Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Chapter 2 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Biology based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Biology for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Worksheets Class 12 Biology
Question. What would be the ploidy of cells of tetrad ?
(a) n
(b) 2n
(c) 3n
(d) 4n
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following statements are correct ?
(a) Pollen grains are rich in nutrients.
(b) In some cereals like rice and wheat pollen grains lose viability within 30 minutes of their release
(c) In some members of rosaceae, leguminosae and solanaceae, pollen grains maintain viability for months
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Wind pollinated flowers often have…..ovule in each ovary.
(a) Many
(b) Two
(c) One
(d) Three
Answer
C
Question. Pollen tube enters into the embryosac through :
(a) Chalaza
(b) Integument
(c) Filiform apparatus
(d) Funiculus
Answer
C
Question. Syngamy results in the formation of :
(a) Zygote
(b) Primary endosperm nucleus
(c) Endosperm
(d) Fruit
Answer
A
Question. From outer to inner what is the sequence of wall layers in anther lobes?
(a) Epidermis, middle layers, tapetum, endothecium
(b) Epidermis, endothecium, tapetum, middle layers
(c) Epidermis, endothecium, middle layer, tapetum
(d) Tapetum, middle layers, endothecium, epidermis
Answer
C
Question. Due to which of the following chemical deposition pollen grains are well preserved as fossils
(a) Pollenkitt
(b) Callose
(c) Sporopollenin
(d) Pectocellulose
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not involved in post fertilisation events
(a) Endosperm and embryo development
(b) Maturation of ovules into seed
(c) Maturation of ovary into fruit
(d) Degeneration of nucellus
Answer
D
Question. The structure in which few leaf primordia and shoot apex of monocot embryo remain enclosed is
(a) Coleoptile
(b) Coleorhiza
(c) Epiblast
(d) Epicotyl
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is not a pollen grain caused disease?
(a) Asthma
(b) Bronchitis
(c) Hayfever
(d) Malaria
Answer
D
Question. The number of ovules in an ovary may be
(a) One
(b) Many
(c) Two
(d) One to many
Answer
D
Question. Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes called
(a) Micropyle
(b) Integuments
(c) Hilum
(d) Chalaza
Answer
B
Question. Regarding to number of ovules in ovary select out the odd one
(a)Wheat
(b) Orchids
(c) Paddy
(d) Mango
Answer
B
Question. What would be the genetic nature of apomictic embryo?
(a) n
(b) 3n
(c) 2n
(d) n or 2n like mother plants
Answer
D
Question. Nucellus, the mass of cells enclosed within the integuments, provide nutrition to
(a) Embryosac
(b) Embryo
(c) Seed
(d) Ovule
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is probable reason of limited distribution of bryophytes and pteridophytes?
(a) Jacketed multicellular sex organs
(b) Absence of roots
(c) Absence of seeds
(d) Need of water for transfer of male gametes
Answer
D
Question. Regarding to type of pollination which of the following is odd one
(a)Vallisneria
(b) Hydrilla
(c) Water lily
(d) Zostera
Answer
C
Question. The genetic mechanism which inhibit pollen germination or pollentube growth in pistil so that self pollination can be prevented is known as
(a) Inbreeding depression
(b) Self incompatibility
(c) Inter specific incompatibility
(d) Heterosis
Answer
B
Question. In mature seed how much amount of moisture is present
(a) 5-10 percent
(b) 10-15 percent
(c) 15-20 percent
(d) 20-25 percent
Answer
B
Question. Seed is the basis of our agriculture. Which of the following is/are crucial for storage of seeds, so that they can be used as food through out the year and also to raise crop in the next season
(a) Dehydration
(b) Dormancy
(c) Vermiculture
(d) Both 1 and 2
Answer
D
Question. Endosperm may persist in mature seed in
(a) Pea
(b) Castor
(c) Groundnut
(d) Beans
Answer
B
Question. Usually, How many embryosacs are present in an ovule?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) Many
Answer
A
Question. In which of the following plants both autogamy and geitonogamy is absent
(a) Maize
(b) Mango
(c) Papaya
(d) Castor
Answer
C
Question. Perisperm is present in
(a) Mango
(b) Guava
(c) Black pepper
(d) Pea
Answer
C
Question. Flowers are highly modified _______.
(a) Root
(b) Shoot
(c) Stem
(d) Leaves
Answer
B
Question. Anther is typically
(a) tetrasporangiate
(b) bisporangiate
(c) trisporangiate
(d) monosporangiate
Answer
A
Question. Microsporogenesis occurs
(a) on margins of leaves.
