Please refer to the Manufacturing Industries Notes Class 10 Social Science given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 10th Social Science book. We have provided chapter-wise Notes for Class 10 Social Science as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science
Students of Class 10 Social Science will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic-wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 10 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Points to Remember: Production of more valuable goods in large quantities after processing the raw material is called manufacturing. The extensive form of manufacturing is called Industry.




Cotton Textile Industry
• First successful cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
• Mahatma Gandhi laid emphasis on the spinning of yarn and wearing khadi so that weavers could get employment.
• In the early years the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belt of Maharashtra and Gujrat. Availability of raw material, market, transport facilities (port), labour and moist climate contributed towards its localisation.
• While spinning continues to be centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamilnadu, weaving is highly decentralized to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and design of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery, etc.
Jute Industry
• India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods and stands at second place as an exporter after Bangladesh.
• In India Jute Industry is highly concentrated mainly around the banks of Hugli River-
(a) Proximity of the jute producing area
(b) Inexpensive transportation,
(c) Cheap labour
(d) Abundant water supply
(e) Kolkata as a large urban centre provides banking, insurance and port facilities for export to the jute goods.
• Challenges faced by the industry include the stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitute and from other competitors like Bangladesh, Brazil etc. However the National Jute policy ensured good prices to jute farmers.
Sugar Industry
• India stands second as a world producer of sugar but occupies the first place in the production of gur and khandsari.
• Sugar mills in India spread over Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Gujarat.
• In recent years there is a tendency for the mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states especially in Maharashtra.
This is because-
(a) Higher sucrose content in the sugar cane,
(b) Cool climate,
(c) Moreover the cooperatives are more successful.
• Major Challenges-
(a) Seasonal nature,
(b) Old and inefficient methods of production,
(c) Transport delay
Iron and Steel Industry
• The iron and steel Industry is the basic industry since all the other industries- heavy, medium, and light depends on it for their machinery.
• Iron ore, coking coal and limestone in the ratio of 4:2:1.
• In the year 2016 with 95.6 million tons of steel production, India ranked third among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge Iron.
• Most of the public sector undertakings market their steel through Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL).
• Chotanagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of Iron and Steel industries. It is because –
(a) Low cost iron ore,
(b) High grade raw materials in proximity,
(c) Cheap labour
(d) Local market
Reasons for its not growing in full potential in India-
(a) High costs and limited availability of coking coal,
(b) Lower productivity of labours,
(c) Irregular supply of energy,
(d) Poor infrastructure
Aluminium Smelting
• Aluminium Smelting is the second most important metallurgical industry in India.
• It is light, resistant to corrosion, a good conductor of heat, mailable and becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals.
• Aluminium smelting plants in India are located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh ,Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
Two key need areas for the establishment of this industry are-
• Uninterrupted power supply,
• Availability of cheap raw material.
Chemical Industry
• Both organic and inorganic types of chemicals are produced in India.
• Organic chemicals include petrochemicals, which are used for manufacturing of synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber, plastics, dye-stuffs, drugs and pharmaceuticals.
• Inorganic chemicals include sulphuric acid, nitric acid, alkaline, soda ash.
• It contributes approximately 3% of the GDP.
• It is the third largest in Asia and occupies the twelfth place in the world.
Fertiliser Industry
• The fertilizer industry is centered around the production of nitrogenous fertilizers (mainly Urea), Phosphatic fertilizers and ammonium phosphate (DAP) and complex fertilizers.
• Potash is entirely imported as the country does not have any reserves of commercially usable potassium compound.
• After the Green Revolution the industry expanded to several other part of the country.
Cement Industry
• This industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone, silica, aluminium and gypsum.
• Coal and electric power are needed apart from rail transportation.
• It is used for construction activities.
• Its plants are located in Gujarat due to its access to the market in the gulf countries.
Automobile Industry
• Automobiles provide vehicle for quick transportation of goods and passengers.
• After the liberalization the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market.
• The industry is located around Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, etc.
