Please refer to Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Question. Boiling points of carboxylic acids are
(a) lower than corresponding alcohols
(b) higher than corresponding alcohols
(c) equal to that of corresponding alcohols
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Which reaction is used for detecting the presence of carbonyl group?
(a) Reaction with hydrazine
(b) Reaction with phenyl hydrazine
(c) Reaction with hydroxylamine
(d) All of the above
Answer
D
Question. In the anion HCOO– the two carbon-oxygen bonds are found to be of equal length. What is the reason for it?
(a) Electronic orbitals of carbon atom are hybridised
(b) The C=O bond is weaker than the C–C bond
(c) The anion HCOO– has two reasonating structures
(d) The anion is obtained by removal of a proton from the acid molecule
Answer
C
Question. Two compounds benzyl alcohol and benzoic acid are formed from this compound, when this compound is heated in the presence of conc.NaOH, this compound is.
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzylalcohol
(c) Acetophenone
(d) Benzophenone
Answer
A
Question. Select the acid(s) which cannot be prepared by Grignard reagent.
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Succinic acid
(c) Formic acid
(d) All of the above
Answer
C
Question. In the reaction

Answer
C
Question. Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenol and alcohol because of
(a) intermolecular hydrogen bonding
(b) formation of dimers
(c) highly acidic hydrogen
(d) resonance stabilization of their conjugate base
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant ?
(a) CH3CHFCOOH
(b) FCH2CH2COOH
(c) BrCH2CH2COOH
(d) CH3CHBrCOOH
Answer
C
Question.
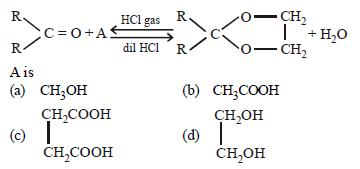
Answer
D
Question. The major product of nitration of benzoic acid is
(a) 3- Nitrobenzoic acid
(b) 4- Nitrobenzoic acid
(c) 2- Nitrobenzoic acid
(d) 2, 4- dinitrobenzoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Among the following acids which has the lowest pKa value?
(a) CH3CH2COOH
(b) (CH3)2CH — COOH
(c) HCOOH
(d) CH3COOH
Answer
C
Question. Wolf-Kishner reduction is
(a) reduction of carbonyl compound into alcohol
(b) reduction of carbonyl compound into alkene
(c) reduction of carboxyl compound into alkane
(d) reduction of nitro compound into aniline
Answer
C
Question.

