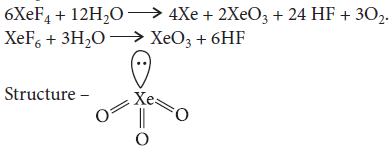Please see Chapter 7 The p – Block Elements Exam Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry. These solved problems for The p – Block Elements in Class 12 Chemistry will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Chapter 7 The p – Block Elements Class 12 Chemistry
Very Short Answer Questions :
Question. Give reason :
Bond dissociation energy of F2 is less than that of Cl2.
Answer : F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than Cl2 because F atom is very small and hence the electron-electron repulsions between the lone pairs of electrons are very large.
Question. Account for the following :
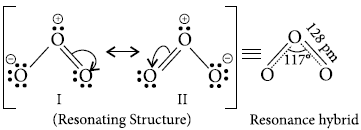
The two O—O bond lengths in the ozone molecule are equal.
Answer : The two O — O bond lengths in the ozone molecule are equal as it is a resonance hybrid of two main forms :

Question. Write the formula and describe the structure of noble gas species which is isostructural with BrO–3
Answer : The central atom Br has seven electrons. Four of these electrons form two double bonds or coordinate bonds with two oxygen atoms while the fifth electron forms a single bond with O– ion. The remaining two electrons form one lone pair. Hence, in all there are three bond pairs and one lone pair around Br atom in BrO–3. therefore, according to VSEPR theory, BrO–3 should be pyramidal.
Here, BrO–3 has 26(7 + 3 × 6 + 1 = 26) valence electrons. A noble gas species having 26 valence electrons is XeO3(8 + 3 × 6 = 26). Thus, like BrO–3, XeO3 is also pyramidal.
Question. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of Cl2 with hot and conc.
NaOH solution. Justify that this reaction is a disproportionation reaction.
Answer : 3Cl2 + 6NaOH → 5NaCl + NaClO3 + 3H2O
This reaction is a disproportionation reaction as chlorine from zero oxidation state is changed to – 1 and + 5 oxidation states.
Question. Account for the following :
Concentrated sulphuric acid has charring ction on carbohydrates.
Answer : Concentrated H2SO4 removes water from organic compounds hence, it has charring action on carbohydrates.
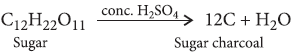
Question. Answer the following :
Which neutral molecule would be isoelectronic with ClO–?
Answer : ClO– has 17 + 8 + 1 = 26 electrons.
A neutral molecule with 26 electrons is OF2 (8 + 2 × 9) = 18 + 8 = 26 electrons.
Question. Why is Ka2 << Ka1 for H2SO4 in water?
Answer : H2SO4(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + HSO–4(aq) Ka1 > 10, very large
HSO–4(aq) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + SO2–4(aq) Ka2 = 1.2 × 10–2
Ka2 is smaller than Ka1 because dissociation of HSO4– is less probable due to presence of negative charge on the ion.
Question. Why are halogens coloured?
Answer : Halogens absorb radiations in visible region which results in excitation of outer electrons to higher level resulting in different colours.
Question. Complete the following equation :
SO3 + H2SO4 →
Answer : SO3 + H2SO4 → H2S2O7
Question. Predict the shape and the asked angle (90° or more or less) in each of the following cases. ClF3 and the angle F—Cl—F
Answer : Hybridisation – sp3d
Structure – Trigonal bipyramidal
Shape – Bent (T-shaped)
Angle F–Cl–F : less than 90°

Question. Complete the following reaction equation :
NaOH (cold & dilute) + Cl2 →
Answer : 2NaOH (dil.) + Cl2(aq) → NaCl(aq) + NaClO(aq.) + H2O(l)
Question. With the help of chemical equation explain the principle of Contact process in brief for the manufacture of sulphuric acid by Contact process.
Answer : (a) Contact process : It involves three stages :
(i) Burning of sulphur or sulphide ore in air to generate SO2.

