Please refer to Electrochemistry HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with solutions. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Electrochemistry Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Question. In a Daniell cell,
(a) the chemical energy liberated during the redox reaction is converted to electrical energy
(b) the electrical energy of the cell is converted to chemical energy
(c) the energy of the cell is utilised in conduction of the redox reaction
(d) the potential energy of the cell is converted into electrical energy.
Answer
A
Question.Limiting molar conductivity of NaBr is
(a) Λ°m NaBr = Λ°mNaCl + Λ°mKBr
(b) Λ°m NaBr = Λ°mNaCl + Λ°mKBr –Λ°mKCl
(c) Λ°m NaBr = Λ°mNaOH + Λ°mNaBr – Λ°mNaCl
(d) Λ°m NaBr = Λ°mNaCl – Λ°mNaBr
Answer
B
Question. Electrode potential for Mg electrode varies according to the equation,
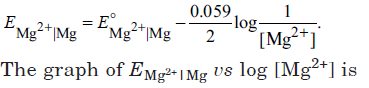
Answer
B
Question. For the cell reaction :
2Cu+(aq) → Cu(s) + Cu2+(aq), the standard cell potential is 0.36 V. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is
(a) 1.2 × 106
(b) 7.4 × 1012
(c) 2.4 × 106
(d) 5.5 × 108
Answer
A
Question. What will be the molar conductivity of Al3+ ions at infinite dilution if molar conductivity of Al2(SO4)3 is 858 S cm2 mol–1 and ionic conductance of SO42– is 160 S cm2 mol–1 at infinite dilution?
(a) 189 S cm2 mol–1
(b) 698 S cm2 mol–1
(c) 1018 S cm2 mol–1
(d) 429 S cm2 mol–1
Answer
A
Question. Molar conductivity of 0.025 mol L–1 methanoic acid is 46.1 S cm2 mol–1, the degree of dissociation and dissociation constant will be (Given : l°H+ = 349.6 S cm2 mol–1 and λ°HCOO– = 54.6 S cm2 mol–1)
(a) 11.4%, 3.67 × 10–4 mol L–1
(b) 22.8%, 1.83 × 10–4 mol L–1
(c) 52.2%, 4.25 × 10–4 mol L–1
(d) 1.14%, 3.67 × 10–6 mol L–1
Answer
A
Question. Limiting molar conductivity for some ions is given below (in S cm2 mol–1) :
Na+ – 50.1, Cl– – 76. 3, H+ – 349.6, CH3COO– – 40.9,Ca2+ – 119.0.
What will be the limiting molar conductivities (Λ°m) of CaCl2, CH3COONa and NaCl respectively?
(a) 97.65, 111.0 and 242.8 S cm2 mol–1
(b) 195.3, 182.0 and 26.2 S cm2 mol–1
(c) 271.6, 91.0 and 126.4 S cm2 mol–1
(d) 119.0, 1024.5 and 9.2 S cm2 mol–1
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is the correct order in which metals displace each other from the salt solution of their salts.
(a) Zn, Al, Mg, Fe, Cu
(b) Cu, Fe, Mg, Al, Zn
(c) Mg, Al, Zn, Fe, Cu
(d) Al, Mg, Fe, Cu, Zn
Answer
C
Question. A galvanic cell has electrical potential of 1.1 V. If an opposing potential of 1.1 V is applied to this cell, what will happen to the cell reaction and current flowing through the cell?
(a) The reaction stops and no current flows through the cell.
(b) The reaction continuous but current flows in opposite direction.
(c) The concentration of reactants becomes unity and current flows from cathode to anode.
(d) The cell does not function as a galvanic cell and zinc is deposited on zinc plate.
Answer
A
Question. Molar conductivity of 0.15 M solution of KCl at 298 K, if its conductivity is 0.0152 S cm–1 will be
(a) 124 Ω–1 cm2 mol–1
(b) 204 Ω– cm2 mol–1
(c) 101 Ω– cm2 mol–1
(d) 300 Ω– cm2 mol–1
Answer
C
Question. A cell is set up as shown in the figure. It is observed that EMF of the cell comes out to be 2.36 V. Which of the given statements is not correct about the cell?
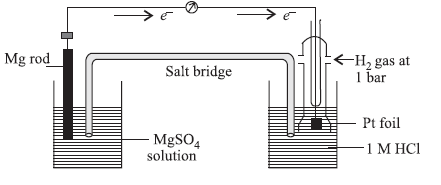
(a) Reduction takes place at magnesium electrode and oxidation at SHE.
(b) Oxidation takes place at magnesium electrode and reduction at SHE.
(c) Standard electrode potential for Mg2+ | Mg will be –2.36 V.
(d) Electrons flow from magnesium electrode to hydrogen electrode.
Answer
A
Question. Mark the correct choice of electrolytes represented in the graph.
