Please refer to Amines MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Chemistry with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for Amines will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
Amines MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry
Please see solved MCQ Questions for Amines in Class 12 Chemistry. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on latest examination guidelines.
Question. The molecular formula ofbenzonitrile is
(a) C6H5CN
(b) C6H5NC
(c) C6H5CNO
(d) C6H5NCO
Answer
A
Question. The reduction of which of the following compound would yield secondary amine?
(a) Alkyl nittile
(b) Carbylamine
(c) Ptimary amine
(d) Secondary nitro compound
Answer
B
Question. Alkyl cyanides undergo Stephen reduction to produce
(a) aldehyde
(b) secondary amine
(c) primary amine
(d) amide
Answer
A
Question. Identify C in the following reaction,

(a) Benzamide
(c) Chlorobenzene
(b) Benzoic acid
(d) Aniline
Answer
D
Question. Toluene is nitrated and the resulting product is reduced with tin and hydrochloric acid. The product so obtained is diazotised and then heated with cuprous bromide. The reaction mixture so formed contains.
(a) mixture of o and p-bromotoluenes
(b) mixture of o and p -dibromobenzenes
(c) mixture of o and p-bromoanilines
(d) mixture of o and m-bromotoluenes
Answer
A
Question. Nitrobenzene is reduced by Zn and alcoholic potash mixture to get
(a) C6H5—NH2
(b) C6H5—NH—NH—C6H5
(c) C6H5—N—N—C6H5
(d) C6H5—NH—CO—C6H5
Answer
B
Question. The structure of the compound formed, when nitrobenzene is reduced by lithium aluminium hydride (LiAIH4 ) is

Answer
C
Question. Nitration ofnitrobenzene at 125°C with mixed acids gives
(a) meta-dinitrobenzene
(b) ortho-dinitrobenzene
(c) para-dinitrobenzene
(d) 1, 3, 5-trinitrobenzene
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following compounds reacts slower than benzene in electrophiJic substitution?
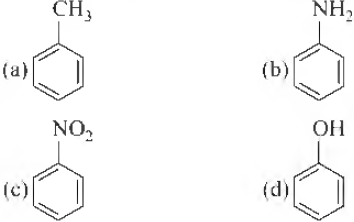
Answer
C
Question. In alkyl cyanide alkyl group attached with
(a) C of CN group
(b) N of CN group
(c) Either C or N of CN group
(d) Both C and N of CN group
Answer
A
Question. Reduction of nitrobenzene in the presence of Zn /NH4 Cl gives
(a) azobenzene
(b) hydrazobenzene
(c) N-phenyl hydroxylamine
(d) aniline
Answer
C
Question. C6H5NO2 →Sn/ HCI C6H5 X, ‘X’ is identified as
(a) NO
(b) -NH2
(c) NHOH
(d) None of the above
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following compounds is soluble in benzene but almost insoluble in water?
(a) C2H5OH
(b) CH3CO2H
(c) CH3CHO
(d) C6H5NO2
Answer
D
Question. The IUP AC name of the following compound is
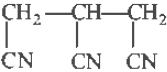
(a) 1, 2, 3-tricyanopropane
(b) propane- 1, 2, 3-trinitrile
(c) 3-cyanopentane- 1, 5-dinitrile
(d) 1, 3, 5-pentanetrinitrile
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following reactions can produce aniline as main product?
(a) C6H5NO2
(a) C6H5NO2 + Zn / KOH
(b) C6H5NO2 + Zn / NH4Cl
(c) C6H5NO2 + LiAIH4
(d) C6H5NO2 + Zn / HCl
Answer
D
Question. In the reaction shown below, the major product(s) formed is/are
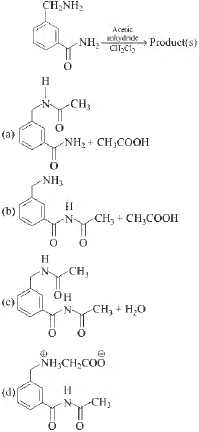
Answer
A
Question. In the reaction,
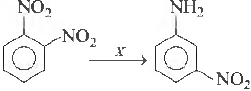
X is
(a) SiC
(b) H2SO4
(c) KMnO4
(d) Fe / HCI
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not a nitro derivative?
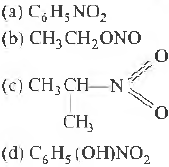
Answer
B
Question. The compound with foul odour among the following is

