Please refer to General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question. Froth floatation process is used for:
(a) cuprite
(b) zincite
(c) copper pyrites
(d) bauxite
Answer
C
Question. The anode mud obtained during electro refining of Cu contains:
(a) Ag
(b) Fe
(c) Au
(d) Zn
Answer
A,C
Question. Which is a copper matte?
(a) Cu2O + FeS
(b) Cu2S + FeO
(c) Cu2S + FeS
(d) Cu2O + FeO
Answer
C
Question. Brass contains:
(a) Cu + Sn
(b) Cu + Ni
(c) Cu + Zn
(d) Mg + Al
Answer
C
Question. The main function of roasting is:
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) to remove volatile matter
(d) to make slag
Answer
C
Question. Flux used in the smelting of copper arc is:
(a) coke
(b) magnesia
(c) silica
(d) lime stone
Answer
C
Question. SiO2 is a :
(a) flux
(b) gangue
(c) slag
(d) catalyst
Answer
A,B
Question. The type of iron obtained from blast furnace is:
(a) pig iron
(b) cast iron
(c) wrought iron
(d) mild steel
Answer
A
Question. Which one is not a process of purification of metals:
(a) chromatrography
(b) zone refining
(c) froth floatation
(d) distillation
Answer
C
Question. Which is not a mineral of Al?
(a) diaspore
(b) bauxite
(c) corundum
(d) galena
Answer
D
Question. In metallurgical process of Al, cryolite is mixed in its molten state, because it
(a) decreases the amount of alumina
(b) oxidises the alumina
(c) increases the melting point of alumina
(d) decreases the melting point of alumina
Answer
D
Question. Which one is leached with cyanide process?
(a) Cu
(b) Al
(c) Ag
(d) Zn
Answer
C
Fill in the blanks type questions
Question. Cresols and aniline are used as ………….. in froth floatation process:
Answer
Froth stabilizer
Question. Haematite is an ore of ……………
Answer
Iron
Match the following type questions
Question. Match the column
Column 1 Column 2
(A) cyanide process P. ultrapure Ge
(B) zone refining Q. extraction of Cu
(C) Froth floatation process R. pine oil
(D) electrolytic refining S. extraction of Au
(a) A–S, B–P, C–R, D–Q
(b) A–R, B–S, C–Q, D–P
(c) A–P, B–Q, C–R, D–S
(d) A–S, B–R, C–P, D–Q
Answer
A
VERY SHORT Answer. TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Although aluminium is above hydrogen in the electrochemical series, it is stable in air and water. Why ?
Answer. Due to formation of inert oxide Al2O3.
Question. Which method of purification is represented by the following reaction :
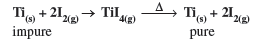
Answer. Van Arkel method
Question. What is the thermodynamic criteria for the feasibility of a reaction ?
Answer. DG should be –ve or log K = + ve.
Question. Zinc is used but not copper for the recovery for metallic silver from the complex [Ag(CN)2]−, although electrode potentials of both zinc and copper are less than that of Ag. Explain why ?
Answer. Zinc reacts at faster rate as compared with copper, further zinc is cheaper than copper.
Question. Why can’t aluminium be reduced by carbon ?
Answer. Al is stronger reducing agent than carbon.
Question. What is the composition of copper matte ?
Answer. Cu2S and FeS
Question. Which form of copper is called blister copper ?
Answer. The solidified copper obtained has blistered appearance due to the evolution of SO2, so it is called blistered copper.
Question. Write the composition of moleten mixture which is electrolysed to extract aluminium.
Answer. Molten Al2O3 + Na3AlF6 or CaF2
Question. A sample of galena is contaminated with zinc blende. Name one chemical which can be used to concentrate galena selectively by froth floatation method.
Answer. NaCN
Question. What are the constituents of German silver ?
Answer. Cu = 25-30%, Zn = 25-30%, Ni = 40-50%
Question. Name three metals which occur in native state in nature.
Answer. Au, Ag and Pt.
Question. What are froth stabilizers ? Give two examples.
Answer. Examples are cresol and aniline.
Question. Give the names and formulae of three ores which are concentrated by froth floatation process.
Answer. Galena (PbS), Zinc blende (ZnS), Cinnabar (HgS).
Question. Name the most important form of iron. Mention its one use.
Answer. Cast iron is used for making gutter pipes, castings, railway sleepers, toys etc.
Question. Why is froth floatation process selected for concentration of the sulphide ore ?
Answer. Sulphide ore particles are wetted by oil (Pine oil) and gangue particles by water.
Question. Among Fe, Cu, Al and Pb, which metal(s) cannot be obtained by smelting ?
Answer. Al.
Question. Write the reaction involved in the extraction of copper from low grade ores.
Answer. First step is leaching of ore with acid or bacteria then,Cu2+ (aq) + H2 (g) → Cu (s) + 2H+ (g)
SHORT Answer.-I TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Why is the reduction of a metal oxide easier if metal formed is in liquid state at the temperature of reduction ?
Answer. Entropy is more positive when the metal is in liquid state as compared with solid state, so DG becomes more –ve.
Question. Mention the role of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium.
Answer. It lowers the melting point of the mixture and brings conductivity.
Question. Mention the role of following :
(a) SiO2 in the metallurgy of Cu.