Answer
B
Question. Which is false in case of carboxylic acids?
(a) They are polar molecules
(b) They form H-bonds
(c) They are stronger than mineral acids
(d) They have higher b.p. than corresponding alcohols
Answer
C
Question. During reduction of aldehydes with hydrazine and potassium hydroxide, the first step is the formation of
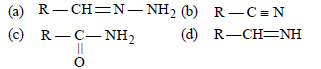
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is the weakest acid ?
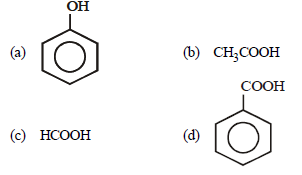
Answer
A
Question. Acetic anhydride is obtained by the reaction of
(a) sodium and acetic acid
(b) ammonia and acetic acid
(c) ethanol and acetic acid
(d) P2O5 and acetic acid
Answer
D
Question. Toluene can be oxidised to benzoic acid by
(a) KMnO4 (alk.)
(b) K2Cr2O7 (alk.)
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b)
Answer
A
Question. Propionic acid with Br2/P yields a dibromo product. Its structure would be:
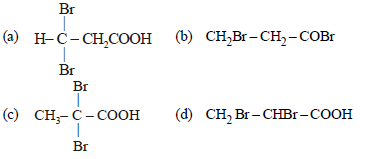
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution?
(a) Butan-1-ol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) Both of these
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. The reaction of carboxylic acid gives effervescences of CO2 with NaHCO3. The CO2 comes from.
(a) R – COOH
(b) NaHCO3
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Benzoic acid reacts with conc. HNO3 and H2SO4 to give :
(a) 3-Nitrobenzoic acid
(b) 4-Benzene sulphonic acid
(c) 4-Nitrobenzoic acid
(d) 2-Nitrobenzoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Lower carboxylic acids are soluble in water due to
(a) low molecular weight
(b) hydrogen bonding
(c) dissociation into ions
(d) easy hydrolysis
Answer
B
Question. Dimerisation of carboxylic acids is due to
(a) ionic bond
(b) covalent bond
(c) coordinate bond
(d) intermolecular hydrogen bond
Answer
D
Question. A carboxylic acid can best be converted into acid chloride by using
(a) PCl5
(b) SOCl2
(c) HCl
(d) ClCOCOCl
Answer
D
Question. Arrange the following four acids in their decreasing order of acidity
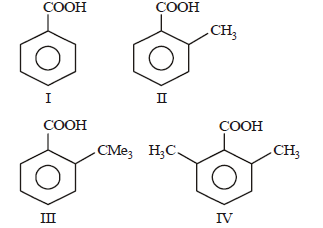
(a) I > II > III > IV
(b) IV > III > II > I
(c) II > IV > III > I
(d) III > IV > II > I
Answer
B
Question.The strongest acid among the following is –
(a) Salicylic acid
(b) m-hydroxybenzoic acid
(c) p-hydroxybenzoic acid
(d) Benzoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Among the following, the most acidic is :
(a) CH3COOH
(b) ClCH2COOH
(c) Cl2CHCOOH
(d) Cl2CHCH2COOH
Answer
C
Question. The elimination of CO2 from a carboxylic acid is known as
(a) hydration
(b) dehydration
(c) decarboxylation
(d) carboxylation
Answer
C
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Read the following statements and choose the correct option
(i) The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are lower than those of alcohols of similar molecular masses
(ii) Alcohols show intermolecular hydrogen bonding whereas aldehydes and ketones do not show intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(iii) The lower members of aldehydes and ketones are miscible with water in all proportions, because they form hydrogen bond with water.
(iv) The solubility of aldehydes and ketones increases rapidly on increasing the length of alkyl chain
(a) TTFF
(b) TFFT
(c) FTTT
(d) TTTF
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following statements are false?
(i) No aldehyde can be prepared by the oxidation of primary alcohol with acidic KMnO4.
(ii) Aldehydes having a boiling point less than 100°C can be prepared by the oxidation of primary alcohol with acidic dichromate.
(iii) Secondary alcohols on oxidation with PCC in dichloromethane give carboxylic acids having lesser number of carbon atoms
(iv) Tertiary alcohols can’t be oxidised at all
(a) (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
C
Question. Read the following statements and choose the correct option
(i) The carbonyl carbon atom is sp2 -hybridised
(ii) The carbonyl carbon is an electrophilic (Lewis acid) centre
(iii) The carbonyl oxygen is a nucleophilic (Lewis base) centre
(iv) Carbonyl compounds are non- polar in nature.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(d) (ii) and (iv) are correct
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true regarding esterification of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol ?
(i) It is carried out in presence of a strong acid which acts as a catalyst.
(ii) The strong acid makes the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic, and hence causes the alcohol, a strong nucleophile to attack on the carbonyl carbon.
(iii) The strong acid makes the carbonyl group more electrophilic which is thus attacked easily by an alcohol, a weak nucleophile.
(iv) Esterification can be done even in absence of a strong acid.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) only
(d) (iv) only
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following statement(s) is/are true regarding preparation of aldehydes and ketones?
(i) Both can be prepared by the oxidation of the concerned alcohol with copper at about 250ºC.
(ii) Both can be prepared by the oxidation of the concerned alcohol by Oppenauer oxidation.
(iii) Both can be prepared by the oxidation of respective alcohol with acidic dichromate.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) All the three
Answer
A
Question.
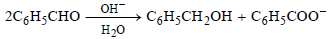
Which of the following statements are correct regarding the above reduction of benzaldehyde to benzyl alcohol?
(i) One hydrogen is coming from H2O as H+ and another from C6H5CHO as H–
(ii) One hydrogen is coming from H2O as H– and another from C6H5CHO as H+
(iii) One hydrogen from H2O and another from C6H5CHO, both in the form of H–
(iv) The reduction is an example of disproportionation reaction
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer
B
Question. Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones in nucleophilic addition reactions. Which of the following statements accounts for this ?
(i) Sterically, the presence of two relatively large substituents in ketones hinders the approach of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon
(ii) Aldehydes show resonance whereas ketones do not
(iii) Electronically, the presence of two alkyl groups reduce the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon more effectively.
(iv) Electronically carbonyl carbon atom in ketones is more electrophilic than in aldehydes
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer
A
Question. (i) Draw the structures of the following :
(a) p-Methylbenzaldehyde,
(b) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one.
(ii) Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate,
(b) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(c) Phenol and Benzoic acid.
Answer.
(b) (CH3)2C = CHCOCH3
(ii) (a) On adding sodium bicarbonate to benzoic acid, brisk effervescence of CO2 is evolved.
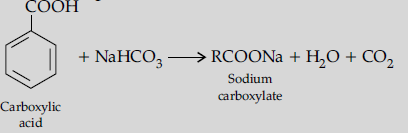
Whereas ethyl benzoate does not.
(b) Acetophenone having at least one –CH3 group on heating with alkaline solution of iodine forms yellow coloured precipitate of iodoform.

