Students should refer to Worksheets Class 12 Biology Biotechnology and its Application Chapter 12 provided below with important questions and answers. These important questions with solutions for Chapter 12 Biotechnology and its Application have been prepared by expert teachers for Class 12 Biology based on the expected pattern of questions in the class 12 exams. We have provided Worksheets for Class 12 Biology for all chapters on our website. You should carefully learn all the important examinations questions provided below as they will help you to get better marks in your class tests and exams.
Biotechnology and its Application Worksheets Class 12 Biology
Question. Process involving silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule is called :
(a) Transcription
(b) RNA interference
(c) DNA interference
(d) None of these
Answer
B
Question. Nematode-specific genes were introduced into the host plant (tabacco plant) by using which vector?
(a) Plasmid vector
(b) Cosmid vector
(c) Bacteriophage vector
(d) BAC
Answer
B
Question. Which one of the following statements are true regarding genetic modifications ?
(a) Genetic modifications reduced reliance on chemical pesticides
(b) Genetic modifications has enhanced nutritional value of food.
(c) Genetic modifications made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses.
(d) All are correct
Answer
D
Question. Bacterium which is known as ‘Super bug’ is :
(a) Pseudomonas putida
(b) Salmonella
(c) Eischerichia
(d) Agrobacterium
Answer
A
Question. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because :
(a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin
(b) toxin is immature
(c) toxin is inactive
(d) bacteria enclose toxin in a special sac
Answer
C
Question. Which one of the following statements about genetically engineered insulin is incorrect.
(a) E.coli is used for producing humulin
(b) Chains A, B were produced separately
(c) Eli lily company prepared it for first time
(d) Genetically engineered insulin has C-peptide
Answer
D
Question. Animals those have had their DNA manipulated to possess and express an extra (foreign) gene are known as :
(a) Transgenic animals
(b) Genetically modified animals
(c) Both (1) and (2)
(d) None of the above
Answer
C
Question. Genetically engineered bacteria are being used in commercial production of :
(a) melatonin
(b) testosterone
(c) thyroxine
(d) human insulin
Answer
D
Question. Insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains, which are linked together by?
(a) Sulphide bridges
(b) Peptide bridges
(c) Chloride bridges
(d) Disulphide bridges
Answer
D
Question. Over 95 percent of all existing transgenic animals are :
(a) Pigs
(b) Cows
(c) Fish
(d) Mice
Answer
D
Question. Genetics modified crops (GMC) are useful in agriculture because :
(a) They are more tolerant to abiotic stresses
(b) They increase reliance on chemical pesticide
(c) They have reduced nutritional value
(d) All the above
Answer
A
Question. Golden rice is enriched in :
(a) Vitamin C
(b) Vitamin D
(c) Vitamin A
(d) Vitamin E
Answer
C
Question. Critical research areas of biotechnology are :
(a) providing the best catalyst in the form of improved organism usually a microbe or pure enzyme.
(b) Creating optimal conditions through engineering for a catalyst to act.
(c) Down stream processing technologies to purify the protein/organic compound.
(d) All the above
Answer
D
Question. Bacterium genetically engineered for cleaning oil spills is :
(a) Eischerichia coli
(b) Pseudomonas putida
(c) Salmonella typhimurium
(d) Agrobacterium tumifaciens
Answer
B
Question. Meloidegyne incognitia which infects the roots of tobacco plants causing a great reduction in yield is a :
(a) Nematode
(b) Bacterium
(c) Virus
(d) Alga
Answer
A
Question. The protien encoded by the gene cryIAc and cryIIAb,controls :
(a) Cotton bollworm
(b) Corn borer
(c) Cotton borer
(d) All the above
Answer
A
Question. Which of the following plants is genetically modified for improved nutritional value of food?
(a) Potato
(b) Wheat
(c) Rice
(d) Maize
Answer
C
Question. Which animal is being used to test the safety of polio vaccine?
(a) Transgenic mice
(b) Transgenic pig
(c) Transgenic cow
(d) Transgenic cat
Answer
A
Question. A nematode Meloidegyne incognitia infects the root of tobacco plant and causes a great reduction in yield. A novel strategy was adopted to prevent this infection which was based on the process of :
(a) DNA interference
(b) RNA interference
(c) PCR technique
(d) DNA test
Answer
B
Question. In RNA interference (RNAi) :
(a) The silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevent translation of the mRNA :
(b) The silencing of a specific mRNA due to dsDNA
(c) The silencing of a specific mRNA due to tRNA
(d) All the above
Answer
A
Question. Transgenic animals produces biological product such as a-1-antitrypsin, which is used to treat :
(a) Emphysema
(b) Cystic fibrosis
(c) Phenyl ketonuria
(d) Sickle cell anaemia
Answer
A
Question. Meloidegyne incognitia infects the root of which plant ?
