Please refer to Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper Term 2 Set E with solutions below. The following CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Social Science has been prepared as per the latest pattern and examination guidelines issued by CBSE. By practicing the Social Science Sample Paper for Class 10 students will be able to improve their understanding of the subject and get more marks.
CBSE Class 10 Social Science Sample Paper for Term 2
Section A
1. Why did large sections of Muslims could not respond to the call for a united struggle through Civil Disobedience Movement ?
Answer : Because:
(a) They felt themselves alienated from the Congress after the decline of the Non-Cooperation Khilafat Movement.
(b) They feared that their culture and identity would be submerged under the domination of a Hindu majority.
2. How did the revival of Indian folklore help to develop the ideas of nationalism ?
Answer : (a) National folk gave a true picture of traditional culture that had been corrupted by outside forces.
(b) National folk song were helpful in discovering one’s national identity.
(c) They were helpful in restoring a sense of pride in one’s past.
3. Describe the importance of formal sources of credit in the economic development.
Answer : Importance of formal sources of credit in economic development are as follows :
(i) It is monitored by the Reserve Bank of India or regulated by the Government of India and thus helps in bringing order to the system of lending and borrowing in the country.
(ii) Provides fixed interest rate to all sections of society.
(iii) Limits the scope of using unfair means to repay the payment.
(iv) Less interest rate and accessible to all, rich or poor.
4. Suggest any three ways to improve public facilities in India.
Answer : The three ways to improve public facilities in India are given below :
(i) Imparting education because it is the most important public facility which is required both by the rich as well as the poor.
(ii) Improving Public Distribution System because it is another important facility which plays an important role in providing food security to the people.
(iii) Improving infrastructure facilities like railway, airways, waterways, banking etc. to become affordable for common people.
5. The following table shows the details of Megha’s housing loan:
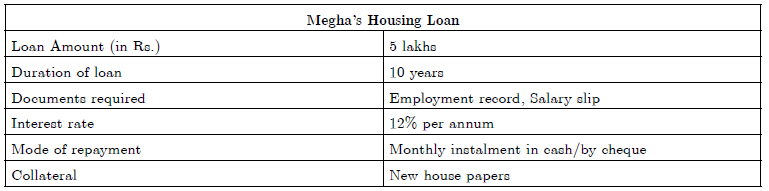
5.1. Calculate the total number of instalments which will be paid by Megha in repayment of loan.
Answer : 12 × 10 = 120 instalments.
5.2. “The bank retained as collateral the papers of the new house.” What do you mean by the word ‘collateral’?
Answer : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns (such as land, building, vehicle, livestocks, deposits with banks) and uses this as a guarantee to a lender until the loan is repaid. If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to obtain payment.
Section B
6. “Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for fast development”. Support the statement with suitable examples.
Answer : 1. Efficient and good transport for speedy movement of goods and services to different parts of the India and to fulfil the needs of the people is needed.
2. Goods and services do not move from supply location to demand locations on their own. This necessitates the need for transport.
3. Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. These are known to traders who make the products come to the consumers by transportation.
4. Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movements over space.
OR
Why are the means of transportation and communication called the lifelines of national economy ? Give any four reasons to support your answer.
Answer : 1. They bring far-flung areas of a country quite closer to each other and carry the greatest number of passengers to longest journey in lesser time with more comforts.
2. They carry thousands of tonnes of different commodities from one part of the country to the other and thus avoid much hardships of the people.
3. In war times, they bring the whole country at the back of the armed forces and facilitate the movement of arms, ammunition and other supplies.
4. Means of transport and communication are also used by the government to maintain law and order.
7. What is a multi-party system? Why has India adopted a multi-party system? Explain.
Answer : (a) If several parties compete for power, and more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power either on their own strength or in alliance with others, it is called a multiparty system. In India, we have a multi-party system.
(b) India has adopted multi-party system because the social and geographical diversity is not easily absorbed by two or three political parties. Secondly, India is such a large country that it may not be possible for a political party to have its organisation or branches in every corner of the country.
Thirdly, people of different regions, castes, religions and communities have different problems which compel them to have their political party to press for demands for their welfare and development.
