Please refer to Amines HOTs Class 12 Chemistry provided below with Amines. All HOTs for Class 12 Chemistry with answers provided below have been designed as per the latest syllabus and examination petter issued by CBSE, NCERT, KVS. Students of Standard 12 Chemistry should learn the solved HOTS for Class 12 Chemistry provided below to gain better marks in examinations.
Amines Class 12 Chemistry HOTs
Question. Which of the following methods of preparation of amines will give same number of carbon atoms in the chain of amines as in the reactant?
(a) Reaction of nitrite with LiAlH4.
(b) Reaction of amide with LiAlH4 followed by treatment with water.
(c) Heating alkylhalide with potassium salt of phthalimide followed by hydrolysis.
(d) Treatment of amide with bromine in aquesous solution of sodium hydroxide.
Answer
C
Question. The basic character of amines is due to
(a) presence of nitrogen atom
(b) lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom
(c) tetrahedral structure
(d) high electronegativity of nitrogen
Answer
B
Question. The IUPAC name of the compound having formula,
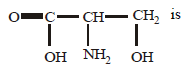
(a) 3-amino-hydroxy propine acid
(b) 2-amino-propan-3-oic acid
(c) amino hydroxy propanoic acid
(d) 2-amino-3-hydroxy propanoic acid
Answer
D
Question. The number of primary amines of formula C4H11N is :
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 2
Answer
C
Question. The correct order of basicity in amines
(i) C2H5NH2
(ii) CH3NH2
(iii) (CH3)2NH
(iv) (CH3)3N
(a) (i) < (iv) < (ii) < (iii)
(b) (iv) < (ii) < (iii) < (i)
(c) (i) < (ii) < (iii) < (iv)
(d) (ii) < (iii) < (iv) < (i)
Answer
B
Question. The correct IUPAC name for CH2 = CHCH2NHCH3 is
(a) Allylmethylamine
(b) 2-amino-4-pentene
(c) 4-aminopent-1-ene
(d) N-methylprop-2-en-1-amine
Answer
D
Question. The conjugate base of (CH3)2NH+2 is
(a) (CH3)2NH
(b) (CH3)2N+
(c) (CH3)3N+
(d) (CH3)2N–
Answer
A
Question. Intermediates formed during reaction of RCONH2 with Br2 and KOH are
(a) RCONHBr and RNCO
(b) RNHCOBr and RNCO
(c) RNHBr and RCONHBr
(d) RCONBr2
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following reactions will not give a primary amine?
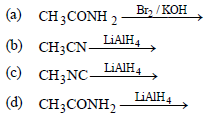
Answer
C
Question. The compound obtained by heating a mixture of a primary amine and chloroform with ethanolic potassium hydroxide (KOH) is
(a) an alkyl cyanide
(b) a nitro compound
(c) an alkyl isocyanide
(d) an amide
Answer
C
Question. Secondary amines could be prepared by
(a) reduction of nitriles
(b) Hofmann bromamide reaction
(c) reduction of amides
(d) reduction of isonitriles
Answer
D
Question. Treatment of ammonia with excess of ethyl iodide will yield
(a) diethylamine
(b) ethylamine
(c) triethylamine
(d) tetraethylammonium iodide
Answer
D
Question. High basicity of Me2NH relative to Me3N is attributed to:
(a) effect of solvent
(b) inductive effect of Me
(c) shape of Me2NH
(d) shape of Me3N
Answer
A
Question. For alkylation of ammonia which of the following is not used?
(a) CH3–X
(b) CH3–CH2–X
(c) (CH3)2CH–X
(d) (CH3)3C–X
Answer
D
Question. A secondary amine is
(a) a compound with two carbon atoms and an –NH2 group.
(b) a compound containing two –NH2 groups.
(c) a compound in which hydrogens of NH3 have been replaced by two alkyl groups.
(d) a compound with an –NH2 group on carbon atom in number two position.
Answer
C
Question. Amongst the given set of reactants, the most appropriate for preparing 2° amine is ___________.
(a) 2°R–Br + NH3
(b) 2°R–Br + NaCN followed by H2/Pt
(c) 1°R–NH2 + RCHO followed by H2/Pt
(d) 1°R–Br (2 mol) + Potassium phthalimide followed by H3O+/heat
Answer
C
Question. Carbylamine reaction is used for the detection of
(a) aliphatic 2° amines
(b) aliphatic 1° amines
(c) aromatic 1° amines
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. The reduction of nitro compounds is most preferred in the presence of
(a) Pd/H2 in ethanol
(b) Sn + HCl
(c) finely divided Ni
(d) iron scrap and HCl.