(b) inside the ovule.
(c) inside the anther.
(d) in essential floral organs.
Answer
C
Question. One of the most resistant known biological material is.
(a) lignin
(b) hemicellulose
(c) sporopollenin
(d) lignocellulose
Answer
C
Question. Pollen grains can be stored in liquid nitrogen at _________.
(a) 70°C
(b) 100°C
(c) – 196°C
(d) 0°C
Answer
C
Question. Ovules are attached to a parenchymatous cushion called
(a) nucellus
(b) obturator
(c) conducting tissue
(d) placenta
Answer
D
Question. Egg apparatus consists of
(a) egg cell and antipodal cells.
(b) egg cell and central cell.
(c) egg cell and two synergids.
(d) egg cell and one synergid.
Answer
C
Question. Filiform apparatus is found in
(a) synergids
(b) anther wall
(c) secondary nucleus
(d) egg cell
Answer
A
Question. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of another flower of the same plant is called
(a) geitonogamy
(b) xenogamy
(c) autogamy
(d) cleistogamy
Answer
A
Question. Both chasmogamous and cleistogamous flowers are present in
(a) Helianthus
(b) Lommelina
(c) Rosa
(d) Gossypium
Answer
B
Question. Bees are important to agriculture as they
(a) produce wax
(b) perform pollination
(c) prevent pollination
(d) produce honey
Answer
B
Question. During double fertilization in plants, one sperm fuses with the egg cell and the other sperm fuses with
(a) synergids cell
(b) central cell
(c) antipodal cell
(d) nucellar cell
Answer
B
Question. Milky water of green coconut is
(a) liquid chalaza
(b) liquid nucellus
(c) liquid endosperm
(d) liquid female gametophyte
Answer
C
Question. Perisperm is a
(a) degenerate part of synergids.
(b) peripheral part of endosperm.
(c) degenerate part of secondary nucleus.
(d) remnant of nucellus.
Answer
D
Question. Seeds are adoptively important because
(a) they maintain dormancy.
(b) they protect young plants during vulnerable stages.
(c) they store food for young plants and facilitate disperal.
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. Apomixis is the
(a) development of plants in darkness.
(b) development of plants without fusion of gametes.
(c) inability to perceive stimulus for flowering.
(d) effect of low temperature on plant growth.
Answer
B
Statement Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. Which of the following statement is correct for the pollen tube?
(a) It shows chemotactic movement.
(b) It shows only tip growth.
(c) It is composed of three non-cellular zones.
(d) It shows radial cytoplasmic streaming.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) When pollen is shed at two-celled stage, double fertilization does not take place.
(b) Vegetative cell is larger than generative cell.
(c) Pollen grains in some plants remain viable for months.
(d) Intine is made up of cellulose and pectin.
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following events takes place after double fertilization?
(a) The pollen grain germinates on the stigma.
(b) The pollen tubes enter the embryo sac.
(c) Two male gametes are discharged into the embryo sac.
(d) The PEN (Primary Endosperm Nucleus) develops into endosperm.
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following statement is correct?
(a) Geitonogamy involves the pollen and stigma of flowers of different plants.
(b) Cleistogamous flowers are always autogamous.
(c) Xenogamy occurs only by wind pollination.
(d) Chasmogamous flowers do not open at all.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect ?
(i) Endosperm formation starts prior to first division of zygote.
(ii) Angiospermic endosperm is mostly 3N while gymnospermic one is N.
(iii) The most common type of endosperm is nuclear.
(iv) Coconut has both liquid nuclear (multinucleate) and cellular endosperm.
(v) Milky water of green tender coconut is liquid female gametophyte.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) Only (iii)
(c) Only (v)
(d) Only (ii)
Answer
C
Question. Study the following statements and select the correct option.
(i) Tapetum nourishes the developing pollen grains.
(ii) Hilum represents the junction between ovule and funicle.
(iii) In aquatic plants, such as water hyacinth and water lily, pollination is by water.
(iv) The primary endosperm nucleus is triploid.
(a) (i) and (ii) are correct but (iii) and (iv) are incorrect.
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct but (iii) is incorrect.
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct but (i) is incorrect.
(d) (i) and (iv) are correct but (ii) and (iii) are incorrect.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the given statements are true?
(i) During the development of a dicot embryo heart shaped embryo is followed by globular enlarge.
(ii) The part of the embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is epicotyl while the part below the level of cotyledons is hypocotyl.