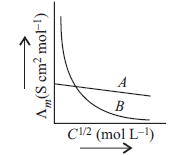
(a) A → NH4OH, B → NaCl
(b) A → NH4OH, B → NH4Cl
(c) A → CH3COOH, B → CH3COONa
(d) A → KCl, B → NH4OH
Answer
D
Question. Electrode potential data of few cells is given below. Based on the data, arrange the ions in increasing order of their reducing power.
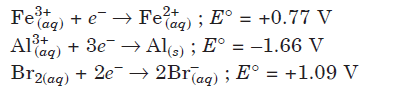
(a) Br– < Fe2+ < Al
(b) Fe2+ < Al < Br–
(c) Al < Br– < Fe2+
(d) Al < Fe2+ < Br–
Answer
A
Question. Fluorine is the best oxidising agent because it has
(a) highest electron affinity
(b) highest reduction potential
(c) highest oxidation potential
(d) lowest electron affinity.
Answer
B
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Reduction potentials of 4 metals A, B, C and D are – 1.66 V, + 0.34 V, + 0.80 V and – 0.76 V. What is the order of their reducing power and reactivity ?
Answer. A > D > B > C
Question. Why does a dry cell become dead even if it has not been used for a long time ?
Answer. NH4Cl is acidic in nature. It corrodes zinc container.
Question. Why Na cannot be obtained by the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl solution ?
Answer. Due to low reduction potential, Na+ ions are not reduced at cathode. Instead, H+ are reduced and H2 is obtained.
Question. What is the use of platinum foil in the hydrogen electrode ?
Answer. It is used for the in and out flow of electrons.
Question. Why Λmº for CH3COOH cannot be determined experimentally ?
Answer. Molar conductivity of weak electrolytes keeps on increasing with dilution and does not become constant even at very large dilution.
Question. Why is it necessary to use a salt bridge in a galvanic cell ?
Answer. To complete the inner circuit and to maintain electrical neutrality of the electrolytic solutions of the half cells.
Question. Why does mercury cell gives a constant voltage throughout its life ?
Answer. This is because the overall cell reaction does not have any ionic concentration in it.
Question. What is the role of ZnCl2 in a dry cell ?
Answer. ZnCl2 combines with the NH3 produced to form a complex salt [Zn(NH3)2]Cl2.
Question. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution ?
Answer. Conductivity of a solution is dependent on the number of ions per unit volume.
On dilution, the number of ions per unit volume decreases, hence the conductivity decreases.
Question. Suggest two materials other than hydrogen that can be used as fuels in fuel cells.
Answer. Methane and methanol.
Question. How does the pH of Al-NaCl solution be affected when it is electrolysed ?
Answer. When Al-NaCl solution is electrolysed, H2 is liberated at cathode, Cl2 at anode and NaOH is formed in the solution. Hence pH of solution increases.
Question. Which reference electrode is used to measure the electrode potential of other electrodes.
Answer. SHE, whose electrode potential is taken as zero.
Question. Out of zinc and tin, which one protects iron better even after cracks and why ?
Answer. Zinc protects better because oxidation of zinc is greater but that of tin is less than that of iron.
Question. Define corrosion. What is the chemical formula of rust ?
Answer. Corrosion is the slow eating away of the surface of the metal due to attack of atmospheric gases. Fe2O3.xH2O.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Define conductivity and molar conductivity for a solution of an electrolyte.
Answer. Conductivity is defined as ease with which current flows through electrolyte. It is reciprocal of specific resistance. Molar conductivity is conductance of all the ions produced by one mole of electrolyte when electrodes are at unit distance apart and have sufficient area of cross-section to hold electrolyte.
Question. The resistance of conductivity cell containing 0.001M KCl solution at 298K is 1500Ω. What is the cell constant if the conductivity of 0.001M KCl solution at 298K is 0.146 × 10–3 S cm–1.
Answer. Cell constant = Conductivity × Resistance
= 0.146 × 10–3 S cm–1 × 1500Ω = 0.219 cm–1
Question. Indicate the reactions which take place at cathode and anode in fuel cell.
Answer. At cathode : O2 (g) + 2H2O + 4e− → 4OH− (aq)
At anode : 2H2 (g) + 4OH− (aq) → 4H2O + 4e–
The overall reaction is : 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
Question. Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the following :
(a) An aqueous solution of AgNO3 with platinum electrodes.
(b) An aqueous solution of CuCl2 with Pt electrodes.
Answer. (a) At anode (Oxidation)
4OH− − 4e− → 2H2O + O2
At cathode (Reduction)
Ag+ + e− → Ag (s)
(b) At anode (Oxidation)
Cl− − e− → Cl (g)
Cl + Cl → Cl2
At cathode (Reduction)
Cu2+ + 2e− → Cu (s)