Please refer to the Lifelines of National Economy Notes Class 10 Social Science given below. These revision notes have been designed as per the latest NCERT, CBSE, and KVS books issued for the current academic year. Students will be able to understand the entire chapter in your class 10th Social Science book. We have provided chapter-wise Notes for Class 10 Social Science as per the latest examination pattern.
Revision Notes Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 Social Science
Students of Class 10 Social Science will be able to revise the entire chapter and also learn all important concepts based on the topic-wise notes given below. Our best teachers for Grade 10 have prepared these to help you get better marks in upcoming examinations. These revision notes cover all important topics given in this chapter.
Key points to remember
Road Density – The length of road per 100 sq kms of area is known as density of roads
Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways – It is major road development project linking the four metropolitan cities-Delh, Kolkata, Mumbai and Chennai by six lane super highways
North South Corridor – Roads linking Srinagar to Kanya Kumari
East-West Corridor – Roads linking Silcher (Assam) to Porbandar (Gujarat)
National Highways – Major roads connecting state capitals and metropolitan cities of a country.
State Highways – Roads linking a state capitals with different district headquarters.
International Trade – Trade between two countries 1s called international trade.
Export: When the goods are sent to other country for sale it is called as export.
Import: When the goods come from other country to be sold in India it is called import.
Balance of Payment: This is the difference between export and import of a country.
(1) Introduction: –
(i) We use various products in our daily life.
(ii) Theseproducts are produced in fields and factories.
(iii) They are brought to us (Consumer’s) by means of transport.
(iv) Traders bring these products to us (Consumer’s) byTrucks, Trains, Ships or Aeroplanes.
(v) The pace of development depends upon two things:-
(a) Production of goods and services.
(b) Their movement from production centres to consumers.
(vi)Transport is very essential for development.
(2) World as a large village:-
(i)Expansion of trade and transport throughout the world is the result of developed science and technology
(ii) The efficient and fast transport has converted the world into a global village.
(iii) Communication has played a key role in the development of trade and transport.
(iv) These three are complementary to each other.
(3) India is well linked: –
(i) In spite of its vast size and diversity India is very well linked with other countries.
(ii) Railways, Radio. TV. etc., are means of transport and communications.
(iii) They have helped with socio-economic progress.
(iv) Local and international trade has helped in the fast development of our economy.
(v) The developed economy has given us various facilities and comforts.
(vi) Means of transport and communications are called the lifelines of our country and economy.
(vii) Development of trade depends on the efficient transport and communication.
(4) Roadways: –
Characteristics: –
(i) One of the largest network in the world.
(ii) Total length 3.3 million kms.
(iii) Precede railways.
(iv) Edge over railways.
(v) Growing importance of Roads.
(4.1) Advantages of Road Transport: –
(i) Easy and low-cost construction.
(ii) Construction in difficult terrain.
(iii)Negotiate higher gradients of slopes.
(iv)Economical.
(v)Suitable for short distances, few persons and small amount of goods.
(vi) Provides door to door services.
(vii) Used as feeder to other mode of transport.
(viii)Link railway stations, sea ports, and air ports.
(ix)Strengthen defence.
(x)Suitablefor rural areas.
(xi) Flexible, reliable and speedy.
(xii) Important for the transport of perishable goods.
(xiii) Promote tourism.
(xiv)Suitable for mass contact.
(xv)Helpful at the time of floods and drought.
(xvi)Suitable for personal transport.
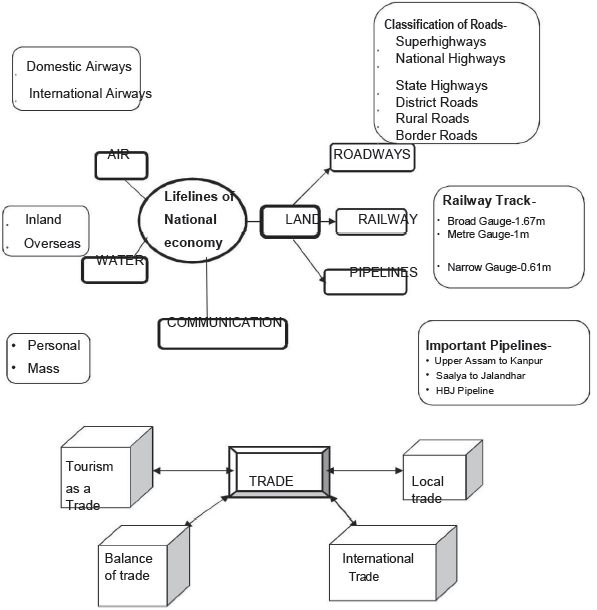
(4.2) Six classes of roads on the basis of capacity: –
(i) Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways.
