Please refer to General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry below. These MCQ questions for Class 12 Chemistry with answers have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE books and syllabus issued for the current academic year. These objective questions for General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements will help you to prepare for the exams and get more marks.
General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry
Please see solved MCQ Questions for General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements in Class 12 Chemistry. All questions and answers have been prepared by expert faculty of standard 12 based on latest examination guidelines.
Question. Which one of the following metals, is extracted on smelting of its ore in blast furnace?
(a) Iron
(b) Sodimn
(c) Potassium
(d) Magnesium
Answer
A
Question. The extraction of which of the following metals involves bessemerisation?
(a) Fe
(b) Ag
(c) Al
(d) Cu
Answer
D
Question. Gold is extracted by hydrometallurgical process, based onits property
(a) of being electropositive
(b) of being less reactive
(c) to form complexes which are water soluble
(d) to form salts which are water soluble
Answer
C
Question. Extraction of zinc from zinc blende is achieved by
(a) electrolytic reduction
(b) roasting followed by reduction with carbon
(c) roasting followed by reduction with another metal
(d) roasting followed by self reduction
Answer
B
Question. During the extraction of copper, the impurity (FeS) is removed as slag by mixing the contaminated copper ore with silica and coke. The molecular formula of slag is
(a) FeSiO3
(b) Fe2O3
(c) FeSi (solid)
(d) FeSi
Answer
A
Question. Hydrometallurgy is based on
(a) calcination
(b) roasting
(c) oxidation
(d) reduction
Answer
D
Question. The chief impurity present in red bauxite is
(a) SiO2
(b) Fe2O3
(c) K2SO4
(d) NaF
Answer
B
Question. Sulphide ores are common for metals
(a) Ag, Cu and Pb
(b) Ag, Cu and Sn
(c) Ag, Mg and Pb
(d) Al, Cu and Pb
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following is an oxide ore?
(a) Malachite
(b) Haematite
(c) Copper glance
(d) Zinc blende
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following statements is false?
(a) During roasting, moisture is removed from the ore
(b) The ore is freed from almost all non-metallic
(c) Calcination of ore is carried out in the absence of any blast of air
(d) The concentrated zinc blende is subjected to calcination during its extraction by pyrometallurgy
Answer
B.D
Question. In aluminothemuc process, Al is used as a/an
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) electrolyte
Answer
A
Question. Bauxite ore is made up of Al2O3 + SiO2 + TiO2 + Fe2O3 . This ore is treated with cone. Na OH solution at 500 Kand 35 bar pressure for few hours and filtered hot. In the filtrate, the species present are
(a) NaAl(OH)4
(b) Na2Ti(OH)6
(c) Na[Al(OH)4 ] and Na2SiO3
(d) Na2SiO3
Answer
C
Question. Which of the following is true for electrolytic refining?
(a) Pure metal is anode and impure metal is cathode
(b) Pure metal is cathode and impure metal is anode
(c) Both are anode
(d) Both are cathode
Answer
B
Question. One of the following metals forms a volatile compound and this property is taken advantage for its extraction. This metal is
(a) iron
(b) nickel
(c) cobalt
(d) tungsten
Answer
B
Question. In metallurgical process, for which metal carbon is used for reduction of metal oxides?
(a) Na
(b) Ag
(c) Fe
(d) Hg
Answer
C
Question. In the electrolytic refining of zinc,
(a) graphite is at the anode
(b) the impure metal is at the cathode
(c) the metal ions get reduced at the anode
(d) acidified zinc sulphate is the electrolyte
Answer
D
Question. The purest zinc is obtained by
(a) electrolytic refining
(b) zone refining
(c) van Arkel method
(d) Mond’s process
Answer
B
Question. Aluminium metal is refined by
(a) Serpeck’s process
(b) Baeyer’s process
(c) Hall’s process
(d) Hoope’s process
Answer
D
Question. Identify the ore not containing iron.
(a) Limonite
(b) Siderite
(c) Carnallite
(d) Chalcopyrites
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following is the chief ore of copper?