8. How is social diversity accommodated in democracy? Explain with examples.
Answer : It is a fair expectation that democracy should produce a harmonious social life. Democracy must fulfill two conditions in order to achieve social harmony even though there is social diversity.
(i) It is necessary to understand that democracy is not simply ruled by majority opinion. The majority always needs to work with the minority so that, the possibility of tensions, becoming explosive or violent reduces. Majority and minority opinions are not permanent.
(ii) It is also necessary that rule of the majority does not become the rule of the majority community in terms of religion or race or linguistic group. Rule of the majority means that in case of every decision or every election, different persons and groups may and should form a majority.
Section C
9. “The Civil Disobedience Movement was different from the Non-co-operation Movement.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Civil Disobedience Movement : It was a movement revealing negligence and defiance towards the British law. It was launched by Mahatma Gandhi in April 1930.
Following were the four features of Civil Disobedience Movement :
(i) The Civil Disobedience Movement was a unique movement. Gandhiji found in salt a motivating and powerful symbol that could unite the nation against the government monopoly over its production. In the beginning, the issue of salt looked ordinary, however, it provide the most stirring one.
(ii) The Civil Disobedience Movement was slightly different from the Non-cooperation Movement. During the Civil Disobedience Movement people were asked not only to deny co-operation with the British but also to break colonial laws.
(iii) The Civil Disobedience Movement spread like wild fire. The strong wind of the movement reenergised all the classes of the nation. Salt law was broken, foreign cloth was boycotted and liquor shops were picketed, peasants declined to pay revenue and Chaukidari taxes.
(iv) The refulgence of the Civil Disobedience Movement blended the colonial government. One of the most important features of this movement was the large scale participation of women. Thousands of women come out of their homes and participated in protest marches, manufactured salt and picketed foreign cloth and liquor shops.
OR
How had Non-Cooperation Movement spread in cities ? Explain.
Answer : The Non-Cooperation Movement spread in cities as mentioned below :
1. In the towns, middle classes participated in the movement in the following ways :
(i) Students left the schools and colleges. Headmasters and teachers resigned. Lawyers gave up their practice.
(ii) Elections were boycotted except in Madras, where Justice Party, took part in elections.
(iii) Foreign goods were boycotted.
(iv) Liquor shops were picketed.
(v) Foreign clothes were burnt in huge bonfires.
(vi) Many traders refused to import foreign cloth or trade in foreign goods.
2. Economic effects of Non-Cooperation Movement were as given below :
(i) The import of foreign cloth decreased from Rs.102 crores to Rs.57 crore between 1921 and 1922.
(ii) In many places merchants and traders refused to trade in foreign goods or finance foreign trade.
(iii) People discarded foreign clothes and started wearing only Indian clothes. This led to increased production by the Indian textile mills and handlooms.
3. The movement however slowed down in towns due to various reason as mentioned below :
(i) Khadi was expensive.
(ii) No alternative Indian institutions in place of British institutions.
10. ‘The challenge of sustainable development requires control over industrial pollution.’ Substantiate the statement with examples.
Answer : While industries contribute significantly to India’s economic growth and development, the increase in pollution of land, water, air and noise resulting degradation of environment that they have caused is significant and cannot be ignored.
(i) Industries are responsible for air, water, land and noise pollution. The polluting industries also include thermal power plants. Air pollution adversely affects human health, animals, plants, buildings and the atmosphere as a whole. Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and affluents discharged into rivers.
(ii) Wastes from nuclear power plants, nuclear and weapon production facilities cause cancers, birth defects and miscarriages. It causes soil pollution. Noise pollution leads not only anger and irritation but cause hearing impairment, increased heart rate and blood pressure among other physiological effects.
(iii) Industries need to minimise the use of water by reusing and recycling water. Industrial wastes need to be treated in effluent plants before dumping them in rivers.
(iv) Electrostatic precipitators, fabric filters, scrubbers and inertial separators should be used to particulate matter being released in the air. Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories. Generators should be avoided to reduce diesel pollution, should be fitted with silencers. All machineries can be re-designed to increase energy efficiency.
