Students should practice questions given in Structure Of The Atom Chapter 4 Class 9 Science Worksheets. These worksheets for Class 9 Science have a good collection of important questions and answers which are expected to come in your class tests and examinations. You should learn these solved worksheet questions for Science Class 9 as it will help you to understand all topics and give you more marks.
Class 9 Science Worksheets Chapter 4 Structure Of The Atom
Please refer to below questions and answers for Structure Of The Atom Chapter 4 Class 9 Science Worksheets. Prepared by expert teachers for Standard 9 Science
Question. Which study led to the conclusion that atoms are not indivisible?
Answer
Study of static electricity and the condition under which electricity is conducted by different substances led to the conclusion that atoms are not indivisible.
Question. What kind of elements have a tendency to lose electrons? What are they commonly called?
Answer
The elements having 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons have the tendency to loose electrons. They are commonly called metals.
Question. Which particles were discovered by Chadwick, Thomson and Goldstein
Answer
(i) Chadwick – Neutron
(ii) Thomson – Electron
(iii) Goldstein – Proton
Question. Find the number of neutrons in 31X15.
Answer
31X15 indicate that no. of proton
= 15 and mass number = 31
Mass number = No. of protons + No. of neutrons = 31
Number of neutrons = 31 – number of protons
= 31 – 15 = 16
Question. Name the isotope used for treatment of cancer.
Answer
Isotope of cobalt : Co-60.
Question. Where is the mass of an atom concentrated?
Answer
Mass of an atom is concentrated in nucleus.
Question. What is the charge and mass of a -particles?
Answer
Charge is 2 and mass is 4 amu.
Question. Who discovered proton?
Answer
Goldstein discovered proton.
Question. If Z = 3, what would be the valency of the element? Also, name the element.
Answer
Atomic number Z = 3
Electronic configuration = 2 (K), 1 (L)
Valence shell has 1 electron in the outermost shell, so valency of element is 1. The element is lithium.
Question. Why do helium, neon and argon have a zero valency?
Answer
Helium, neon and argon have 2, 8 and 8 electron in outermost shell, thus there is no need to gain or loose electrons. So, they have zero valency.
Question. What is the mass of a neutron?
Answer
The mass of a neutron is 1.675 × 10–24 g.
Question. Which is much closer to the nucleus of an atom out of K and L shells?
Answer
K shell is much closer to the nucleus of an atom.
Question. Which shell can accommodate a maximum of 32 electrons?
Answer
Fourth shell can accommodate a maximum of 32 electrons.
Question. Name the radioisotope used for examining the circulation of blood in the body.
Answer
Na-24 is the radioisotope used for examining the circulation of blood in the body.
Question. Can the addition of neutron to the nucleus of an atom determine the atomic mass or number?
Answer
It will increase the atomic mass of the atom.
Question. Why do some elements possess fractional atomic mass?
Answer
Some elements possess fractional atomic mass because they occur in nature in different isotopic forms. So,accordingly their average mass is calculated.
Question. Do isotopes of an element have similar chemical properties?
Answer
Isotopes of an element have similar chemical properties because they have the same atomic number and valence electrons.
Question. What is an orbit?
Answer
Orbit is the path of electron around the nucleus.
Question. What are valence electrons?
Answer
The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom are known as valence electrons.
Question. What is an anion?
Answer
When an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is known as anion.
Question. Why helium have zero valency?
Answer
Helium have zero valency because its outermost orbit is completely filled.
Question. Why isotopes of an element are chemically similar?
Answer
Isotopes of an element are chemically similar because these have same electronic configuration.
Question. Why an atom is electrically neutral?
Answer
An atom is electrically neutral because it contains equal number of positively charged particles and negatively charged particles, i.e. protons and electrons.
Question. Is C1-35 and C1-37 have different valencies?
Answer
No, it is because these are isotopes of chlorine that have same atomic number but different mass number.
Question. Why noble gases show least reactivity?
Answer
Noble gases have their outermost octet completely filled up, so these gases show least reactivity.
Question. Define atomic number. How it is denoted?
Answer
Number of protons of an atom determines its atomic number. It is denoted by ‘Z’.
Question. The atomic number of calcium and argon are 20 and 18 respectively, but the mass number of both these elements is 40. What is the name given to such a pair of elements?
Answer
Isobars.
Question. Electron attributes negative charge, protons attribute positive charge. An atom has both but why there is no charge?
Answer
The negative and positive charges of electrons and protons respectively are equal in magnitude. So, the atom as a whole is electrically neutral.
Question. On the basis of Rutherford’s model of an atom, which subatomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
Answer
The positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom is called ‘proton’.
Question. Write the charge and mass of an electron.
Answer
Its mass is 1/2000 times that of proton and it is negatively charged.
Question. What type of charge is present on the nucleus of an atom?