Question. How would you account for the following?
Halogens are strong oxidizing agents
Answer : General electronic configuration of halogens is ns2np5. They easily accept one electron to complete their octet. This makes them a good oxidising agent.
Question. Describe the conditions and the steps involved in the manufacture of sulphuric acid by Contact process. Write the necessary reactions. (No diagram is required.)
Answer : (a) Contact process : It involves three stages :
(i) Burning of sulphur or sulphide ore in air to generate SO2.

Question. Account for the following :
Chlorine water loses its yellow colour on standing.
Answer : Chlorine water on standing loses its yellow colour due to the formation of HCl and HClO.
Question. Explain the following situations :
SF4 is easily hydrolysed whereas SF6 is not easily hydrolysed.
Answer : In SF6, six F atoms protect the sulphur atom from attack by the reagent to such an extent that even thermodynamically most favourable reactions like hydrolysis do not occur. But in SF4, S is not sterically protected as it is surrounded by only four F atoms hence, SF4 is reactive.
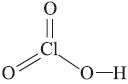
Question. Write the structure of the following species :
H2SO5.
Answer :

Question. What happens when
Sulphur dioxide gas is passed through an aqueous solution of a Fe (III) salt?
Answer : 2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO42– + 4H+
Question. Account for the following :
Acidic character increases from HF to HI.
Answer : The acidic strength of the hydrohalic acids in the order :
HF < HCl < HBr < HI
This order is a result of bond dissociation enthalpies of H — X bond decreases from H — F to H — I as the size of halogen atom increases
Question. Excess of SO2 reacts with sodium hydroxide solution.
Answer : 2NaOH + SO2 → Na2SO3 + H2O
Question. Describe the Contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid with special reference to the reaction conditions, catalysts used and yield in the process.
Answer : In Contact process, the rate determining step is 2SO2 + O2 →V2O5 2SO3, ΔfH° = –196.6 kJ mol–1 This reaction is reversible and exothermic i.e., ΔH is negative. Thus, according to Le-Chatelier’s principle, the conditions to maximise the yield are as follows :
(a) At lower temperature : As heat is evolved in the reaction so, at lower temperature the reaction proceeds more in forward direction.
(b) At higher pressure : As three moles of gaseous reactants give two moles of gaseous products thus, at higher pressure reaction moves in forward direction.
(a) Contact process : It involves three stages :
(i) Burning of sulphur or sulphide ore in air to generate SO2.

Question. Draw the structure of the following : HClO3
Answer :
Question. Answer the following :
Why are halogens strong oxidising agents?
Answer : General electronic configuration of halogens is ns2np5. They easily accept one electron to complete their octet. This makes them a good oxidising agent.
Question. Ozone is thermodynamically unstable?
Answer : Ozone is thermodynamically unstable and decomposes into oxygen.
2O3 →Δ 3O2; ΔH = –ve
The above conversion is exothermic i.e., ΔH is negative. Also, entropy increases i.e., ΔS = + ve.
Thus, ΔG for the decomposition of ozone is negative. Hence, it is thermodynamically unstable.
Question. Account for the following :
Fluorine does not form oxoacids.
Answer : Fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF. Because for the formation of other oxoacids d orbitals are required for the multiple pπ – dπ bonding between extra oxygen atoms and fluorine.
High electronegativity and small size of fluorine also favours only the formation of one oxoacid.
Question. With the help of chemical equations explain the principle of contact process in brief for the manufacture of sulphuric acid. (No diagram).
Answer : (a) Contact process : It involves three stages :
(i) Burning of sulphur or sulphide ore in air to generate SO2.