(a) Potato
(b) Soyabean
(c) Tobacco
(d) Tomato
Answer
C
Question. How many documented varities of basmati rice distinct for its unique aroma and flavour are grown in India?
(a) 27 varities
(b) 25 varities
(c) 28 varities
(d) 26 varities
Answer
A
Question. The first transgenic cow was ‘Rosie’, produces :
(a) Human protein-enriched milk (a-lactabumin)
(b) Human protein a-1 antitrypsin riched milk
(c) Human protein enriched milk (insulin)
(d) All the above
Answer
A
Case Based MCQs
Case I : Read the following passage and answer the questions from given below.
Insulin used to cure diabetes was earlier extracted from pancreas of slaughtered cattle and pigs. Insulin extracted from an animal source, though caused some patients to develop allergy or other types of reactions to the foreign protein. Human insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains : chain A and chain B, that are linked together by disulphide bridges.
In mammals including humans, insulin is synthesised as a pro-hormone which contains an extra stretch called the C-peptide. This C peptide is not present in mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin.
Question. The following is a list of some stages involved in producing human insulin from genetically engineered bacteria.
1. The bacteria are cultured in a fermenter for large scale production.
2. Recombinant insulin is extracted from the bacterial cells that expresses insulin gene.
3. The same restriction enzyme is used again to cut the bacterial plasmid for insertion of the human insulin gene.
4. Bacteria take up the plasmid carrying the insulin gene.
5. A restriction enzyme is used to cut human DNA to extract the insulin gene.
Select the correct order of these stages.
(a) 1, 5, 3, 4, 2
(b) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1
(c) 4, 5, 3, 2, 1
(d) 5, 3, 4, 1, 2
Answer
D
Question. Why is the fermentor important for the production of human insulin by transgenic bacteria?
(a) It provides optimal conditions for the transgenic to multiply rapidly.
(b) It facilitates the extraction and purification of insulin from the transgenic bacteria.
(c) It maximise the rate of fermentation of the transgenic bacteria.
(d) It provides the low-oxygen conditions that are important for insulin production.
Answer
A
Case II : Read the following passage and answer the questions from given below.
Transgenic cows have extra gene or genes inserted into their DNA. Firstly the genes for the desired product is identified and sequenced.
Then a gene construct containing this desired gene is introduced into female cow cells.
Transgenic bovine cells are selected and fused with bovine oocytes that have had all of their
chromosomes removed. Once fused with the oocyte, the transgenic cells chromosomes are
reprogrammed to direct development which can be implanted into a recipient cow. The resulting
transgenic cow only express the transgene in her milk. This is because expression of the transgene
is controlled by a promoter specific to lactating mammary cells.
Question. The gene construct with desired gene is introduced into female cow cells by
(a) transformation
(b) transduction
(c) transfection
(d) transplantation.
Answer
C
Question. The name of first transgenic cow is
(a) Tracy
(b) Dolly
(c) Rosie
(d) ANDI.
Answer
C
Question. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement I : Transgenes only express in the mammary glands of transgenic cow.
Statement II : Transgenes are present in chromosomes of every cell in transgenic cow.
(a) Both statements I and II are true.
(b) Both statements I and II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but statement II is true.
Answer
A
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
Two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason.
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Genetically modified microbes help in crop protection.
Reason : Transgenic bacteria control insects by producing endotoxins.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is popular in genetic engineering because this bacterium is associated with the roots of all cereal and pulse crops.
Reason : Agrobacterium tumefaciens, is pathogen of several dicot plants is able to cause crown gall tumors. These tumors are incited by the conjugative transfer of DNA segment (T DNA).
Answer
D
Question. Assertion : Agrobacterium tumefaciens is called natural genetic engineer.
Reason : Agrobacterium tumefaciens infects all broad-leaved agricultural crops but does not infect cereal crops.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : PCR is routinely used for early diagnosis of HIV in suspected AIDS patients.
Reason : PCR can detect low amounts of DNA.
Answer
B
Question. Assertion : Molecular probes are available for diagnosing genetic disorders, e.g., Duchenne muscular dystrophy, cystic fibrosis, Tay-sach’s disease.
Reason : The molecular probes are usually double stranded pieces of DNAs, labelled with radioisotopes such as 32P.
Answer
C
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. State the role of C peptide in human insulin.
Answer : The C-peptide joins the A-peptide with B-peptide in the proinsulin. It is not present in mature insulin and is removed during processing of proinsulin to insulin.
Question. What is a patent ?
Answer : A patent is the right granted by a government to an inventor to prevent others from commercial use of his/her invention.
Question. Give the full form of SCID.
Answer : Severe combined immunodeficiency disease.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Name the cry genes that control cotton bollworm and corn borer respectively.
