Please see Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Exam Questions Class 11 Biology below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 11 Biology Exam Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 11 Biology. These solved problems for The Living World in Class 11 Biology will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Class 11 Biology
Objective Type Questions
Question. Which one is correct about intercalary meristem?
(a) It occurs between mature tissues
(b) It occurs in grasses and regenerate parts removed by grazing herbivores
(c) It is a primary meristem
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. Secondary tissues are produced by all except
(a) Fascicular cambium
(b) Interfascicularcambium
(c) Apical meristem
(d) Phellogen
Answer
C
Question. Primary tissues of a plant
(a) Add to the length of roots and shoots
(b) Add to the diameter of existing roots and shoots
(c) Are found only in the embryo
(d) Are found only in the seedling
Answer
A
Question. Cells of permanent tissue are specialised
(a) Functionally
(b) Only structurally
(c) Both structurally and functionally
(d) For mitosis
Answer
C
Question. Grass stem elongates after initial growth due to
(a) Lateral meristem
(b) Secondary meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) Apical meristem
Answer
C
Question. Root apex is sub terminal because it is
(a) Covered with root hair
(b) Covered with root cap
(c) Covered with epidermis
(d) Under the soil
Answer
B
Question. Which one is secondary lateral meristem?
(a) Intercalary
(b) Cork cambium
(c) Interfascicularcambium
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. The following characters are attributed to
A.Cell wall-thin, cellulosic
B.Shape of cells-generally isodiametric
C.Intercellular space -present/absent
D.Photosynthetic, storage, or secretoryin functions
Options :
(a) Collenchyma
(b) Parenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Vascular tissue
Answer
B
Question. Root hairs are present in
(a) Zone of cell division
(b) Zone of cell elongation
(c) Zone of maturation
(d) Root cap
Answer
C
Question. Fibres and sclereids are the types of
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Xylem
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statement is incorrect about sclreids?
(a) Variously shaped
(b) Highly thickened + lignified cell wall and lumen is narrow
(c) Commonly found in fruit wall of nuts, seed coat of legumes and leaves
(d) They are type of parenchyma
Answer
D
Question. Xylem in angiosperms consists of how many types of elements
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer
A
Question. In each vascular bundle, the tissue nearest to the centre of stem is
(a) Phloem
(b) Fibres
(c) Vascular cambium
(d) Xylem
Answer
D
Question. Unlike tracheids, vessel elements
(a) Function when dead
(b) Are spindle shaped
(c) Are found primarily in angiosperm
(d) Lose part or all of end walls
Answer
C
Question. Tracheids and vessel elements
(a) Die before they become functional
(b) Are important constituents of all plants
(c) Are found in the secondary plant body
(d) Are without lignified cell wall
Answer
A
Question. Xylem parenchyma stores
(a) Starch
(b) Fat
(c) Tannins
(d) all
Answer
D
Question. The living and non-lignified components of vascular bundle is/are
(a) Vessels and tracheid
(b) Vessels and phloem
(c) Wood fibreand phloem
(d) Wood parenchyma and sieve tube
Answer
D
Question. Heterogenous tissues are
(a) Vascular and cork cambium
(b) Xylem and phloem elements
(c) Dermal layer and ground tissue
(d) Parenchyma and sclerenchyma
Answer
B
Question. Sieve tube is
(a) Multicellular, vessel like structure
(b) Provided with porous septa
(c) The main conducting element for translocation of food
(d) All of above
Answer
D
Question. Albuminous cell of gymnosperm are equivalent to
(a) Sieve tubes
(b) Sieve cells
(c) Companion cells
(d) Cork cambium
Answer
C
Question. Sieve tubes are best suited for translocation of solutes because
(a) They are much broader than long
(b) They posses no end wall
(c) They have higher number of pits
(d) They posses interconnected lumen
Answer
A
Question. Which of the bastfibres is of great commercial value?
(a) Jute
(b) Flax
(c) Hemp
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. The primary function of epidermis is
(a) Protection
(b) Photosynthesis
(c) Conduction of water and solute
(d) Mechanical support
Answer
A
Question. Excessive loss of water is prevented by
(a) Epidermis
(b) Endodermis
(c) Cortex
(d) Xylem
Answer
A
Question. Stomata develop from
(a) Dermal tissue
(b) Ground tissue
(c) Accessory tissue
(d) Vascular tissue
Answer
A
Question. Ground tissue includes
(a) cortex + pericycle
(b) pith
(c) medullaryray
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. Pit field allow plasmodesmatato travel through
(a) The primary cell wall
(b) The secondary cell wall
(c) Both primary and secondary cell wall
(d) Neither primary nor secondary cell wall
Answer
C
Question. In the development of a root, the protoderm give rise to the
(a) Cortex
(b) Root hair
(c) Endodermis
(d) Pith
Answer
B
Question. Which one is not a part of stele
(a) Pericycle
(b) Pith
(c) Vascular bundle
(d) Cortex
Answer
D
Question. The innermost layer or last layer of cortex is called
(a) Pericycle
(b) Conjuctivetissue
(c) Endodermis
(d) Exodermis
Answer
C
Question. Monocot root differs from dicotroot in having
(a) Polyarchxylem bundles
(b) Large and well developed pith
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Radial vascular bundle and exarchxylem
Answer
C
Question. In dorsiventralleaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem respectively is
(a) Adaxialand abaxial
(b) Abaxialand adaxial
(c) Adaxialand adaxial
(d) Abaxialand abaxial
Answer
A
Question. Which one is correct?
