VBQs Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology with solutions has been provided below for standard students. We have provided chapter wise VBQ for Class 12 Biology with solutions. The following Biotechnology Principles and Processes Class 12 Biology value based questions with answers will come in your exams. Students should understand the concepts and learn the solved cased based VBQs provided below. This will help you to get better marks in class 12 examinations.
Biotechnology Principles and Processes VBQs Class 12 Biology
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the technique that is used to alter the chemistry of genetic material (DNA, RNA) to obtain desired result.
Answer : Genetic Engineering / Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology.
Question. Name the material used as matrix in gel electrophoresis and mention its role.
Answer : Agarose is the most commonly used matrix in DNA gel electrophoresis. It provides sieving effect for separation of DNA fragments according to their size.
Question. Name the host cells in which micro–injection technique is used to introduce an alien DNA.
Answer : Animal cell.
Question. Mention the type of host cells suitable for the gene guns to introduce an alien DNA.
Answer : Plant cells.
Question. State what happens when an alien gene is ligated at Pvu I site of pBR322 plasmid.
Answer : When an alien gene is ligated at the Pvu I site of ampicillin resistance gene in the vector pBR322, the recombinant plasmids lose ampicillin resistance due to insertion of the foreign DNA.
Question. How is the action of normal endonuclease enzymes different from that of restriction endonuclease ?
Answer : Normal endonuclease cuts at random position within a DNA sequence, whereas restriction endonuclease recognizes and cut specific nucleotide sequences within DNA.
Question. Why EtBr is used in gel electrophoresis in spite of it being highly carcinogenic ?
Answer : EtBr is an intercalating agent. It stacks itself in the DNA bases, and fluoresce under U.V light, thus helps in identification of DNA.
Question. Why is it essential to have ‘selectable marker’ in cloning vector.
Answer : Selectable marker helps in the identification and elimination of non-transformants and permitting the growth of the transformants. Therefore, they are considered essential in cloning vector.
Question. Name two enzymes that are essential for constructing a recombinant DNA.
Answer : Restriction enzymes / polymerase enzymes / ligase
Question. Write the two components of the first artificial recombinant DNA molecule constructed by Cohen and Boyer.
Answer : The two components are antibiotic resistant gene and plasmid vector of Salmonella typhimurium.
Question. How can following be made possible for biotechnology experiments?
(i) Isolation of DNA from bacterial cell.
(ii) Reintroduction of recombinant DNA into a bacterial cell.
Answer : (i) By treating the cell with the enzyme lysozyme.
(ii) By making the bacterial cell competent.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain palindromic nucleotide sequence with the help of a suitable example.
Answer : Palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs that reads the same on two strands when orientation of reading is the same.
Example : 5’ — GAATTC — 3’
3’—CTTAAG — 5’ 2
Question. Explain with the help of a suitable example the naming of a restriction endonuclease.
Answer : EcoRI.
The first letter of the name comes from the genus and the next two from the name of the species of the bacterium i.e. prokaryotic cell. Thus Eco stands for the genus and species of the prokaryotic cell from which the enzyme was isolated i.e. E. coli R stands for strain. ‘I’ follows order in which enzyme was isolated.
Question. How are ‘sticky ends’ formed on a DNA strand ? Why are they so called ?
Answer : Restriction enzymes cut the strands of the DNA, a little away from the centre of the palindromic sites, but between the same two bases on opposite strands.
These overhang stretches are called as sticky ends.
They form hydrogen bonds with their complementary cut counterparts.
Question. Explain how to find whether E. coli bacterium has transformed or not, when, a recombinant DNA bearing ampicillin-resistant gene is transferred into it.
Answer : The recombinant / transformant may be found out from non-recombinant / non-transformant by plating the transformants on ampicillin containing medium. The transformants growing on ampicillin containing medium are then transferred to tetracycline containing medium. The recombinant will grow on ampicillin containing medium but not on that containing tetracycline. But nonrecombinant will grow on both tetracycline and ampicillin containing media.
Question. List the key tools used in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer : Restriction enzymes / Polymerase enzymes / Ligase enzymes / Vectors / Host organisims / E. coli/ Agrobacterium.
Question. What is EcoRI ? How does EcoRI differ from an exonuclease ?
Answer : EcoRI is restriction endonuclease enzyme.
Exonuclease removes nucleotides from the ends of DNA.
EcoRI makes cuts at specific position within the DNA.
Question. Explain the role of Ti plasmid in biotechnology.
Answer : (i) The Ti plasmid (tumor-inducing plasmid) of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has been modified (does not cause tumour) and used as a cloning vector. The Ti plasmid integrates a segment of its DNA, termed T-DNA into the chromosomal DNA of its host plant cells.