Question. What happens when :
SO2 gas is passed through an aqueous solution Fe3+ salt?
Answer : 2Fe3+ + SO2 + 2H2O → 2Fe2+ + SO42– + 4H+
Question. How would you account for the following :
The oxidising power of oxoacids of chlorine follows the order :
HClO4 < HClO3 < HClO2 < HClO
Answer : As the stability of the oxoanion increases, its tendency to decompose to give O2 decreases and hence its oxidising power decreases. Since the stability of the oxoanion decreases in the order :
ClO4– > ClO3– > ClO2– > ClO– therefore oxidising power of their oxoacids increases in the reverse order :
HClO4 < HClO3 < HClO2 < HClO.
Question. How the supersonic jet aeroplanes are responsible for the depletion of ozone layers?
Answer : Nitrogen oxide emitted from the exhausts of supersonic jet aeroplanes readily combines with ozone to form nitrogen dioxide and diatomic oxygen. Since supersonic jets fly in the stratosphere near the ozone layer, they are responsible for the depletion of ozone layer.
Question. Account for the following
HClO4 is stronger acid than HClO.
Answer : As the number of oxygen bonded to the central atom increases, the oxidation number of the oxidation atom increases causing a weakening of the O—H bond strength and an increase in the acidity. Hence, HClO4 is stronger acid than HClO.
Question. HF is a weaker acid than HCl. Why?
Answer : HF is the weakest acid because of its high bond dissociation energy due to small size of fluorine atom.
Question. Account for the following :
HF is not stored in glass bottles but is kept in wax-coated bottles.
Answer : HF acid attacks glass with the formation of fluoro silicate ions. Thus it is stored in wax-coated glass bottles to prevent the reaction.
Question. Explain the following observations.
Despite lower value of its electron gain enthalpy with negative sign, fluorine (F2) is a stronger oxidising agent than Cl2.
Answer : Fluorine is the strongest oxidising agent as it accept electron easily. It oxidise other halide ions in solution or even in solid phase.
F2 + 2X– → 2F– + X2 (X = Cl, Br or I)
Cl2 + 2X– → 2Cl– + X2 (X = Br or I)
Br2 + 2I– → 2Br– + I2
Question. Account for the following :
O3 acts as a powerful oxidising agent.
Answer : Ozone is a powerful oxidising agent because ozone has higher energy content than dioxygen hence, decomposes to give dioxygen and atomic oxygen.
O3(g) → O2(g) + O(g)
Ozone Dioxygen Atomic oxygen
The atomic oxygen thus liberated brings about the oxidation while molecular oxygen is set free.
Question. Fluorine exhibits only –1 oxidation state whereas other halogens exhibit +1, +3, +5 and +7 oxidation state also. Why is it so?
Answer : This is due to non-availability of d-orbitals in valence shell of fluorine.
Question. F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than Cl2. Why?
Answer : F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than Cl2 because F atom is very small and hence the electron-electron repulsions between the lone pairs of electrons are very large.
Question. Explain giving reason for the following situation.
In aqueous medium HCl is stronger acid than HF.
Answer : In aqueous medium HCl is stronger acid than HF because bond dissociation enthalpy of H—Cl is lower than that of HF
Question. Assign reasons for the following :
The negative value of electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less than that of chlorine.
Answer : The electron gain enthalpy of fluorine is less negative than that of chlorine due to the small size of fluorine atom.
Question. Give reasons for the following :
OF6 compound is not known.
Answer : OF6 compound is not known because oxygen cannot expand its octet due to unavailability of d-orbital.
Question. Arrange HClO3, HClO2, HOCl and HClO4 in order of increasing acid strength. Give reason for your answer.
Answer : Acid strength of oxoacids of the same halogen increases with increase in oxidation number of the halogen.
Thus the increasing order of acid strength is
HOCl < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4
+1 +3 +5 +7
Question. Fluorine exhibits only – 1 oxidation state in its compounds whereas other halogens exhibit many other oxidation states. Why?
Answer : This is due to non-availability of d-orbitals in valence shell of fluorine.
Question. Compare the oxidizing action of F2 and Cl2 by considering parameters such as bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy.
Answer : Oxidising power of a substance depends on the factors like bond dissociation enthalpy, electron gain enthalpy and hydration enthalpy. Due to small ize of fluorine, its electron gain enthalpy is less than that of chlorine. However, its low bond dissociation enthalpy and high hydration enthalpy compensate the low electron gain enthalpy. Fluorine because of its small size has higher hydration enthalpy than chlorine. Also, due to repulsion between electrons it has lower bond dissociation energy. Thus, fluorine has better oxidising action than chlorine.
Question. Arrange the following in order property indicated for each set.
(i) F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
(iii) HF, HCl, HBr, HI increasing acid strength
Answer : (i) Increasing bond dissociation enthalpy order is
I2< F2 < Br2 < Cl2
Bond dissociation enthalpy of F2 is less than that of Br2 and Cl2 due to the lone pair – lone pair repulsions.
(ii) The acidic strength of the hydrohalic acids in the order :
HF < HCl < HBr < HI
This order is a result of bond dissociation enthalpies of H — X bond decreases from H — F to H — I as the size of halogen atom increases
Question. Complete the following chemical equation :
F2(Excess) + Cl2 →300°C
Answer : 3F2 (excess) + Cl2 →300°C 2ClF3
Question. Complete the following reaction equation :
I2 + H2O + Cl2 →
Answer : I2 + 6H2O + 5Cl2 → 2HIO3 + 10HCl
Iodic acid
Question. Describe the following about halogens (Group 17 elements):
(i) Relative oxidising power of halogens.
(ii) Relative acidic strength of the hydrogen halides.
Answer : (i) From top to bottom in group – 17 oxidising power of halogens decreases
F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2.
(ii) F2 has lower bond dissociation enthalpy than Cl2 because F atom is very small and hence the electron-electron repulsions between the lone pairs of electrons are very large.
Question. Write balanced equation for the following reactions :
Chlorine reacts with dry slaked lime.
Answer : 2Cl2 + 2Ca(OH)2(dil.) →Cold CaCl2 + Ca(OCl)2 + 2H2O
Calcium hypochlorite
Question. Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas.
Answer : (i) Phosgene (ii) Mustard gas
Question. Give reasons : ICl is more reactive than I2.
Answer : Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogens (except flourine) because X — X′ bond (I—Cl bond) in interhalogens is weaker than X—X bond (I—I bond) in halogens except F — F bond. In other words I —Cl bond is weaker than I — I bond. That’s why ICl is more reactive than I2.
Question. Draw the structure of O3 molecule.
Answer :
Question. Arrange the following in the order of property indicated against each set :
HF, HCl, HBr, HI – increasing bond dissociation enthalpy
Answer : HI < HBr < HCl < HF
Question. Draw the structure of the following : ClF3
Answer : Hybridisation – sp3d
Structure – Trigonal bipyramidal
Shape – Bent (T-shaped)
Angle F–Cl–F : less than 90°