(a) Galena
(c) Sphalerite
(b) Copper pyrites
(d) Siderite
Answer
B
Question. Argentite is an ore of
(a) Fe
(b) AI
(c) Cu
(d) Ag
Answer
D
Question. Calamine is
(a) CaCO3
(b) MgCO3
(c) ZnCO3
(d) CaCO3 + CaO
Answer
C
Question. Extraction of metal from the ore cassiterite involves
(a) carbon reduction of an oxide ore
(b) self-reduction of a sulphide ore
(c) removal of copper impurity
(d) removal of iron impurity
Answer
A,D
Question. Which one of the following ores is best concentrated by froth floatation method?
(a) Magnetite
(b) Cassiterite
(c) Galena
(d) Malachite
Answer
C
Question. Observe the following statements regarding purification of bauxite.
I. During Hall’s process, silica is removed as Si (vapour).
II. Bauxite ore contaminated with FeiO3 is purified in Baeyer’s process.
III. During Serpeck’s process, AIN is formed. The correct answer is
(a) I, II and III
(b) I and II
(c) I and III
(d) II and III
Answer
D
Question. Refining of impure copper with zinc impurity is to be done by electrolysis using electrodes as
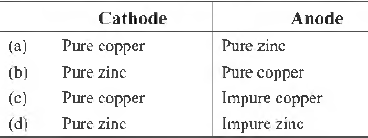
Answer
C
Question. Upon heating with Cu2S, the reagent(s) that given copper metal is/are
(a) CuFeS2
(b) CuO
(c) Cu2O
(d) CuSO4
Answer
B,C,D
Question. The method of zone refining of metals is based on the principle of
(a) greater noble character of the solid metal than that of the impurity
(b) greater solubility of the impurity in the molten state than in the solid
(c) greater mobility of the pure metal than that of impurity
(d) higher melting point of the impurity than that of the pure metal
Answer
B
Question. Aluminium is obtained by
(a) reducing Al2O3 with coke
(b) electrolysing Al2O3 dissolved in Na3 AIF6
(c) reducing Al2O3 with chromium
(d) heating alumina with cryolite
Answer
B
Question. Composition ofazmite mineral is
(a) CuCO3 • CuO
(b) Cu(HCO3)2 · Cu(OH)2
(c) 2CuCO3 · Cu(OH)2
(d) CuCO3 · 2 Cu(OH)2
Answer
C
Question. Cyanide process is used for extraction of
(a) Ag
(b) Ni
(c) Pt
(d) Zn
Answer
A
Question. During the process of electrolytic refining of copper, some metals present as impurity settle as ‘anode mud’. These are
(a) Fe and Ni
(b) Ag and Au
(c) Pb and Zn
(d) Se and Ag
Answer
B
Question. In the electrolytic method for obtaining aluminium from purified bauxite, cryolite is added to
(a) minimise the heat loss due to radiation
(b) protect aluminium produced from oxygen
(c) dissolve bauxite and render it conductor of electricity
(d) lower the melting point of bauxite
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following ores is an ore of copper?
(a) Argentite
(b) Haematite
(c) Malachite
(d) Calamine
Answer
C
Question. From the Ellingham graph on carbon, which of the following statements is false?
(a) CO reduces Fe2O3 to Fe at less than 983 K
(b) CO is less stable than CO2 at more than 983 K
(c) CO reduces Fe2O3 to Fe in the reduction zone of blast furnace
(d) CO2 is more stable than CO at less than 983 K
Answer
B
Question. On igniting Fe2O3 at 1400°C, the product obtained is
(a) Fe2O3 melt
(b) FeO
(c) Fe3O4
(d) metallic iron
Answer
D
Question. In the cyanide extraction process of silver from argentite ore, the oxidising and reducing agents used are
(a) O2 and CO
(b) O2 and Zn dust
(c) HNO3 and Zn dust
(d) HNO3 and CO
Answer
B
Question. Impurities of Cu and Ag from gold are removed by
(a) boiling impure gold with di!. H2SO4
(b) boiling impure gold with cone. H2 SO4
(c) electrolytically
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
D
Question. Identify the reaction that does not take place in a blast furnace.
