Please see Money and Credit Exam Questions Class 10 Social Science below. These important questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest examination guidelines and syllabus issued by CBSE, NCERT, and KVS. We have provided Class 10 Social Science Questions and answers for all chapters in your NCERT Book for Class 10 Social Science. These solved problems for Money and Credit in Class 10 Social Science will help you to score more marks in upcoming examinations.
Exam Questions Money and Credit Class 10 Social Science
Objective Type Questions
Question. Who supervises the functioning of formal source of loans?
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) State Bank of India
(c) Central Bank of India
(d) Informal money lenders
Answer : (a) Reserve Bank of India
Question. Find the incorrect option:
(a) Demand deposit share the essential features of money
(b) With demand deposit payments can be made without cash
(c) Demand deposits are safe way of money transformation
(d) Demand deposit facility is like cheque
Answer : (d) Demand deposit facility is like cheque
Question. Arrange the following sentences in correct sequence
(i) Banks accept the deposits and also pay an amount as interest on the deposits.
(ii) They deposit it with the banks by opening a bank account in their name.
(iii) Workers who receive their salaries at the end of each month have extra cash at the beginning of the month.
(iv) People also have the provision to withdraw the money as and when they require.
Options:
(a) (i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii), (iv), (i)
(c) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv)
(d) (iv), (ii), (i), (iii)
Answer : (c) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv)
Question. Which of the following is a formal source of credit?
(a) Commercial banks
(b) Traders
(c) Borrowers
(d) Moneylenders
Answer : (c) Borrowers
Question. State whether the following statements are true or false
SHGs are the building blocks of organisation of the rural poor.
Answer : True
Question. Correct and Rewrite Questions
Loan is sactioned in the name of SHGs and is meant to create job opportunities for the members.
Answer : Loan is sanctioned in the name of SHGs and is meant to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
Question. Read the following given table and find out what was the outcome of Swapna?
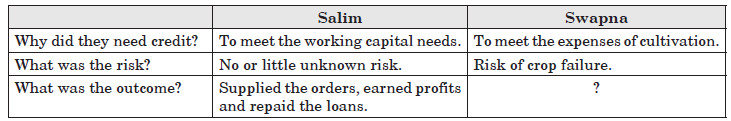
(a) Crop failed
(b) Found herself in the debt trap
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Repaid the loans
Answer : (c) Both (a) and (b)
Question. Study the given information carefully and answer the question that follows:
Krishna is working in a neighbouring field with very less wages. Expenses on sudden illnesses or functions in the family are also met through loans. The landowner charges an interest rate of 5 per cent per month. At present she owes landowner ₹ 5,000.
Analyse the credit arrangement given above.
Answer : The credit arrangement comes under the informal source of credit.
Question. Read the information given below and select the correct option.
Mohan is an agricultural labourer. There are several months in a year when he has no work and needs credit to meet his daily expenses. He depends upon his employer, the landowner for credit who charges an interest rate of 5 per cent per month. Mohan repays the money by working physically for the landowner on his farmland.
(i) Over the years his debt will –
(a) Increase – because of increasing interest and non-payment of monthly amount
(b) Remain constant – as he is working for the employer but is repaying less
(c) Reduce – as amount equivalent to his salary is being counted as monthly repayment
(d) Be totally repaid – as he is repaying the debt in the form of physical labour
Answer : (a) Increase – because of increasing interest and non-payment of monthly amount
(ii) Most of the agricultural labourers like Mohan depend upon loans from informal sector. Which of the following statements about this sector is correct–
(a) There are government bodies to supervise informal sector.
(b) Moneylenders ask for a reasonable rate of interest.
(c) Cost of informal loans to the borrower is quite high.
(d) Moneylenders use fair means to get their money back.
Answer : (c) Cost of informal loans to the borrower is quite high.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things? Give an example.
Answer : A person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she might want.
Example: The shoe manufacturer will first exchange shoes that he has produced for money and then exchange the money for wheat.
Question. Explain the meaning of currency?
Answer : Currency is modern forms of money that includes paper notes and coins and accepted as a medium of exchange. It is issued by the Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the central government.
Question. Define collateral.