(b) CaCO3 in the metallurgy of Fe.
(c) CO in the metallurgy of iron.
(d) I2 in the purification of zirconium.
Answer. (a) Flux
(b) CaCO3 decomposed to CaO, which acts as flux.
(c) Reducing agent
(d) To form a volatile complex with Zr.
Question. Write the method to produce copper matte from copper pyrites.
Answer. Froth floatation.
Question. Copper can be extracted by hydrometallurgy but not zinc. Explain why ?
Answer. Eº2n2+ / 2n = – ve, Eºcu+2 /cu = + ve
Question. Extraction of copper directly from sulphide ore is less favourable than from its oxide through reduction. Explain.
Answer. 2CuS (s) + C (s) → CS2 (l) + 2Cu (s)
CuO (s) + C (s) → CO (g) + Cu (s)
G value is more –ve in second case as compared with first case.
Question. What is hydrometallurgy ? Give one example where it is used for metal extraction.
Answer. Leaching followed by reduction is called hydrometallurgy. It is used in extraction of copper.
Question. Write the chemical formulae of the following ores :
(a) Haematite (b) Magnetite
(c) Limonite (d) Siderite
Answer. (a) Fe2O3 (b) Fe3O4
(c) Fe2O3.2H2O (d) FeCO3
Question. Name the elements present in anode mud during refining of copper. Why does it contain such elements ?
Answer. Au and Ag. They are not oxidized at anode. They are less electropositive than copper.
Question. Name the process for the benefaction/concentration of (i) an ore having lighter impurities, (ii) sulphide ore.
Answer. (i) Gravity separation
(ii) Froth floatation
Question. How are impurities separated from bauxite ore to get pure alumina ?
Answer. By leaching.
(i) Al2O3 (s) + 2NaOH (aq) + 3H2O (l) → 2Na[Al(OH)4] (aq)
(ii) 2Na[Al(OH)4] (aq) + CO2 (g) → Al2O3.xH2O (s) + 2NaHCO3 (aq)
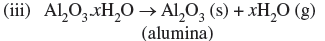
Question. Gibbs energy of formation ΔGf G of MgO (s) and CO (g) at 1273 K and 2273 K are given below :
ΔGf [MgO (s)] = − 941 kJ mol−1 at 1273 K
ΔGf [CO (g)] = − 439 kJ mol−1 at 1273 K
ΔGf [MgO (s)] = − 314 kJ mol−1 at 2273 K
ΔGf [CO (g)] = − 628 kJ mol−1 at 2273 K
On the basis of above data, predict the temperature at which carbon can be used as a reducing agent for MgO (s).
Answer. For the reaction, MgO (s) + C (s) → Mg (s) + CO (g)
At 1273 K, ΔGr = ΔGf [CO (g)] – ΔGf [MgO (s)] = − 439 – (− 941) kJ mol−1 = 502 kJ mol−1
At 2273 K, ΔGr = − 628 – (− 314) kJ mol−1 = − 314 kJ mol−1
The temperature is 2273 K.
Question. What is pyrometallurgy ? Explain with one example.
Answer. A process of reducing a metal oxide by heating with either coke or some other reducing agent. E.g., Al, Mg etc.
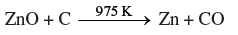
Question. Give equations for the industrial extraction of zinc from calamine.
Answer. ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2 (Calcination)
ZnO + C → Zn + CO (Reduction)
SHORT Answer.-II TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. How is pure copper obtained from its principle ore ? Write the chemical reactions occurring during the extraction.
Answer. (i) 2CuFeS2 + O2 → Cu2S + 2FeS + O2
(ii) Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
(iii) Cu2O + C → 2Cu + CO
(iv) 2Cu2O + Cu2S → 6Cu + SO2
Question. In the cynamide extraction process of silver ore argentite from, name the oxidizing and reducing agents. Write the chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Answer. 4Ag + 8NaCN + 2H2O + O2 → 4Na[Ag(CN)2] + 4NaOH
2[Ag(CN)2]− (aq) + Zn (s) → [Zn(CN)4]2− (aq) + 2Ag (s)
(i) Oxidising agent – O2 (ii) Reducing agent = Zn
Question. Name the method of refining of the following metals :
(a) Hg (b) Sn (c) Cu (d) Ge (e) Ni (f) Zr
Answer. (a) Distillation, (b) Liquation, (c) Electrolytic refining, (d) Zone refining, (e) Mond process, (f) Van Arkel process
Question. State the principle of refining of metal by the following methods :
(a) Zone refining
(b) Electrolytic refining
(c) Vapour phase refining
Answer.(a) The impurities are more soluble in the melt than in the solid state of the metal.
(b) Impure metal is made to act as anode, while the strip of same metal in pure form as cathode.
Question. The native silver forms a water soluble compound (B) with dilute aqueous solution of NaCN in the presence of a gas (A). The silver metal is obtained by the addition of a metal (C) to (B) and complex (D) is formed as a byproduct. Write the structures of (C) and (D) and identify (A) and (B) in the following sequence :
Ag + NaCN + [A] + H2O [B] + OH− + Na+ [C] + [B][D] + Ag
Answer. [A] = O2
[B] = Na[Ag(CN)2]
[C] = Zn
[D] = Na2[Zn(CN)4]