Question. Account for the following :
Fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF.
Answer : Fluorine forms only one oxoacid HOF. Because for the formation of other oxoacids d orbitals are required for the multiple pπ – dπ bonding between extra oxygen atoms and fluorine.
High electronegativity and small size of fluorine also favours only the formation of one oxoacid.
Question. How would you account for the following?
The value. of electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for sulphur is higher than that for oxygen.
Answer : The electron gain enthalpy of oxygen is less negative than sulphur. This is due to its small size. As a result of which the electron-electron repulsion in the relatively small 2p-subshell are comparatively larger and hence the incoming electrons are not accepted with same ease as in case of other (sulphur) elements of this group.
Question. Account for the following :
BrCl3 is more stable than BrCl5.
Answer : O.S. of Br in BrCl5 is +5, whereas in case of BrCl3 is +3. As Br is more stable in +3 oxidation state than +5, due to inert pair effect. Therefore, it is unstable and readily reduces from +5 to +3 oxidation state.
Short Answer Questions :
Question. Draw the structures of the following : XeF2
Answer : XeF2 :
Total valence electron pair
= 8 + 2/2 = 5
Bond pairs = 2
Lone pairs = 5 – 2 = 3
Hybridisation = sp3d
Geometry = Trigonal bipyramidal
Shape = Linear