Information Technology and Electronic Industry
• It covers a wide range of products from transistor sets to television, telephone, cellular telecom, pager, telephone exchange, radars. Computers and many more equipment.
• Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India.
• The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the success of IT industry in India.
Methods to Control Pollution
• Use of three R’s (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle)
• Rainwater harvesting
• Treatment of Industrial waste
• Use of renewable sources of energy
• Development of new techniques which is durable and cause less pollution.
Objective Type Questions
Question. Which of the following industries use bauxite as a raw material?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c) Jute
(d) Steel
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question.

(a) (i)-(b), (ii)-(a), (iii)-(d), (iv)-(c)
(b) (i)-(c), (ii)-(d), (iii)-(b), (iv)-(a)
(c) (i)-(d), (ii)-(c), (iii)-(a), (iv)-(b)
(d) (i)-(a), (ii)-(b), (iii)-(c), (iv)-(d)
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Study the table given below and answer the following question:
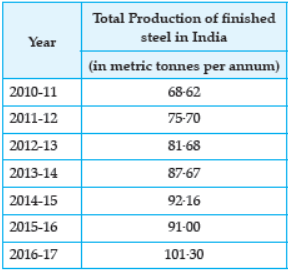
How much steel was produced in the year 2014-15?
(a) 101.30 metric tonnes
(b) 75.70 metric tonnes
(c) 92.16 metric tonnes
(d) 91.00 metric tonnes
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Which one of the following industries manufactures Telephones, Computer, etc.?
(a) Steel
(b) Electronic
(c) Aluminium Smelting
(d) Information Technology
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Question. Study the picture given below and answer the following question:

Where is this Sewage Treatment Plant under Yamuna Action Plan situated?
(a) Faridabad
(b) Firozabad
(c) Ahmedabad
(d) Nasirabad
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question. Which one of the following industries uses limestone as a raw material?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c) Plastic
(d) Automobile
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Question. Analyze the information given below, considering one of the following correct options:
These plants are smaller, have electric furnaces, use steel scrap and sponge iron. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots as well. They produce mild and alloy steel of given specifications.
(a) Heavy Steel Plants
(b) Major Steel Plants
(c) Mini Steel Plants
(d) Light Steel Plants
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Which one of the following agencies markets steel for the public sector plants?
(a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Assertion and Reason Based
Question. Assertion (A): India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods and stands at second place as an exporter after Bangladesh.
Reason (R): Other problems are the low output of labour and stiff competition with the synthetic fibre industry.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (c) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A) : Rain water harvesting increases industrial pollution.
Reason (R): Rain water helps industry to meet water requirements.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
Question. Assertion (a) : The handspun Khadi provides large scale employment to weavers in their homes as a cottage industry.
Reason (R) : Mahatma Gandhi laid emphasis on spinning yarn and weaving khadi.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
Question. Assertion (A) : The economic strength of the country is measured by the development of manufacturing industries.
Reason (R) : India’s prosperity lies in diversifying its manufacturing industries.
Option:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false and R is true.
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is a negative effect of Industrialisation?
Answer : Pollution
Question. Classify industries on the basis of source of raw materials used.
Answer : Classification:
(i) Agro-based: Cotton, wool, jute, silk textile, etc.
(ii) Mineral-based: Iron and steel, cement, etc
Question. Examine what are the causes of industrial pollution of freshwater resources.
Answer : Freshwater resources are polluted by:
(a) Organic and inorganic wastes;
(b) Effluents discharged by industries into rivers.
The main culprits are paper and pulp, chemical, textile, petroleum refineries, tanneries, electroplating industries, etc.
Question. Define Public Sector Industries.
Answer : Industries which are owned and operated by Government Agencies are called Public Sector Industries.
Question. What is thermal pollution?
Answer : The pollution caused by the discharge of hot water from factories and thermal plants into rivers and ponds before cooling.
Question. How is Public Sector different from Private Sector?