Answer
Positive charge.
Question. Who discovered neutron?
Answer
James Chadwick.
Question. Define the following terms :
(i) Electronic configuration
(ii) Valence shell
(iii) Valency
Answer.
(i) The distribution of electrons amongst different orbits of an atom is known as electronic configuration.
(ii) The outermost shell of an atom is called its valence shell.
(iii) The combining capacity of an atom is called its valency or the number of electrons lost or gained by an atom to acquire noble gas configuration.
Question. Is there any relationship between atomic number, mass number, isotopes, isobars and valency of an atom? Explain.
Answer. Atomic number : It tells the number of protons (Z).
Atomic Mass : Total number of proton and neutron (A) is called atomic mass.
Isotopes : When atoms of same element have same number of protons but different number of neutrons is called isotopes.
Isobars : When atoms of different element have same atomic mass but different atomic number, such atoms are called isobars.
Valency : It is the combining capacity of an atom or it is defined as number of electrons lost or gained by an atom to acquire noble gas configuration.
Question. Two elements denoted as follows : 2040X and 1840Y.
(i) Find the number of electrons present in X and Y.
(ii) Find the number of nucleons present in X and Y.
(iii) Explain the term used to represent X and Y.
Answer.
(i) The elements X and Y have 20 and 18 electrons respectively.
(ii) Both have 40 nucleons.
(iii) Isobars.
Question. What is discharge tube?
Answer. A discharge tube is a glass tube about 70 cm long and 5 cm of diameter. Two metal electrodes are sealed at the two ends, one is connected to negative terminal of battery and other to the positive terminal. A side tube is fused at the centre of the glass tube which serves to pump out air from it, using a suction pump.
Question. Give important properties of cathode rays.
Answer.
(i) Cathode rays travel in straight line.
(ii) Cathode rays can rotate a light wheel placed in their path.
(iii) They ionise gas through which they pass.
(iv) They are deflected by magnetic field.
(v) They can penetrate through thin metallic sheet.
(vi) Mass of cathode ray particle is too small.
Question. If K and L shells of an atom are full, then what would be the total number of electrons in the atom? What is the valency of this element? Name the element.
Answer. The maximum numbers of electrons that can occupy K and L shells of an atom are 2 and 8 respectively.
Therefore, if K and L shells of an atom are full then the total number of electrons in the atom would be 2 + 8 = 10 electrons. So, the valency of this element is zero. The element is neon (Ne).
Question. What was Chadwick’s experiment?
Answer. In Chadwick’s experiment, he bombarded beryllium atoms with high speed particles.
(i) The rays emitted from beryllium during bombardment had speeded about one-tenth the speed of light.
(ii) Later Chadwick was able to show that these rays consisted of neutral particles called neutron.
Question.Give the mass numbers of A and B, What is the relation between the two species?
Answer. Mass number of A = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
= 6 + 6 = 12u
Mass number of B = No. of protons + No. of neutrons
= 6 + 8 = 14u
The species A and B are isotopes, as they have same atomic number but different mass number.
Question. Answer the following question with the help of table :

Give :
(i) The electronic distribution of element B.
(ii) The valency of element A.
(iii) The atomic number of element B.
(iv) The atomic mass of element D.
Answer.
(i) The electronic distribution of element B = 2, 8, 6
(ii) The valency of element A = +1
(iii) The atomic number of element B = 16
(iv) The atomic mass of element D = 17 + 22 = 39
Question. How has atomic number improved the definition of an element?
Answer.
(i) Atomic number of an element = number of proton = number of electron
(ii) Atomic number gives the position of the element in periodic table. An element can now be defined as a substance comprising of atoms all of which have same atomic number.
Question.In what way the Rutherford proposed atomic model?
Answer. Rutherford proposed a model in which electrons revolve around the nucleus in well-defined orbits.There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. He also proposed that the size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is centered in the nucleus.
Question. What is the difference between Rutherford’s atomic model and Thomson’s atomic model?
Answer. Rutherford proposed a model in which electrons revolve around the nucleus in well-defined orbits.There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. He also proposed that the size of the nucleus is very small as compared to the size of the atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is centred in the nuclei. Thomson proposed the model of an atom to be similar to a christmas pudding. The electrons are studded like currants in a positively charged sphere like Christmas pudding and the mass of the atom was supposed to be uniformly distributed.
Question. (i) An ion X2+ contains 10 electrons and 12 neutrons.
What is the atomic number and mass number of the element X?
(ii) Is it possible in an atom to have 12 protons and 13 electrons?
(iii) Why helium gas is inert?
Answer.
(i) Atomic number = 12,Mass number = 24.
(ii) No, it is not possible. An atom is electrically neutral. The number of positively charged particles (protons) is always equal to the number of negatively charged particles (electrons).