(ii)National Highways.
(iii) State Highways.
(iv) District Roads.
(v) Other Roads.
(vi) Border Roads.
(4.3)Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways: –
(i) Six Lane Super Highways link Delhi-Kolkata- ChennaiMumbai and Delhi.
(ii) North-South Corridor-Srinagar to Kanyakumari.
(iii) East-West Corridor-Silcher toPorbandar.
(iv) Major objective- reduce time and distance.
(v)National Highway Authority of India
(4.4)National Highways: –
(i) Links extreme parts.
(ii) Primary Road system.
(iii) Maintained by Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
(iv)Run North-South and East –West.
(v) Sher Shah Suri Marg is National Highway no-1 between Delhi to Amritsar.
(4.5)State Highways: –
(i) Link District Headquarters.
(ii) Construction and Maintenance by State PWD.
(4.6)District Roads: –
(i) Link district headquarters.
(ii) Construction and Maintenance by Zila Parishads.
(4.7) Other Roads: –
(i) This category includes rural roads.
(ii) Link villages with town.
(iii)Under Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojna (PMGSY) every village is to be linked to towns.
(4.8) Border Roads: –
(i) Roads of border areas.
(ii) Constructed by Border Road Organisation (BRO) ofIndia.
(iii) Established in 1960.
(iv) Strategic importance in Northern and North-Eastern border areas.
(v) Improved accessibility in these areas.
(vi) Helped in Economic development.
(4.9) Classification of Roads on the basis of Material: –
(i) Metalled Roads, made of Cement, all Weather Road.
(ii) Unmettaled Roads not usable in Rainy Season.
(4.10) Road Density: –
(i) Road Density means the length of Roads per 100 sq. km of area.
(ii) Not uniform distribution of Roads.
(iii) Varies from 10 km J&K to 375 km in Kerala.
(iv) National average is 75 km.
(4.11) Problems of Road Transportation: –
(i) Inadequacy of road network.
(ii)Large volume of traffic and passengers.
(iii) Unmetalled roads unusable in rainy season.
(iv) Nationalhighways also inadequate.
(v) Congested in cities.
(vi) Poor quality and narrow.
(vii) Large number of crossing and traffic signals.
(viii)Total number of vehicles has more than doubled.
(5)Railways: –
(i)Principle mode of Transportation.
(ii) Perform various activities like Business, Tourismetc.
(iii) Useful for long distances.
(iv) Integrating force.
(v) Build economic life.
(vi) Acceleratedevelopment of industry and agriculture.
(vii) First train of India in 1953, between Mumbai and Thane.
(viii) 16 Railway zones.
(ix) Three Gauges: –
(a) Broad Gauge (1.676m
(b) Metre Gauge (1.000m)
(c) NarrowGauges(0.72 to 0.610m).
(5.1) Distribution of Railways: –Distribution of railways is very uneven.
(5.2) Statistics of Railways: – Stations-7133, Route length-63, 465, Locomotives-7817, Passenger
Service Vehicals-42,441, Other Coach Vehicals-5882, Wagons-2, 22,379(Approx.).
(5.3) Factors influencing the distribution: –
(i) Physiography.
(ii) Economy.
(iii) Administration.
(iv)Density of population.
(5.4) Railways in Northern Plains: –
(i) Favourable conditions:-level land, dense population, and developedagriculture.
(ii) Unfavourable conditions: -Rivers, posed problems for bridges, increased cost.
(5.5)Railways in Peninsular Region: – Tracks though Hill Gaps or Tunnels.
(5.6)Railways in Himalayas: – Unfavourable conditions: -High Relief, Sparse population,Underdeveloped Economy.
(5.7)Railways in Rajasthan: – Difficult to construct and maintain tracks in sands and swaps of Rajasthan& Gujarat.
(5.8)Railways in Forest Area: -Dense forest poses problems in track laying in Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Orissa.