Question. Write the formulae and the structure of noble gas species which are isostructural with
(i) ICl–4
(ii) BrO–3
Answer :


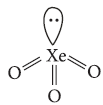
Question. Draw the structure of the following : XeO3
Answer : XeO3 :
Hybridisation = sp3
Geometry = Tetrahedral
Shape = Pyramidal
Question. Noble gases have low boiling points. Why?
Answer : Noble gases being monoatomic gases are held together by weak London dispersion forces, therefore they have low boiling points.
Question. Complete the following reactions :
(i) XeF4 + O2F2
(ii) XeF4 + SbF5
Answer : (i) XeF4 + O2F2 →143 K XeF6 + O2
(ii) XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3]+ [SbF6]–
Question. Complete the following equation : XeF2 + H2O
Answer : 2XeF2(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2Xe(g) + 4HF(aq) + O2(g)
Question. Give reasons for the following :
Helium is used in diving apparatus as a diluent for oxygen.
Answer : Helium is used in diving apparatus as diluent for oxygen because of its low solubility (as compared to N2) in blood, a mixture of oxygen and helium is used in diving apparatus used by deep sea divers.
Question. Account for the following :
Helium is used in diving apparatus.
Answer : Helium is used in diving apparatus as diluent for oxygen because of its low solubility (as compared to N2) in blood, a mixture of oxygen and helium is used in diving apparatus used by deep sea divers.
Question. Write the chemical equation for the following process : PtF6 and xenon are mixed together
Answer : PtF6 + Xe → Xe+[PtF6]–
Question. Complete the following chemical reaction equation : XeF4 + H2O
Answer : 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 2XeO3 + 24HF +3O2 + 4Xe
Question. Write the balanced chemical equations for obtaining XeO3 and XeOF4 from XeF6.
Answer : XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
Question. Complete the following chemical reactions equations :
XeF6 + H2O
Answer : XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
Question. Predict the shape and asked angle (90° or more or less) in each of the following case.
XeF2 and the angle F – Xe – F
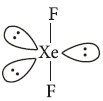
Answer : XeF2 :
Total valence electron pair
= 8 + 2/2 = 5
Bond pairs = 2
Lone pairs = 5 – 2 = 3
Hybridisation = sp3d
Geometry = Trigonal bipyramidal
Shape = Linear
Question. (i) How does xenon atom form compounds even though the xenon atom has a closed shell electronic configuration?
(ii) Draw the structure of XeOF4.
(iii) Complete and balance the following equation : XeF4 + H2O
Answer : (i) Except radon which is radioactive, Xe has least ionisation energy among noble gases and hence it readily forms chemical compounds particularly with oxygen and fluorine.
(ii) XeOF4 is square pyramidal.
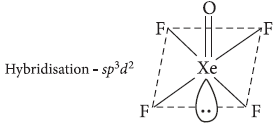
(iii) 6XeF4 + 12H2O → 2XeO3 + 24HF +3O2 + 4Xe
Question. Complete the following reaction equation :
XeF2 + PF5
Answer : XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+[PF6]–
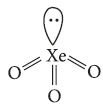
Question. Draw structure of
(i) XeOF4
(ii) XeO3.
Answer : (i) XeOF4 is square pyramidal.