(v) Thermal plants should be avoided. Wastes should be recycled. All industries and factories should have license. Central Pollution Control Board should keep regular check on the industries.
OR
Explain with examples any five factors that are responsible for industrial location.
Answer : Factors responsible for industrial location are as follows :
(i) Availability of raw material is one major basic factor for the location of any industry, e.g. : Jute mills in West bengal are concentrated close to the source of raw material.
(ii) Climate also plays a major role in the concentration of industries at a certain place. Favourable weather conditions required for the growth and harvesting of the crop causes its industries to be located in certain places. For e.g. Cotton textile industry are generally found in Maharastra and Gujarat because of favourable climatic conditions.
(iii) Availability of capital and other infras-tructural facilities is also one reason. It is due to the availability of capital that Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai became big industrial centres. These places have banking facilities and well developed infrastructure.
(iv) Availability of both skilled and unskilled labour also governs the location of an industry. Cheap and abundant labour is one necessary condition which affects location of an industry.
(v) The entire process of manufacturing is futile until the finished products reach the market and the consumers. Thus, availability of a good market near by also benefits the owners.
(vi) Government policies, peace, protection of environment play a vital role in the location of industries.
Section D
11. Read the sources given below and answer the questions that follows:
Source A- Dignity and Freedom of the Citizens
Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings. Often conflicts arise among individuals because some feel that they are not treated with due respect. The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy. Democracies throughout the world have recognised this, at least in principle. This has been achieved in various degrees in various democracies.
Source B- Non-democratic Regimes
Democracy stands much superior to any other form of government in promoting dignity and freedom of the individual. Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings. Non-democratic regimes often turn a blind eye to or suppress internal social differences. Ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts is thus a definite plus point of democratic regimes. It is necessary to understand that democracy is not simply rule by majority opinion.
Source C- Strength of Democracy
Whenever possible and necessary, citizens should be able to participate in decision making that affects them all. Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity. There are instances still of caste-based inequalities and atrocities, but these lack the moral and legal foundations. Perhaps it is the recognition that makes ordinary citizens value their democratic rights.
Question :
11.1. What are the basis of democracy?
Answer : The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy.
11.2. Why democracy is considered as the superior form of government?
Answer : The democracy is considered as the superior form of government because it promotes dignity and freedom of the individual.
11.3. How does the Indian democracy strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes?
Answer : Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity as they are able to participate in decision making that affects them all.
12. Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Tax on imports is an example of trade barrier. It is called a barrier because some restriction has been set up. Governments can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and how much of each, should come into the country. The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment. This was considered necessary to protect the producers within the country from foreign competition. Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s, and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to come up. Thus, India allowed imports of only essential items such as machinery, fertilisers, petroleum etc. Note that all developed countries, during the early stages of development, have given protection to domestic producers through a variety of means. Starting around 1991, some far reaching changes in policy were made in India. The government decided that the time had come for Indian producers to compete with producers around the globe. It felt that competition would improve the performance of producers within the country since they would have to improve their quality. This decision was supported by powerful international organisations. Thus, barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment were removed to a large extent. This meant that goods could be imported and exported easily and also foreign companies could set up factories and offices here. Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is what is known as liberalisation.
Question :
12.1. What is trade barrier? Give one example.
Answer : When the government puts some restriction on the foreign trade and foreign investment then it is called trade barrier. One example of trade barrier is tax.
12.2. What do you mean by the term liberalisation?
Answer : Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as liberalisation.
12.3. How does government regulate foreign trade?
Answer : Governments can use trade barriers:
(i) To increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade.
(ii) To decide what kinds of goods and how much of each should come into the country.
Section E
13. On the given outline Political Map of India, locate the following:
A. The place where Indian National Congress session was held in December, 1920
B. Singrauli Thermal Power Plant
OR
C. Gandhinagar Software Technology Park
D. Kochi Port
Answer : A. Nagpur
B. Singrauli Thermal Power Plant
OR
C. Gandhinagar Software Technology Park
D. Kochi Port