Answer : In public sector, government owns most of the assets and provides all the services, e.g., railways or post office. While in the private sector, ownership of assets and delivery of services is in the hands of private individuals or companies, e.g., Tata Iron and Steel Company Limited (TISCO) or Reliance Industries Limited (RIL).
Question. Mention any one factor that has contributed to a healthy growth of the automobile industry in India.
Answer : (i) The introduction of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the Market.
(ii) Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) brought in new technology and aligned the industry with global developments.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. “Industrialisation and Urbanisation go hand in hand”. Validate the statement.
Answer : (i) After an industrial activity starts in a town, urbanisation follows. Industry provides employment to the people of the area. Population migrates from rural hinterlands to seek jobs. Housing and transport facilities are developed to accommodate these people. Other Infrastructural developments take place leading to growth and development of the town into a city.
(ii) Sometimes Industries are located in or near the cities.
(iii) Cities provide markets for manufactured goods.
(iv) Cities provide various services like Banking and Insurance, etc.
Question. Classify Industries on the basis of source of raw material. How are they different from each other?
Answer : On the basis of sources of raw material, industries are classified as follows:
(i) Agro-based industries: These industries are based on agricultural raw material, e.g., cotton, jute, silk, rubber, sugar, tea, coffee and edible oils.
(ii) Mineral-based industries: Industries that use minerals and metals as raw materials are called mineral-based industries, e.g., iron and steel, cement, aluminium, machine tools, petrochemicals, etc.
Question. What are Software Technology Parks? State any two points of significance of Information Technology Industry in India.
Answer : Software Technology Park: Software Technology parks provide single window service and high data communication facility to software experts.
Significance of IT industry:
(i) A major impact of this industry has been an employment generation. Up to 31st March, 2005, the IT industry employed over one million persons.
(ii) It is encouraging to know that 30 per cent of the people employed in this sector are Women.
Question. Why is there a tendency for the Sugar Mills to concentrate in Southern states of India in recent years? Give three reasons.
Answer : Shifting of Sugar Industries to Southern states is because:
(i) Sugarcane that grows there has higher sucrose content.
(ii) Favourable climate provides longer crushing period and growing season.
(iii) Cooperatives are successful in these states.
Question. Mention any two factors that have contributed to a healthy growth of the Automobile Industry in India? Name two centres where this industry is located.
Answer : (i) The introduction of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market.
(ii) Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) brought in new technology and aligned the Industry with Global Developments.
The two Centres of Automobile Industry are Jamshedpur and Gurugram.
Question. “The Iron and Steel Industry is the Basic as well as Heavy Industry.” Support the statement with three points.
OR
Why is Iron and Steel Industry called a Basic Industry? Explain.
Answer : Iron and Steel Industry is the Basic Industry as:
(i) All the other Industries depend on it for their machinery.
(ii) Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of Engineering goods.
(iii) It provides variety of Consumer goods.
(iv) Construction material, Defence, Medical, Telephonic, Scientific equipment, etc., are the gift of Iron and Steel Industry.
Question. Describe the importance of manufacturing sector in countries like India.
OR
“Manufacturing sector is considered as the backbone of economic development of the country.” Support the statement with examples.
OR
Describe the importance of manufacturing.
Answer : The economic strength of a country lies in the development of Manufacturing Industries because:
(i) Manufacturing industries help in modernising agriculture which forms the backbone of our economy.
(ii) It reduces the heavy dependence of people on the agriculture sector and creates jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
(iii) It is necessary for the removal of unemployment and poverty.
(iv) It brings down regional disparities.
Question. Explain the ways through which the Industrial Pollution of fresh water can be reduced.
Answer : The ways through which the Industrial Pollution of fresh water can be reduced are:
(i) Treated waste water can be recycled for reuse in industrial processes.
(ii) Harvesting of rain water to meet water requirement for industrial process.
(iii) Treating hot and polluted waste water from industries before releasing it into our rivers and lakes.
(iv) Installing water treatment plants at the industrial sites for recycling.