Whereas benzaldehyde does not.
(c) Benzoic acid reacts with NaHCO3 giving CO2 gas with effervescence whereas phenol does not.
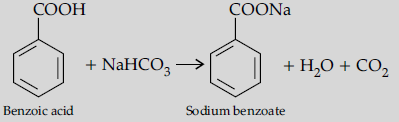
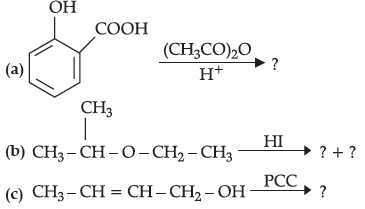
Question. (a) Draw structures of the following derivatives :
(i) Cyanohydrin of cyclobutanone
(ii) Hemiacetal of ethanal
(b) Write the major product(s) in the following :

(c) How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone?
Answer. (a) (i) Cyanohydrin of cyclobutanone
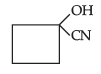
(c) By iodoform test : Propanone on treatment with I2/NaOH undergoes iodoform test to give a yellow ppt. of iodoform.
Propanal does not give this test.
Question. (a) Write the structures of A and B in the following reactions :
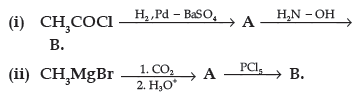
(b) Distinguish between :
(i) C6H5 – COCH3 and C6H5 – CHO,
(ii) CH3COOH and HCOOH.
(c) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling points :
CH3CHO, CH3COOH, CH3CH2OH.
Answer. (a) (i) A : CH3CHO, B : CH3CH=N–OH
(ii) A : CH3COOH , B : CH3COCl
(b) (i) Heat both compounds with NaOH and I2, C6H5COCH3 forms yellow ppt. of CHI3 whereas C6H5CHO does not.
(ii) Add ammonical solution of silver nitrate (Tollens’ reagent) to both the compounds,HCOOH gives silver mirror but CH3COOH does not.
(c) CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH < CH3COOH
Question. (i) Write the product(s) in the following reactions:
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Ethanol and Phenol
(b) Propanol and 2-methylpropan -2-ol
Answer. (i) (a)