(a) CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
(b) CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
(c) 2Fe2O3 + 3C → 4Fe + 3CO2
(d) CO2 + C → 2CO
Answer
C
Question. Metallic silver may be obtained from AgCl by
(a) heating it in the current of H2
(b) fusing it with sand
(c) treating with carbon monoxide
(d) fusing it with Na2CO3
Answer
D
Question. Gravity separation process is used for the concentration of
(a) calamine
(b) haematite
(c) chalcopyrite
(d) bauxite
Answer
B
Question. In Mac Arthm Forrest method, silver is extracted from the solution of Na [Ag(CN)2 ] by the use of
(a) Fe
(b) Mg
(c) Cu
(d) Zn
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following metal is correctly matched with its ore?
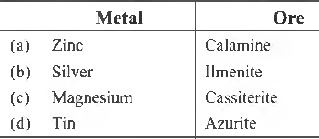
Answer
A
Question. Siderite is an ore of
(a) Cu
(b) Al
(c) Ag
(d) Fe
Answer
D
Question. Which ore contains both iron and copper?
(a) Cuprite
(b) Chalcocite
(c) Chalcopyrite
(d) Malachite
Answer
C
Question. Carbon cannot be used in the reduction of Al2O3 because
(a) it is an expensive proposition
(b) the enthalpy of formation of CO2 is more than that of Al2O3
(c) pure carbon is not easily available
(d) the enthalpy of formation of Al2O3 is too high
Answer
D
Question. Which one of the following metals is extracted by a carbon reduction process?
(a) Copper
(b) Iron
(c) Aluminium
(d) Magnesium
Answer
B
Question. Blister copper is
(a) impure Cu
(b) Cu alloy
(c) pure Cu
(d) Cu having 1% impurities
Answer
D
Question. In blast furnace, iron oxide is reduced by
(a) hot blast of air
(b) carbon monoxide
(c) carbon
(d) silica
Answer
B
Question. In electrorefining of copper, some gold is deposited as
(a) cathode
(b) e lectrode
(c) cathode mud
(d) anode mud
Answer
D
Question. In the extraction of Fe from Fe2O3 , the reducing agent used is
(a) C
(c) electrolytic reduction
(b) Al
(d) Cu
Answer
A
Question. The temperature of the slag zone in the metallurgy of iron using blast furnace is
(a) 1200- 1500°C
(b) 1500-1600°C
(c) 400-700°C
(d) 800-1000°C
Answer
D
Question. When copper pyrites is roasted in excess of air, a mixture of CuO + FeO is formed. FeO is present as impurities. This can be removed as slag during reduction of CuO. The flux added to form slag is
(a) SiO2 , which is an acidic flux
(b) limestone, which is a basic flux
(c) SiO2 , which is a basic flux
(d) Cao, which is a basic flux
Answer
A
Question. Heating mixture of Cu2O and Cu2 Swill give
(a) Cu2 SO3
(b) CuO + CuS
(c) Cu+ SO3
(d) Cu+ SO2
Answer
D
Question. Identify the reaction that does not take place during the smelting process of extraction.
(a) 2FeS + 3 O2 → 2 FeO + 2 SO2 ↑
(b) Cu2O + FeS → Cu2S + FeO
(c) 2 Cu2S + 3 O2 → 2 Cu2O + 2 SO2 ↑
(d) FeO+ SiO2 → FeSiO3
Answer
A
Question. During the extraction of gold, the following reactions take place
Au+ CN– + H2O →O2 X
X + Zn → Y + Au
X and Y respectively, are
(a) [Au (CN)2 r and [Zn (CN)6 J4-
(b) [Au (CN)4]2- and [Zn (CN)4]2-
(c) [Au (CN)4]3- and [Zn (CN)4]2-
(d) [Au (CN)2]–and [Zn(CN)4]2-
Answer
D