(iii) Monocot seeds possess a single cotyledon represented by scutellum.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (i) (ii) and (iii)
Answer
B
Assertion/Reason Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) If both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : Endosperm is a nutritive tissue and it is triploid.
Reason: Endosperm is formed by fusion of secondary nucleus to second male gamete. It is used by developing embryo.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Insects visit flower to gather honey.
Reason : Attraction of flowers prevents the insects from damaging other parts of the plant.
Answer
D
Matching Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. Match the biotic agent of cross pollination given in column-I with their feature given in column-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Zoophily | I. Pollination by birds |
| B. Ornithophily | II. Pollination by insects |
| C. Entomophily | III. Pollination by bats |
| D. Chiropterophily | IV. Pollination by animals |
(a) A – III; B – II; C – I; D – IV
(b) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV
(c) A – IV; B – I; C – II; D – III
(d) A – IV; B – II; C – I; D – III
Answer
C
Question. Match the items given in column-I with their examples given in column-II and choose the correct option given below.
| Column-I (Items) | Column-II (Examples) |
| A. Ovary | I. Groundnut, mustard |
| B. Ovule | II. Guava, orange, mango |
| C. Wall of ovary | III. Pericarp |
| D. Fleshy fruits | IV. Seed |
| E. Dry fruits | V. Fruit |
(a) A – V; B – IV; C – III; D – II; E – I
(b) A – I; B – II; C – III; D – IV; E – V
(c) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV; E – V
(d) A – V; B – IV; C – I; D – II; E – III
Answer
A
Question. Match the items given in column-I with those given in column-II and chose the correct option given below.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Tapetum | I. Irregular in shape with abundant food reserve |
| B. Exine | II. Acts as nutritive layer |
| C. Pollenkit | III. Thick, rigid protective layer |
| D. Vegetative cell | IV. Involve in the formation of microspores |
| E. Sporogenous | V. Oily and sticky layer, help tissue in pollination. |
(a) A – II; B – III; C – V; D – IV; E – I
(b) A – I; B – III; C – II; D – IV; E – V
(c) A – II; B – III; C – I; D – IV; E – V
(d) A – II; B – IV; C – V; D – I; E – III
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is a mismatched pair?
(a) Microsporangium – Pollen sac
(b) Megasporangium – Ovule
(c) Microsporophyll – Stamen
(d) Megasporophyll – Filament
Answer
D
Diagram Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. The given diagram refers to a T. S. of anther. Identify A to E respectively
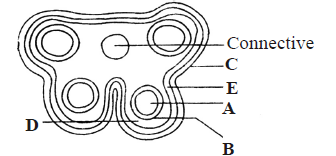
(a) Sporogenous tissue, tapetum, epidermis, middle layer, endothecium
(b) Sporogenous tissue, epidermis, tapetum, middle layer, endothecium
(c) Sporogenous tissue, epidermis, middle layer, tapetum, endothecium
(d) Sporogenous tissue, tapetum, middle layer, epidermis, endothecium
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following figure, showing types of gynoecium, is associated with wind pollination ?
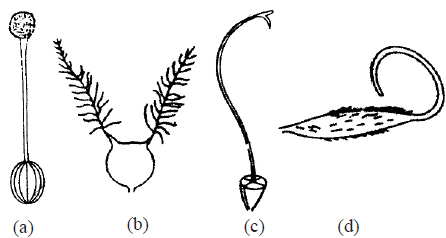
Answer
B
Question. The given figure represent the L.S of a flower showing growth of pollen tube. Few structures are marked as A, B, C, D & E. Identify A, B, C, D and E respectively.

(a) Antipodal cells, Polar nuclei, Stigma, Style, Chalaza
(b) Antipodal cells, Polar nuclei, Style, Stigma, Chalaza
(c) Antipodal cells, Polar nuclei, Stigma, Chalaza, Style
(d) Antipodal cells, Polar nuclei, Chalaza, Stigma, Style
Answer A
A
Question. Identified A, B, C and D in the given figure of false fruit of apple.
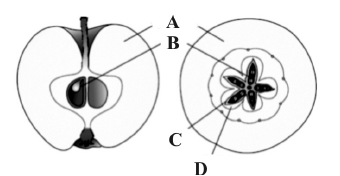
(a) A – Mesocarp; B – Endocarp; C – Seed; D – Thalamus
(b) A – Seed; B – Thalamus; C – Mesocarp; D –Endocarp
(c) A – Thalamus; B – Seed; C – Endocarp; D – Mesocarp
(d) A – Mesocarp; B – Endocarp; C – Seed; D – Thalamus
Answer
C
Question. The given diagram shows two plants of the same species. Identify the type of pollination indicated as P1, P2 and P3.

