Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Mathematics Differential Equations Chapter 9 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 9 Differential Equations have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Mathematics based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Mathematics for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Differential Equations Worksheets Class 12 Mathematics
Question. The solution of the differential equation cos2x d2y/dx2 = 1 is:
(a) y = log cos x + cx
(b) y = logsec x + c1x + c2
(c) y = logsec x − c1x + c2
(d) None of these
Answer
B,C
Question. The differential equation of system of concentric circles with centre (1,2) is

Answer
D
Question. The differential equation of all circles which pass through origin and whose centres lie on y-axis is

Answer
C
Question. The differential equation of the family of curves y2=4a (x +a) is

Answer
D
Question. The differential equation of the rectangular hyperbola whose axes are the asymptotes of the hyperbola, is
(a) ydy/dx= x
(b) xdy/dx= – y
(c) xdydx= y
(d) xdy+ y dx =C
Answer
B
Question. The differential equation by eliminating A and B in
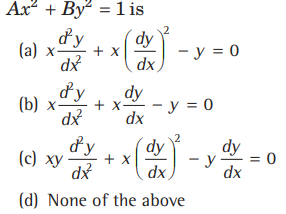
Answer
C
Question. The equation of the curve through the point (1,1) and whose slope is 2ay/x(y-a), is

Answer
A
Question. The differential equation of the family of curves y2=4a (x +a) is 20
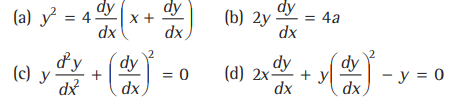
Answer
A
Question. The differential equation of all circles passing through the origin and having their centres on the x-axis is

Answer
A
Question. The differential equation of the family of parabolas with focus at the origin and the x-axis as axis, is

Answer
B
Question. A particular solution of the differential equation x-0, is
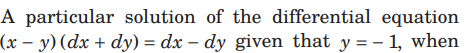
Answer
A
Question. The particular solution of the differential equation
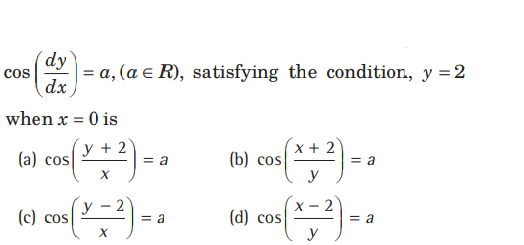
Answer
C
Question. The differential equation that represents all parabolas each of which has a latusrectum 4a and whose axes are parallel to x-axis, is

Answer
B
Question. The particular solution of the differential equation

Answer
C
Question. The equation of a curve passing through the point (0, 0) and whose differential equation is y’= ex sin x is
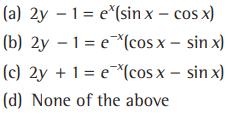
Answer
A
Question. The equation of the curve passing through the point
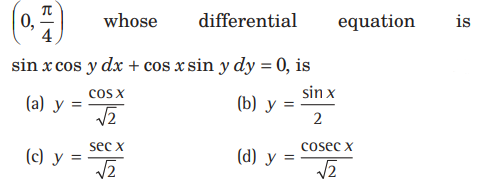
Answer
C
Question. The particular solution of the differential equation
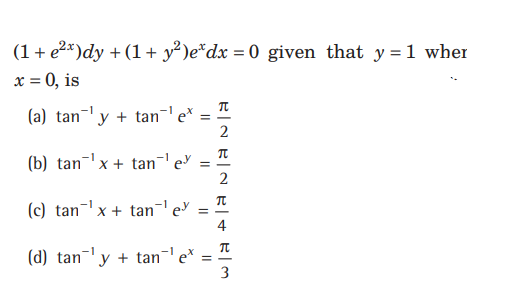
Answer
A
Question. Particular solution of the differential equation
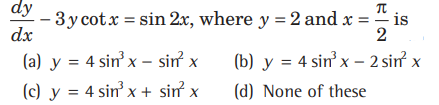
Answer
B
Question. Solution of the differential equation
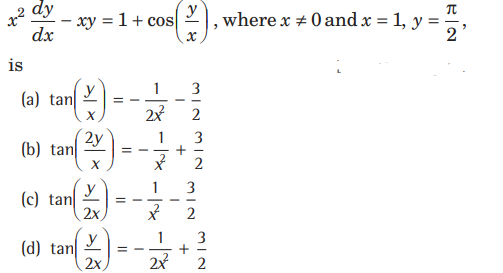
Answer
D
Question. If y(x) is a solution of (2+sin x /1+y)dy/dx=-cos x and y(0) =1,then the value of y(π/2) is
(a) 1/3
(b) 1/2
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer
A
Question. If y (t) is a solution of (1+t)dy/dt-ty=1 and y (0)=-1,then the value of y(1) is
(a) 1
(b) -1
(c) -1/2
(d) 0 C
Question.