Answer : Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns and given to the lender as a guarantee that he will repay the loan. If the borrower is unable to repay the loan, then the lender having the right to sell it and get the money back.
Question. Given that a large number of people in our country are poor, does it in any way affect their capacity to borrow?
Answer : If a large number of people in our country are poor, it will affect their capacity to borrow because they will not be having enough collateral, which decides how much amount of loan a person is eligible.
Question. Prove with an argument that there is a great need to expand formal sources of credit in rural India.
Answer : To expand formal sources of credit in rural India, dependence on informal sources of credit has to be reduced.
Question. How do the deposits with banks become their source of income?
Answer : Banks charge higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on deposits. The difference of interest is the main source of income of banks.
Question. Why is the supervision of the functioning of formal sources of loans necessary?
Answer : It is necessary because banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they are lending, to whom they are lending and what interest rate, etc.
Question. How does money eliminate the need for double coincidence of wants?
Answer : If we have money in our pocket we can purchase anything at anytime as we wish.
Question. Explain the importance of formal sector loans in India.
Answer : Importance of formal sector loans in India:
(i) They provide loans at a fixed rates and terms.
(ii) They give loans not just to profit making business and traders but also to small cultivators, small scale industries too small borrowers, etc.
Question. What are the two major objectives of a self-help groups?
Answer : The two major objectives of the self-help group are:
(i) To make the rural poor women self-reliant.
(ii) To provide platform to discuss and act on a variety of social issues.
Question. Why are demand deposits considered as money?
Answer : Demand deposits are considered as money because the depositors get the facility of cheque against their demand deposits when they open an account in the bank, which is used to settle the transaction without the use of money.
Question. Why do banks maintain cash reserve?
Answer : Banks maintain cash reserve to arrange for daily withdrawals by depositors.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Discuss the negative role of credit with example.
OR
In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
Answer : Negative role of credit: Sometimes credit is very painful as it pushes the borrower into such a situation from where loan recovery is very difficult. In this situation the borrower is not able to repay the loan and many a times caught in the situation of debt-trap. For example, a small farmer, Swapna took loan for crop cultivation but due to some reason she faced the situation of crop failure. So she took another loan for spraying pesticides but the production was not enough to repay the loan. So she was caught in debt-trap.
Question. Why do banks and cooperative socities need to lend more? Explain.
Answer : Banks and cooperative societies need to lend more:
(i) This would lead to higher incomes.
(ii) People could borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(iii) They could grow crops and set up small-scale industries etc.
(iv) Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the country’s development.
(v) To save and reduce the dependence on informal sources of credit.
(vi) It is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that the poor can benefit from the cheaper loans.
Question. Why is credit a crucial element in the economic development?
Answer : Credit is a crucial element in economic development of a country because:
(i) It helps to meet the ongoing expenses of production
(ii) It helps in increasing earnings
(iii) It helps in completing production in time.
Question. Why is money transaction system better than barter system? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Transaction system is better than barter system because double coincidence of wants creates problem.
(ii) For example, shoe manufacturer wants to sell shoes in the market and wants to buy wheat. For this, he would look for a wheat growing farmer who would exchange his wheat with the shoes.
(iii) In barter system, goods are exchanged without the use of money.
(iv) In contrast, in an economy where money is in use; money by providing the crucial intermediate step eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants.
Question. Formal credit meets only about half of the total credit needs of the rural people. Where does the other half come from?
Answer : (i) Compared to formal lenders, most of the informal lenders charge much higher interest rates on loans like 3% to 5% per month, i.e., 36% a year.
(ii) Besides the high interest rate, informal lenders impose various other tough conditions. For example, they make the farmers promise to sell the crop to him at a low price. There is no such condition in formal sector.
(iii) Loans taken by poor people from informal lenders sometimes, lead them to debt trap because of high interest rate.
(iv) The formal sources of credit in India still meets only about half of the total credit needs of the rural people.
Question. What are the modern forms of money? Why is the ‘rupee’ widely accepted as a medium of exchange? Explain two reasons.
OR
“The rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.” Explain.