(b) (CH3)2 CHOH and CH3 CH2I
(c) CH3CH=CHCHO
(ii) (a) Add neutral FeCl3 to both the compounds, phenol gives violet complex.
(b) Add anhy ZnCl2 and conc. HCl to both the compounds, 2-methyl propan-2-ol gives turbidity immediately.
Question. (i) How will you convert:
(a) Benzene to acetophenone
(b) Propanone to 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
(ii) Give reasons:
(a) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid take place at meta-position.
(b) Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
(c) Propanal is more reactive than propanone in nucleophilic addition reactions.
Answer. (i) (a)
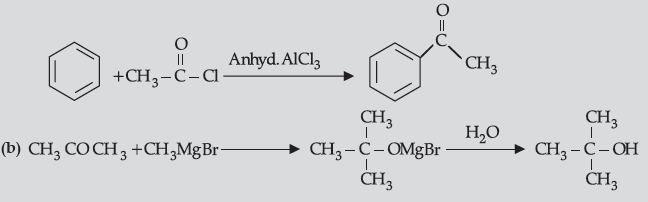
(ii) (a) Because it is a deactivating group/due to electron withdrawing carboxylic group resulting in decreased electron density at o- and p- position.
(b) Due to extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
(c) Due to steric and +I effect of two methyl groups in propanone.
Question. (a) Write the chemical reaction involved in Wolff-Kishner reduction.
(b) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction :
C6H5COCH3, CH3 – CHO, CH3COCH3
(c) Why carboxylic acid does not give reactions of carbonyl group ?
(d) Write the product in the following reaction.

(e) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and I2, isomer B forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer A does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.
Answer.
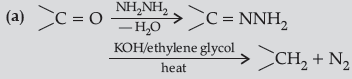
(b) C6H5COCH3 < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
(c) Because of resonance in carboxylic group, the carbonyl group, loses a double bond character.
(d) CH3CH2CH=CH–CH2CHO
(e) A : CH3CH2CHO
B : CH3COCH3
Question. (i) Describe the following giving chemical equations :
(a) Decarboxylation reaction
(b) Friedel-Crafts reaction
(ii) How will you bring about the following conversions ?
(a) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
(c) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
Answer. (i) (a) Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with
sodalime (NaOH and CaO).
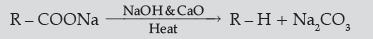
(b) The alkyl / acyl group is introduced at ortho- and para- positions by reaction of anisole with alkyl halide / acyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (a Lewis acid) as catalyst.
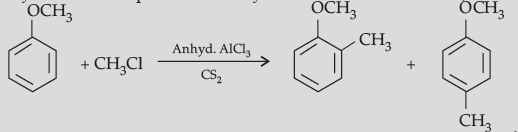
Question. (i) Complete the following equations :
(ii) Distinguish between :