Answer : The genes cryIAc and cryIIAb control the cotton bollworms, whereas cryIAb controls corn borer.
Question. Name the transgenic plant from which hirudin is extracted.
Answer : Brassica napus
Question. Biopiracy should be prevented. State why and how?
Answer : Some multinational companies of industrialised nations have a good economic status but are poor in biodiversity and are exploiting biodiversity of developing and underdeveloped countries without authorisation and proper compensation.
There has been growing realisation of the injustice, inadequate compensation and benefit sharing between developed and developing countries. Therefore, some nations are developing laws to prevent such unauthorised exploitation of their bioresources and traditional knowledge.
Question. What is the full form of SCID? Mention the cure of this disorder. Mention any one point how SCID is different from AIDS.
Answer : SCID stands for severe combined immunodeficiency disease. The SCID patient has a defective gene for the enzyme adenosine deaminase. He/she lacks functional T-lymphocytes and therefore fails to fight with infecting pathogens. It can be cured by gene therapy.
In SCID, the patient lacks functional T-lymphocytes and it is congenital while in AIDS only T-helper cells are destroyed by virus, but is not congenital.
Question. What are cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Answer : The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis is a common soil bacterium which produces a protein toxin that kills certain insects. The toxin is a crystal (Cry) protein. There are several kinds of Cry proteins which are toxic to different groups of insects. The gene encoding Cry protein is called cry gene.
Biotechnologists have been able to isolate the gene responsible for production of toxin and introduce it into a number of plants to produce genetically modified plants resistant to insects, e.g., Bt cotton (resistant to bollworm) and GM tobacco (resistant to hornworms).
Question. Why do lepidopterans die when they feed on Bt cotton plant? Explain how does it happen.
Answer : Bt cotton plant contains Bacillus thuringiensis, which produces Bt toxin, an insecticidal protein. This Bt toxin protein exist as inactive form but once an insect ingest the inactive toxin, it is converted into active form of toxin due to alkaline pH of the insects gut which solublise the crystals. The activated toxin binds to surface of midgut epithelial cells and creates pores that cause cell swelling and lysis and causes the death of the insect.
Question. What is special of “Flavr Savr” variety of tomato ? Why is it preferred to its normal native variety ?
Answer : Flavr Savr, a variety of tomato is a genetically modified plant. In this variety one gene, which produces polygalactouronase enzyme is inactivated. The non availability of this enzyme prevents over ripening. Thus, fruit remains fresh for long time and it also retains flavour, superior taste and higher quantity of total soluble solids. So it prevents post harvest and over ripening losses. Thus, it is preferred over normal native variety.
Question. Explain the structure of human insulin with the help of a diagram.
Answer : Insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains: chain A and chain B, that are linked together by disulphide bridges.
In mammals, including humans, insulin is synthesised as a prohormone which contains an extra stretch called the C peptide. This C peptide is not present in the mature insulin and is removed during maturation into insulin. The given diagram explains the maturation of proinsulin into insulin:

Question. Explain the various steps involved in the production of artificial insulin.
Answer : The steps involved in the production of artificial insulin or humulin are as follows:
(i) Isolation of donor or DNA segment – A useful DNA segment is isolated from the donor organism.
(ii) Formation of recombinant DNA (rDNA) – Both the vector and donor DNA segments are cut in the presence of restriction endonuclease. In the presence of ligase DNA segments of both are joined to form rDNA.
(iii) Production of multiple copies of rDNA – In this process multiple copies of this recombinant DNA are produced.
(iv) Introduction of rDNA in the recipient organism – The rDNA is inserted into a recipient organism.
(v) Screening of the transformed cells – The recipient (host) cells are screened in the presence of rDNA and the product of donor gene. The transformed cells are separated and multiplied.
Question. Name the soil bacterium that produces a protein/chemical that is toxic to insect pests.
Show with example that these are encoded by different forms of the genes.
Answer : Soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produces proteins that kill certain insects like lepidopterans (tobacco budworm, armyworm), coleopterans (beetles) and dipterans (flies, mosquitoes), etc., B. thuringiensis forms some protein crystals.
These crystals contain a toxic insecticidal protein. This toxin does not kill the Bacillus (bacterium) because it exists as inactive protoxins in them. But, once an insect ingests the crystals, it is converted into an active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the alimentary canal that solubilises the crystals.
The activated toxin binds to the surface of mid gut epithelial cells and creates pores which cause cell swelling and lysis and finally cause death of the insect.
cry genes code for certain crystal (cry) proteins that are toxic to insect larvae. The genes cryIAc and cryIIAb control cotton bollworm. When these genes are introduced into cotton plants through genetic engineering, these plants become resistant to the attack of cotton bollworm.