(iii) Helium atom has completely filled outermost shell. Thus, it is inert.
Question. State the major drawback in Rutherford’s model of an atom. Mention two features of Bohr’s model which helped compensate this drawback.
Answer. The major drawback of Rutherford’s model of an atom is that it does not explain the stability of an atom. Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo acceleration. During acceleration, charged particles would radiate energy. So, revolving electron would lose energy and finally fall into the nucleus.
Two features of Bohr’s model which helped to resolve this drawback :
Only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons are allowed inside the atom.While revolving in these discrete orbits, the electrons do not radiate energy.
Question. Write the conclusions drawn by Rutherford for the following observation during his scattering experiment :
(i) Most of the alpha-particles passed straight through the gold foil.
(ii) Some alpha-particles getting deflected from their path.
(iii) Very small fraction of alpha-particles getting deflected by 180°.
Answer.
(i) Most of the space inside the atom is empty.
(ii) It indicates that the positive charge of the atom occupies a very little space.
(iii) All the positive charge and mass of the gold atom were concentrated in a very small volume within the atom.
Question. From the symbol 16S32, give :
(i) Atomic number of sulphur
(ii) Mass number of sulphur
(iii) Electronic configuration of sulphur
(iv) Which of the two elements given would be chemically more reactive? S, Ar
Answer.
(i) 16
(ii) 32
(iii) Electronic configuration : 2, 8, 6.
(iv) Element S, having atomic number 16 is chemically more reactive than element Ar of atomic number 18. It is because the outermost shell of the atom of element S has six electrons only and has to complete its octet, whereas the outermost-shell of the atom of element Ar is completely filled up,i.e., its octet is complete and thus it shows little chemical activity.
Question. Describe briefly Thomson’s model of an atom.
Answer. Thomson’s model of an atom :
An atom consists of a positively charged sphere and the electrons are embedded in it.
The negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude. So, the atom as a whole is electrically neutral.
Question. How was the neutron discovered?
Answer. Atom was considered to have electrons and protons only till 1920. But electrons have negligible mass. Then entire mass of the atom was considered to be only due to the protons present in it. In 1920, Rutherford found that atomic masses of all elements are higher than the mass of all protons and electrons in their atoms. Chadwick discovered the presence of an electrically neutral particle inside the atom in 1932.
Question. Describe in brief the Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment with the help of labelled diagram. Write any three important conclusions drawn from the experiment.
Answer. Rutherford took a very thin gold foil and born bared it with a -particles and he observed that :
(i) Most of the fast moving a-particles passed straight through the gold foil.
(ii) Some of the alpha-particles were deflected by the foil by small angle.
(iii) Out of every 12000 particles, one appeared to rebound.
From the above observations, he concluded :
(i) There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. Nearly all mass of an atom resides in the nucleus.
(ii) The electrons revolve around the nucleus in well defined orbits.
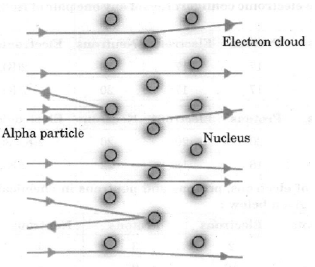
(iii) The size of the nucleus is very small as compared with the size of the atom.
Question. Give the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory.
Answer.
(i) Every element is composed of extremely small particles called atoms.
(ii) Atoms of a given element are identical, both in mass and properties. Different chemical elements have different kinds of atoms; in particular, their atoms have different masses.
(iii) Atoms cannot be created, destroyed or transformed into atoms of other elements.
(iv) Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other in small whole number ratios.
(v) The relative number and kinds of atoms in a given compound are constant.
Question. Give the number of electron, proton and neutron in 59CO27 and 108Ag47.
Answer.
(i) Number of protons in Co = 27
(ii) Number of electrons in Co = 27
(iii) Number of neutrons in Co = 59 – 27 = 32
(iv) Number of protons in Ag = 47
(v) Number of electrons in Ag = 47
(vi) Number of neutrons in Ag = 108 – 47 = 61
Question. Elaborate the postulates put forward by E. Rutherford about the structure of atom based on the a -particle scattering experiment.
Answer.
(i) Most of the space inside the atom is empty because most of the a -particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected.
(ii) Very few particles are deflected from their path,indicating that positive charge of the atom occupies very little space.
(iii) A very small fraction of particles was deflected by 180°, indicating that all the positive charge and mass of the gold atom were concentrated in a small volume within the atom.
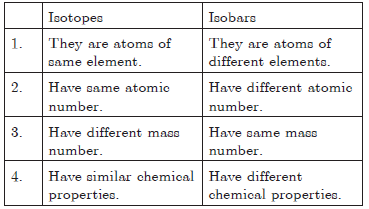
Question.Give difference between isotopes and isobars.
Answer.