(ii) The T-DNA plasmid causes tumours. As gene transfer occurs without human effort, the bacterium is known as ‘natural genetic engineer’ of plants. Ti plasmids as vectors, transfer foreign genes of interest into the target cells.
Question. (i) Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322. Mention the role they play.
(ii) Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme β-galactosidase a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above ?
Answer : (i) ampR / ampicillin resistance genes, tetR/ tetracycline resistance gene.
They help in identifying and eliminating nontransformants / non- recombinants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants / recombinants.
(ii) Simpler process / less cumbersome, in the presence of chromogenic substrate recombinants are colourless and non recombinants are blue in colour.
Detailed Answer :
(i) In cloning vector pBR322, ampicillin and tetracycline resistance genes serve as selectable markers. Selectable markers help in the identification and selection of transformed cells from non-transformed cells to distinguish the recombinant cells from the non-recombinant cells.
(ii) The coding sequence of an enzyme β-galactosidase is preferred over antibiotic resistance genes because recombinants can be easily visualised and the process is comparatively
simple and less cumbersome. When the foreign gene is inserted within the β-galactosidase gene, the enzyme β-galactosidase gets inactivated (insertional inactivation). Thus, when the bacteria are grown on a chromogenic substrate, non-recombinants will produce blue-coloured colonies while the recombinants will produce colourless colonies.
Question. (i) In pBR322, foreign DNA has to be introduced in tetR region. From the restriction enzymes given below, which one should be used and why :
Pvul, EcoRI, BamHI
(ii) Give reasons, why the other two enzymes cannot be used.
Answer : (i) Bam HI should be used, as restriction site for this enzyme is present in tetR region.
(ii) Pvu I will not be used as restriction site for this enzyme is present in ampR region (not in tetR ).
EcoRI will not be used, as restriction site for this enzyme is not present in selectable marker tetR .
Question. How does a restriction endonuclease help in DNA recombinant technology ?
OR
Explain the mode of action of EcoRI.
Answer : Restriction endonuclease (EcoRI) inspects length of DNA and recognises specific palindromic nucleotide sequence, binds with DNA, cuts each of the two strands of double helix at specific points.
This leaves the single stranded overhanging stretches at the ends. They are called sticky ends.
They form H-bonds with their complementary cut counterparts. This stickiness facilitates action of DNA ligase, when cut by the same restriction enzyme. The resultant DNA fragments have the same kind of sticky ends and these are joined together by DNA ligase.
Question. (i) Differentiate between exons and introns.
(ii) What is a plasmid ? Why is it selected as a vector ?
Answer : (i) Exons are the coding or expressed sequences that appear in mature or processed RNA, introns are intervening sequences that do not appear in mature or processed RNA / Exons are codons that code for amino acid sequence, introns do not code for amino acids.
(ii) Autonomously replicating circular DNA / extra chromosomal DNA, exclusively present in bacteria.
Plasmid is selected as vector because it has ability to replicate in the bacterial cell independent of chromosomal DNA and also has high copy number.
Question. Name and describe the technique that helps in separating the DNA fragments formed by the use of restriction endonuclease.
Answer : Gel electrophoresis.
DNA are negatively charged forced to move towards anode, electric field in agarose gel matrix, separate according to their size / sieving effect, smaller fragments moves faster and farther than the larger.
Detailed Answer :
Gel electrophoresis, Since DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules, they can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium / matrix. The most commonly used matrix is agarose which is a natural polymer extracted from sea weeds.
The DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel. Hence, the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Question. (i) Identify (A) and (B) illustrations in the following :
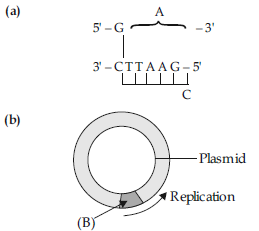
(ii) Write the term given to (A) and (B) and why ?
(iii) Expand PCR. Mention its importance in biotechnology.
Answer : (i) (A)–AATTC / Sticky end.
(B)–Ori / Origin of Replication.
(ii) Palindromic sequence, because the sequence of base pair reads same on the two strands, when orientation of reading is kept the same.
(iii) PCR – Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Importance – amplification of gene of interest (in vitro).
Detailed Answer :
(i) The part labelled A is the sticky end.
The part labelled B is the foreign DNA insert.
The part labelled C is the Ori or Origin of Replication.
(ii) The term used for A and C are called the palindromic nucleotide sequence. These are named so because they read the same forward and backward.
(iii) PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction.
PCR is a technique in molecular biology, used to amplify a gene or a piece of DNA to obtain its several copies. It is extensively used in the process of gene manipulation.