Question. Two children, A and B aged 4 and 5 years respectively visited a hospital with a similar genetic disorder. The girl A was provided enzyme replacement therapy and was advised to revisit periodically for further treatment. The girl, B was, however, given a therapy that did not require revisit for further treatment.
(a) Name the ailments the two girls were suffering from.
(b) Why did the treatment provided to girl A required repeated visits?
(c) How was the girl B cured permanently?
Answer : (a) Both the girls A and B were suffering from SCID (Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency) syndrome produced by the deficiency of enzyme Adenosine deaminase (ADA).
(b) The treatment provided to girl A required repeated visits because enzyme replacement therapy is not permanent cure. This is because these patients do not have functional T-lymphocytes, therefore they cannot provide immune responses against invading pathogens.
(c) The girl B was treated by the transplanted stem cells that are injected into the bloodstream. They will then become healthy white blood cells that replenish immune functions – essentially building a whole new, functional immune system for the girl B. The immune system regains complete function and hence girl B was permanently cured.
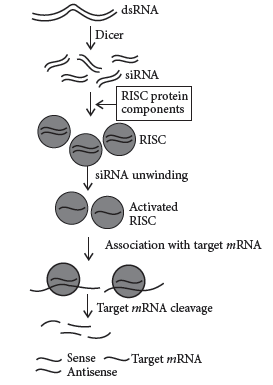
Question. Diagrammatically show steps involved in RNA interference.
Answer : The Steps in RNA interference
Question. Explain enzyme- replacement therapy to treat adenosine deaminase deficiency. Mention two disadvantages of this procedure.
Answer : Adenosine deaminase (ADA) enzyme is crucial for the immune system to function. Its deficiency is caused due to the deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase. In some patients, ADA deficiency can be cured by the bone marrow transplantation. It can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to the patient by injection.
Two disadvantages of enzyme replacement therapy are :
(i) It is not permanent cure because the replacement patient of ADA deficiency do not have functional T-lymphocytes, they cannot provide immune responses against invading pathogens.
(ii) It is a costly method.
Question. How is the Bt cotton plant created as a GM plant? How is it protected against bollworm infestation?
Answer : Two genes cryIAc and cryIIAb control cotton bollworms.
These two genes were isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis and incorporated into cotton plant. The genetically modified plant is called Bt cotton as it contains Bt toxin genes. The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produces Bt toxin proteins in mature form. When the insect larvae ingest any plant part, toxin becomes active in the alkaline pH of the gut and kills the insect pests. That is how Bt cotton attains resistance against bollworm.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Neeraj was having a debate with Mohit regarding the advantages and disadvantages of transgenic animals. Neeraj was of the view that production of transgenic animals violates the integrity of species and animals suffer from cruelty so, it is unethical. On the other hand, Mohit emphasised the benefits that transgenic animals provide to the human race in various fields especially medicine.
(a) How do transgenic animals benefit humans?
(b) List the ethical issues related with the production of transgenic animals.
Answer : (a) Benefits derived from transgenic animals are as follows:
(i) They produce useful biological products, that can be created by introduction of portion of gene, which codes for a particular product such as human protein (a ‑1- antitrypsin) from transgenic sheep is used to treat emphysema.
(ii) Transgenic mice are being developed for use in testing the safety of vaccine before they are used in humans.
(iii) They carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals. They are then exposed to toxic substances and the effects are studied.
(b) The ethical issues concerned with the production of transgenic animals include:
(i) Introduction of a transgene from one species into another species violates the ‘integrity of species’.
(ii) Transfer of human genes into animals (and vice-versa) dilutes the concept of ‘humanness’.
(iii) When animals are used for production of pharmaceutical proteins, they are virtually reduced to the status of a ‘factory’.
(iv) Use of animals in biotechnology causes great suffering to them.
(v) It is disrespectful to living beings, and only exploits them for the benefit of human beings.
Question. Briefly explain the principle, procedure and the role of ELISA.
Answer : Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a nonisotopic immunoassay. ELISA is based on the immunochemical principles of antigen antibody reaction. The stages of ELISA are summarized as follows:
(i) The antibody against the protein to be determined is fixed on an inert solid such as polystyrene. The biological sample containing the protein to be estimated is applied on the antibody coated surface. The protein antibody complex is then reacted with a second protein specific antibody to which an enzyme is covalently linked. Peroxidase, amylase and alkaline phosphatase are commonly used.
(ii) After washing the unbound antibody linked enzyme, the enzyme bound to the second antibody complex is assayed.
The enzyme activity is determined by its action on a substrate to form a product (usually coloured). This is related to the concentration of the protein being estimated.
ELISA is widely used for the determination of small quantities of proteins (hormones, antigens, antibodies) and other biological substances. The most commonly used pregnancy test for the detection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine is based on ELISA. ELISA is also been used for diagnosis of HIV viruses in AIDS patient.