Answer.
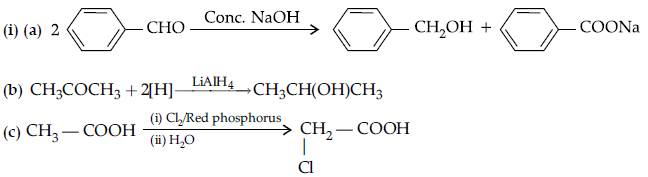
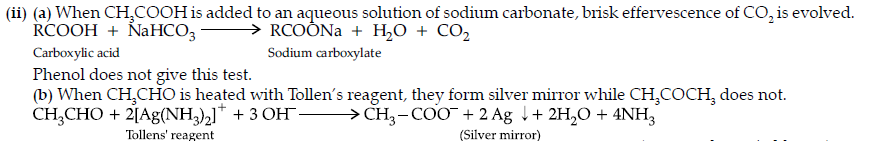
Question. (i) Give reasons :
(a) HCHO is more reactive than CH3 – CHO towards addition of HCN.
(b) pKa of O2N – CH2 – COOH is lower than that of CH3 – COOH.
(c) Alpha hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones is acidic in nature.
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(a) Ethanal and Propanal
(b) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
Answer. (i) (a) Due to +I effect of methyl group in CH3CHO.
(b) Due to –I effect of nitro group in nitroacetic acid.
(c) Due to the strong electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group and resonance stabilisation of the conjugate base.
(ii) (a) Add NaOH and I2 to both the compounds and heat, ethanal gives yellow ppt of iodoform.
(b) Add NaOH and I2 to both the compounds and heat, pentan-2-one gives yellow ppt of iodoform.
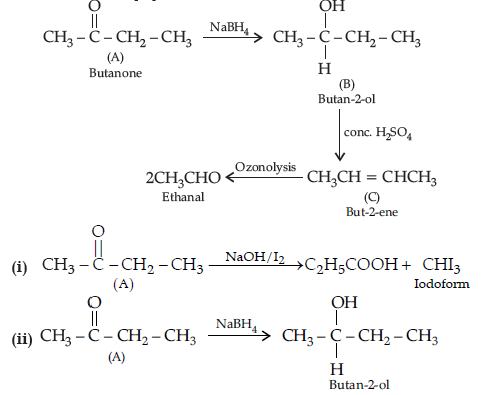
Question. (a) An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C4H8O gives orange red precipitate with 2, 4-DNP reagent. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but gives yellow precipitate of iodoform on heating with NaOH and I2. Compound (A) on reduction with NaBH4 gives compound (B) which undergoes dehydration reaction on heating with conc. H2SO4 to form compound (C). Compound (C) on ozonolysis gives two molecules of ethanal.
Identify (A), (B) and (C) and write their structures. Write the reactions of compound
(A) with (i) NaOH/I2 and (ii) NaBH4.
(b) Give reasons :
(i) Oxidation of propanal is easier than propanone.
(ii) a-hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones is acidic in nature.
Answer. (a) Compound A (C4H8O) gives positive, 2, 4-DNP test, it must be carbonyl compound. It gives iodoform test.
(b) (i) Oxidation of propanal is easier than propanone because aldehydes have one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl group while ketones have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the carbonyl group. Propanal easily oxidised to form acid with same number of carbon atoms whereas propanone is difficult to be oxidise and form acids with less number of carbon atoms.
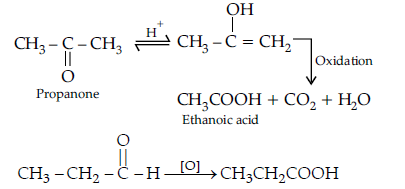
(ii) a-hydrogen of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature because carbonyl group has the great electron withdrawing effect and the molecule thus formed after the removal of a-Hydrogen is resonance stabilised.
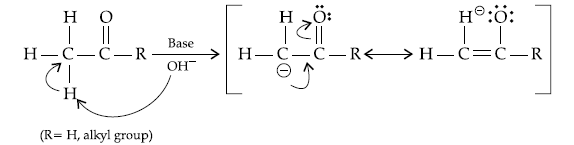
Question. (i) Write the products of the following reaction:
(ii) Write simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds ?
(a) Propanal and propanone
(b) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
Answer. (i) (a)
(b) CH3COOH
(c) CH3 — CH(Br)— COOH
(ii) (a) Add ammonical solution of silver nitrate / Tollen’s reagent to both the compounds, propanal will give silver mirror while propanone does not.
(b) Add NaHCO3 solution to both the compounds, benzoic acid will give effervescence and liberate CO2 while benzaldehyde will not.
Question. (i) Give a plausible explanation for each one of the following :
(a) Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
(b) There are two -NH2 groups in semicarbazide.
However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(ii) Carry out the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(a) Phenyl magnesium bromide to benzoic acid.
(b) Acetaldehyde to But-2-enal.
(c) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone.
Answer.
(b) Semicarbazide has two —NH2 groups.
One of them, which is directly attached to

is involved in resonance. Thus, electron density on this group decreases and it does not act as a nucleophile. In contrast, the lone pair of electrons on the other —NH2 group is available for nucleophilic attack.
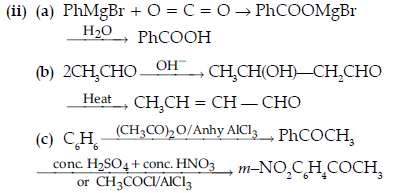
Question. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions :

Answer. A-C6H5COCH3
B-C6H5CH2CH3
C-C6H5COOH
D ,E -C6H5COONa, CHI3
Question. An aromatic compound ‘A‘ of molecular formula C7H6O2 undergoes a series of reactions as shown below.
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions :

Answer.
Question. (i) Account for the following :
(a) Propanal is more reactive than propanone towards nucleophilic reagents.
(b) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at meta-position.
(c) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group.
(ii) Give simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Acetophenone and benzaldehyde
(b) Benzoic acid and ethylbenzoate
Answer. (i) (a) Due to steric and +I effect of two methyl groups in propanone.
(b) Because it is a deactivating group/due to electron withdrawing carboxylic group resulting in decreased electron density at o- and p- position.
(c) Due to resonance, electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon is reduced.
(ii) (a) Add NaOH and I2 to both the compounds and heat, acetophenone forms yellow ppt of iodoform.
(b) Add NaHCO3 solution to both the compounds, benzoic acid will give effervescence and liberates CO2.
Question. (a) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in Cannizzaro reaction.
(b) Draw the structure of the semicarbazone of ethanal.
(c) Why pKa of F – CH2 – COOH is lower than that of Cl – CH2 – COOH ?
(d) Write the product in the following reaction
(e) How can you distinguish between propanal and propanone ?
Answer.

(or any other example)
(b) CH3CH=N–NHCONH2
(c) Stronger -I effect of fluorine, stronger acid less pka / strong electron withdrawing power of fluorine.
(d) CH3CH=CHCH2 CHO
(e) Silver mirror formed on adding ammonical silver nitrate to propanal and not with propanone.
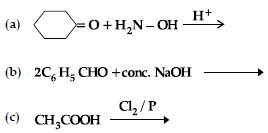
Question. (i) Write structures of A, B, C and D in the following reaction sequence:
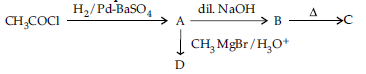
(ii) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points :
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3COOH
Answer. (i) A: CH3CHO; B: CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-CHO;
C: CH3-CH=CH-CHO; D: CH3-CH(CH3)-OH 1x4
(ii) CH3-O-CH3<CH3CHO<CH3-CH2-OH < CH3-COOH
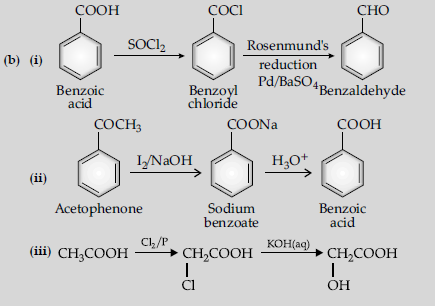
Question. (a) Write the reactions involved in the following :
(i) Etard reaction (ii) Stephen reduction
(b) How will you convert the following in not more than two steps :
(i) Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde
(ii) Acetophenone to benzoic acid
(iii) Ethanoic acid to 2-hydroxyethanoic acid
Answer.