(5.9)Railways in Sahyadri: – Tracks through passes.
(5.10)Konkan Railway: – (i) Konkan is important economic region.(ii) Konkan rail has facilated movements of goods and passengers. (iii) Problems:- sinking of tracks and landslides.
(5.11) Problems of Railways: – Railways are more important than all other means of transport.
(i)Ticketless travellers
(ii) Thefts
(iii) Damage to property
(iv) Chain pulling.
(6)Pipelines: –
(i)New mode.
(ii) Used for water in cities.
(iii) Now transport Crude oil, Petroleumproducts and Natural Gas to Refineries, Factories,Thermal plants etc.
(iv) Solids in the form of Slurry aretransported now through pipelines.
(v) Initial cost is high.
(vi) Running cost is low.
(vii) No delay andlosses.
(viii) Inland refineries like Mathura possible because of these pipelines.
(6.1)Networks of Pipeline: –
(i) Assam to Kanpur:-Branches:-Barauni to Haldia and Guwahati to Siliguri.
(ii) Salaya (Gujarat) to Jalandhar (Punjab):-Branches: – connect Koyali, Chakshu.
(iii) Hazira toJagdishpur: a gas Pipeline extended beyond Delhi.
(7)Waterways: –
Characteristics: –
(i) Use since time immemorial.
(ii) Spread of commerce and Indianculture.
(iii) Cheapest.
(iv) Suitable for heavy and bulky goods.
(v) Full efficient and environmentalfriendly.
(vi) Length of inland waterways-14500 kms.
(vii) 37, 00 km navigable by mechanised boats.
(7.1)National Waterways: –
(i) No-1 Ganga between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km).
(ii) No-2Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km.
(iii)No-3 West Coast canal in Kerala (Kottapuram– Komman, Udyogamandal and Champak Kara canals- 205 KM).
(7.2)Other Viable Waterways: –Godavari, Krishna, Barak, etc.
(7.3)Ocean Transport: –
(i) Coastline-7516.6 km.
(ii)Major ports-12.
(iii) Minor ports-181.
(iv) Foreigntrade handeled-95%.
(7.4)Major Ports of West Coast:-
(a)Kandla: –
(i)Developed after independence.
(ii)Eased pressure on Mumbai port.
(iii) Tidal Port.
(iv)Hinterland-rich in agriculture and industrially developed.
(v) Hinterlands includes-Jammu and Kashmir,Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
(b)Mumbai: –
(i) Biggest.
(ii) Natural and Sheltered Harbour.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. The northern plains provide favourable conditions for the growth of the railways. Mention any two.
Answer : Vast level land.
High population density.
Question. Why is tourism considered as a trade?
Answer : (i) Foreign tourist’s arrival in the country contributing to foreign exchange.
(ii) Many people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
(iii) Tourism provides support to local handicrafts.
(iv) Tourists visit India for medical tourism, eco-tourism, adventure tourism,cultural tourismand business tourism
Question. Which port was the first port developed after independence and why?
Answer : Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port developed after independence to ease the volume of trade on Mumbai port in the wake of loss of Karachi port of Pakistan after the Partition.
Question. Which are the different types of transport ?
Answer : The transport can be classified into land, water and, air transport.
Question. In which states special provisions have been made to provide air services to the common people?
Answer : It is only in the north-eastern states that special provisions are made to extend the air services to the common people.
Question. Mention two types of airways.
Answer : Domestic Airways and International Airways.
Question. When and where the first train steamed off in India?
Answer : In India, the first train steamed off from Mumbai to Thane in 1853, covering a distance of 34 km.
Question. Why railway track are laid with difficulty in Rajasthan?
Answer : It is difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plain of Rajasthan.
Question. Why is there the need for transport system ? Mention any one reason.
Answer : The movement of goods and products from the supply locations to demand locations (markets) necessitates the need for transport.
Question. What is the use of pipelines transport?
Answer : Pipelines are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power plants.
Question. What is road density?
Answer : The length of road per 100 sq. km of area is known as density of roads.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Write three advantage of waterways.
Answer : Cheapest means of transport, can carry heavy and bulky goods, do not cause air pollution.
Question. Why is air travel preferred in North-East?
Answer : Uneven and mountain terrain, Dense forests, Presence of big rivers, frequent floods, international frontiers.