Answer : The modern forms of money are listed below:
(i) Paper currency (ii) Coins (iii) Demand deposits (iv) Cheques
The rupee is accepted as a medium of exchange in the following ways:
(i) The currency is authorised by the government of the country.
(ii) In India, the Reserve Bank of India issues, currency notes on behalf of the central government.
(iii) The law legalises the use of rupee as a medium of payment that cannot be refused in setting transactions in India.
(iv) No individual in India can legally refuse a payment made in rupees. Hence, the rupee is widely accepted as a medium of exchange.
Question. Should there be a supervisor, such as the Reserve Bank of India, that looks into the loan activities of informal lenders? Why would its task be difficult?
Answer : Yes, there should be a supervisor, such as the Reserve Bank of India to look into the loan activities of informal lenders so that the informal sector credit sources will not be able to charge very high rate of interest. They will also have to maintain the records and they will not be able to use unfair means to get their money back. It will be difficult for the RBI to supervise the loan activities of the informal sector credit sources because mostly they do not maintain any record.
Question. What are the drawbacks of informal sources of credit?
OR
“The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : (i) Most of the informal lenders charge a much higher interest on loans. Thus the cost to the borrower of the informal loans is much higher.
(ii) Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of earning of the borrowers is used to repay the loan and they have less income left for themselves.
(iii) The high rate of interest of borrowing can mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower and it can lead to increasing debt and debt-trap.
(iv) People who might wish to start an enterprise by borrowing may not do so because of the high cost of borrowing.
Question. Why is cheap and affordable credit important for the country’s development? Explain any three reasons.
Answer : Cheap and affordable credit is important for the country’s development because of the following reasons:
(i) This would lead to higher incomes and many people could then borrow cheaply for a variety of needs.
(ii) With the help of cheap credit they could grow crops, do business, set up small scale industries which will generate employment and help in country’s development.
(iii) They could set up new industries or trade in goods. It will lead to the country’s development.
Question. Explain any three reasons for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas.
Answer : The three reasons for the banks and cooperative societies to increase their lending facilities in rural areas are:
(i) India is an agricultural country so the people in rural areas deserve a special attention, hence, the banks and cooperative society should help the needy people in rural areas.
(ii) Mostly the people in rural areas are illiterate and hence they can be easily cheated by the money lenders.
(iii) Only the banks and cooperative societies can provide loans to the rural household at cheap rates which can easily save them from the clutches of the money lenders.
Question. How far is it correct to say that money in your pocket cannot buy the basic needs to live well? Explain.
Answer : (i) Income by itself is not a completely adequate indicator.
(ii) Money cannot buy you a pollution-free environment.
(iii) Money may also not be able to protect you from infectious diseases.
Therefore, the whole community needs to take preventive steps, i.e.
(i) Collective security for the whole society.
(ii) Public facilities such as schools.
(iii) Public Distribution System in some states.
(iv) All can only be done collectively and not individually.
Question. What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
Answer : Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have 15 to 20 members and pool their savings and after some time, it becomes a large amount which is used to give loans to the needy ones at a very nominal rate of interest.
Its role:
(i) Help to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit.
(ii) Able to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
(iii) To organise rural poor particularly women and pool their savings. SHGs are becoming popular for the following reasons:
(i) They help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(ii) They can get timely loans for variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate.
(iii) They are building blocks of the organisation of the rural poor.
(iv) It helps women to become self-reliant.
(v) The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on various social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
Question. Dhananjay is a government employee and belongs to a rich household, whereas Raju is a construction worker and comes from a poor rural household. Both are in need and wish to take loan. Create a list of arguments explaining who between the two would successfully be able to arrange money from a formal source. Why?
Answer : Dhananjay will be able to get loan from a formal source.
Arguments :
Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources. Bank loans require proper documents and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans. Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence, are often willing to give a loan without collateral.
Question. Discuss the different phases of medium of exchange.
Answer : Different phases of medium of exchange:
Ancient phase: It is the time before the introduction of coins. Barter system (double coincidence of wants) was prevalent during this time. Goods and services were exchanged with goods and services. For example, grains and cattle were used in the exchange process.