Question. Explain the roles of the following with the help of an example each in recombinant DNA technology:
(a) Restriction Enzymes
(b) Plasmids
Answer : (a) It recognizes a specific sequence of base pairs palindromes and cuts the DNA strand at a specific site.
E.g. EcoRI / Hind II or any other correct example.
(b) Act as vectors / cloning of desired alien gene / foreign gene.
E.g. pBR322 / plasmid of Salmonella / plasmid of Agrobacterium / Ti plasmid/ Tumour inducing plasmid.
Question. (i) Explain the significance of ‘palindromic nucleotide sequence‘ in the formation of recombinant DNA.
(ii) Write the use of restriction endonuclease in the above process.
Answer : (i) Palindromic nucleotide sequence is the recognition (specific) sequence present both on the vector and on a desired / alien DNA for the action of the same (specific) restriction endonuclease to act upon.
(ii) Same restriction endonuclease binds to both the vector and the foreign DNA, cut each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in their sugar phosphate backbone of recognition sequence for restriction endonucleases / palindromic sequence of vector and foreign DNA, to cut strand a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites, creates overhanging stretches / sticky ends.
Question. Name and explain the technique that helps in the separation of DNA fragments for DNA recombinant technology experiments.
How can these separated DNA fragments be visualised ?
Answer : Gel electrophoresis, Since DNA fragments are negatively charged, they move towards anode (under an electric field) through a medium / matrix / agarose gel. The fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by agarose gel. The separated DNA fragments can be visualised after staining the DNA with ethidium bromide, followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Detailed Answer :
Electrophoresis is a technique of separation of charged molecules under the influence of an electrical field so that they migrate in the direction of electrode bearing the opposite charge, through a medium / matrix The most commonly used matrix is agarose which is a polysaccharide extracted from sea weeds.
DNA fragments separate according to their size through the pores of agarose gel.
The separated DNA fragments can be seen only after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide (Et + Br) followed by exposure to UV radiation as bright orange colored bands.
Question. Mention the role of (i) selectable marker, (ii) Ori and (iii) rop in E. coli cloning vector pBR322.
Answer : (i) Selectable marker : Helps in identifying and eliminating non transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants.
(ii) Ori : Helps to start replication and any piece of DNA when linked to this sequence can be made to replicate within host cell, responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA.
(iii) Codes for the proteins involved in the replication of the plasmid.
Question. Given below is the diagram of agarose gel kept under UV light :
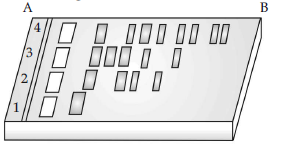
(i) Mark the positive and negative terminals.
(ii) What is the charge carried by DNA molecule.
(iii) How are the separated DNA fragments finally isolated ?
Answer : (i) Positive terminal-‘B’
Negative terminal-‘A‘
(ii) DNA being negatively charged, moves towards the positive electrode (anode).
(iii) By elution-separated bands of DNA are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from the gel piece.
Question. Rajesh was doing gel electrophoresis to purify DNA fragments. Given below is the sketch of the observations of the experiment performed by him.
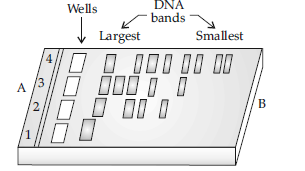
(i) At which end he would have loaded the samples and where ?
(ii) Analyse the reason for different positions taken up by the DNA bands.
(iii) Elaborate the step he would have followed to visualize DNA bands.
Answer : (i) He would have loaded the samples near end A, in the wells.
(ii) The DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel. Hence, the smaller is the fragment size, the farther it moves.
(iii) After staining the DNA with ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiations, the DNA bands fluoresce.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Unless the vector and source DNA are cut, fragments separated and joined, the desired recombinant vector molecule cannot be created.
(i) How are the desirable DNA sequence cut ?
(ii) Explain the technique used to separate the cut fragments.
(iii) How are the resultant fragments joined to the vector DNA molecule?
Answer : (i) DNA sequences of the vector as well as the source are cut by the same restriction enzyme like EcoRI, in a palindromic sequence.
(The cut ends overhang as sticky ends in the medium.)
(ii) These cut ends fragments are to be extracted from the culture medium using gel electrophoresis.
This has an agarose gel matrix. Fragments are fed in the wells. DNA are negatively charged so, they move towards anode under an electric field through the gel. Smaller fragments move faster, thus separated.
(iii) Fragments are now added to the medium containing the vector DNA.
The sticky ends facilitates the action of the enzyme ligase and join the source DNA to the vector.