Answer
D
Question.
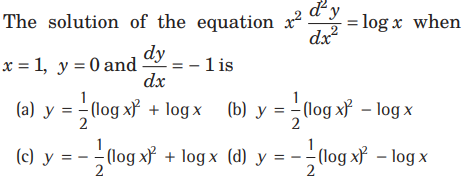
Answer
D
Question. A continuously differential function Φ (x) in (0,π) satisfying y’=1+y2,y(0)=0=y(π), is
(a) tan x
(b) x (x-π)
(c) (x-π)(1-ex)
(d) Not possible
Answer
D
Question. The differential equation d2y/dx2=2 represents
(a) a parabola whose axis is parallel to x-axis
(b) a parabola whose axis is parallel to y-axis
(c) a circle
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question.
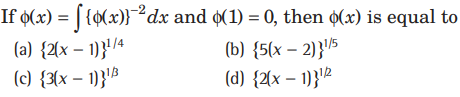
Answer
C
Question. The solution of dy/dx=x2+y2+1/2xy, satisfying y(1)=1,
is given by a
(a) hyperbola
(b) circle
(c) ellipse
(d) parabola
Answer
A
Question. The general solution of differential equation
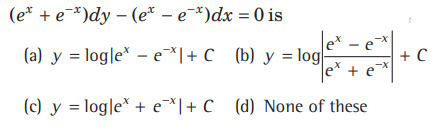
Answer
C
Question. Solution of the differential equation

Answer
A
Question. Solution of the differential equation

Answer
A
Question. Solution of the differential equation
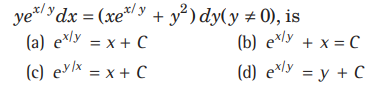
Answer
D
Question. If d2y/dx2 = 0,then:
(a) y = ax + b
b) y2 = ax + b
(c) y = log x
(d) y = ex + c
Answer
A
Question. The order of the differential equation, whose general solution is y= c1ex + c2e2x + c3e3x + c4ex+c3 , where c1,c2,c3, c4, c5 are arbitrary constants is:
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 2
Answer
C
Question. The degree of the differential equation satisfying √1− x2 + √1− y2 = a(x − y) is:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
A
Question. Family y = Ax + A3 of curve represented by the differential equation of degree:
(a) Three
(b) Two
(c) One
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The second order differential equation is:
(a) y′2 + x = y2
(b) y′y′′ + y = sin x
(c) y′′′ + y′′ + y = 0
(d) y′ = y
Answer
B
Question. The degree of differential equation d2y/dx2 +(dy/dx)3 + 6y =0 is:
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 5
Answer
A
Question. The solution of the differential equation xcos ydy = (xe logx + ex)dx is:
(a) sin y = 1/x ex + c
(b) sin y + ex logx + c = 0
(c) sin y = ex logx + c
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The solution of the differential equation dy/dx = sec x(sec x + tan x) is:
(a) y = sec x + tan x + c
(b) y = sec x + cot x + c
(c) y = sec x − tan x + c
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The degree and order of the differential equation of the family of all parabolas whose axis is x–axis, are respectively:
(a) 2, 1
(b) 1, 2
(c) 3, 2
(d) 2, 3
Answer
B
Question. The order and degree of the differential equation x(dy/dx)3 + 2(d2y/dx2)3 + 3y +x = 0 are respectively:
(a) 3, 2
(b) 2, 1
(c) 2, 2
(d) 2, 3
Answer
C
Question. The order of differential equations of all parabolas having directrix parallel to x-axis is:
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 2
Answer
A
Question. The differential equation for the line y = mx + c is: (where c is arbitrary constant)
(a) dy/dx = m
(b) dy/dx + m
(c) dy/dx = 0
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The differential equation found by the elimination of the arbitrary constant K from the equation y = (x+K)e−x is:
(a) dy/dx−y = e−x
(b) dy/dx−yex = 1
(c) dy/dx+ yex = 1
(d) dy/dx + y = e−x
Answer
D
Question. The elimination of the arbitrary constants A, B and C from y = A + Bx Ce−x leads to the differential equation:
(a) y′′′ − y′ = 0
(b) y′′′ − y′′ + y′ = 0
(c) y′′′ + y′′ = 0
(d) y′′ + y′′ − y′ = 0
Answer
C
Question. The solution of the differential equation dy/dx = (4x + y +1)2 is:
(a) 4x – y + 1 = 2 tan (2x – 2c)
(b) 4x – y – 1 = 2 tan (2x – 2c)
(c) 4x + y + 1 = 2 tan (2x + 2c)
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. The order and degree of the differential equation