Medieval phase: After the barter system, it came the use of metallic coins like gold, silver and copper coins. As these were made of precious metals they had value of their own.
Modern phase: In the modern phase, currency comprising paper notes and coins are used as a medium of exchange. These are not made of any precious metals even after being used as a medium of exchange because the government of the country authorises the currency.
Question. Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender? Discuss.
Answer : Manav will decide on whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender on the basis of various factors:
(i) He must have a collateral or asset which can guarantee his loan. If he lacks such an asset, he can’t get a loan from the bank. In this scenario, he will have to go to a moneylender, even though the latter charges a higher interest rate.
(ii) If Manav is not aware of the banes of borrowing from the informal sector, he might not even consider taking a bank loan.
(iv) If there are no banks in or near his area of residence or work place, then he will borrow from a moneylender.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. How does the use of money make exchange of things easier? Explain with examples.
Answer : (i) Money means wealth around which the whole economic activities of every country move. It acts as an intermediate in the exchange process and therefore, called a medium of exchange.
(ii) In our day to day transactions, goods are being bought and sold with the use of money. At times we do exchange services with money.
(iii) Use of money has made things easier to exchange as we can exchange it for any commodity we need.
(iv) The transactions are made in money because a person holding money can easily exchange it for any commodity or service that he or she wants.
(v) Thus, the main function of money in an economic system is to facilitate the exchange of goods and services. Without exchange of money nobody can fulfil his all needs and requirements.
Question. How are deposits with the bank beneficial for individual as well as for the nation? Explain with examples.
Answer : The deposits with banks are beneficial for individual as well as for nation:
(i) Banks accept deposit and also pay an amount as interest and in this way people earn money.
(ii) People’s money is safe with banks.
(iii) It is easy for individuals to get credit who have savings and current account in the banks.
(iv) Poor people who are engaged in production need credit.
(v) Credit provided by the banks for government projects help in development of the nation.
Question. Describe the vital and positive role of credit with examples.
OR
What is credit? How does credit play a vital and positive role? Explain with an example.
Answer : Credit refers to an agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment. Credit plays a vital and positive role as:
(i) Credit helps people from all walks of life in setting up their business, increase their income and support their families.
(ii) To some people loan helps a lot in constructing their houses and get relief from monthly rent.
(iii) To others it helps a lot in raising their standards.
(iv) Example: It is festival season two months from now and the shoe manufacturer, Salim, has received an order from a large trader in town for 3,000 pairs of shoes to be delivered in a month time. To complete production on time, Salim has to hire a few more workers for stitching and pasting work. He has to purchase the raw materials. To meet these expenses, Salim obtains loans from two sources. First, he asks the leather supplier to supply leather now and promises to pay him later. Second, he obtains loan in cash from the large trader as advance payment for 1000 pairs of shoes with a promise to deliver the whole order by the end of the month. At the end of the month, Salim is able to deliver the order, make a good profit, and repay the money that he had borrowed.
The credit helps him and now he is able to increase his earnings.
Question. “Poor households still depend on informal sources of credit.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer : (i) Banks are not present everywhere in rural India. Even when they are present, getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from informal sources.
(ii) Bank loans require proper document and collateral. Absence of collateral is one of the major reasons which prevents the poor from getting bank loans.
(iii) Informal lenders such as moneylenders, on the other hand, know the borrowers personally and hence are often willing to give a loan without collateral. The borrowers can, if necessary, approach the moneylenders even without repaying their earlier loans.
Question. Which are the two major sources of formal sectors in India? Why do we need to expand the formal sources of credit?
Answer : The two major sources of formal sources of credit are:
(i) Banks and
(ii) Cooperatives.
Need to expand formal sources of credit are:
(i) To save the poor farmers and workers from the exploitation by the informal sector credit.
(ii) Informal sector charges a higher interest on loans which means that a large part of the earnings is used to repay the loan.
(iii) Formal credit can fulfil various needs of the people through providing cheap and affordable credit.
Question. What is the role of SHGs? What are the reasons of its growing popularity?
OR
What are Self-Help Groups? Describe, in brief, their functioning.
