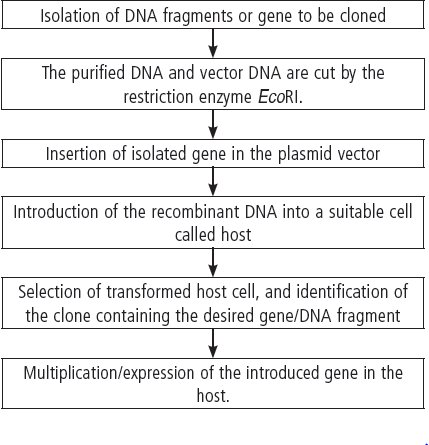
Question. Prepare a flow chart in formation of recombinant DNA by the action of restriction endonuclease enzyme EcoRI.
Answer :
Question. Differentiate between rDNA and cDNA.
Answer : Differences between rDNA and cDNA are as follows:

Question. What are bioreactors ? List five growth conditions that a bioreactor provides for obtaining the desired product.
Answer : A bioreactor is a device in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products by microbes, plant/animal cells etc. These are used for food processing,fermentation, waste treatment, etc.
Growth conditions that a bioreactor provides for obtaining the desired products are :
(i) Controlled environment for optimum product yield.
(ii) Aseptic fermentation for a number of days and prevention of escape of viable cells.
(iii) Adequate mixing and aeration for optimum growth and production, without damaging the microorganism.
(iv) Easy and dependable temperature control
(v) Facility of sampling.
Question. Give reasons why:
(a) DNA cannot pass into a host cell through the cell membrane.
(b) Proteases are added during isolation of DNA for genetic engineering.
(c) Single cloning site is preferred in a vector.
Answer : (a) DNA is a hydrophilic molecule, so it cannot pass into a host cell through cell membrane. The cell membrane consists of lipid bilayers that are generally impermeable to hydrophilic molecules.
(b) DNA is interwined with proteins like histones and RNA.
To obtain purified DNA, proteases are added during isolation of DNA which convert proteins into amino acids. The purified DNA finally precipitates out after the addition of chilled ethanol.
(c) In order to link the alien DNA, the vector needs to have very few, preferably single, recognition sites for the commonly used restriction enzymes. Presence of more than one recognition sites within the vector will generate several fragments, which will complicate the gene cloning process.
Question. Name the technique to obtain multiple copies, of a DNA segment of interest, synthesized in vitro. Name two sets of primers that are necessary for reaction to occur. Mention three diagnostic applications of this technique.
Answer : PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction).
The two sets of primers (small chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to the regions of DNA) are required in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction.
Primers hybridise to target DNA region and allow synthesis of the DNA towards one another whereas DNA polymerase synthesise DNA region between the primers using dNTPs and Mg2+. Three diagnostic applications of PCR are :
(i) Diagnosis of pathogens
(ii) Diagnosis of specific mutations
(iii) Prenatal diagnosis
Question. Explain the role of Ti plasmids in biotechnology.
Answer : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil-inhabiting bacterium that may invade growing plants at the junction of root and stem, where it can cause a cancerous growth known as a crown gall. A. tumefaciens contains Ti plasmid which carries gene for tumour formation for using Agrobacterium
tumefaciens as a cloning vector researchers deleted the genes which governs auxin and cytokinin production (the oncogene) from T-DNA of Ti plasmid, it is known as disarming. After disarming, this T-DNA is inserted into chromosomes of the host plant where it produces copies of itself.
Question. Read the following base sequence of a certain DNA strand and answer the questions that follow:
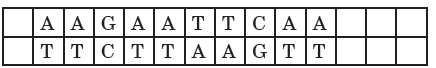
(i) What is called a ‘palindromic sequence’ in a DNA ?
(ii) Write the palindromic nucleotide sequence shown in the DNA strand given and mention the enzyme that will recognise such a sequence.
(iii) State the significance of enzymes that identify palindromic nucleotide sequences.
Answer : (i) The palindromic sequence in DNA is a sequence of base pairs that reads same on the two strands when orientation of reading is kept the same.
(ii) The palindrome sequence in the given DNA strand is :
GAATTC
CTTAAG
This is the recognition sequence for restriction enzyme EcoRI.
(iii) Each restriction endonucleases recognise a specific palindromic nucleotide sequences in the DNA. Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands. This leaves single stranded portions at the ends. These are overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand. These are named so because they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts.
This stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. If a desired gene is identified in an organism for some experiments, explain the process of the following :
(a) Cutting of desired gene at specific locations.
(b) Synthesis of multiple copies of the desired gene.
Answer : (a) Desirable DNA sequences are cut by the use of enzyme restriction endonuclease. The restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, between the same two bases on the opposite strands, it leaves single stranded portions at the ends. This forms overhanging stretches called sticky ends on each strand. They are called sticky as they form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. The stickiness of the ends facilitates the action of the enzyme DNA ligase.
(b) The three steps involved in each cycle of PCR are :
(i) Denaturation
(ii) Annealing
(iii) Extension
PCR is based on the principle that a DNA molecule, when subjected to high temperature, splits into two strands due to denaturation. These single stranded DNA molecules are then converted to original double stranded molecules, in the presence of enzyme DNA polymerase. A double stranded molecule of DNA is duplicated in this way and multiple copies of original DNA sequence can be generated by repeating the process several times. Such repeated amplification is achieved by the use of thermostable DNA polymerase (isolated from Thermus aquaticus), which remain active during the high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA.