(a) In dorsiventralleaf, stomata is on lower surface
(b) Protoxylemdisintegrates to produce lacuna in monocot stem
(c) Reticulate venation in dicotleaf, parallel venation in monocot leaf
(d) All
Answer
D
Question. In dicotstem lateral branch comes out from
(a) Pericycle
(b) Cortex
(c) Pith
(d) Epidermis
Answer
B
Critical Thinking Type Questions
Question. Trees at sea do not have annual rings because
(a) soil is sandy.
(b) there is climatic variation.
(c) there is no marked climatic variation.
(d) there is enough moisture in the atmosphere.
Answer
C
Question. When we peel the skin of a potato tuber, we remove
(a) periderm
(b) epidermis
(c) cuticle
(d) leaves
Answer
A
Question. The length of different internodes in a culm of sugarcane is variable because of
(a) size of leaf lamina at the node below each internode
(b) intercalary meristem
(c) shoot apical meristem
(d) position of axillary buds
Answer
B
Question. The trees growing in desert will
(a) show alternate rings of xylem and sclerenchyma.
(b) have only conjunctive tissue and phloem is formed by the activity of cambium.
(c) show distinct annual rings.
(d) not show distinct annual rings.
Answer
D
Question. Apical and intercalary meristems are primary meristems because
(a) they occur in the mature region of roots and shoots of many plants.
(b) they made up of different kinds of tissues.
(c) they involved in secondary growth.
(d) they appear early in life of a plant and contribute to the formation of the primary plant body.
Answer
D
Question. A piece of wood having no vessels (trachea) must be belonged to
(a) teak
(b) mango
(c) pine
(d) palm
Answer
C
Question. Cambium is considered as a lateral meristem because
(a) it gives rise to lateral branches.
(b) it causes increase in girth.
(c) it increases height and diameter of a plant.
(d) it adds bulk to a plant.
Answer
B
Question. The vessel elements of angiosperms differ from other elements of xylem in having
(a) simple pits on their radial walls.
(b) bordered pits on their lateral walls.
(c) simple and bordered pits on their end walls.
(d) simple perforation on their end walls.
Answer
D
Question. Tissues are classified into two main groups, namely meristematic and permanent tissues on the basis of
(a) whether the cells being able to divide or not.
(b) position of the cells.
(c) whether they are living or dead.
(d) none of the above
Answer
A
Question. Gymnosperms are also called soft wood spermatophytes because they lack
(a) cambium
(b) phloem fibres
(c) thick-walled tracheids
(d) xylem fibres
Answer
D
Question. In an experiment, a student cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant which he has taken from his school garden. After observing it under the microscope how would he ascertain whether it is a monocot stem or a dicot stem?
(a) With the help of bulliform cells.
(b) With the help of casparian strips.
(c) With the help of vascular bundles.
(d) With the help of stomatal apparatus.
Answer
C
Diagram Type Questions
Question. The given figure shows apical meristem of root apex with few part marked as A, B and C. Identify the correct labelling of A, B and C.

(a) A – Vascular structure, B – Protoderm, C – Root cap
(b) A – Cortex, B – Endodermis, C – Root cap
(c) A – Cortex, B – Protoderm, C – Root cap
(d) A – Tunica, B – Protoderm, C – Root cap
Answer
C
Question. Identify the types of simple tissue indicated by A, B, C and D and their function.
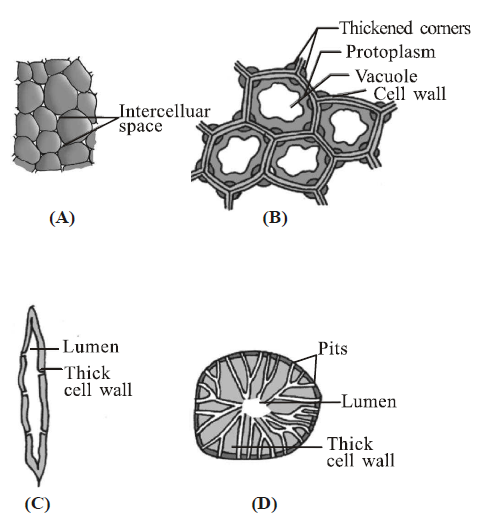
(a) A – Parenchyma, Photosynthesis, Storage and Secretion.
(b) B – Sclerenchyma Scleriods; Transport food material
(c) C – Collenchyma; Provides mechanical support to organs.
(d) D – Sclerenchyma Fibres; Provide Mechanical support to the growing parts of the plant such as young stem and petiole of a leaf.
Answer
A
Question. In the given figure of phloem tissue, identify the marked part (A, B and C) which help in maintaining the pressure gradient in the sieve tubes.