Answer : Self-Help Groups (SHGs) have 15 to 20 members and pool their savings and after some time, it becomes a large amount which is used to give loans to the needy ones at a very nominal rate of interest.
Its role:
(i) Help to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit.
(ii) Able to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
(iii) To organise rural poor particularly women and pool their savings. SHGs are becoming popular for the following reasons:
(i) They help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(ii) They can get timely loans for variety of purposes and at a reasonable interest rate.
(iii) They are building blocks of the organisation of the rural poor.
(iv) It helps women to become self-reliant.
(v) The regular meetings of the group provide a platform to discuss and act on various social issues such as health, nutrition, domestic violence, etc.
Question. “Credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer : In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves considerable costs on seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, water, electricity, repair of equipment, etc. There is a minimum stretch of three to four months between the time when the farmers buy these inputs and when they sell the crop. Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest. Repayment of the loan is crucially dependent on the income from farming.
If the failure of the crop made loan repayment impossible then farmers had to sell part of the land to repay the loan. Credit, instead of helping those farmers to improve their earnings, left them worse off and they came into the debt-trap. In this case credit pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.
In one situation credit helps to increase earnings and therefore the person is better off than before. In another situation, because of the crop failure, credit pushes the person into debt trap. To repay the loan farmers have to sell a portion of their land. They are now clearly much worse off than before. Whether credit would be useful or not, therefore, depends on the risks in the situation and whether there is some support in case of loss.
Thus, through the above situation or example, we can easily say that credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.
Question. “The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.” Support the statement with arguments.
Answer : The credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged because:
(i) About 85% of loans taken by the poor households in the urban areas are from informal sources.
(ii) Informal lenders charge very high interest on their loans.
(iii) There are no boundaries and restrictions.
(iv) Higher cost of borrowing means a larger part of the earnings of the borrowers is used to repay the loan.
(v) In certain cases, the high interest rate for borrowing call mean that the amount to be repaid is greater than the income of the borrower.
(vi) This could lead to increasing debt and debt trap, therefore the credit activities of the informal sector should be discouraged.
Picture/Graph Based Question
Question. Study the graph and answer the question.

Which of the following statements best signifies this graph?
(a) In the urban areas 85 per cent of the loans taken by poor households are from the informal sectors.
(b) Only 10 per cent of the loan taken by rich urban households are from informal sectors.
(c) 90 per cent are from formal sectors.
(d) All of the above
Answer : (d) All of the above
Case Based Questions
Question. Read the source given below and answer the questions by choosing the most appropriate option.
In recent years, people have tried out some newer ways of providing loans to the poor. The idea is to organise rural poor, in particular women, into small Self Help Groups (SHGs) and pool (collect) their savings. A typical SHG has 15-20 members, usually belonging to one neighbourhood, who meet and save regularly. Saving per member varies from ₹ 25 to ₹ 100 or more, depending on the ability of the people to save. Members can take small loans from the group itself to meet their needs. The group charges interest on these loans but this is still less than what the moneylender charges. After a year or two, if the group is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from the bank.
(i) Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct about Self-Help Groups?
(a) The SHGs help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
(b) The SHGs are the building blocks of organisation of the rural poor.
(c) The SHGs is the group which is not responsible for the repayment of the loan.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer : (d) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) Which among the following is the basic idea behind the SHGs for poor?
(a) Help to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit
(b) Help to reduce the functioning of formal sectors of credit
(c) Help the men to become self-retiant
(d) Organise urban poor people particularly women
Answer : (a) Help to reduce the functioning of informal sectors of credit
(iii) Which of the following options signifies the definition of SHGs?
(a) It is the small groups of 15 to 20 members.
(b) It is mostly active in rural areas especially women for the improvement of their economic and social conditions.
(c) It is able to create self-employment opportunities for the members.
(d) All of the above
Answer : (d) All of the above
(iv) Which of the following is/are the reason(s) for the banks willing to provide credit to the self-help groups without collateral?
(a) SHGs used to be regular in saving.
(b) The group decides the loan activities and any case of non-repayment of the loan is taken seriously by the group members.
(c) This group helps the poor rural women to become economically self-reliant and women empowerment.
(d) All of the above
Answer : (d) All of the above
