Please see Market Equilibrium Exam Questions Class 12 Economics below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 12 Economics Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 12 Economics. These solved problems for Market Equilibrium in Class 12 Economics will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Market Equilibrium Class 12 Economics
MCQs
Question 1.
Which is a characteristic of the market ?
(a) One Area
(b) Presence of both Buyers and Sellers
(c) Single Price of the Commodity
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 2.
Which is a basic for the classification of the market ?
(a) Perfect Competition
(b) Zero Competition (Monopoly)
(c) Imperfect Competition
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 3.
Which of the following is a feature of perfect competition ?
(a) Large Number of Buyers and Sellers
(b) Homogeneous Units of the Product
(c) Perfect Knowledge of the Market
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 4.
In which market product differentiation is found ?
(a) Pure Competition
(b) Perfect Competition
(c) Monopoly
(d) Monopolistic Competition
Answer: (c) Monopoly
Question 5.
Which of the following is true in perfect competition ?
(a) Firm is price-taker, not price-maker
(b) Firm’s demand curve is perfectly elastic
(c) AR = MR
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 6.
Which one is a feature of monopoly ?
(a) Single Seller and Many Buyers
(b) Lack of Close Substitutes
(c) Restrictions of New Firm entry
(d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 7.
Which one of the following is true for monopoly ?
(a) Firm is price-maker
(b) Demand curve slopes downward
(c) Price discrimination possibility arises
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 8.
Which one is a feature of monopolistic competition ?
(a) Differentiated Product
(b) Selling Cost
(c) Imperfect Knowledge of the Market
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 9.
A market in which there is free entry and exit, the market is:
(a) Monopolistic Competitive Market
(b) Imperfect Competitive Market
(c) Perfectly Competitive Market
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Perfectly Competitive Market
Question 10.
What does a monopolist market show ?
(a) Production process
(b) Distribution system
(c) Nature of market
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Nature of market
Question 11.
Price discrimination is found in which market ?
(a) Pure Competition
(b) Perfect Competition
(c) Monopoly
(d) Monopolistic Competition
Answer: (c) Monopoly
Question 12.
Which of the following is the feature of pure competition ?
(a) Perfect knowledge of the market
(b) Perfect mobility of factors
(c) Homogenity by products
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 13.
Market situation where there is only one buyer is:
(a) Monopoly
(b) Monopsony
(c) Duropoly
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Monopsony
Question 14.
The concept of monopolistic competition is given by:
(a) Hicks
(b) Chamberlin
(c) Mrs. Robinson
(d) Samuelson
Answer: (b) Chamberlin
Question 15.
Which of the following is not a feature of perfect competition ?
(a) Large number of buyers and sellers
(b) Homogeneity of product
(c) Advertisement and selling cost
(d) Perfect knowledge of the market
Answer: (c) Advertisement and selling cost
Question 16.
In which market is AR equal to MR ?
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Oligopoly
(c) Imperfect competition
(d) Monopoly
Answer: (a) Perfect competition
Question 17.
Which factor determines Equilibrium Price ?
(a) Demand for Commodity
(b) Supply of Commodity
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 18.
“Price is determined by Demand and Supply. Whose statement is this ?
(a) Jevons
(b) Walras
(c) Marshall
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Marshall
Question 19.
Price of a commodity is determined at a point where :
(a) Demand exceeds
(b) Supply exceeds
(c) Demand equals supply
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Demand equals supply
Question 20.
What is true for perfect competition market ?
(a) Price is determined by both Demand and Supply Forces
(b) Price is determined by the industry
(c) Each firm of the industry is Price-taker
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 21.
Who gave the concept of ‘Time Element’ in price determination process ?
(a) Ricardo
(b) Walras
(c) Marshall
(d) J. K. Mehta
Answer: (c) Marshall
Question 22. How many categories of production duration have been made by Marshall on the basis of supply ?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Seven
Answer: (b) Three
Question 23. Which is a reason of change in demand ?
(a) Change in Consumer’s Income
(b) Change in Prices of Related Goods
(c) Population increase
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 24.
Which statement is correct ?
(a) In very short period, supply is perfectly inelastic, price is affected by both demand conditions.
(b) Supply curve elasticity depends on time period
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 25.
Market Price is found in:
(a) Short Period Market
(b) Long Period Market
(c) Very Long Period Market
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Short Period Market
Question 26. The price of a good is determined by:
(a) Demand
(b) Supply
(c) Both demand and supply
(d) Government
Answer: (c) Both demand and supply
Question 27.