Answer
A
Question. Which is not the property of ethanenitrile (CH3CN)?
(a) Undergoes acidic hydrolysis to give carboxylic acid
(b) Undergoes alkaline hydrolysis to give salt of carboxylic acid
(c) It tautometises to give methyl isocyanide
(d) It gives carbylamine reaction with chloroform
Answer
D
Question. Final product of hydrolysed alkyl cyanide is
(a) RCOOH
(b) RCONH2
(c) R—C= NH
l
OH
(d) R—C= N⊕H
Answer
A
Question. Identify A and Bin the reaction given below.
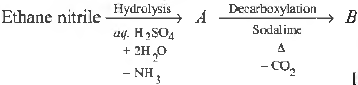
(a) acetic acid, methanol
(b) acetone, methane
(c) ethanoic acid, ethane
(d) ethanoic acid, methane
Answer
D
Question. Benzamide can be converted into benzonitrile with
(a) H3O+
(b) OH–/ H2O
(c) KCN
(d) P2O5
Answer
D
Question. Aliphatic nitrites are prepared by the treatment of alkyl halides with
(a) sodium cyanide
(b) sodium isocyanide
(c) sodium isocyanate
(d) cyanamide
Answer
A
Question. How many sigma and pi-bonds are there in the molecule of dicyanoethene (CN—CH=CH—CN)?
(a) 3 sigma and 3 pi
(b) 5 sigma and 2 pi
(c) 7 sigma and 5 pi
(d) 2 sigma and 3 pi
Answer
C
Question.
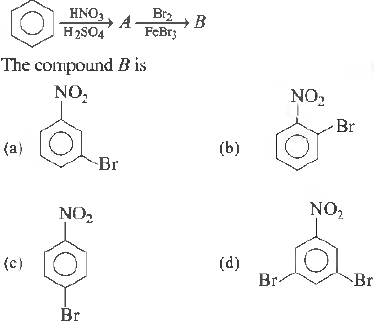
Answer
A
Question. Which compound is known as alkyl carbylamine?
(a) R · CN
(b) R · NC
(c) Ar · CN
(d) Ar · NC
Answer
B
Question. Ethyl isocyanide on hydrolysis in acidic medium generates
(a) ethylamine salt and methanoic acid
(b) propanoic acid and ammonium salt
(c) ethanoic acid and ammonium salt
(d) methylamine salt and ethanoic acid
Answer
A
Question. Choose the inco1Tect statement.
(a) Primary amines show intermolecular hydrogen bonds
(b) tert-butylamine is a primary amine
(c) Tertiary amines do not show intermolecular hydrogen bonds
(d) Iso-propylamine is a secondary amine
(e) Amines have lower boiling points as compared to those of alcohols of comparable molecular mass
Answer
D
Question. Reduction of alkyl nitriles, produces
(a) secondary amine
(b) primary amine
(c) tertiary amine
(d) amide
Answer
B
Question. Which one does not liberate NH3 when undergoes hydrolysis?
(a) AcetaniIide
(c) Acetamide
(b) Acetonittile
(d) Phenyl isocyanide
Answer
D
Question. n-butylamine (I), diethylamine (II) and N, N-dimethylethylamine (III) have the same molar mass.
The increasing order of their boiling point is
(a) III < II < I
(b) I < II < III
(c) II < III < I
(d) II < I < III
(e) III < I < II
Answer
A
Question. In the reaction,
CH3CN + 2H →SnCI2HCI X →Boiling H2O Y
The term Y is
(a) acetone
(b) ethanamine
(c) acetaldehyde
(d) dimethyl amine
Answer
C
Question. Methyl cyanide gives on hydrolysis
(a) methyl amine
(b) acetic acid
(c) formic acid
(d) ethyl amine
Answer
B
Question. Compare boiling point of isomeric alkyl amines.
(a) 1° > 2° > 3°
(b) 1° > 2° < 3°
(c) 1° < 2° < 3°
(d) 1° < 2° > 3°
Answer
A
Question. Which one of the following does not have sp2 hybridised carbon?
(a) Acetone
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Acetonitrile
(d) Acetamide
Answer
C
Question. Secondary nitro alkanes can be converted into ketones by using Y. Identify Y from the following.
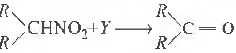
(a) Aqueous HCl
(b) Aqueous NaOH
(c) KMnO4
(d) CO
Answer
A
Question. Acetonitrile on reduction gives
(a) propanamine
(b) methanamine
(c) ethanamine
(d) None of these
Answer
C
Question. KCN reacts readily to give a cyanide with
(a) ethyl alcohol
(b) ethyl bromide
(c) bromobenzene
(d) chlorobenzene
Answer
B
Question. Amongst the following, the most basic compound is
(a) benzylamine
(b) aniline
(c) acetanilide
(d) p-nitroaniline
Answer
A
Question. What is Zin the following reaction sequence?
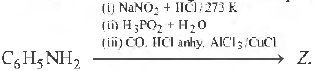
(a) C6H5CO2H
(b) C6H5OH
(c) C6H5CHO
(d) C6H6
Answer
C
Question. Aniline+ Excess of Br2 →?
(a) Tribromo benzene
(b) m -bromo aniline
(c) 3, 4, 5-tribromo aniline
(d) 2, 4, 6-tribromo aniline
Answer
D
Question. The major product of the following reaction is
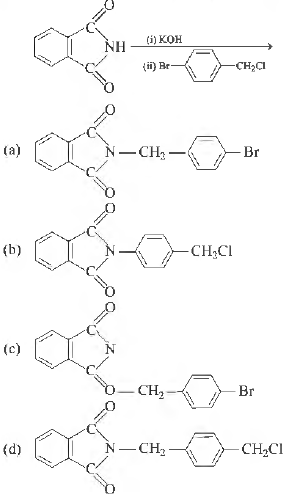
Answer
A
Question. C6H5NH2 →180°CH2SO4 NH2C6H4 (SO3H)
para-fonn
The true statement about the product is
(a) it does not exist as Zwitter ion
(b) it does not act as inner salt
(c) —SO3 diminishes the basic character of —NH2
(d) —NH2 displays a powerful basic character
Answer
C
Question.
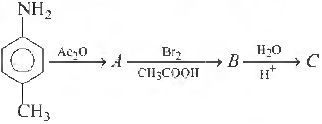
The final product C in the above reaction is