Question. Advancement of international Trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : i. It is considered as the economic barometer of a country.
ii. Export and import are the components of a trade.
iii. When the value of export exceeds than value of import it is called favourable balance of trade.
iv. International trade helps in earning foreign exchange.
v. India has trade relations with all major trading blocks of the world.
Question. “Dense and efficient network of transport is a pre-requisite for local and national development.” Analyse the statement.
Answer :
(i) The movement of the goods and services from their supplylocations to demand locations necessitates the need for transportation.
(ii) Development of country depends upon the production of goods and services as well asmovement to their destinations.
(iii) Transport helps in both production and distribution of goods.
(iv) Supports all sectors of the economy.
Question. Rail transport suffers from certain problems in India. Support the statement with examples.
Answer :
i. Many passengers travel without tickets.
ii. Theft and damaging of Railway property.
iii. Unnecessary chain pulling.
iv. Late runningof trains.
Question. the pace of change in the communication sector has been rapid in modern Times. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : Long distance communication is far easier without physical movement of the communicator or receiver.
i. Personal communication and mass communication including television, radio, press, films, etc. are the major means ofcommunication in the country.
ii. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personalwritten communications.
iii. Cards and envelopes are considered first-class mail and are airlifted between stations coveringbothland and air. The second-class mail includes book packets, are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport.
iv. Tofacilitate quick delivery of mails in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced.
They are called RajdhaniChannel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel.
v. India has one of thelargest telecom networks in Asia.
vi. Villages in India have already been covered with Subscriber Trunk Dialing (STD)telephone facility.
Question. Explain any three major problems faced by road transport in India.
Answer : i. The road network is inadequate.
ii. About half of the roads are unmetalled.
iii. This limits their usage during the rainy season.
iv. The roadways are highly congested in cities.
v. Most of the bridges adculverts are old and narrow.
vi. Most of the roads are not fit for smooth running.
Question. Roadways heave an edge over railways. Support the statement with examples
Answer : i. Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
ii. Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
iii. Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
iv. Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
v. It also provides door-to-door service; thus, the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
vi. Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
Question. International trade it is called the economic barometer for a country. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : i. Advancement of International Trade is considered index of economic prosperity.
ii. Value of Export exceeds of a nation raise its economy.
iii. Value of import exceeds of nation create downfall in economy.
iv. Large Foreign exchange can be collected by export of nation.
Question. Efficient means of transport are pre requisites for fast development of the country. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : (i) For carrying passengers and things from one place to another.
(ii) Raw material can reach factories faster.
(iii) The movement of the finished goods from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport.
(iv) Mobility of labour force also increases.
(v) Some people are engaged in facilitating the movements are known as traders who make the products come to the consumers by transportation.
(vi) Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient & fast moving transport.
Question. railways in India by the economic life of the country as well as accelerate the development ofthe industry and agriculture. Supportthe statement with examples.
Answer :
i. Railways are the principal mode of transport in India.
ii. Railways make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, transportation of goods.
iii. Railways have huge network in India that influence Indian Economy.
iv. Railways carry out businesses and various multifarious activities such as pilgrimage tourism,travel,commuting etc.
v. Help in the transportation of raw materials from the source to the industries, and themanufactured goods tothe market.
vi. Help in the linking of the industries with the market and develop them.
Question. Why are efficient means of transport pre-requisites for the fast development of the country? Explain.
Answer :
(a) the transportation system joins the various regions in the country, from developed to the underdeveloped, from rural to urban,helping in the migration processes.
(b) it helps in speedy movement of goods and services to different parts of the country
(c) it helps the traders to send their goods to different parts of the country, thereby, fulfilling the needs of the people. Thus,people living in mountainous areas etc. also have an access to goods and services, leading to development of these areas.
Question. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : i. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications.
ii. First class mails are air lifted between stations covering both Land and air.
iii. Second class mail are carried by surface mail by land and water transport.
iv. For quick delivery of mails, six channels are introduced.
Question. Describe any three features of waterways in India.
Answer : 1) India has been one of the seafaring countries.
2) Sea men sailed far and near; carrying and spreading Indian commerce and culture.
3) Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
4) They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distance.
5) It is fuel efficient, environment friendly mode of transport.