Question. Explain any three factors responsible for the location of Cotton Textile Industry in Mumbai and Ahmedabad.
Answer : (i) Availability of raw cotton, market and transport including accessible port facilities.
(ii) Cheap labour.
(iii) Moist climate has caused the concentration of cotton textile industries in Mumbai and Ahmedabad region.
Question. ‘‘Consequences of environmental degradation do not respect National or State boundaries.’’ Justify the statement.
Answer : Consequences of Environmental degradation do not respect National or State boundaries because:
(i) The increase in pollution of land water, air, noise and resulting in degradation of the environment cannot be overlooked.
(ii) Pollution of river waters affects all as most of the rivers pass through different states.
(iii) Air pollution caused by the presence of a high proportion of undesirable gases adversely affects human health and the atmosphere as a whole.
(iv) Thermal pollution of river water affects aquatic life irrespective of State and National Boundaries.
Question. What is the importance of the Information Technology sector for the Indian economy? Explain.
Answer : The importance of IT sector is as follows:
(i) It has provided employment to over one million people.
(ii) This Industry is said to be a major Foreign Exchange earner.
(iii) It has helped in the growth of the Service Sector.
Case Based Questions
I. Read the text given below and answer the questions that follow:
Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, which forms the backbone of our economy, they also reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors. Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country. This was the main philosophy behind public sector industries and joint sector ventures in India. It was also aimed at bringing down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas. Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange. Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide variety of finished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible. Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
1. Manufacturing industries fall in and agriculture in .
(a) Primary, Secondary Sector
(b) Secondary, Tertiary Sector
(c) Primary, Tertiary Sector
(d) Secondary, Primary Sector
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
2. Manufacturing provides job opportunities to reduce dependence on agriculture. Identify which sector the following jobs belong to:

Choose the correct option:
(a) a-1, b-2, c-3, d-4
(b) a-3, b-4, c-2, d-1
(c) a-2, b-3, c-1, d-4
(d) a-4, b-1, c-2, d-3
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
3. Which of the following options does not help in modernising agriculture?
(a) Manufacturing farm equipment
(b) Providing unskilled labour force
(c) Supplying fertilizers and pesticides
(d) Producing tube well pumps and sprinklers
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
4. In order to attract foreign manufacturing firms, a country needs to develop:
(a) Agrarian facilities
(b) Cultivable lands
(c) Media facilities
(d) Infrastructure facilities
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
II. Read the text given below and answer the questions that follow:
The iron and steel industry is the basic industry since all the other industries — heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods. Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country’s development. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as finished goods are heavy and bulky, entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore, coking coal and limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4: 2: 1. Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel. Where should the steel plants be ideally located? Remember that the finished products also need an efficient transport network for their distribution to the markets and consumers. In 2016, with 95.6 million tonnes of crude steel production, India ranked 3rd among the world crude steel producers. It is the largest producer of sponge iron. In 2016, per capita consumption of steel in the country was only around 63 kg per annum against the world average of 208 kg.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
1. Which industry is called the basic industry of India?
(a) Textile Industry
(b) Sugar Industry
(c) Cement Industry
(d) Iron and Steel Industry
Answer : Option (d) is correct.
2. Index of a country’s development is regarded on what basis? Select the appropriate option:
(a) Extraction and processing of steel.
(b) Production and consumption of steel.
(c) Production and manufacturing of steel.
(d) Consumption and manufacturing of steel.
Answer : Option (b) is correct.
3. Apart from iron ore, coking coal and limestone in a fixed proportion, minor quantities of which of the following is also used in manufacturing of steel?
(a) Manganese
(b) Copper
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) Neither of the above
Answer : Option (a) is correct.
4. Manufacturing steel is not every person’s business. Suppose you are working in a Steel Industry, what will be the proportion of Iron Ore, coking coal and limestone you would use to produce steel?
(a) 2: 1: 4
(b) 4: 1: 2
(c) 4: 2: 1
(d) 2: 4: 1
Answer : Option (c) is correct.