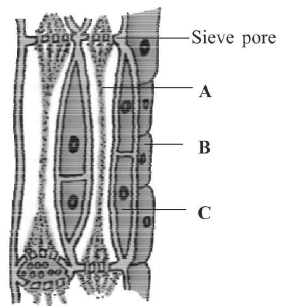
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Identify types of vascular bundles in given figures A, B and C.
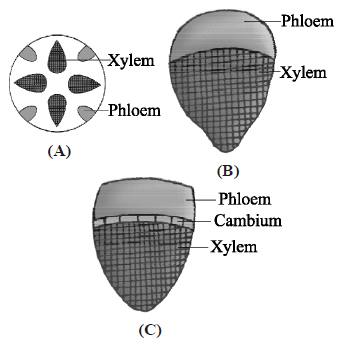
| A | B | C | |
| (a) | Radial; | Conjoint closed; | Conjoint open |
| (b) | Conjoint closed; | Conjoint open; | Radial |
| (c) | Conjoint open; | Conjoint closed; | Radial |
| (d) | Bicollateral; | Concentric; | Radial |
Answer
A
Question. The given figure shows the T.S of dicot root. Some parts are marked as A, B, C, D, E, & F. Choose the option which shows the correct labelling of marked part.
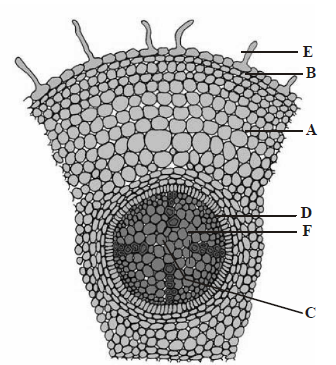
(a) A – Epiblema, B – Root hair, C – Cortex, D – Endodermis, E – Pith, F – Pericycle
(b) A – Cortex, B – Pith, C – Epiblema, D – Endodermis, E – Root hair, F – Pericycle
(c) A – Epiblema, B – Endodermis, C – Cortex, D – Root hair, E – Pith, F – Pericycle
(d) A – Cortex, B – Epiblema, C – Pith, D – Endodermis, E – Root hair, F – Pericycle
Answer
D
Question. The given figure shows T.S. of monocot stem. Identify the correct labelling of A to F marked in the given figure.

(a) A – Epidermis, B – Hypodermis, C – Vascular bundles, D – Phloem, E – Xylem, F – Ground tissue
(b) A – Cuticle, B – Epidermis, C – Sclerenchymatous sheath, D – Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, E – Parenchymatous sheath, F – Phloem
(c) A – Cuticle, B – Epidermis, C – Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, D – Sclerenchymatous sheath, E – Parenchymatous sheath, F – Phloem
(d) A – Cuticle, B – Epidermis, C – Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, D – Sclerenchymatous sheath, E – Parenchymatous sheath, F – Protoxylem
Answer
A
Question. T.S. of monocot leaf is given below, certain parts have been marked by alphabets (A – G). Which one is the option showing there correct labelling?
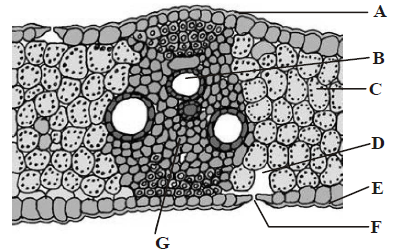
(a) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Xylem, C – Mesophyll, D – Sub-stomatal cavity, E – Abaxial epidermis, F – Stoma, G – Phloem
(b) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Abaxial epidermis, C – Xylem, D – Sub-stomatal cavity, E – Stoma, F – Mesophyll, G – Phloem
(c) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Phloem, C – Mesophyll, D – Sub-stomatal cavity, E – Abaxial epidermis, F – Xylem, G – Stoma
(d) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Xylem, C – Stoma, D – Sub-stomatal cavity, E – Abaxial epidermis, F – Phloem, G – Mesophyll
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the followings option shows the correct labelling of the parts marked as A, B, C and D in the given figure of a lenticel?

(a) A – Epidermis, B – Secondary cortex, C – Cork cambium, D – Cork
(b) A – Pore, B – Cork cambium, C – Secondary cortex, D – Cork
(c) A – Pore, B – Cork, C – Complimentary cells, D – Cork cambium
(d) A – Epidermis, B – Complimentary cells, C – Cork cambium, D – Secondary cortex
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following figure is a type of permanent tissue having many different types of cell?
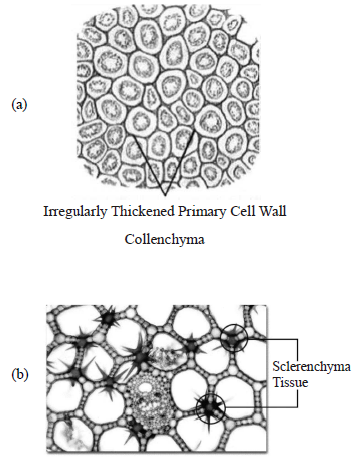

Answer
C