Please refer to Class 10 Science Sample Paper Term 1 Set B with solutions below. The following CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Science has been prepared as per the latest pattern and examination guidelines issued by CBSE. By practicing the Science Sample Paper for Class 10 students will be able to improve their understanding of the subject and get more marks.
CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper for Term 1
Section – A
1. Methane is a one-carbon compound in which the carbon is attached by single bonds to four hydrogen atoms. It is a colourless, odourless, non-toxic but flammable gas (b.p. -161°C). Study the electron dot structure of methane.
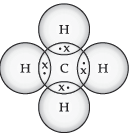
(a) Name the type of bonds formed in this compound.
(b) Why are such compounds poor conductors of electricity?
Ans. Recall covalent bonds.
2. An element “X” has atomic number 13. The atomic number or proton number (symbol Z) of a chemical element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. In an uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.
(a) What is the group and period number to which this element “X” belongs?
(b) Is this element “X” a metal or a non- metal? Justify your answer.
Ans. (a) The element X belongs to the 3rd period and 15th group
(b) X is a metal
3. Fertilization and implantation are the most critical events in the reproduction process. In this process, both egg and sperm are fused together to form a zygote. Later, it gets implanted into the uterus and the development of an organism starts. The given flowchart explains the process. Study the chart and answer the questions given below:
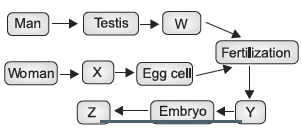
(a) Identify the labels X, Y and Z.
(b) Where does the process of fertilisation takes place in female body?
Ans. Fertilisation is the fusion of male and female gamete to form diploid zygote which divides further to from embryo.
4. In biology class, a teacher shows here students, the process of germination of pollen on stigma. Also, she told that the germination of pollen grain in stigma occurs in ‘in vivo’ conditions. It is called as fertilisation. Pollen grains are the male gametes and stigma is the female floral part. Ovule contains the egg cell. Based on the information and diagram given below, answer the questions given below:
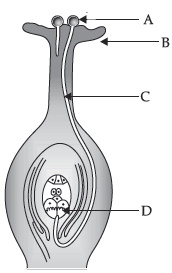
(a) Identify ‘A’ and explain how it reaches part ‘B’.
(b) What happens to the part marked ‘D’ after fertilisation is over?
Ans. Part ‘A’ is pollen grain, Part ‘D’ is an egg cell.
5. In a cross between plants with purple flowers and plants with white flowers, the F1 had all white flowers. When F1 generation was self bred, the F2 generation gave rise to 100 individuals, 75 of which had white flowers. Make a cross and find the genotypes of F2 individual? What is the ratio of purple and white flowered plants in F2 generation?
Ans. Ratio between White: Purple flowers are: 3:1
OR
Chromosomes are long thread-like structures which contain hereditary information of the individual and are thereby the carriers of genes and hereditary characteristics.
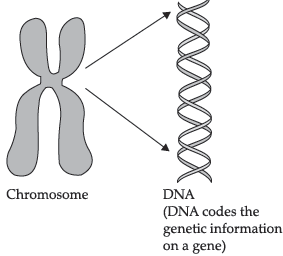
Explain how in sexually reproducing organisms the number of chromosomes in the progeny is maintained?
Ans. When two gametes fuse, the zygote formed contains the full set of chromosomes. Hence, The formation of gametes by meiosis helps to maintain the number of chromosomes in the progeny.
6. A compass consists of a small metal needle which is magnetised itself and which is free to turn in any direction. Therefore in the presence of a magnetic field, the needle is able to line up in the same direction as the field. Shivani placed a magnetic compass needle in the plane of paper near point A as shown in the figure.
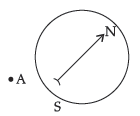
(a) In which plane should a straight current carrying conductor be placed so that it passes through point A and there is no change in the deflection of the compass?
(b) Under what condition is the deflection maximum and why?
Ans.Right hand thumb rule is followed to find magnetic field in a straight current carrying conductor.
OR
(a) What is magnetic effect of current?
(b) How can you determine the polarity of a current carrying circular loop just by watching the direction of current?
Ans. (a) When an electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet. This is the magnetic effect of the electric current
(b) Clock rule determines the polarity of a circular current loop.
7. Rahul was studying a terrestrial food chain. He observed the flow of energy as follows:
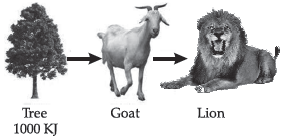
(a) If autotrophs occupying the first trophic level are called producers, what are herbivores called as ?
(b) How much energy does the lion get in the above food chain ?
Ans. (a) Primary consumers.
(b) Apply 10 percent law
OR
The diagram shows the flow of energy through an ecosystem.
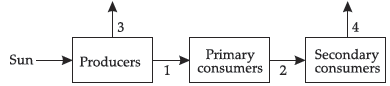
The smallest amount of energy transferred between organisms and the largest amount of energy lost to the ecosystem is represented by which arrows?
Ans. The smallest amount of energy transferred is represented by arrow 2 and largest energy loss by arrow 3.
Section – B
8. Valency is the combining capacity of an element. The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom are known as ‘Valence electrons’. Based on the group valency of elements, write the molecular formula of the following compounds giving justification for each:
(a) Oxide of first group elements.
(b) Halide of the elements of group thirteen, and
(c) Compound formed when an element A of group 2 combines with an element B of group 17.
Ans. (a) Valency of first group elements is , Hence, oxide of first group is X2O
(b) Group 13 has a valency of 3 , Hence, halide of group 13 is MX3
(c) The valency of the Group 2 elements is +2 and that of Group 16 elements is -2. Group 2 loses electrons and group 16 accepts electrons. Hence, compounds formed are MY.
9. Explain the following:
(a) CH3COOH is a weak acid.
(b) Propene undergoes addition reaction.
(c) The gas stoves have inlets for air.
Ans. (a) CH3COOH is weak acid because it is partially ionised.
(b) Propene is an alkene, i.e it contains a double bond. This double bond is weak, hence upon external interference it will easily break. That’s why when propene reacts with something, say bromine, this double bond breaks and the bromine atoms get ‘added’ to the unsaturated propene compound (forming a dibromide).
(c) Both the gas stoves and the kerosene stoves have inlets for Air because ,The oxygen present in the air is needed for complete combustion and it produces the blue flame which signifies the fuel is completely combusting and this flame is the most fuel efficient and time saving flame for cooking purpose.
10. Study the given cross showing self pollination in F1
RRYY × rryy (Parents)
(Round Yellow) (Wrinkled Green)
RrYy × ______ (F1 generation)
(Round Yellow)
Fill in the blank and answer the questions that follows:
(a) In the above question, what is the combination of characters in the F2 progeny? What are the ratios?
(b) What does the result in F1 generation, signifies?
Ans. Recall dihybrid cross.
11. B1, B2 and B3 are three identical bulbs connected as shown in the figure. When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3 A is recorded by the ammeter A.
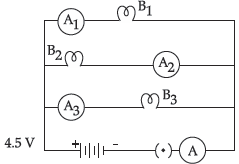
(a) What happens to the glow of the other two bulbs when the bulb B1 gets fused?
(b) What happens to the reading of A1, A2, A3 and A when the bulb B2 gets fused?
Ans. When B3 fuses, rest bulbs glow with same intensity.
12. Calculate the equivalent resistance and potential difference between the points A and B is the circuit where 2A is the circuit current as shown below:

(a) Find the equivalent resistance between the points D and B.
(b) Find the current through DAB, DCB and DB path.
Ans. Resistances in series connections, Req = R1 + R2
Resistances in parallel connection, Req = R1R2 / R1 + R2
13. Layer P shields the surface of the earth from the UV radiation. It is found in the stratosphere around 15–30 km above the earth’s surface. It protects the life on earth by absorbing harmful ultraviolet-B (UVB) radiation from the sun.

(a) Identify “the layer P”. How it is produced?
(b) Name the synthetic chemicals mainly responsible for its drop in the atmosphere. How can the use of these chemicals be reduced?
Ans. Ozone layer act as a protective blanket around the earth that prevents harmful UV rays from entering the earth. CFCs are mainly responsible for its depletion.
Section – C
14. In a pea plant, the phenotypes like round seed and yellow colour are completely dominant over the other i.e., green wrinkled seeds. Sanjana decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with yellow round and green wrinkled seeds and obtained the following result. Based on the schematic diagram, answer the following questions.

(a) Write the phenotypes of F1 progeny.
(b) Name the phenotypes produced in F2 progeny upon self pollination of F1 progeny.
(c) Identify 1, 4, 5 and 6 in the diagram.
Ans. Phenotype of all the plants is Round and yellow seeds. The above cross shows round and yellow seeds in the F1 generation.
OR
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea seeds that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
Ans. 1. Tallness and dwarfness.
2. Green seed and yellow seed.
15. A student fixes a sheet of white paper on a drawing board. He places a bar magnet in the centre of it. He sprinkles some iron filings uniformly around the bar magnet. Then he taps the board gently and observes that the iron filings arrange themselves in a particular pattern.
(a) Why do the iron filings arrange in a pattern?
(b) What do the lines along which the iron filings align represent?
(c) What does the crowding of iron filings at the end of the magnet indicate? How the strength of magnetic field is indicated?
Ans. (a) Due to the force exerted by the magnet within its magnetic field the iron fillings get attracted and arrange themselves in a particular pattern which is given by the magnetic lines of bar magnet.
(b) The lines along which the iron fillings arrange themselves represent magnetic field lines of the bar magnet.
(c) Crowding of iron filings at the ends of the magnet indicates that the magnetic field is strongest near the poles of the magnet.