Market price is associated with:
(a) Price of very short period
(b) Normal price
(c) Permanent price
(d) All of these
Answer: (a) Price of very short period
Question 28.
The price of a goods in perfect competition is determined by:
(a) Bargaining
(b) Production cost
(c) Marginal utility
(d) Demand and supply
Answer: (d) Demand and supply
Question 29.
In perfect competition, a firm:
(a) Determines price
(b) Obtains price
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Obtains price
Question 30.
In very short period, supply will be:
(a) Perfectly elastic
(b) Perfectly Inelastic
(c) Elastic
(d) None of these
Answer: (b) Perfectly Inelastic
Question 31.
Which is not a condition for equilibrium of a monopoly form ?
(a) Average Revenue = Marginal Cost
(b) Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
(c) Marginal Cost should cut the Marginal Revenue Curve from below
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer: (a) Average Revenue = Marginal Cost
Question 32.
In perfect competition, these is……. profit
(a) Normal
(b) Maximum
(c) Zero
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Normal
Question 33.
A Seller Cannot influence the market price under:
(a) Perfect Competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Monopolistic Competition
(d) All of these
Answer: (a) Perfect Competition
Question 34.
Which determines the equilibrium price ?
(a) Demand
(b) Supply
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 35. Which is the component of factor price determination ?
(a) Rent
(b) Wages
(c) Interest
(d) All of these
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 36. Price of a goods is determined at a point where :
(a) Demand > Supply
(b) Demand < Supply
(c) Demand = Supply
(d) None of these
Answer: (c) Demand = Supply
Question 37.
None of these Rent is = ?
(a) Actual Income – Transfer Earnings
(b) Actual Income + Transfer Earnings
(c) Transfer Earnings
(d) None of these
Answer: (a) Actual Income – Transfer Earnings
Question 38.
Which of the following is correct ?
(a) Labour Demand comes from producer
(b) Demand of labour depends on its productivity.
(c) Marginal productivity of labour is its maximum wage
(d) All the above
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 39.
Main feature of perfectly competitive market is:
(a) Uniform price
(b) Homogeneous product
(c) Large number of buyers and sellers
(d) All of the above.
Answer: (d) All of the above.
Question 40.
The market in which there is free entry and exit is:
(a) Monopolistic competition market
(b) Imperfect competition market
(c) Perfect competitions market
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c) Perfect competitions market
Question 41.
There is inverse relation between demand and price of goods in:
(a) Only monopoly
(b) Only monopolistic competition
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Only perfect competition.
Answer: (d) Only perfect competition.
Question 42.
According to which economist “Price of a commodity is determined by the forces of demand and supply”:
(a) Jevons
(b) Valros
(c) Marshall
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c) Marshall
Question 43.
Not a condition of equilibrium of monopoly firm:
(a) Average revenue = Marginal revenue
(b) Marginal revenue = Marginal cost
(c) Marginal cost curve cuts marginal revenue curve from downwards.
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Answer: (a) Average revenue = Marginal revenue
Question 44.
Market price is found in:
(a) Short period market
(b) Long period market
(c) Very long period market
(d) None of these.
Answer: (a) Short period market
Question 45.
Demand curve of a firm is perfectly elastic in:
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Monopolistic competition
(d) Oligopoly.
Answer: (a) Perfect competition
Questions 46.
Administrative price is:
(a) Price ceiling
(b) Price floor
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Questions 47.
Minimum support price of wheat is called:
(a) Price ceiling
(b) Price floor
(c) Market price
(d) Equilibrium price.
Answer: (b) Price floor
Questions 48.
Which of the following is the component of instrument pricing:
(a) Rent
(b) Wages
(c) Interest
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c) Interest
Questions 49.
Which factors help in the determination of equilibrium price:
(a) Demand
(b) Supply
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above.
Answer: (d) None of the above
Questions 50.
Which among the following statement is not true:
(a) Demand of labor is done by the producer
(b) Demand of labor depends open its productivity
(c) Marginal productivity of a labor is his maximum wages
(d) All of the above.
Answer: (d) All of the above
Questions 51.
Excess demand can be seen in:
(a) Fixed market price
(b) Lowest fixed price
(c) Highest fixed price
(d) None of these.