6) 95% of the country’s trade volume is moved by sea.
Question. Distribution of roads is not uniform in India. Support the statement with examples.
Answer : i. Density of roads uneven in all states.
ii. Kerala has high road density whereas Jammu Kashmir has very low density of roads.
iii. About half of the total roads are unmetalled.
iv. Road network is not inadequate in India.
v. National Highways are inadequate.
Question. Examine with example the role of means of transport and communication in making our life prosperous and comfortable.
Answer :
i. Efficient means of transport are pre requisites for fast development.
ii. Today the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast-moving transport.
iii. Today, India is well linked with the rest of the world despite its large size.
iv. Railways, Airways, Waterways, Newspapers, Radio, Television, Cinema and Internet etc. have been contributing to the socio-economic progress in many ways.
v. The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy.
vi. It has enriched our lives and added substantially to growth and comfort.
Question. Name three National waterways.
Answer :
- The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia
- Brahamaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri
- West Coast Canal in Kerala.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. What are the Problems Faced by Indian Railways?
Answer :
- Requires huge investment at the time of installation. Maintenance and upkeep is very costly.
- Construction is difficult and costly in uneven and high hills and deserts.
- Not suitable for transportation of perishable goods.
- Ticket-less travellers.
- Thefts and damaging of railway property.
- Unnecessarily chain pulling to stop train.
- Gauge Conversions.
- Sinking and slipping oftracks in rains.
- Modernization and Electrification.
Question. What are the advantages of transport?
Answer :
- Facilitates easy and free movement of people from one place to another.
- Helps to carry goods and materials from one place to another
- Helps in production and distribution of goods.
- Connect markets with the production centres.
- Promotes easy accessibility of goods and services.
- Helps in development of trade and commerce.
- Helps to increase the volume of the Trade.
Question. Describe the benefits of Roadways.
Answer :
(i) Roads need less capital than the railways.
(ii) Road transport provides door-to-door service.
(iii) The road transport provides flexible service to men and materials.
(iv) Road transport is useful in small distances.
(v) Road transport is helpful in production of perishable goods as it facilitates the distribution
ofperishable goods from point of production topoint of consumption.
(vi) Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
Question. Highlight any five major problems faced by road transport in India.
Answer : Problems faced by the Road Transport
i. Inadequate road network.
ii. About half of the roads are unmetalled.
iii. The National Highways are inadequate.
iv. Roadways are highly congested mainly in cities.
v. Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
Question. Describe the physical and economic factors that influence the distribution pattern of the Indian railways network.
Answer :
i. Northern Plain: Development due to level land, high population density and rich agricultural recourses.
ii. Peninsular region and theHimalayan region; It is a hilly terrain. The railway tracks are laid through low hills, gap or tunnels.
iii. Deserts of Rajasthan: It is verydifficult to lay railway lines due to sandy plain of western Rajasthan.
iv. Development not suitable in the Swamps of Gujarat, forestedtracts of Madhya Pradesh,Chhattisgarh, Orissa and Jharkhand.
v. The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gapsor passes.
vi. Although the Konkan railway along west coast has been developed but it has also faced a numberof problems such assinking of track in some stretches and landslides.
vii. Railways, being the principle of mode of transportation for freight and passengersin India make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage etc.
Question. ‘‘Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its prosperity.’’ Support the statement with suitableexamples.
Answer :
Advancement of international trade means, a country is getting involved in trade with more and more foreign countries. Thismeans that the value of exports exceeds the value of imports. It is called favorable balance of trade. For example- the developedcountries. The following points justify that advancement to international trade is an index of prosperity:
1. Opening up of an economy to international trade facilitates import and export. Following comparative advantage enables theeconomy to produce more output than what was possible with its own resources.
2. The coming up of MNCs add to the employment opportunities in the country.
3. The country also benefits from the technological and production efficiency brought by theMNCs.
4. Foreign trade enables a country to earn foreign exchange.
5. Foreign investment helps to accelerate the process of growth and development in the country.
Thus, we can say that international trade paces up the process of growth and development in the country, thereby; it can be seenas an index of prosperity of the country.
Question. Describe the role of mass communication in India.
Answer :
(i) Mass communication provides entertainment.
(ii) Creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines,books and films.
(iii) All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages.