(ii) XeO3 :
Hybridisation = sp3
Geometry = Tetrahedral
Shape = Pyramidal
Question. Account for the following :
Unlike xenon, no distinct chemical compound of helium is known.
Answer : Extremely small size and fully filled outer orbital makes helium very stable and reistant to chemical reaction and hence, it does not form compounds unlike bigger atoms of other elements of noble gas family.
Question. Complete the following equation : XeF4 + O2F2
Answer : XeF4 + O2F2 →143 K XeF6 + O2
Question. Explain the following observations:
Helium forms no real chemical compound.
Answer : Helium has completely filled ns2 electronic configurations in its valence shell. Due to its small size and high IE, helium is chemically unreactive. That’s why it forms no real chemical compound.
Question. Explain the following situations :
XeF2 has a straight linear structure and not a bent angular structure.
Answer : Since there are two Xe—F covalent bonds and three one pairs in XeF2. According to VSEPR theory, the shape of XeF2 is linear.
Question. Draw the structures of the following molecules: XeF6
Answer : XeF6
Total valence electron pairs = 8 + 6/2 = 7
Bond pair = 6
Lone pair = 7 – 6 = 1
Hybridisation = sp3d3
Shape = Distorted octahedral
Geometry = Pentagonal bipyramidal

Question. What happens when XeF4 reacts with SbF5?
Answer : XeF4 + SbF5 → [XeF3]+ [SbF6]–
Question. Assign reasons for the following :
Of the noble gases only xenon is known to form well-established chemical compounds.
Answer : Except radon which is radioactive, Xe has least ionisation energy among noble gases and hence it readily forms chemical compounds particularly with oxygen and fluorine.
Question. Why do some noble gases form compounds with fluorine and oxygen only?
Answer : Fluorine and oxygen are the most electronegative elements and hence are very reactive. Therefore, they form compounds with noble gases particularly with xenon.
Question. List the uses of neon and argon gases.
Answer : Neon is used in discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs for advertisement display purposes.
Argon is used to provide an inert atmosphere in high temperature metallurgical processes and for filling electric bulbs.
Question. Explain the following observations :
The majority of known noble gas compounds are those of Xenon.
Answer : Since, xenon (Xe) has least ionization energy among noble gases hence it readily forms chemical compounds particularly with O2 and F2.
Question. Write balanced chemical equations for the following reaction : XeF6 is hydrolysed
Answer : XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
Question. What inspired N. Bartlett for carrying out reaction between Xe and PtF6?
Answer : Neil Bartlett first prepared a red compound which is formulated as O2+PtF6–. He then realised that the first ionisation enthalpy of molecular oxygen (1175 kJ/mol) is almost identical with Xe (1170 kJ/mol). He made efforts to prepare same type of compound with Xe and was successful in preparing another red compound Xe+PtF6–.
Question. (i) Which noble gas is used in filling balloons for meteorological observations?
(ii) Complete the equation :
XeF2 + PF5
Answer : (i) Helium is used for filling balloons for meteorological observations because it is non-inflammable.
(ii) XeF2 + PF5 → [XeF]+[PF6]–
Question. Complete the following reaction :
XeF6 + KF
Answer : XeF6 + KF → K+[XeF7]–
Question. Draw the structures of XeF4 and predict their shapes.
Answer :

Question. Explain the following :
(i) Xenon does not form such fluorides as XeF3 and XeF5.
(ii) Out of noble gases, only Xenon is known to form real chemical compounds
Answer : (i)
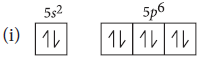
All the orbital of Xe have paired electrons. The promotion of one, two or three electrons from 5p-filled orbitals to the 5d-vacant orbitals will give rise to two, four and six-half filled orbitals. Therefore, xenon can combine with even number of fluorine atoms, not add. Thus, it cannot form XeF3 and XeF5.
(ii) Except radon which is radioactive, Xe has least ionisation energy among noble gases and hence it readily forms chemical compounds particularly with oxygen and fluorine.
Question. Write the structures of the following molecule : XeOF4.
Answer: XeOF4 is square pyramidal.

Question. Explain the following :
XeF2 is linear molecule without a bend.
Answer : Since there are two Xe—F covalent bonds and three one pairs in XeF2. According to VSEPR theory, the shape of XeF2 is linear.
Question. How is XeO3 obtained? Write the related chemical equations. Draw the structure of XeO3.
Answer : XeO3 can be obtained by hydrolysis of XeF4 and XeF6.