Question. (i) Write the products of the following reactions :
(ii) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
(b) Propanal and Propanone
Answer.
(c) Cl–CH2–COOH
(ii) (a) NaHCO3 test.
(b) lodoform test./Fehling’s Test/Tollen’s Test
Question. (i) Describe the following reactions :
(a) Acetylation (b) Aldol condensation
(ii) Write the main product in the following equations :
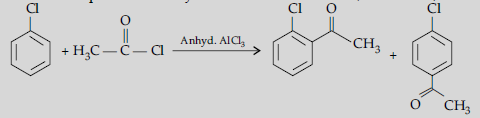
Answer. (i) (a) The acyl groups are introduced at ortho- and para- positions by reaction of chlorobenzene with acyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (a Lewis acid) as catalyst.
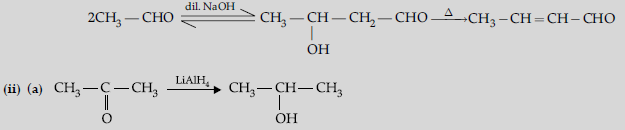
(b) Aldehydes and ketones having at least one a-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form b-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or b-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively.
Question. (i) Write the chemical reaction involved in Etard reaction.
(ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of their reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction:
CH3 – CHO, C6H5COCH3, HCHO
(iii) Why pKa of Cl — CH2 — COOH is lower than the pKa of CH3COOH?
(iv) Write the product in the following reaction.
(v) A and B are two functional isomers of compound C3H6O. On heating with NaOH and l2, isomer A forms yellow precipitate of iodoform whereas isomer B does not form any precipitate. Write the formulae of A and B.
Answer. (i) Etard reaction :
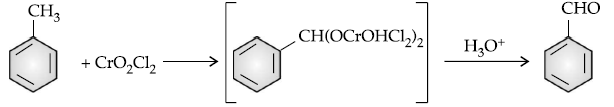
(ii) C6H5COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO
The reactivity of the compound towards nucleophilic addition reaction is directly proportional to electrophilic character of carbonyl carbon. In ketone, the +I group lowers the electrophilicity. Whereas, +I of methyl group in ethanal is less than that of –C6H5. Hence, ethanal is most reactive than acetophenone.
(iii) –Cl being electron withdrawing group stabilizes the ClCH2COO– anion and increases the acidic strength.
Therefore, chloroacetic acid has lower pKa value than acetic acid.
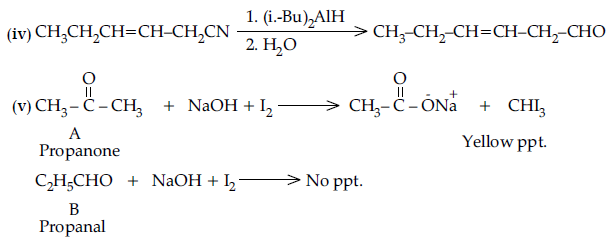
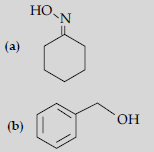
Question. (i) Draw the structures of the following derivatives :
(a) Propanone oxime,
(b) Semicarbazone of CH3CHO.
(ii) How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds ? Give the chemical equations involved.
(a) CH3—CH3
(c) CH3CH2OH
Answer.

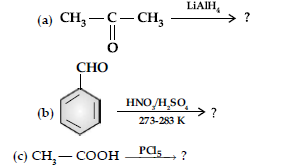
Question. (i) Write structure of the product(s) formed :

(ii) How will you bring the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(a) Propanone to propene
(b) Benzyl chloride to phenyl ethanoic acid
Answer.

Question. (i) Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the pair of organic compounds :
Ethanal and Propanal.
(ii) Name and complete the following chemical reaction :

(iii) Draw the structures of the following derivatives :
(a) The 2, 4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde,
(b) Acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
(c) Cyclopropanone oxime.
Answer. (i) Ethanal and propanal can be distinguished by Iodoform test.
Ethanal gives a yellow precipitate of iodoform with an alkaline solution of NaOH. Propanal does not gives this test.
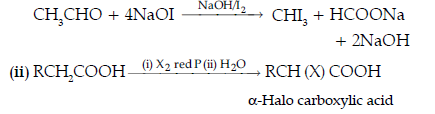
The name of the reaction is Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction.
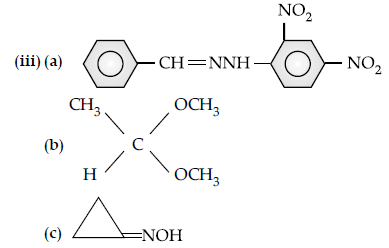
Question. (a) Write the product(s) in the following reactions:

(b) Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Butanal and Butan-2-one
(ii) Benzoic acid and Phenol
Answer.
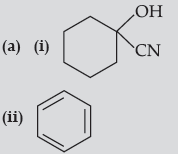
(iii) CH3 — CH = CH — CHO
(b) (i) Tollen’s reagent test : Add ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent) in both the solutions. Butanal gives silver mirror whereas Butan-2-one does not.
(ii) Add neutral FeCl3 in both the solutions, phenol forms violet colour but benzoic acid does not.