(a) 1, 2
(b) 2,1
(c) 1, 1
(d) 2,2
Answer
A
Question. The order and degree of the differential equation
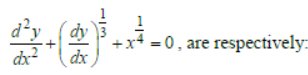
(a) 2,3
(b) 3,3
(c) 2,6
(d) 2,4
Answer
A
Question. The solution of the differential equation 3ex tan ydx + (1–ex )sec2ydy = 0 is:
(a) tan y = c(1−ex)3
(b) (1−ex)3 tan y = c
(c) tan y = c(1−ex)
(d) (1−ex) tan y = c
Answer
C
Question. The solution of the equation sin−1(dy/dx) = x+y is:
(a) tan(x + y) + sec(x + y) = x + c
(b) tan(x + y) − sec(x + y) = x + c
(c) tan(x + y) + sec(x + y) + x + c = 0
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Solution of y(2xy + ex )dx = exdy is:
(a) yx2 + ex = cy
(b) xy2 + ex = cx
(c) xy2 + e−x = c
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Solution of differential equation x dy − y dx = 0 represents:
(a) Rectangular hyperbola
(b) Straight line passing through origin
(c) Parabola whose vertex is at origin
(d) Circle whose centre is at origin
Answer
B
Question. A particle starts at the origin and moves along the x–axis in such a way that its velocity at the point (x, 0) is given by the formula dy/dx = cos2πx . Then the particle never reaches the point on:
(a) x = 1/4
(b) x = 3/4
(c) x = 1/2
(d) x = 1
Answer
C
Question. The general solution of the differential equation (x + y) dx + xdy = 0 is:
(a) x2 + y2 = c
(b) 2x2 − y2 = c
(c) x2 + 2xy = c
(d) y2 + 2xy = c
Answer
C
Question. The solution of ydx − xdy + xdy + 3x2y2ex3 dx = 0 is:
(a) x/y + ex3 = c
(b) x/y − ex3 = c
(c) −x/y + ex3 = c
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Solution of (xy cos xy + sin xy)dx + x2 cos xy dy = 0 is:
(a) xsin(xy) = k
(b) xy sin(xy) = k
(c) x/y sin(xy)
(d) x sin(xy)+ xy cos xy = k
Answer
A
Question. If c is any arbitrary constant, then the general solution of the differential equation ydx − xdy = xy dx is given by:
(a) y = cx e−x
(b) x = cye−x
(c) y + ex = cx
(d) yex = cx
Answer
D
Question. The equation of the curve which passes through the point (1, 1) and whose slope is given by 2y/x , is:
(a) y = x2
(b) x2 − y2 = 0
(c) 2x2 + 2y2 = 3
(d) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Equation of curve through point (1, 0)which satisfies the differential equation (1+ y2)dx − xydy = 0 , is:
(a) x2 + y2 = 0 =1
(b) x2 − y2 = 0 =1
(c) 2x2 + y2 = 0 = 2
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The general solution of the differential equation (x + y)dx + xdy = 0 is:
(a) x2 + y2 = c
(b) 2x2 – y2 = c
(c) x2 + 2xy = c
(d) y2 + 2xy = c
Answer
C
Question. The general solution of the differential equation (2x − y +1) dx + (2y − x +1)dy = 0 is:
(a) x2 + y2 + xy − x + y = c
(b) x2 + y2 − xy + x + y = c
(c) x2 + y2 + 2xy − x + y = c
(d) x2 + y2 − 2xy + x − y = c
Answer
B
Question. The differential equation y dy/dx + x = a (a is any constant) represents:
(a) A set of circles having centre on the y-axis
(b) A set of circles centre on the x-axis
(c) A set of ellipses
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The solution of the differential equation x d2y/dx2 = 1 given that y = 1 , dy/dx when x =1, is:
(a) y = x log x + x + 2
(b) y = x log x − x + 2
(c) y = x log x + x
(d) y = x log x − x
Answer
B