Please refer to the Consumer Rights Revision Notes given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 10th Consumer Rights book. We have provided chapter wise Notes for Class 10 Consumer Rights as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 5 Consumer Rights
Students of Class 10 Consumer Rights will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 10 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Consumer is a person who buys and uses a good or service from the market after making a payment.
Consumer International: An international umbrella organization to over 240 members Organizations from over 220 countries.
COPRA: The consumer Protection Act enacted by the government of India on 24th December 1986.
Codex Alimentarius Commission: It was created in 1963 by food and agricultural organization.
Right to information act 2005: This act gives rights to the citizen to have information about the government departments, their policies practices and procedures.
MRP: It is the maximum retail price printed on packages goods. The seller cannot charge more than this price.
ISI Mark: a certification mark for industrial products in India developed by the Bureau of Indian Standards.
AGMARK: A certification mark employed on agricultural products in India by the directorate of Marketing and Inspection
Hallmark: An official mark struck on items made of precious metals like gold silver platinum etc.
Adulteration: Mixing unwanted substances in foods.
Consumer Forum: The consumer movement in India has led to the formation of various organizations locally known as consumer forums or consumer protection councils. They guide consumers on how to file cases in the consumer court.
Short Answer type Questions
Question. Explain the three-tier quasi-judicial machinery to redress the grievances ofthe consumers?
Ans.
- District courts – The district level court deals with cases involving claims up to Rs.20 lakh.
- Redressal forums at State level – The state level court deals with cases between Rs. 20 lakh and Rs.1 crore
- Redressal forums at National level – The national level court dealt with cases which involve claims exceeding Rs.1crore.
Question. What are the different ways of exploitation of consumers in the market?
Ans.
- Higher price
- Quality lapse
- Underweight & under measurement
Question. What is the difference between consumer protection council and consumer court?
Ans.
- The consumer protection council promotes and protects the various rights of the consumer.
- The consumer court is made to hear the cases regarding a consumer complaint.
- Consumer protection council is an advisory body, while consumer court is a quasi judiciary body.
Question. How to make a complaint to the District forum.
Ans.
- District courts deals with cases involving claims up to 20 lakhs
- No need for lawyers
- Application can be made on plain paper
Question. What are the reasons for the emergence of consumer movement in India?
Ans.
- The dissatisfaction of the consumers regarding the market practices
- The gradual withdrawal of the government from production fields after the introduction of New Economic Policy.
- Increasing awareness of the people
Question. What are the certifications for Quality assurance?
Ans.
- lSI Mark
- AGMARK
- HALLMARK
Question. How to make a com plaint to the District forum.
Ans.
- District courts deals with cases involving claims up to 20 lakhs
- No need for lawyers
- Application can be made on plain paper.
Long Answer type Questions
Question. Critically examine the progress of consumer movement in India?
Ans.
- Started out of frustration of consumers against the unfair practices by the sellers
- Food shortages
- Black-marketing
- Formation of consumers group and exerting pressure on business firms and governments to correct the business activities.
- Passing of the Consumer Protection Act in 1986
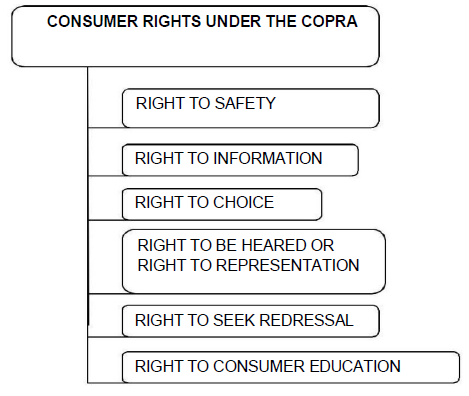
Question. What are the rights of the consumers?
Ans.
- Right to be informed
- Right to choose
- Right to safety
- Right to seek redressal
- Right to represent
- Right to consumer education
Question. What are the reasons for exploitation of consumers?
Ans.
- Lack of awareness
- Lack of information about goods & markets
- Limited supplies and competitions.
- Lack of government support to consumers
- Lack of interest on the part of the consumers in responding
- Inadequacy of consumer movement
Question. What is the need for standardization of products?
Ans.
- Every producer is liable to be prosecuted if he does not print the sale price of an article on it
- For certain articles lSI mark is essential to ensure quality and originality.
- As far as food items are concerned it is essential to indicate weight on each packet Date of manufacture and date of expiry is a must on medicines
- Government departments like Food and Supply, Drug Control, Weight and Measure etc conduct raids from time to time so that consumers are not cheated.
Question. What are the salient features of COPRA 1986?
Ans.
- It applies to all goods and services.
- It covers all the sections whether Private, Public or Cooperative.
- It offers various rights to the consumers.
- It establishes consumer protection councils at the central and state and district levels to promote and protect the right ofthe consumers.
- It provides separate three- tier quasi-judicial machinery at the national state and district levels. at the national level if is known as National Consumer Court (Commission) at the state level, it is known as State consumer court (commission)and at the District level ,it is called District forum.
- Provisions of the Act are compensatory in nature
Question. What factors gave birth to consumer movement in India.
Ans.
- The dissatisfaction of the consumers regarding the market practices
- The gradual withdrawal of the government from production fields after the introduction of New Economic Policy.
- Increasing awareness ofthe people
- Increasing unfair trade practices
- Emergences of foreign companies
Question. What are the duties of the Consumer?
Ans.
- Be alert about the price and quality of goods and setvices.
- To assert and act to ensure that he gets a fair deal.
- To organize together to promote the interest of the consumers.
- To purchase quality marked goods such as lSI, AGMARK etc.
- To insist a cash memo after every purchase.
- To make complaints for genuine grievances
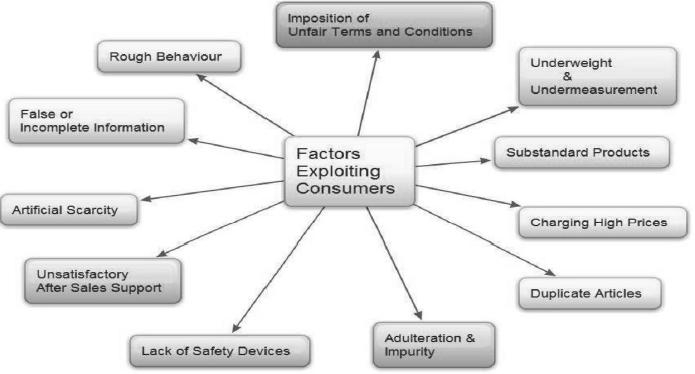
Question. What are the ways by which consumers get exploited in the market?
Ans.
- Higher price
- Quality lapse
- Underweight & under measurement
- False information and promises
- Poor after sale service
- Rude behaviour
- Inadequate safety measures
- Market malpractices such as adulteration black marketing, duplicate articles etc.