Answer
D
Question. The total number of electrons around the nitrogen atom in amines are
(a) 8
(b) 7
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer
C
Question. An alkyl or benzyl halide on reaction with an ethanolic solution of ammonia undergoes
(a) electrophilic substitution reaction
(b) nucleophilic substitution reaction.
(c) free radical mechanism.
(d) nucleophilic addition reaction.
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following will give primary amine only ?
(i) ammonia + propylchloride
(ii) potassium pthalimide + ethylchloride
(iii) potassium pthalimide + chlorobenzene
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
A
Question. The general formula of quaternary ammonium compound is
(a) R–NH2
(b) R3N
(c) R4N+ X–
(d) NH4X
Answer
C
Question. Amines have
(a) Garlic odour
(b) Fishy odour
(c) Jasmine odour
(d) Bitter almonds odour
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following statements about primary amines is ‘False’ ?
(a) Alkyl amines are stronger bases than aryl amines
(b) Alkyl amines react with nitrous acid to produce alcohols
(c) Aryl amines react with nitrous acid to produce phenols
(d) Alkyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is not characteristic of amines?
(a) They smell like ammonia
(b) They are inflammable in air
(c) They show the property of hydrogen bonding
(d) They are amphoteric in nature
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following should be most volatile?
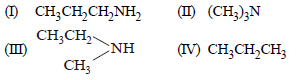
(a) II
(b) IV
(c) I
(d) III
Answer
B
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below.
(a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion.
(b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion
(c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect
(d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : Acetanilide is less basic than aniline.
Reason : Acetylation of aniline results in decrease of electron density on nitrogen.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Nitrating mixture used for carrying out nitration of benzene consists of conc. HNO3 + conc. H2SO4.
Reason : In presence of H2SO4, HNO3 acts as a base and produces NO2+ ions.
Answer
A
Question. Assertoin : Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Reason : –NH2 group of aniline reacts with AlCl3 (Lewis acid) to give acid-base reaction.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Amines are basic in nature.
Reason : Amines have lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Aromatic 1°amines can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Reason : Aryl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
Answer
A
Question. Assertion : Nitration of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason : Acetylation increases the electron-density in the benzene ring.
Answer
C
Question. Assertion : Only a small amount of HCl is required in the reduction of nitro compounds with iron scrap and HCl in the presence of steam.
Reason : FeCl2 formed gets hydrolysed to release HCl during the reaction.
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Acylation of amines gives a monosubstituted product whereas alkylation of amines gives polysubstituted product.
Reason : Acyl group sterically hinders the approach of further acyl groups
Answer
C
Very Short Answer questions:
Question. Write the structure of N‐Ethyl‐N‐methylaniline.
Answer.
Question. Why is aniline acylated before its nitration?
Answer. To prevent it from oxidation
Question. Write structures and IUPAC names of the amide which gives propanamine by Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Answer.
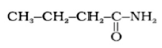
, Butanamide
Question. What is Hinsberg’s reagent?
Answer. Benzene sulphonyl chloride
Question. Ethylamine is soluble in water but aniline is not, why?
Answer. Ethylamine forms intermolecular H‐bond with water, but aniline does not form H‐bond to a very large extent due to the presence of large hydrophobic –C6H5 group.
Short Answer questions:
Question. Write the structure and IUPAC name of t-butylamine.
Answer. 2-Methylpropan-2-amine
Question. Which diazonium salt is insoluble in water at room temprature?
Answer. Benzene diazonium fluoro borate (C6H5N2 F).
Question. Why ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not ?
Answer. Ethylamine when added to water forms intermolecular H−bonds with water. Hence, it is soluble in water.
Question. Out of CH3NH2 and CH3CH2NH2 which has higher boiling point and why ?
Answer. CH3CH2NH2 because bigger the alkyl group more is the surface area higher is the magnitude of van der Waals force.
Question. What is the hybridisation of N in (CH3)3N and shape of (CH3)3N ?
Answer. Hybridisation of N in (CH3)3N is sp3 and shape of (CH3)3N is trigonal pyramidal.
Question. Out of Butan-1-ol and butan-1-amine ,which will be more soluble in water and why?