Answer: (c) Highest fixed price
Question. The quantity to be sold by a firm under perfect competition is also fixed by the market.
a) True
b) Can’t say
c) None of these
d) False
Answer
D
Question. Under perfect competition, market price can be influenced by both buyers and sellers.
a) True
b) False
c) None of the these
d) Cannot say
Answer
B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. What is price maker firm?
Answer : A price maker firm is one which can influence price on its own.
Question. What is cooperative oligopoly?
Answer : When in an oligopoly market, the firms cooperate with each other in determining price and output, that situation is called cooperative oligopoly.
Question. What is meant by normal profit?
Answer : Normal profit is the minimum amount of profit which is required to keep an entrepreneur in production in the long run.
Question. Why AR is equal to MR under perfect competition?
Answer : AR is equal to MR under perfect competition because price is constant.
Question. In which market form is there product differentiation?
Answer : Monopolistic competition market
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why is the number of firms small in oligopoly? Explain.
Answer : The main reasons why the number of firms are small in oligopoly is that there are barriers which prevent enty of firms into industry. Patents, large captial requiremnts control over the critical raw meterials,e tc all prevents new firm from entering the industry. Only those who are able to cross these barriers able to enter and stay in market.
Question. Explain the implications of the following:
a) Interdependence between firms in oligopoly
b) Large number of sellers in perfect competition
Answer : A) Oligopolies are typically composed of a few large firms. Each firm is so large that its actions affect market conditions. Therefore, the competing firms will be aware of a firm’s market actions and will respond appropriately. Mutual interdependence exists when the actions of one firm has a major impact on the other firms in the industry.
B) A perfectly competitive market is dominated by the presence of large number of buyers and sellers of a commodity, which means that there is no such buyer or seller in the market whose purchase or sale is so large as to impact the total sale or purchase in the market. Each buyer/seller has only a fractional share in the market demand/market supply.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous increase both in demand and supply of the goods. Explain its effects on market price.
Answer : Equilibrium exits when there is no reason for a situation to change. When equilibrium exits, the quantity people plan to buy is equal to the quantity that producers plan to sell. The laws of demand and supply cause the market to move to equilibrium. The effect of increase in both demand and supply on equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity is discussed under three different cases:-
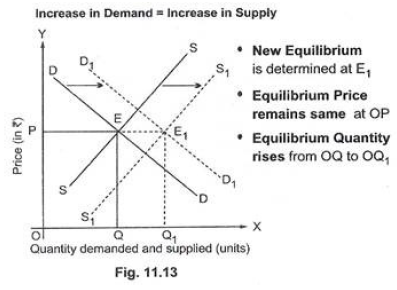
1. When increase in demand is equal to increase in supply: When increase in demand is proportionately equal to increase in supply, then rightward shift in demand curve from DD to D1D1 is proportionately equal to rightward shift in supply curve from SS to S1S1. The new equilibrium is determined at E1. As both demand and supply increase in the same proportion, equilibrium price remains the same at OP, but equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to OQ1.
2. When increase in demand is more than increase in supply: When increase in demand is proportionately more than increase in supply then rightward shift in demand curve from DD to D1D1 is proportionately more than rightward shift in supply curve from SS to S1S1. The new equilibrium is determined at E1 equilibrium price rises from OP to OP1 and equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to OQ1.

3. When increase in demand is less than increase in supply: When increase in demand is proportionately less than increase in supply, then rightward shift in demand curve from DD to D1D1 is proportionately less than rightward shift in supply curve from SS to S1S1. The new equilibrium is determined at E1 equilibrium price falls from OP to OP1 whereas, equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to OQ1.

Question. How an equilibrium price and an equilibrium quantity of a normal commodity is affected by an increase in an income of the buyers? Explain with the help of diagram.
Answer : When an income of the consumers rises, demand curve for normal goods would shift to the right. Supply curve remains unaffected. However, when consumers are willing to pay higher price for the same quantity or because of increase in their income. This will tend price would tend to rise. Consequently, quantity supplied by the producers would tend to rise.
Thus, increase in demand and the consequent shift in demand curve to the right impacts producer’s decisions by way of extension of supply in response to increase in price. Finally, you would end up in a situation, when an equilibrium price as well as an equilibrium quantity tend to rise, in response to an increase in demand.
OP = Initial equilibrium price
OQ = Initial equilibrium quantity
OP1 = New equilibrium price
OQ1 = New equilibrium quantity