(a) Allogamy Chasmogamy Cleistogamy
(b) Autogamy Xenogamy Geitonogamy
(c) Autogamy Geitonogamy Xenogamy
(d) Geitonogamy Allogamy Autogamy
Answer
C
Question. The given figure shows the L.S. of a monocot embryo.
Choose the correct labelling for A, B, C and D marked in the figure from the options given below.
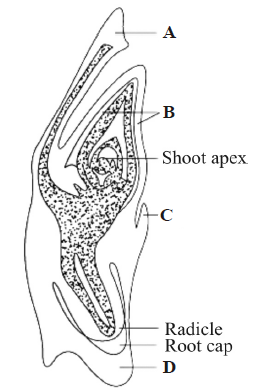
(a) A – Coleoptile; B – Scutellum; C – Epiblast; D – Coleorhiza
(b) A – Scutellum; B – Coleoptile; C – Coleorhiza; D – Epiblast
(c) A – Scutellum; B – Epiblast; C – Coleoptile; D – Coleorhiza
(d) A – Scutellum; B – Coleoptile; C – Epiblast; D – Coleorhiza
Answer
D
Critical Thinking Type Questions for Class 12 Biology Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Question. The largest cell in a embryo sac is
(a) egg
(b) central cell
(c) synergid
(d) antipodal cell
Answer
B
Question. In a fertilized ovule, n, 2n and 3n conditions occur respectively in
(a) antipodal, egg and endosperm.
(b) egg, nucellus and endosperm.
(c) endosperm, nucellus and egg.
(d) antipodals, synergids and integuments.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following floral parts forms pericarp after fertilization ?
(a) Nucellus
(b) Outer integument
(c) Ovary wall
(d) Inner integument
Answer
C
Question. Sequence of development during the formation of embryo sac is
(a) Archesporium → Megaspore → Megaspore mothercell → Embryo sac.
(b) Megasporocyte → Archesporium → Megaspore → Embryo sac.
(c) Megaspore → Megaspore mother cell → Archesporium → Embryo sac.
(d) Archesporium → Megaspore mother cell → Megaspore → Embryo sac.
Answer D
Question. Megaspores are produced from the megaspore mother cells after
(a) meiotic division.
(b) mitotic division.
(c) formation of a thick wall.
(d) differentiation.
Answer
A
Question. The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilization in angiosperms are
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer
D
Question. Albuminous seeds store their reserve food mainly in
(a) perisperm
(b) endosperm
(c) cotyledons
(d) hypocotyl
Answer
B
Question. An advantage of cleistogamy is that
(a) it leads to greater genetic diversity.
(b) seed dispersal is more efficient and wide spread.
(c) each visit of pollinator brings hundreds of pollen grains.
(d) seed set is not dependent upon pollinators.
Answer
D
Question. While planning for an artificial hybridization programme if the female parent have unisexual flowers, then which of the following steps would not be relevant?
(a) Bagging of female flower.
(b) Dusting of pollen on stigma.
(c) Emasculation.
(d) Collection of pollen.
Answer
C
Question. Total number of meiotic division required for forming 100 zygotes/100 grains of wheat is
(a) 100
(b) 75
(c) 125
(d) 50
Answer
C
Question. For artificial hybridization experiment in bisexual flower, which of the following sequences is correct ?
(a) Bagging -> Emasculation -> Cross-pollination ->Rebagging
(b) Emasculation -> Bagging -> Cross-pollination ->Rebagging
(c) Cross-pollination -> Bagging -> Emasculation ->Rebagging
(d) Self-pollination -> Bagging -> Emasculation ->Rebagging
Answer
B
Question. In a seed of maize, scutellum is considered as cotyledon because it
(a) protects the embryo.
(b) contains food for the embryo.
(c) absorbs food materials and supplies them to the embryo.
(d) converts itself into a monocot leaf.
Answer
C
Question. Multinucleate condition is present in
(a) quiescent centre
(b) maize
(c) meristematic tissue
(d) liquid endosperm of coconut
Answer
D
Question. What is the main function of filiform apparatus present at the micropylar part of the ovule?
(a) It prevents the entry of more than one pollen tube into the embryo sac.
(b) It helps in the entry of pollen tube into an antipodal cell.
(c) It helps the pollen tube to enter the ovule through chalazal end.
(d) It guides the entry of pollen tube into a synergid and discharge the male gametes.
Answer
D