Answer
D
Question. Considering the basic strength of amines in aqueous solution, which one has the smallest pK b value?
(a) (CH3)2 NH
(b) CH3NH2
(c) (CH3)3N
(d) C6H5NH2
Answer
A
Question. Arrange the following in correct order of basicity.

(a) I > II > III
(b) IIl > II > I
(c) II > I > III
(d) I > III > II
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following processes does not yield a primary amine?
(a) CH3COCH3 + NH3 + H2 →Ni
(b) CH3CH2CN + H2 →Ni140°C
(c) CH3CHO + H2NOH →Na,C2H5OH
(d) CH3CHO + N2CH2 →NaBH4
Answer
D
Question. N-methyl aniline on reaction with nitrous acid gives
(a) N-nitroso-N-methylaniline
(b) p-nitroso-N-methylaniline
(c) p-nitro-N-methylaniline
(d) N-nitro-N-methylaniline
Answer
A
Question. When aniline reacts oil of bitter almonds, condensation takes place and benzyl derivatives are formed. These are known as
(a) Millon’s base
(b) Scruff’s reagent
(c) Benedict reagent
(d) Scruff’s base
Answer
D
Question. An aromatic compound A (C7H9N) on reacting with NaNO2 /HCl at 0°C forms benzyl alcohol and nitrogen gas. The number of isomers possible for the compound A is
(a) 5
(b) 7
(c) 3
(d) 6
Answer
A
Question. An amine C3H9N reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride to form a white precipitate which is insoluble in aq. NaOH. The amine is
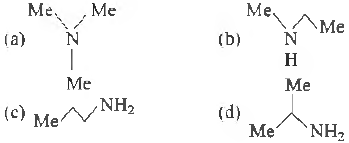
Answer
B
Question. Aromatic primary amines can be distinguished from aliphatic primary amines by
(a) Tollen’s test
(b) action on red litmus paper
(c) azo dye test
(d) action with dil. HCI
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following compounds will dissolve in an alkali solution after it has undergo reaction with Hinsberg’s reagent?
(a) CH3NH2
(b) (CH3)3 N
(c) (C2H5)2NH
(d) C6H5NHC6H5
Answer
A
Question. An organic compoundA having molecular formula C2H3N on reduction gave another compound B, upon treatment with nitrous acid B gave ethyl alcohol. On warming with chloroform and alcoholic KOH, it formed an offensive smelling compound C. The compound C is
(a) CH3CH2NH2
(b) CH3CH2N=C
(c) CH3C= N
(d) CH3CH2 ·OH
Answer
B
Question. The correct order of basic strength in aqueous solution is
(a) (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N
(b) (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2
(c) CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH
(d) (CH3)3N > CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH
Answer
A
Question. Amongst the compounds given, the one that would form a brilliant coloured dye on treatment with NaNO2 in dil.HCI followed by addition to an alkaline solution of β-naphthol is
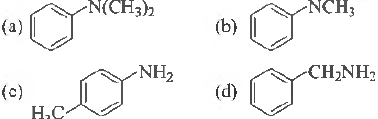
Answer
C
Question. What is IUP AC name of iso-propylamine?
(a) Propan-2-amine
(b) Ethanamine
(c) 2-aminotoluene
(d) Propan-1-amine
Answer
A
Question. Acetonitriles on hydrolysis produce which of the following?
(a) Amine
(b) Acid
(c) Amides
(d) Carbonyl compounds
Answer
D
Question. Unpleasant smell of carbylamine is obtained when chloroform and alcoholic KOH are heated with
(a) any aliphatic amine
(b) any amine
(c) any primary amine
(d) any aromatic amine
Answer
C
Question. The main product of the reaction of CH3CONH2 with Br2 in aqueous potassium hydroxide medium is
(a) CH3—CH2—NH2
(b) CH3Br
(c) CH3CONHBr
(d) CH3NH2
Answer
D
Question. In the reaction, R—C= N + 4 (H)→x RCH2NH2 X can be
(a) LiAIH4
(b) H2SO4
(c) Ni
(d) 2KBr
Answer
A