(iv) Doordarshan broadcasts programmes of entertainment, educational, sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
(v) India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually
(vi) Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects to create awareness among people in different parts of the country.
(vii) India produces short films; video feature films and video short films.
(viii) Mass media creates awareness among people on various socio-economic and political issues.
Question. Highlight the significance of pipelines as the means of transportation, with the help of suitable examples.
Answer : Significance of Pipelines:
i. Use for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from field to refineries.
ii. Solids can also be transported when converted into slurry.
iii. Inland locations of the refineries.
iv. Initial cost of laying is high but subsequent running cost is minimal.
v. It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
vi. Example- From oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur, Gas Pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur in UP.
Question. Roadways have an edge over the Railways.’’ Justify the statement.
Answer :Roadways have an edge over railways.
i. Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railw ay liens.
ii. Road can traverse comparatively more dissected an d undulating topography.
iii. Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse m ountains such as the Himalayas.
iv. Road transport economical in transpiration of few person and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances.
v. It also provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
vi. Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and ports.
Question. Why is air travel preferred in North-Eastern States of India? Explain with examples.
Answer : Air travel in the N-E states:
i. North Eastern states as a whole is dissected relief.
ii. It covers dense forests.
iii. Floods are frequent in these states.
iv. States have international frontiers along with.
v. Other means of transport – road and railway network are inadequate and not maintainedproperly.
vi. Air Travel saves time in spite of costly fare.
Question. Why is transport and communication called lifelines of a country?
Answer :
- Connects far lying areas ofthe country
- They benefit trade and commerce
- Help in the development of agriculture and industry.
- Helpful during calamities
- Promotes unity of the country
Question. What are the problems faced by Indian roadways?
Answer :
- Road network is inadequate for increasing volume of traffic.
- About half of the roads are unmetalled.
- The National Highways are inadequate and are poorly maintained.
- The roadways are highly congested in cities and are lacking safety measures.
- Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.
- Lack of proper security measures.
Case Based Questions
1. Read the given text and answer the following questions:
Ever since humans appeared on the earth, they have used different means of communication. But, the pace of change, has been rapid inmodern times. Long distance communication is far easier without physical movement of the communicator or receiver. Personalcommunication and mass communication including television, radio, press, films, etc. are the major means of 4 communication in thecountry. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications. Cards andenvelopes are considered first-class mail and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air. The second-class mail includes bookpackets, registered
newspapers and periodicals. They are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport. To facilitate quickdelivery of mails in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently. They are called Rajdhani Channel, MetroChannel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel and Periodical Channel.
(i) Examine the role of the Indian postal network.
Answer :
(i) It has helped the country to engage in communication and social-economic development.
(ii) It provides various facilities like speed post,business post, registered post, ordinary post.
(ii) Analyse the significance of communication for a nation.
Answer :
(i) This is the age of communication using the telephone, television, films, and the Internet.
(ii) Even books, magazines and newspapers areimportant means of communication.
(iii) Various means of communication have connected the world closer.
(iv) It is the source ofentertainment and knowledge.
(iii) Differentiate between mass communication and personal communication.
Answer :
Mass Communication is the medium which provides entertainment as well as creates awareness among the masses. It includes radio,television, newspapers, magazines, books, films etc. whereas Personal Communication is between person to person.
2. Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast-moving transport. Transport has beenable to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication and trade arecomplementary to each other.
Today, India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity and linguistic and socio-cultural plurality.
Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema and internet, etc. have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways.
The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of its economy. It has enriched our life and addedsubstantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life. It is thus, evident that a dense and efficient network oftransport and communication is a prerequisite for local, national and global trade of today.
(i) Why is there a need to interlink with the world?
Answer : For development, advancement and globalization
(ii) How does trade add vitality to economy?
Answer :
i. Trade between nation and countries are the index to its economic prosperity ii. It generates employment.
ii. It Helps in earningforeign exchange.
(iii) Why are means of transportation and communication important for socio- economic progress?
Answer :
i. They are the very basis of industries and trade of country.
ii. Create job employment opportunities.
iii. Help to grow economy.
iv. Transport maintains the movement of persons and products from one region to another region of the country.
v. in sending and receiving messages.
vi. Interlinking world vii. Increases awareness among the people at national level.
viii. Help in defending the independence and the national unity of a country.