Answer. Butan-1-ol are more polar than amines and forms stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonds with water molecules than amines.
Question. Why are primary amines higher boiling than tertiary amines ?
Answer. Primary amines have two hydrogen atoms on the N atom and therefore form intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Tertiary amines do not have hydrogen atoms on the N atom and therefore,these do not form hydrogen bonds.
Question. Which diazonium salt is stable at room temprature.
Answer. Benzene diazonium fluoro borate(C6H5N2 F).
Question. Which one is more basic CH3NH2 or (CH3)3N in gaseous phase and why ?
Answer. (CH3)3N is more basic because greater number of alkyl groups increase the magnitude of +I effect so increase the basicity .
Question. Which one is more basic CH3NH2 or (CH3)3N in gaseous phase and why ?
Answer. (CH3)3N is more basic because greater number of alkyl groups increase the magnitude of +I effect so increase the basicity .
Question. Give plausible explanation for each of the following:
(a) Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
(b) Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than aromatic amines?
Answer. (a) Due to strong intermolecular H‐bonding in primary amines.
(b) In aromatic amines lone pair is engaged with benzene in resonance.
Question. Arrange the following:
(a) In decreasing order of the pKbvalues:
C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2NH and C6H5NH2
(b) In increasing order of basic strength: Aniline, p‐nitroaniline and p‐toluidine
Answer. (a) C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3,C2H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH
(b) p‐Nitroaniline , aniline, p‐toluidine
Question. How can you convert an amide into an amine having one carbon less than the starting compound?
Name the reaction.
Answer. By using Hoffmann bromamide reaction
Question. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds and classify them into primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
(a) C6H5NHCH3
Answer. (a) N‐Methyl aniline 20
(b) (CH3CH2)2NCH3
(b) N‐Ethyl‐N‐methylethanamine 30
Question. Write the structures of: (a) 3‐Bromobenzenamine (b) 3‐Chlorobutanamide
Answer. (a)
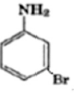
(b) CH3CH(Cl)CH2CONH2
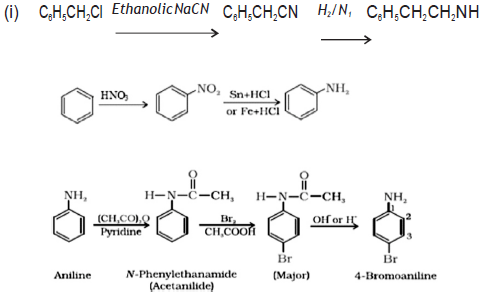
Question. How will you convert:
(a) Benzyl chloride to 2‐phenylethanamine
(b) Benzene to Aniline
(c) Aniline to p‐bromoaniline
Answer.
Question. Account for the following:
(a) Although amino group is o, p− directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions,aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m‐nitroaniline.
(b) Aniline does not undergo Friedel‐Crafts reaction.
(c) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesizing primary amines.
Answer. (a) Because nitration is carried out in an acidic medium. In an acidic medium, aniline is protonated to give anilinium ion which is meta‐directing.
(b) Friedel‐Craft reaction is carried out in the presence of AlCl3. But AlCl3 acts as a Lewis acid, while aniline acts as a Lewis base. Thus, aniline reacts with AlCl3 to form a salt.
(c) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis results in the formation of primary amines only. Secondary and tertiary amines are not formed in this synthesis. Thus, a pure primary amine can be obtained.Therefore,Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesizing primary amines.
Question. Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
(a) Methylamine and dimethylamine
(b) Ethylamine and aniline
(c) Aniline and benzylamine
Answer. (a) Carbylamine reaction
(b) Azo dye Test
(c) Azo dye Test
Question. Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions:
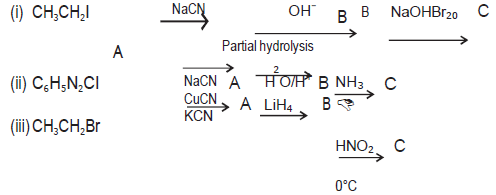
Answer. (a) (A)CH3CH2CN (B)CH3CH2CONH2 (C)CH3CH2NH2
(b) (A)C6H5CN (B)C6H5COOH (C)C6H5CONH2
(c) (A)CH3CH2CN (B)CH3CH2CH2NH2 (C)CH3CH2CH2OH